Aptamer-Based Sensor for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Ofloxacin in Meat Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Methods
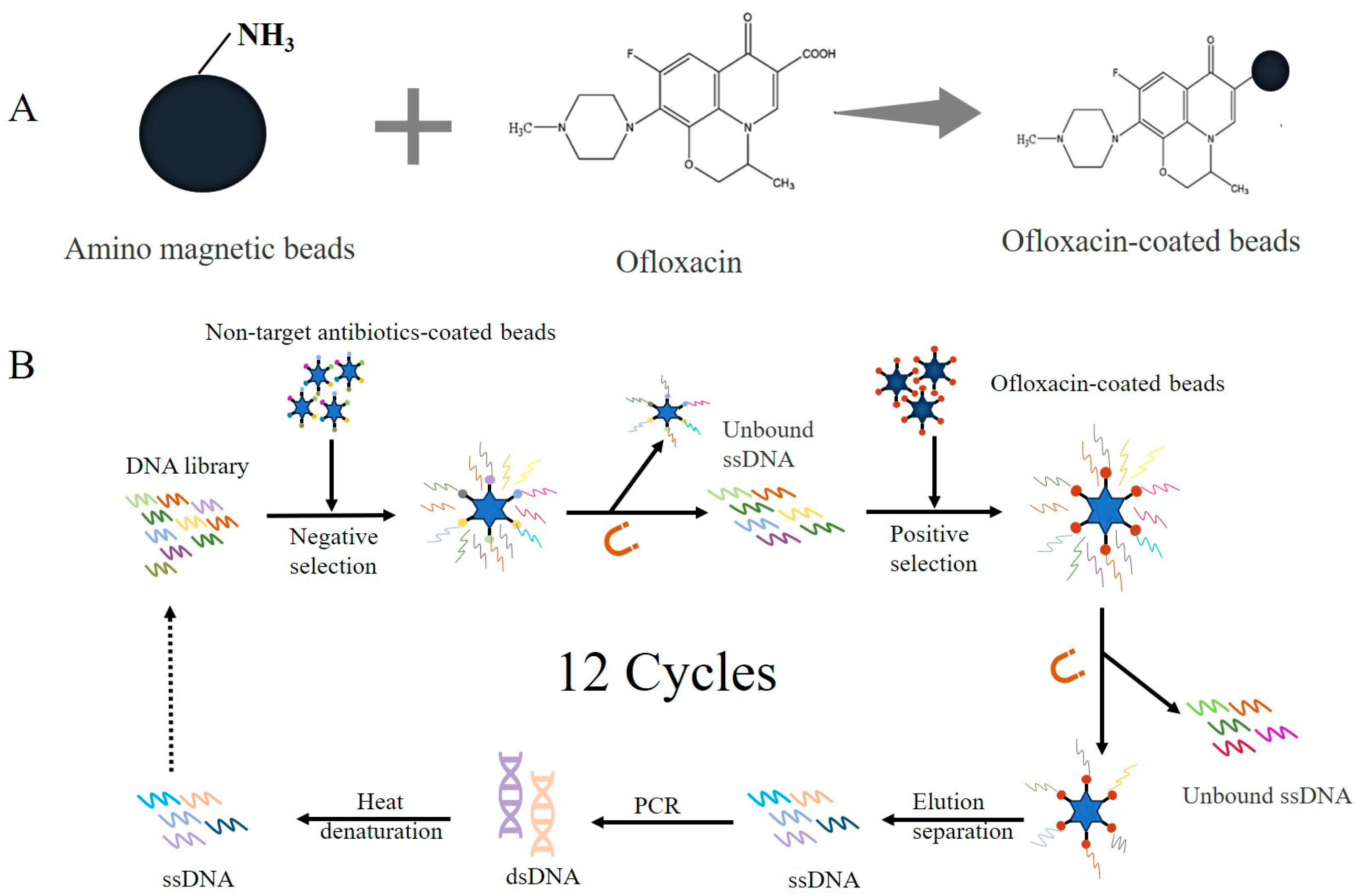
2.2.1. Immobilization of OFL on Amino Magnetic Beads
2.2.2. Aptamer Screening
2.2.3. Sequencing and Analysis
2.2.4. OFL Measurement
2.2.5. Affinity and Specificity of Aptamers
2.2.6. Optimization of Aptamer Reaction Conditions
2.2.7. Preparation of the Aptamer Sensor
2.2.8. Characteristics of Aptamer Sensor
2.2.9. Testing of Actual Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Aptamer Screening, Sequencing, and Analysis
3.2. Characterization of Aptamers
3.3. Optimization of Reaction Conditions
3.4. Optimization of Reaction Conditions for the Developed Sensor
3.5. Detection of OFL in the Meat Products
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, X.; Dudley, E.G.; Pinto, C.N.; M’ikanatha, N.M. Fluoroquinolone sales in food animals and quinolone resistance in non-typhoidal Salmonella from retail meats: United States, 2009–2018. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2022, 29, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Long, H.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Le, T. A novel Zn/Eu-MOF for the highly sensitive, reversible and visualized sensing of ofloxacin residues in pork, beef and fish. Food Chem. 2023, 422, 136250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, S.; Chatterjee, S. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics: Occurrence, mode of action, resistance, environmental detection, and remediation—A comprehensive review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 315, 120440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, P.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.; Huo, D.; Hou, C.; Ren, K. Graphene oxide mediated CdSe quantum dots fluorescent aptasensor for high sensitivity detection of fluoroquinolones. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 305, 123497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Yan, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Yan, R.; Zhang, D.; Shen, G.; Zhou, S. Fluorometric determination for ofloxacin by using an aptamer and SYBR Green I. Mikrochim. Acta 2019, 186, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilehvar, S.; Reinemann, C.; Bottari, F.; Vanderleyden, E.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; Blust, R.; Strehlitz, B.; De Wael, K. A joint action of aptamers and gold nanoparticles chemically trapped on a glassy carbon support for the electrochemical sensing of ofloxacin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 240, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Geng, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y. Photoelectrochemical aptasensing of ofloxacin based on the use of a TiO2 nanotube array co-sensitized with a nanocomposite prepared from polydopamine and Ag2S nanoparticles. Mikrochim. Acta 2019, 186, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Faria, L.V.; Lisboa, T.P.; da Silva Campos, N.; Alves, G.F.; Matos, M.A.; Matos, R.C.; Munoz, R.A. Electrochemical methods for the determination of antibiotic residues in milk: A critical review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1173, 338569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xue, Q.; Chen, T.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Shan, X.; Liu, F.; Jia, J. Recent advances in electrochemical sensors for antibiotics and their applications. