Sensing Data Concealment in NFTs: A Steganographic Model for Confidential Cross-Border Information Exchange
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Related Work
1.3. Contribution
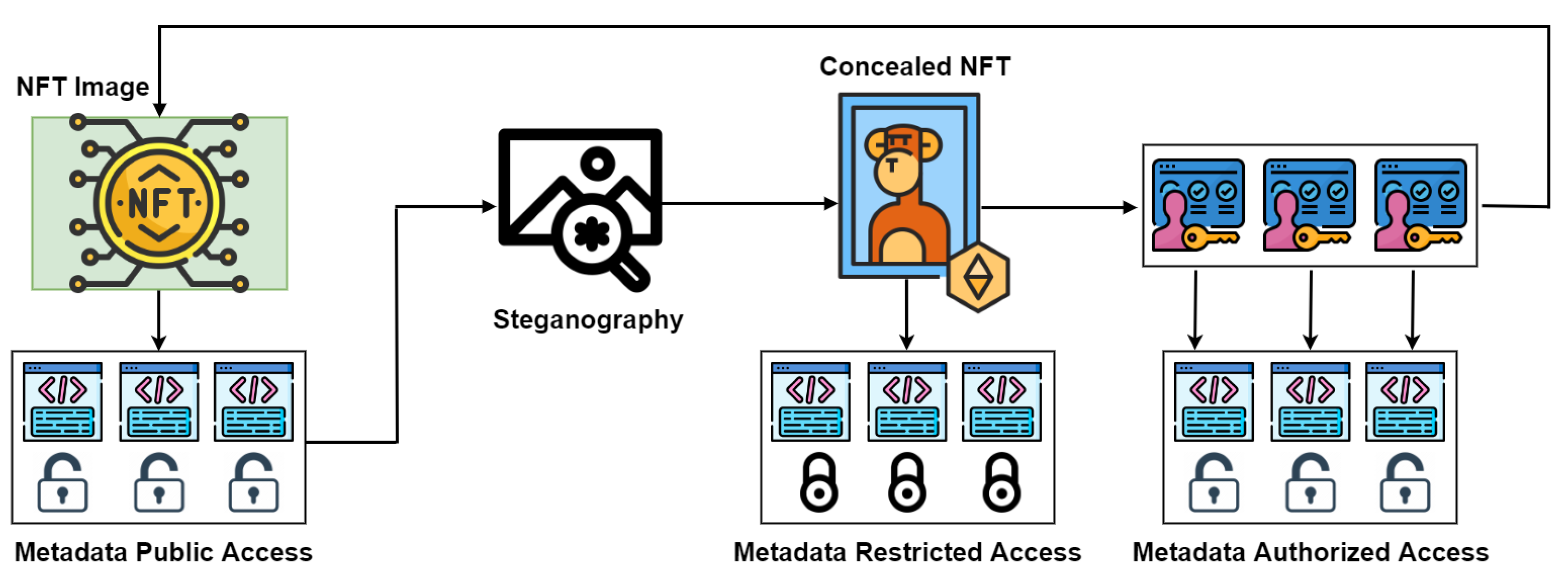
- We propose using NFTs as carriers for sensitive data in cross-border transfers, ensuring secure and authorized access. Harnessing the unique properties of NFTs, we employ the immutable NFT data as a tamperproof pointer, guaranteeing the authenticity and provenance of the sensitive information. Meanwhile, the mutable NFT data serve as a secure container for the sensitive content itself. This allows for dynamic updates to reflect changes in users’ data, ensuring the information remains current and relevant.
- To address the public accessibility of NFT metadata, we propose leveraging the power of steganography. This enables us to both conceal sensitive information and enhance its protection, offering an effective solution for privacy-conscious users.
- To ensure secure and private user mobility across businesses, we propose an approach that prioritizes user data privacy and integrity during transitions. This objective is achieved through the application of a strong cryptographic technique, specifically OTP, which aligns with our model’s security requirements.
- A structured performance analysis is conducted to assess the practicality and effectiveness of implementing this proposed methodology in real-world scenarios.
