Matched Stochastic Resonance Enhanced Underwater Passive Sonar Detection under Non-Gaussian Impulsive Background Noise
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Signal Model
2.1. Periodogram-Based Energy Detector (PED) for Passive Sonars
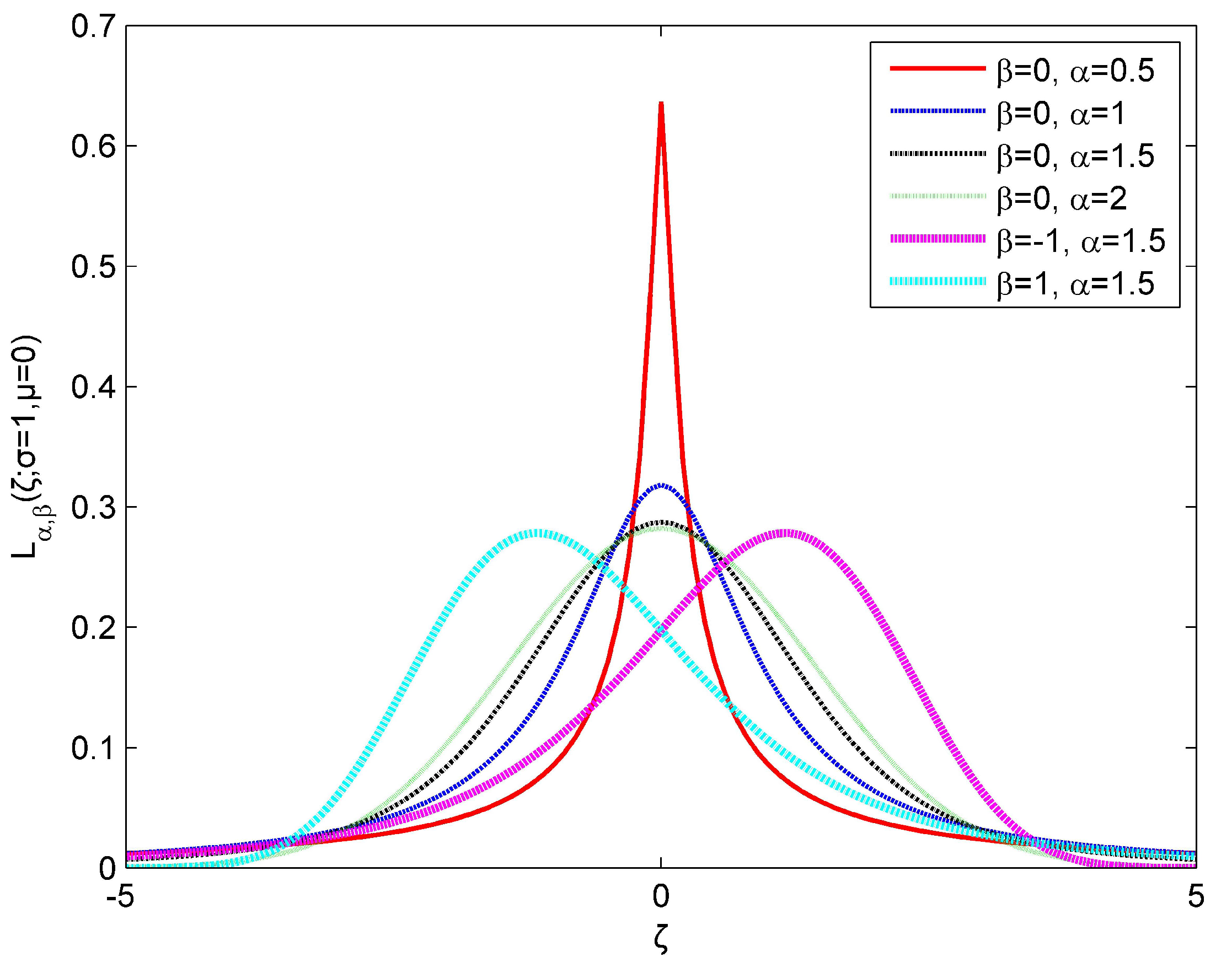