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Yue, F.; Zhai, S.; Hu, M.; Qi, G.; Chen, S.; Li, B.; Sun, X.; Guo, Y.; Marrazza, G. Screening of broad-spectrum aptamers to construct an electrochemical aptasensor for the sensitive detection of tetracycline antibiotic residues in milk. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 398, 134765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zein, M.I.; Hardianto, A.; Zakiyyah, S.N.; Devi, M.J.; Manan, N.S.; Ibrahim, A.U.; Hartati, Y.W. Recent development of electrochemical and optical aptasensors for detection of antibiotics in food monitoring applications. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 124, 105644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Gao, X.; Shabbir, M.A.; Peng, D.; Tao, Y.; Chen, D.; Hao, H.; Cheng, G.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, Z.; et al. Rapid multi-residue screening of antibiotics in muscle from different animal species by microbiological inhibition method. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Shabbir, M.A.; Peng, D.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, Y. Microbiological inhibition-based method for screening and identifying of antibiotic residues in milk, chicken egg and honey. Food Chem. 2021, 363, 130074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Shabbir, M.A.; Sattar, A.; Peng, D.; Tao, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Z. The search for a microbiological inhibition method for the rapid, broad-spectrum and high-throughput screening of six kinds of antibiotic residues in swine urine. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehata, A.K.; Suseela, M.N.; Gokul, P.; Malik, A.K.; Viswanadh, M.K.; Singh, C.; Selvin, J.; Muthu, M.S. Fast and highly efficient liquid chromatographic methods for qualification and quantification of antibiotic residues from environmental waste. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Cheng, G.; Ahmed, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Hao, H.; Yuan, Z. New methodologies in screening of antibiotic residues in animal-derived foods: Biosensors. Talanta 2017, 175, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Tian, D.; Phan, A.; Seididamyeh, M.; Alanazi, M.; Xu, Z.P.; Sultanbawa, Y.; Zhang, R. Luminescent sensors for residual antibiotics detection in food: Recent advances and perspectives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 498, 215455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdinasab, M.; Mishra, R.K.; Tang, X.; Marty, J.L. Detection of antibiotics in food: New achievements in the development of biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 127, 115883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Thakur, B.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Khatri, M.; Kim, K.H.; Bhardwaj, N. Nanomaterial-based fluorescent biosensors for the detection of antibiotics in foodstuffs: A review. Food Chem. 2023, 426, 136657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zou, H.; Sun, C.; Li, Y. Recent advances in biosensors for antibiotic detection: Selectivity and signal amplification with nanomaterials. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Niu, Z.; Rodas-Gonzalez, A.; Li, K.; Li, L.; Yang, Q. CoNi bimetallic metal–organic framework and gold nanoparticles-based aptamer electrochemical sensor for enrofloxacin detection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 604, 154369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Han, S. Recent advances in aptamer-based optical and electrochemical biosensors for detection of pesticides and veterinary drugs. Food Control 2022, 131, 108399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnappan, R.; Zaghloul, N.S.; AlZabn, R.; Malkawi, A.; Rahman, A.A.; Abu-Salah, K.M.; Zourob, M. Aptamer selection and aptasensor construction for bone density biomarkers. Talanta 2021, 224, 121818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; He, L.; Wang, J.; Fang, X.; Zhang, L. Developing a combined strategy for monitoring the progress of aptamer selection. Analyst 2017, 142, 3136–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinemann, C.; Von Fritsch, U.F.; Rudolph, S.; Strehlitz, B. Generation and characterization of quinolone-specific DNA aptamers suitable for water monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhamis, O.; Canoura, J.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Y. Innovative engineering and sensing strategies for aptamer-based small-molecule detection. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 121, 115699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Ma, P.; Mahmood, K.I.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. A review: Construction of aptamer screening methods based on improving the screening rate of key steps. Talanta 2023, 253, 124003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Su, R.; Bie, J.; Sun, H.; Qiao, S.; Ma, X.; Sun, R.; Zhang, T. Label-free fluorescent sensor based on aptamer and thiazole orange for the detection of tetracycline. Dye. Pigment. 2018, 149, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jia, B.; Song, P.; Long, N.; Shi, L.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L.; Kong, W. Precision-SELEX aptamer screening for the colorimetric and fluorescent dual-readout aptasensing of AFB1 in food. Food Chem. 2024, 436, 137661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; He, K.; Gunasekaran, S. Self-assembled tetrahedral DNA nanostructures-based ultrasensitive label-free detection of ampicillin. Talanta 2022, 243, 123292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Y.; Yang, D.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; He, C.; Wang, B. Truncated affinity-improved aptamer for selective and sensitive detection of streptomycin in dairy products with label-free electrochemical aptasensor. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 121, 105422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Li, S.; Fan, Z.X.; Hoque, M.N.; Fan, Z. Ultrahigh-rate supercapacitors with large capacitance based on edge oriented graphene coated carbonized cellulous paper as flexible freestanding electrodes. J. Power Sources 2016, 325, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lan, L.; Yao, Y.; Ping, J.; Li, Y.; Ying, Y. An unmodified gold nanorods-based DNA colorimetric biosensor with enzyme-free hybridization chain reaction amplification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; You, Y.; Xia, Z.; Han, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, N. Graphene oxide-based selection and identification of ofloxacin-specific single-stranded DNA aptamers. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 99540–99545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Gao, Z.; Li, H. Real milk sample assisted selection of specific aptamer towards sarafloxacin and its application in establishment of an effective aptasensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 343, 130113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Food Safety Standard-Maximum Residue Limits for 41 Veterinary Drugs in Foods. Available online: http://down.foodmate.net/standard/sort/3/126484.html (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Elaslani, K.; Loudiki, A.; Chhaibi, B.; Laghrib, F.; El Houssame, S.; Bakasse, M.; Lahrich, S.; Farahi, A.; Mhammedi, M.E. Enhancing of ofloxacin oxidation current through the overvoltage position displacement using carbon paste electrode modified by silver particles: Analytical application in water. Chem. Inorg. Mater. 