1.4. Paper Organization
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Technical Definitions
2.1.1. Steganography
2.1.2. One-Time Pad (OTP)
2.1.3. NFTs
2.1.4. Smart Contract
2.2. Tracing Model Operations
2.2.1. Sensing Data Collection
2.2.2. Priming NFTs for Use
2.2.3. Scenario
2.2.4. User Mobility
| Algorithm 1: Secure password transmission. |
Input: Steganography password P, User’s OTP K Output: Decrypted password P for sensitive data access
|
| Algorithm 2: User data migration from B1 to B2. |
 |
3. Setup and Implementation
3.1. Environment Setup
3.2. Performance Metrics
3.3. Parameter Settings and Configurations
3.3.1. Embedding Algorithm
3.3.2. Data Size
3.3.3. Image Type and Size
3.3.4. Password Complexity
3.3.5. Encryption Mode
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Impact of Embedding Algorithm
4.2. Impact of Data Size
4.3. Image Type
4.4. Impact of Password Complexity
4.5. Impact of Encryption Mode
4.6. Discussion
4.7. Comparison with Related Works
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krishnamurthi, R.; Kumar, A.; Gopinathan, D.; Nayyar, A.; Qureshi, B. An overview of IoT sensor data processing, fusion, and analysis techniques. Sensors 2020, 20, 6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanagala, P. Effective cyber security system to secure optical data based on deep learning approach for healthcare application. Optik 2023, 272, 170315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Luo, Y.; Li, P.; Mathew, J. A review of secure and privacy-preserving medical data sharing. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 61656–61669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Z. A blockchain-based framework of cross-border e-commerce supply chain. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 102059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdulatif, A.; Thilakarathne, N.N.; Lawal, Z.K.; Fahim, K.E.; Zakari, R.Y. Internet of nano-things (iont): A comprehensive review from architecture to security and privacy challenges. Sensors 2023, 23, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandridis, A.; Al-Sumaidaee, G.; Zilic, Z.; Jeon, G.; Wang, J. An IoT Ecosystem Platform for the Evaluation of Blockchain Feasibility. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 21515–21527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, D. Securing the Cyber Resilience of a Blockchain-Based Railroad Non-Stop Customs Clearance System. Sensors 2023, 23, 2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H. A cross-border E-commerce approach based on blockchain technology. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2021, 2021, 2006082. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Xue, W.; Zheng, X.; Xu, X. The challenges and countermeasures of blockchain in finance and economics. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2020, 37, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelius, K. Betraying blockchain: Accountability, transparency and document standards for non-fungible tokens (nfts). Information 2021, 12, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, W.; e Zainab, H.; Imran, J.; Bawany, N.Z. NFTs: Applications and challenges. In Proceedings of the 2021 22nd International Arab Conference on Information Technology (ACIT), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 22–24 November 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Friedmann, D. Jumping from mother monkey to bored ape: The value of NFTs from an artist’s and intellectual property perspective. Asia Pac. Law Rev. 2023, 31, 100–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julianto, I.T.; Kurniadi, D.; Khoiriyyah, F.M. Price Prediction of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) using Data Mining Prediction Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Computer Science, Information Technology and Engineering (ICCoSITE), Jakarta, Indonesia, 16 February 2023; pp. 633–637. [Google Scholar]
- Teplova, T.; Kurkin, A.; Baklanova, V. Investor sentiment and the NFT market: Prediction and interpretation of daily NFT sales volume. Ann. Oper. Res. 2023, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasbi, N.; Shan, G.; French, A.M. Identifying Washtrading Cases in NFT Sales Networks. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.Y.; Bae, Y.S.; Chie, E.K.; Lee, S.B. Predicting Deterioration from Wearable Sensor Data in People with Mild COVID-19. Sensors 2023, 23, 9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Han, K.; Alexandridis, A.; Chen, Z.; Zilic, Z.; Pang, Y.; Jeon, G.; Piccialli, F. A blockchain-based eHealthcare system interoperating with WBANs. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 110, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.H. IoT based clinical sensor data management and transfer using blockchain technology. J. Iot Soc. Mob. Anal. Cloud 2020, 2, 154–159. [Google Scholar]
- Anbarasan, H.S.; Natarajan, J. Blockchain Based Delay and Energy Harvest Aware Healthcare Monitoring System in WBAN Environment. Sensors 2022, 22, 5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taralunga, D.D.; Florea, B.C. A blockchain-enabled framework for mhealth systems. Sensors 2021, 21, 2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wei, X. A New NFT Model to Enhance Copyright Traceability of the Off-chain Data. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Culture-Oriented Science and Technology (CoST), Lanzhou, China, 18–21 August 2022; pp. 