2.2. Non-Gaussian Impulsive Noise Assumption
3. Matched Stochastic Resonance-Based Weak Signal Detector
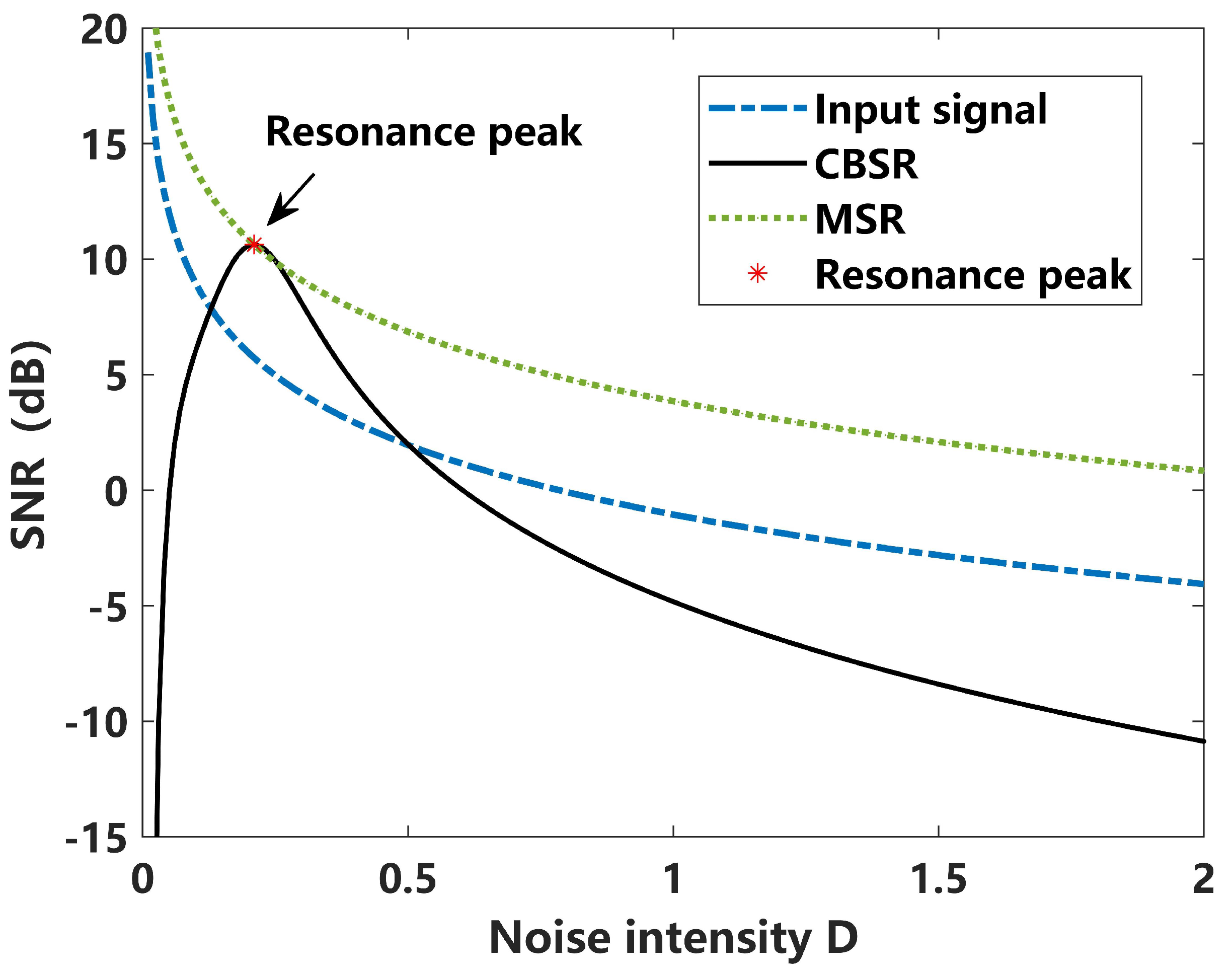
3.1. Classical Bistable Stochastic Resonance (CBSR)
3.2. Framework of Matched Stochastic Resonance (MSR)
