Temporal Super-Resolution Using a Multi-Channel Illumination Source
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The demonstration of a novel approach for optical coding to achieve high temporal frequencies with a fixed sensor sampling rate working in real time.
- The development of a substantial theoretical background to increase temporal resolution from subsamples.
- Providing an anti-aliasing algorithm to improve system performance over a wide range of frequencies.
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Temporal Model for an Image Sensor
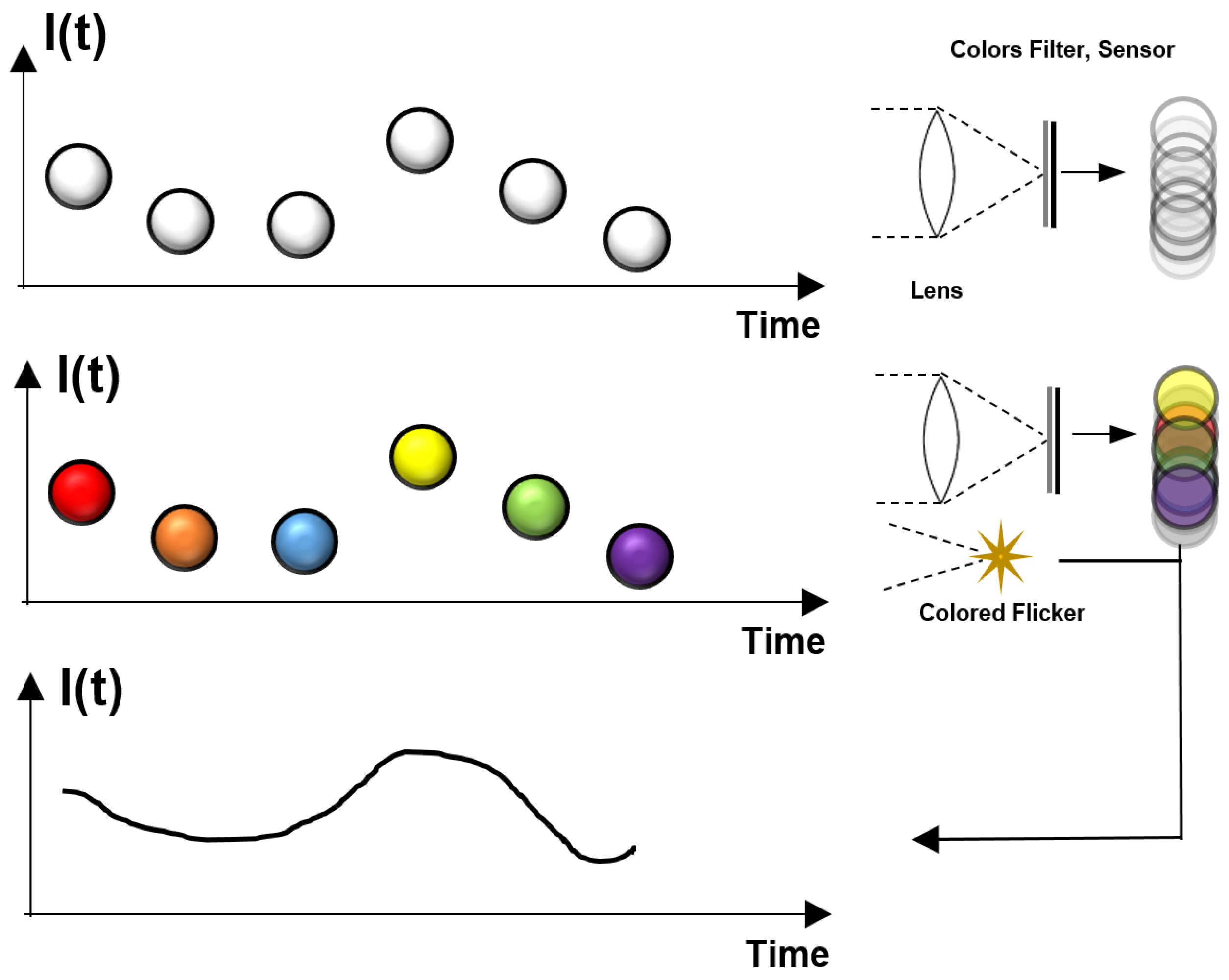
2.2. Multi-Channel Approach and Assumptions
2.3. Definitions
3. Method
3.1. Spatial Regularization
3.2. Solution with Lagrange Multipliers
3.3. Colored Light Source
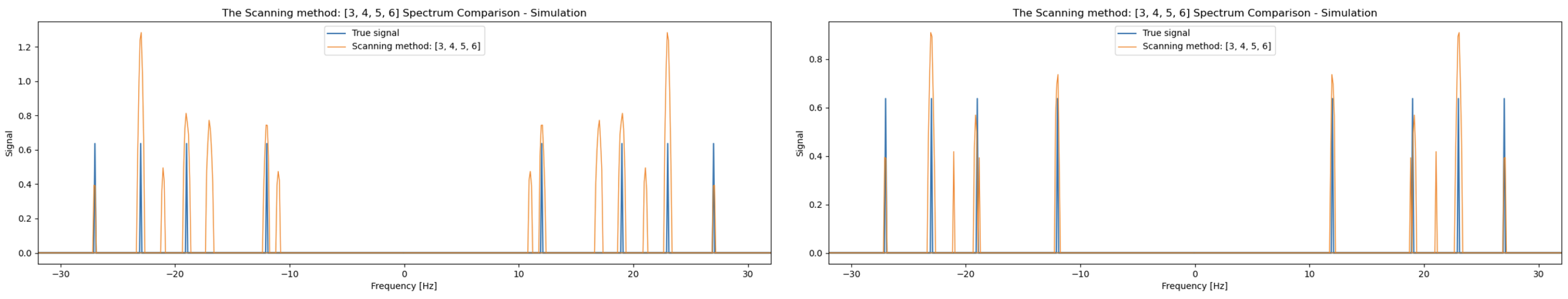
3.4. The Scanning Mode and Anti-Aliasing Algorithm
| Algorithm 1: Anti-aliasing algorithm |
 |
3.5. Performance Analysis and Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
4. Numerical Simulations and Analysis
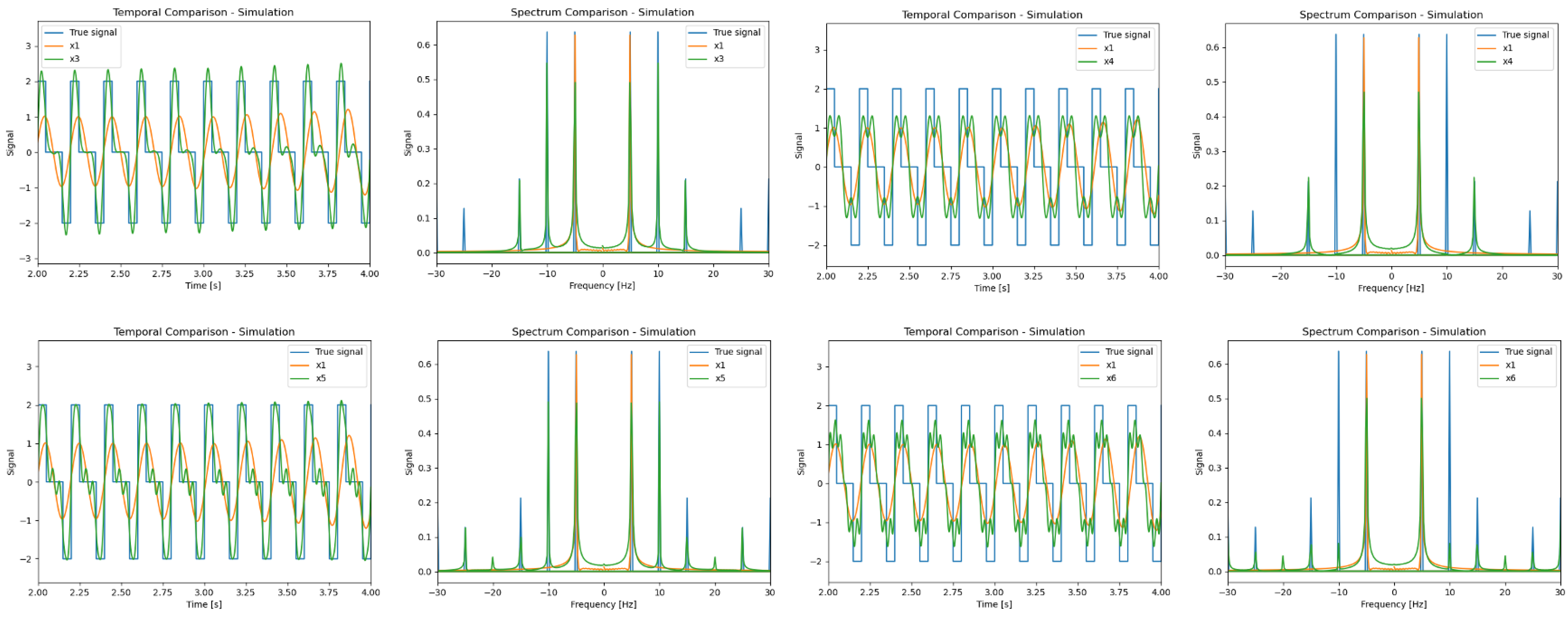
4.1. Flicker Pattern Analysis
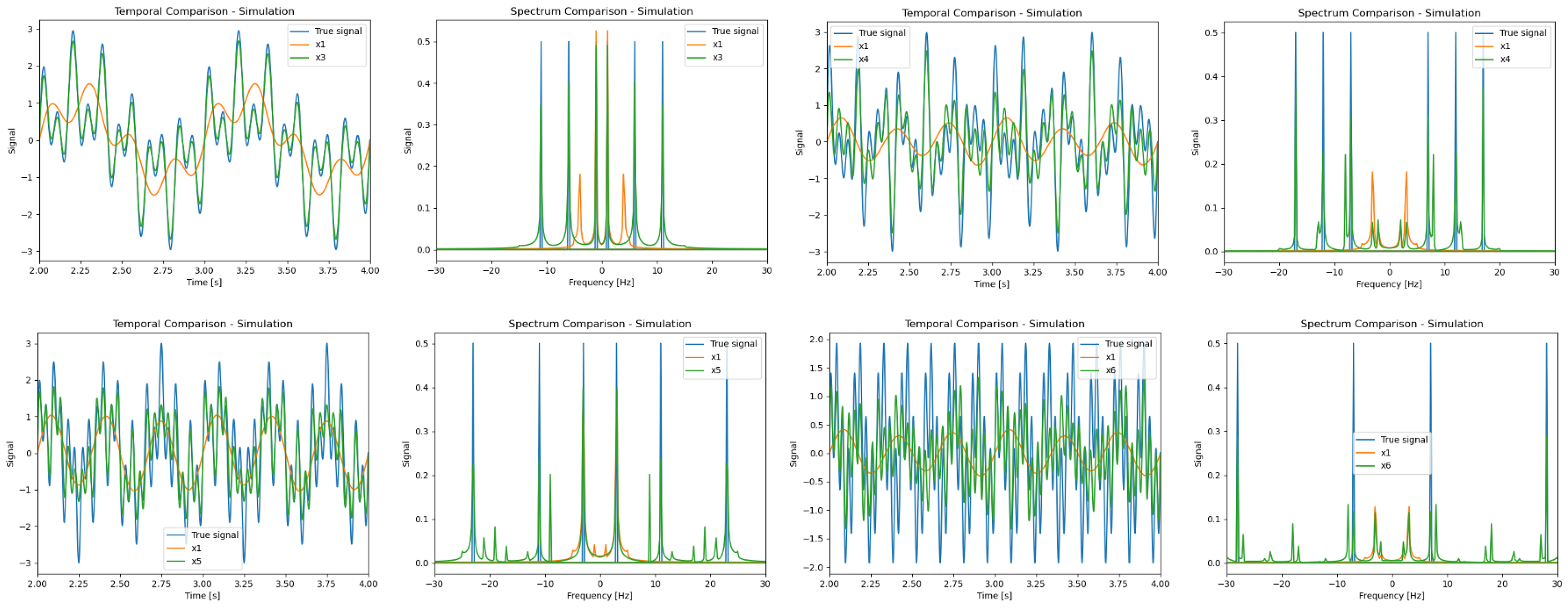
4.2. Simulations Results
5. Experimental Results
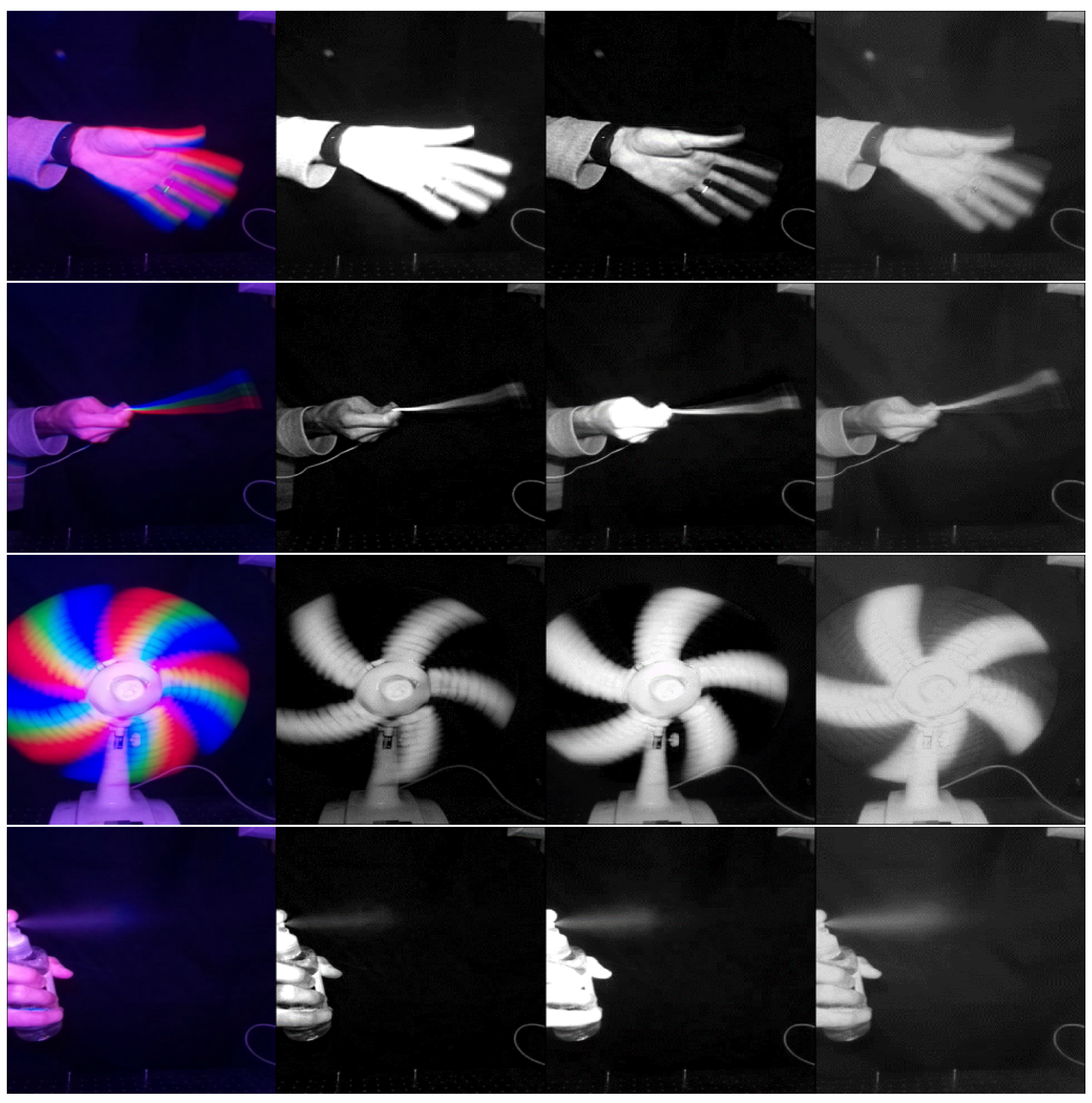