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Sajjanhar, A.; Xiang, Y.; Gao, L. A Robust NFT Assisted Knowledge Distillation Framework for Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Testbeds and Research Infrastructures, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 23–25 November 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- Hocaoğlu, M.; Habbal, A. NFT based model to manage educational assets in Metaverse. Avrupa Bilim Teknol. Derg. 2022, 42, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Elmessiry, A.; Elmessiry, M.; Bridgesmith, L. NFT student teacher incentive system (NFT-stis). SSRN 2021, 4120879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Xie, R.; Yu, F.R.; Huang, T.; Liu, Y. NFT-based intelligence networking for connected and autonomous vehicles: A quantum reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Netw. 2022, 36, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sumaidaee, G.; Alkhudary, R.; Zilic, Z. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) as a Means for Blockchain Networks Integration in Healthcare. In Proceedings of the 2023 5th Conference on Blockchain Research & Applications for Innovative Networks and Services (BRAINS), Paris, France, 11–13 October 2023; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Gebreab, S.A.; Hasan, H.R.; Salah, K.; Jayaraman, R. NFT-based traceability and ownership management of medical devices. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 126394–126411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koptyra, K.; Ogiela, M.R. Steganography in IoT: Information Hiding with Joystick and Touch Sensors. Sensors 2023, 23, 3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Han, J.; Park, C.; Yi, O. Analysis of vulnerabilities that can occur when generating one-time password. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, I.; Gubareva, M.; Teplova, T. Connectedness of non-fungible tokens and conventional cryptocurrencies with metals. N. Am. J. Econ. Financ. 2023, 68, 101995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sumaidaee, G.; Alkhudary, R.; Zilic, Z.; Swidan, A. Performance analysis of a private blockchain network built on Hyperledger Fabric for healthcare. Inf. Process. Manag. 2023, 60, 103160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Jindal, R.; Borah, M.D. A review of smart contract-based platforms, applications, and challenges. Clust. Comput. 2023, 26, 395–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saladi, S.; Amutha Prabha, N. Analysis of denoising filters on MRI brain images. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2017, 27, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Al Omar, A.; Bhuiyan, M.Z.A.; Basu, A.; Kiyomoto, S.; Wang, G. Accountable cross-border data sharing using blockchain under relaxed trust assumption. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2020, 67, 1476–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, X.; Zhao, R.; Lu, W.; Xu, J.; Xue, F. A blockchain-based model with an incentive mechanism for cross-border logistics supervision and data sharing in modular construction. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 375, 133460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Dong, J.; Dai, Z.; Liu, Y. Sales data sharing to improve product development efficiency in cross-border e-commerce. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2022, 51, 101112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| PSNR (dB) | SSIM | Encryption Execution Time (s) | Decryption Execution Time (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSB | 85.36 | 0.99 | 0.089 | 0.025 |
| DCT | 32.92 | 0.97 | 0.022 | 0.001 |
| DWT | 30.72 | 0.94 | 0.058 | 0.007 |
| PSNR (dB) | SSIM | Encryption Execution Time (s) | Decryption Execution Time (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 KB | 82.009 | 0.999 | 0.053 | 0.021 |
| 10 KB | 62.872 | 0.999 | 0.163 | 0.119 |
| 20 KB | 59.747 | 0.999 | 0.273 | 0.209 |
| PSNR (dB) | SSIM | Encryption Execution Time (s) | Decryption Execution Time (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPEG | 79.669 | 0.999 | 0.059 | 0.021 |
| PNG | 93.845 | 0.999 | 0.262 | 0.054 |
| PSNR (dB) | SSIM | Encryption Execution Time (s) | Decryption Execution Time (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weak | 81.941 | 0.999 | 0.052 | 0.029 |
| Moderate | 82.483 | 0.999 | 0.053 | 0.020 |
| Strong | 81.836 | 0.999 | 0.054 | 0.020 |
| PSNR (dB) | SSIM | Encryption Execution Time (s) | Decryption Execution Time (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBC | 82.027 | 0.999 | 0.053 | 0.019 |
| CFB | 82.379 | 0.999 | 0.051 | 0.018 |
| CTR | 82.070 | 0.999 | 0.052 | 0.019 |
| OFB | 82.050 | 0.999 | 0.049 | 0.017 |
| GCM | 81.949 | 0.999 | 0.051 | 0.020 |
| ECB | 82.035 | 0.999 | 0.050 | 0.018 |
| Metric | [35] | [36] | [4] | [37] | Our Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ownership | No | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| Privacy | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| Decentralization | Yes/No | Yes/No | Yes/No | No | Yes |
| Immutability | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Interoperability | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| Robustness Against Attacks | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| User-Friendly Deployment | No | No | No | No | No |
| Analysis | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Sumaidaee, G.; Žilić, Ž. Sensing Data Concealment in NFTs: A Steganographic Model for Confidential Cross-Border Information Exchange. Sensors 2024, 24, 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24041264
Al-Sumaidaee G, Žilić Ž. Sensing Data Concealment in NFTs: A Steganographic Model for Confidential Cross-Border Information Exchange. Sensors. 2024; 24(4):1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24041264
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Sumaidaee, Ghassan, and Željko Žilić. 2024. "Sensing Data Concealment in NFTs: A Steganographic Model for Confidential Cross-Border Information Exchange" Sensors 24, no. 4: 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24041264
APA StyleAl-Sumaidaee, G., & Žilić, Ž. (2024). Sensing Data Concealment in NFTs: A Steganographic Model for Confidential Cross-Border Information Exchange. Sensors, 24(4), 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24041264