3.3. MSR-Based Passive Sonar Detection
3.3.1. Periodogram-Based Energy Detector (MSR-PED)
3.3.2. Peak SNR-Based Detector (MSR-PSNR)
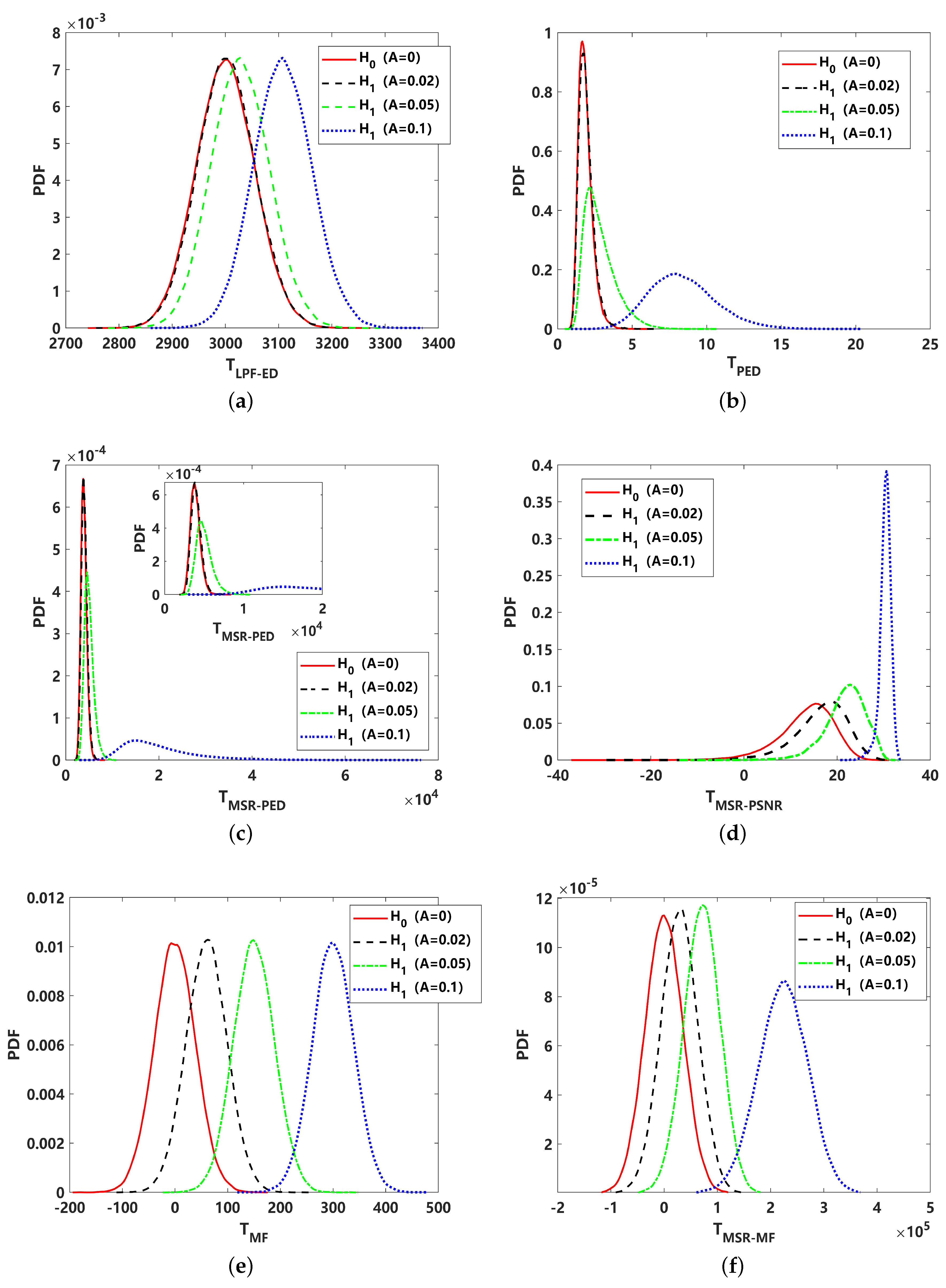
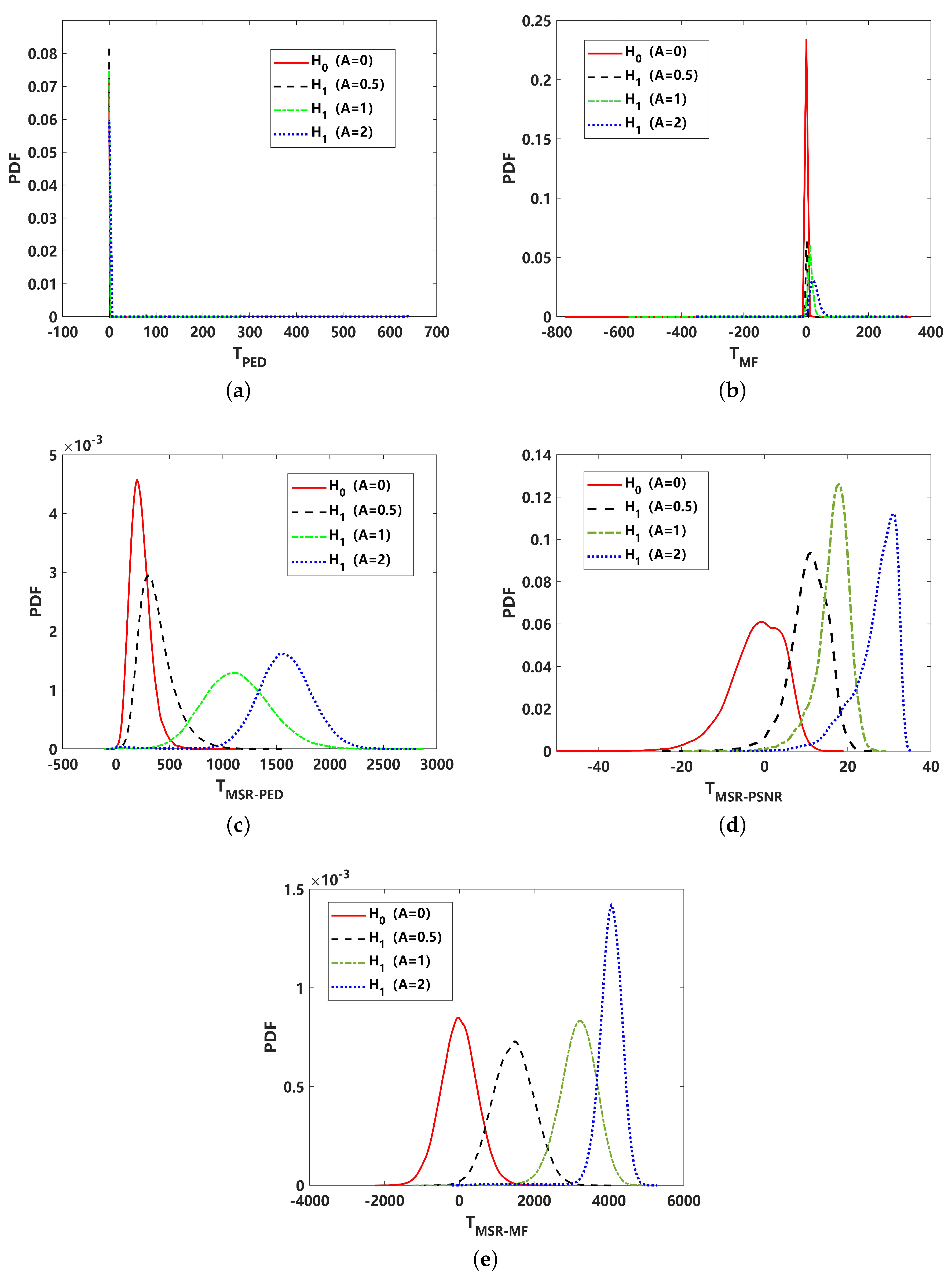
4. Numerical Analyses
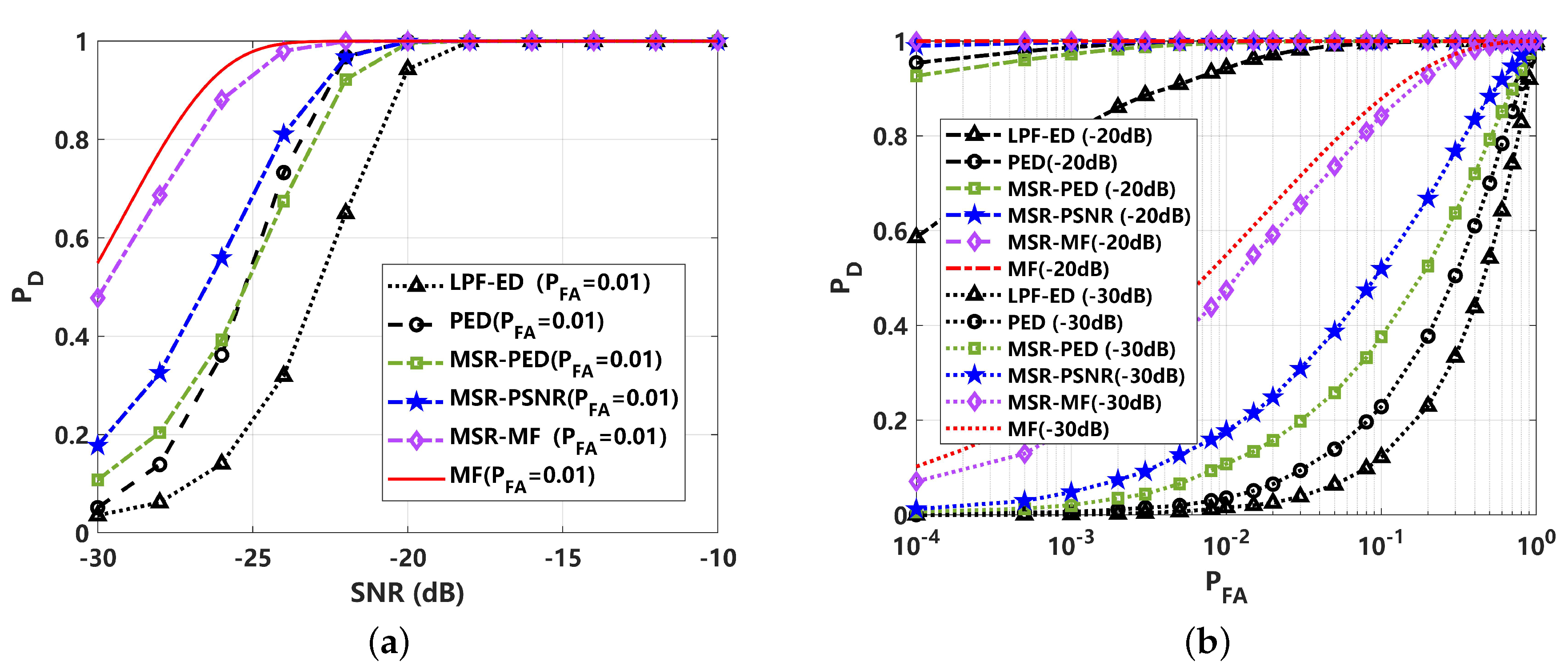