2023, 1, 100013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.W.; Wu, H.L.; Huang, Y.L. Automated on-line microdialysis sampling coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography for simultaneous determination of malondialdehyde and OFL in whole blood. Talanta 2009, 79, 1071–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Guo, Z.; Gao, S.; Ma, L.; Xu, J.; Yu, Z.; Bu, D. Assessment of veterinary antibiotics from animal manure-amended soil to growing alfalfa, alfalfa silage, and milk. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 224, 112699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, M.; Wang, M.; Zhang, R.; Wang, W.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Wang, X. Integration of phase separation with ultrasound-assisted salt-induced liquid–liquid microextraction for analyzing the fluoroquinones in human body fluids by liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 985, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, S.; Chen, D.W.; Zhao, Y.F.; Wu, Y.N.; Qi, K.M. Selective extraction and enhanced-sensitivity detection of fluoroquinolones in swine body fluids by liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry: Application in long-term monitoring in livestock. Food Chem. 2021, 341 Pt 2, 128269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Ding, S.; Jiang, H.; Shen, J.; Xia, X. Multiresidue analysis of sulfonamides, quinolones, and tetracyclines in animal tissues by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Name | DNA Sequences (5′-3′) | ΔG (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| Apt-WO-01 | GAACTTGAGTGTATGATTGCTTCGAATCTAGCCGC | −3.60 |
| Apt-WO-02 | GGGGGTCCCTGATACGCGGTTATTCGATTACGACT | −4.54 |
| Apt-WO-03 | CAGAATAGGGATTGTACGGGAAAATGCGGTGGCGG | −2.78 |
| Apt-WO-04 | CAGACGAGGCTTTCGGAAAAGGAATGATGGACGTC | −4.29 |
| Apt-WO-05 | GAACGCGAGGATTGTATCCAGACAAAGGTCCCATC | −4.41 |
| Apt-WO-06 | GTGAGTTTACATGGGGTCCTATAGGCGAACAATCG | −4.80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Bao, X.; Liu, M.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Kang, X.; Lyu, M.; Wang, S. Aptamer-Based Sensor for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Ofloxacin in Meat Products. Sensors 2024, 24, 1740. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24061740
Wang S, Bao X, Liu M, Hao Q, Zhang S, Li S, Zhang L, Kang X, Lyu M, Wang S. Aptamer-Based Sensor for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Ofloxacin in Meat Products. Sensors. 2024; 24(6):1740. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24061740
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Siyuan, Xiuli Bao, Mingwang Liu, Qingfang Hao, Shuai Zhang, Siying Li, Lei Zhang, Xinxin Kang, Mingsheng Lyu, and Shujun Wang. 2024. "Aptamer-Based Sensor for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Ofloxacin in Meat Products" Sensors 24, no. 6: 1740. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24061740
APA StyleWang, S., Bao, X., Liu, M., Hao, Q., Zhang, S., Li, S., Zhang, L., Kang, X., Lyu, M., & Wang, S. (2024). Aptamer-Based Sensor for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Ofloxacin in Meat Products. Sensors, 24(6), 1740. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24061740