5.1. The Setup
5.2. Signal Reconstruction Results
5.3. Imaging Reconstruction Results
5.4. SNR and Performance Results
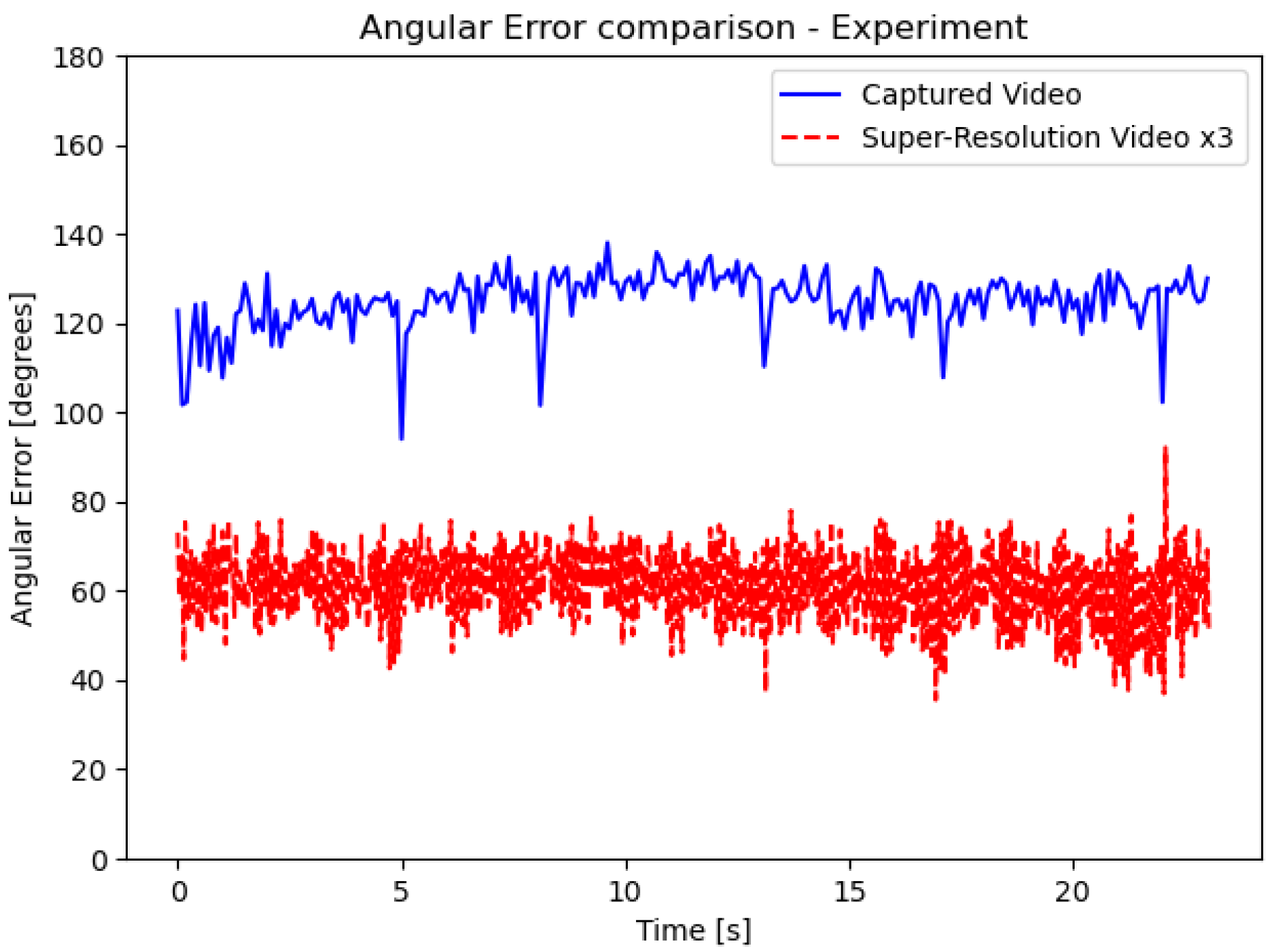
5.5. Motion Estimation Improvement
5.6. Motion Estimation Analysis
5.7. Discussion
6. Conclusions
7. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TSR | Temporal super resolution |
| FPS | Frames per second |
| HR | High resolution |
| LR | Low resolution |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Definitions
Appendix A.2. Solving the Optimization Problem for Lagrange Multipliers
Appendix A.3. Expanding to Spatial Regularization
Appendix A.4. Signals Similarity Metrics
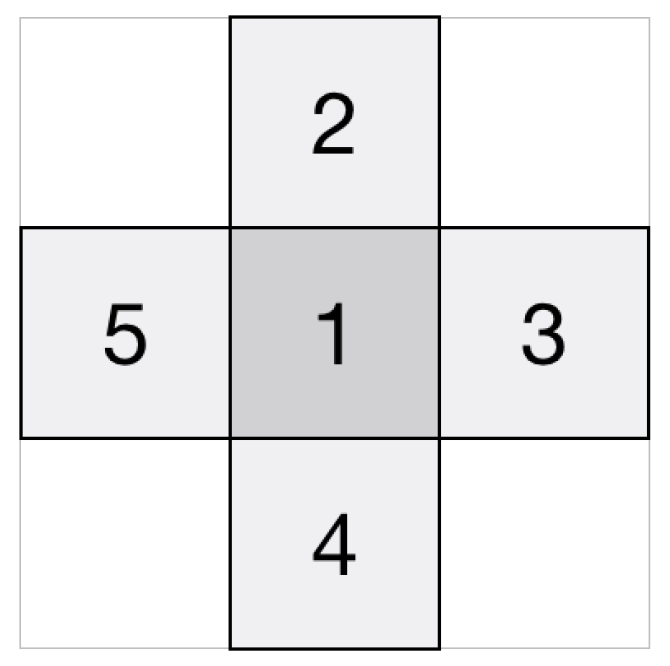
Appendix A.5. Flicker Order Choices

Appendix A.6. SNR Analysis
Appendix A.7. Regularization Analysis

References
- Gustafsson, M.G.L. Surpassing the lateral resolution limit by a factor of two using structured illumination microscopy. J. Microsc. 2000, 198, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendlovic, D.; Lohmann, A.W. Space bandwidth product adaptation and its application to superresolution, fundamentals. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1997, 14, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, E.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Z. Speckle structured illumination endoscopy with enhanced resolution at wide field of view and depth of field. Opto. Electron. Adv. 2023, 6, 220163-1–220163-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.J. Equivalence relations and symmetries for laboratory, LIDAR, and planetary Müeller matrix scattering geometries. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2014, 31, 2789–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzig, E.; Trautman, J.K. Near-Field Optics: Microscopy, Spectroscopy, and Surface Modification Beyond the Diffraction Limit. Science 1992, 257, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- di Francia, G.T. Degrees of Freedom of an Image. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1969, 59, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukosz, W. Optical Systems with Resolving Powers Exceeding the Classical Limit∗. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1966, 56, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.; Micó, V.; Cojoc, D.; Zalevsky, Z. Full field of view super-resolution imaging based on two static gratings and white light illumination. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 3080–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, A.M.; Heritage, J.P.; Kirschner, E.M. High-resolution femtosecond pulse shaping. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1988, 5, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabo, E.; Zalevsky, Z.; Mendlovic, D.; Konforti, N.; Kiryuschev, I. Superresolution optical system with two fixed generalized Damman gratings. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 5318–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Wei, Q.; Basarab, A.; Dobigeon, N.; Kouame, D.; Tourneret, J.Y. Fast Single Image Super-Resolution. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1510.00143. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Jiang, K.; Wang, Z.; Bai, X.; Hu, R. CycMuNet+: Cycle-Projected Mutual Learning for Spatial-Temporal Video Super-Resolution. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 13376–13392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Hoi, S.C.H. Deep Learning for Image Super-resolution: A Survey. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1902.06068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepcha, D.C.; Goyal, B.; Dogra, A.; Goyal, V. Image super-resolution: A comprehensive review, recent trends, challenges and applications. Inf. Fusion 2023, 91, 230–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, X. Medical image super-resolution reconstruction algorithms based on deep learning: A survey. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2023, 238, 107590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Yuan, Q.; He, J.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Su, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, L. Space-time super-resolution for satellite video: A joint framework based on multi-scale spatial-temporal transformer. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 108, 102731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Ma, J. Deep Learning-based Face Super-Resolution: A Survey. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.03749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Asraf, S.; Zalevsky, Z. Superresolved space-dependent sensing of temporal signals by space multiplexing. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 4234–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llull, P.; Liao, X.; Yuan, X.; Yang, J.; Kittle, D.; Carin, L.; Sapiro, G.; Brady, D.J. Coded aperture compressive temporal imaging. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 10526–10545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Sonoda, T.; Nagahara, H.; Endo, K.; Sugiyama, Y.; Taniguchi, R. High-Speed Imaging Using CMOS Image Sensor With Quasi Pixel-Wise Exposure. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2020, 6, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskar, R.; Agrawal, A.; Tumblin, J. Coded Exposure Photography: Motion Deblurring Using Fluttered Shutter. ACM Trans. Graph. 2006, 25, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yeh, R.A.; Tang, X.; Liu, Y.; Agarwala, A. Video Frame Synthesis using Deep Voxel Flow. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.02463. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, S.; Wang, O.; Zimmer, H.; Grosse, M.; Sorkine-Hornung, A. Phase-Based Frame Interpolation for Video. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niklaus, S.; Liu, F. Context-aware Synthesis for Video Frame Interpolation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.10967. [Google Scholar]
- Pollak Zuckerman, L.; Naor, E.; Pisha, G.; Bagon, S.; Irani, M. Across Scales and Across Dimensions: Temporal Super-Resolution using Deep Internal Learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Son, S.; Lee, J.; Nah, S.; Timofte, R.; Lee, K.M. AIM 2020 Challenge on Video Temporal Super-Resolution. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.12987. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C. Communication in the Presence of Noise. Proc. IRE 1949, 37, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SNR Model of an Image. Available online: https://camera.hamamatsu.com/jp/en/learn/technical_information/thechnical_guide/calculating_snr.html (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Agrawal, A.; Gupta, M.; Veeraraghavan, A.; Narasimhan, S.G. Optimal coded sampling for temporal super-resolution. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Sun, D.; Jampani, V.; Yang, M.H.; Learned-Miller, E.; Kautz, J. Super SloMo: High Quality Estimation of Multiple Intermediate Frames for Video Interpolation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1712.00080. [Google Scholar]
- Barron, J.; Fleet, D.; Beauchemin, S. Performance Of Optical Flow Techniques. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1994, 12, 43–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
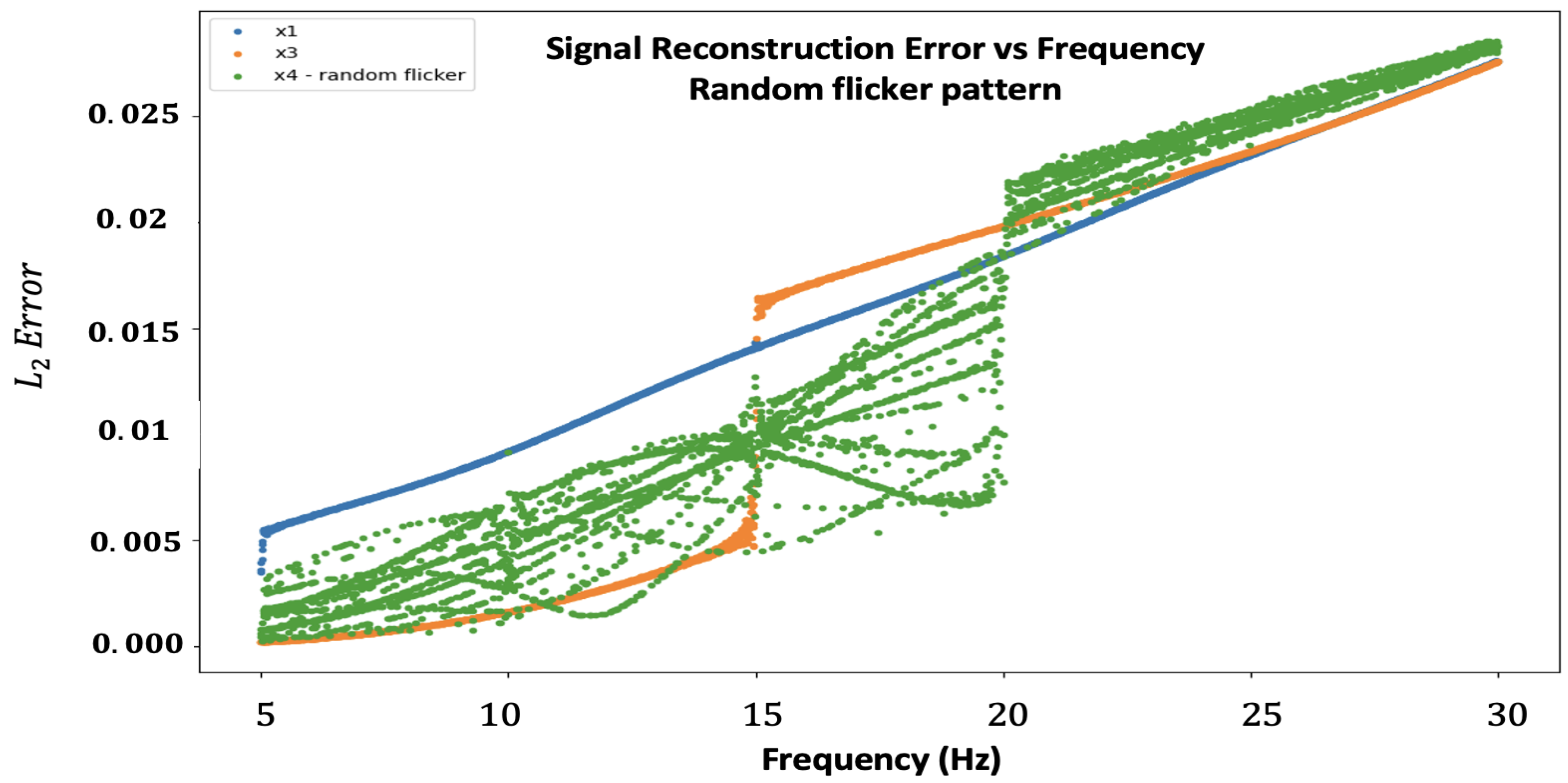
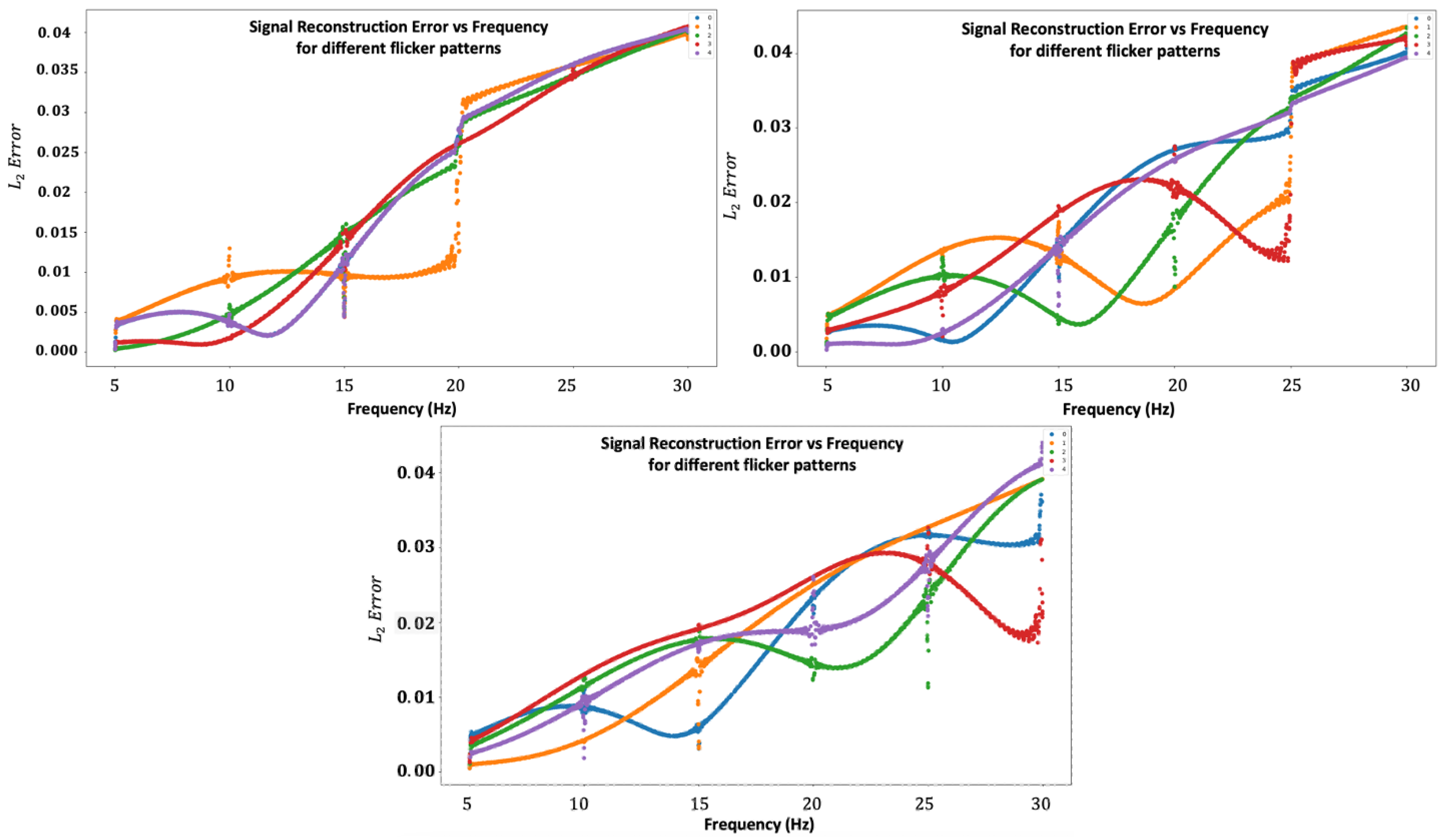



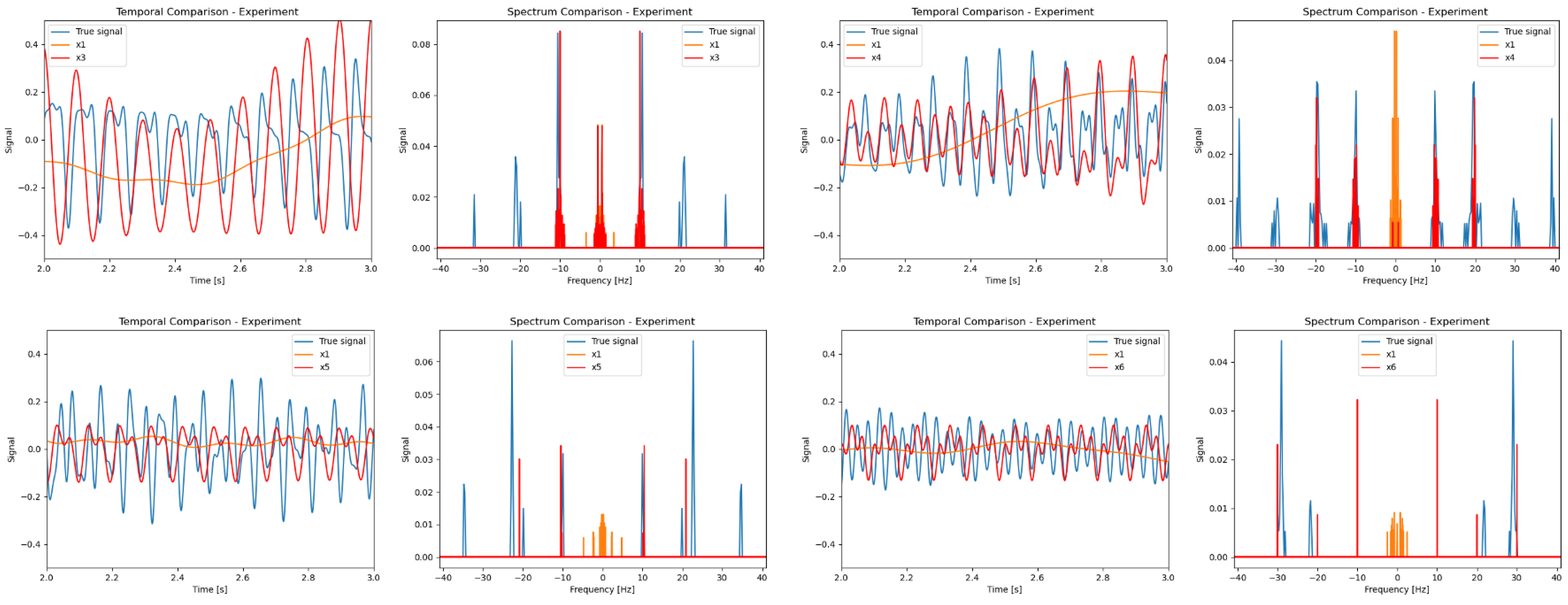

| N | Frequencies [Hz] | L2 Error [×] | Normalized Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 5–15 | 1 | |
| 4 | 15–20 | ||
| 5 | 23–25 | ||
| 6 | 28–30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cohen, K.; Mendlovic, D.; Raviv, D. Temporal Super-Resolution Using a Multi-Channel Illumination Source. Sensors 2024, 24, 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24030857
Cohen K, Mendlovic D, Raviv D. Temporal Super-Resolution Using a Multi-Channel Illumination Source. Sensors. 2024; 24(3):857. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24030857
Chicago/Turabian StyleCohen, Khen, David Mendlovic, and Dan Raviv. 2024. "Temporal Super-Resolution Using a Multi-Channel Illumination Source" Sensors 24, no. 3: 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24030857
APA StyleCohen, K., Mendlovic, D., & Raviv, D. (2024). Temporal Super-Resolution Using a Multi-Channel Illumination Source. Sensors, 24(3), 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24030857