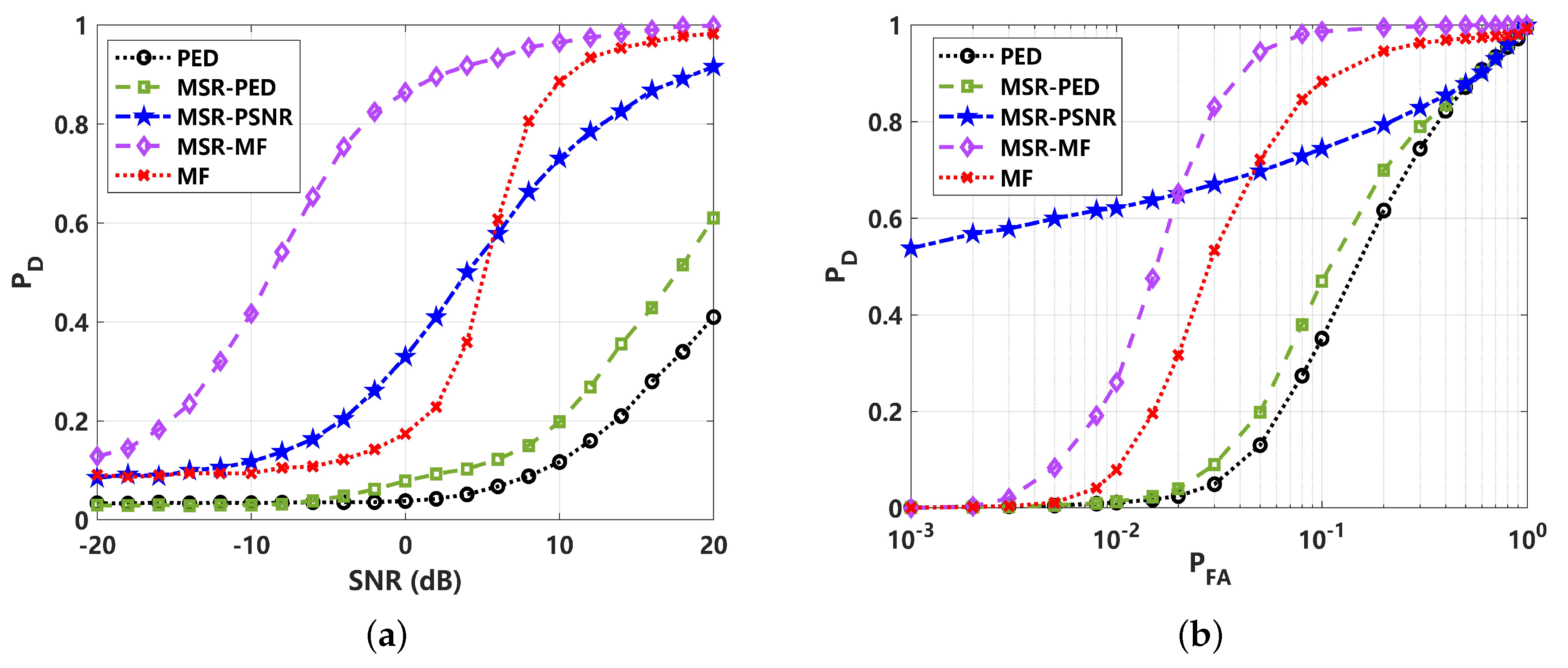
4.1. Detection Performance Analysis under Gaussian Noise ()
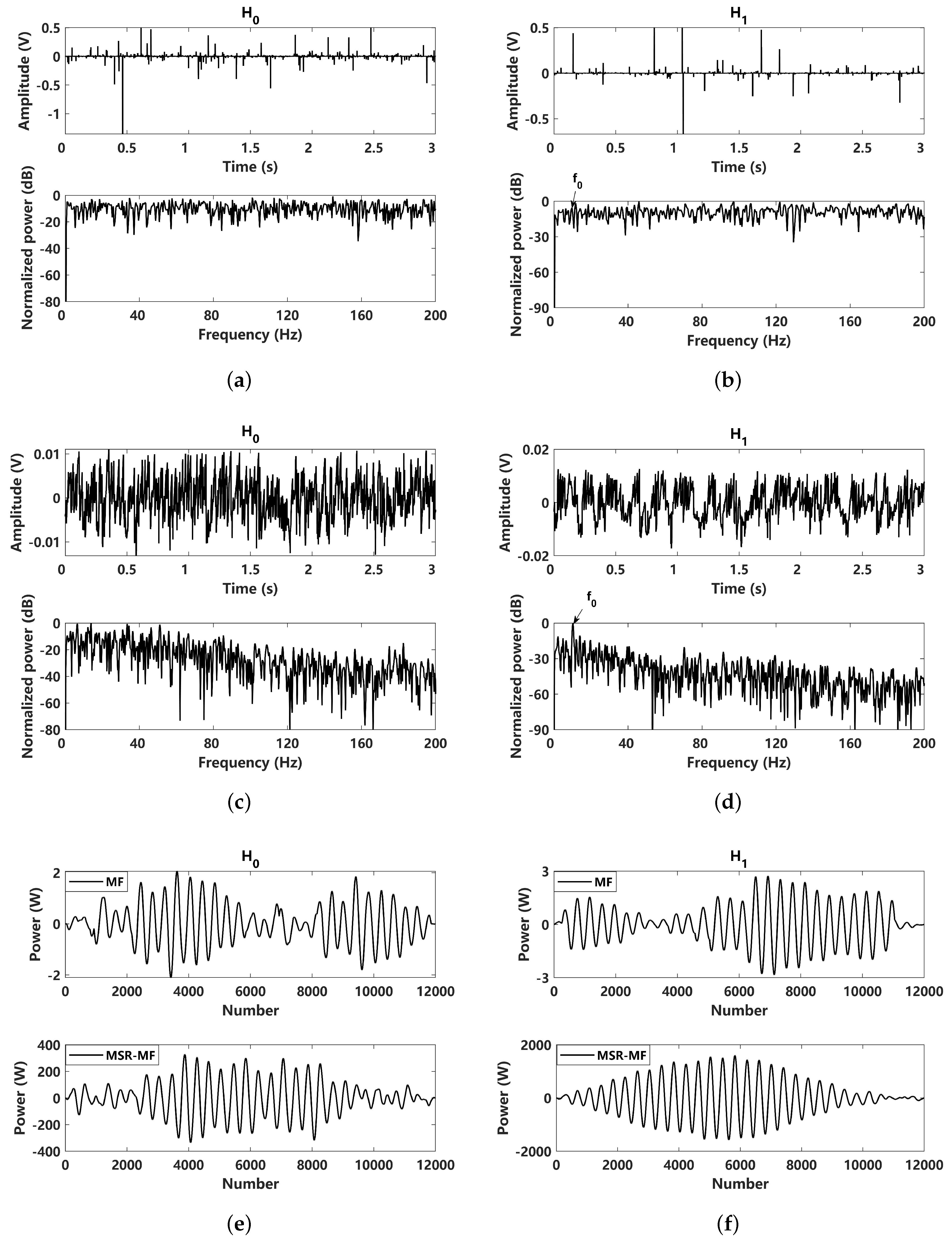
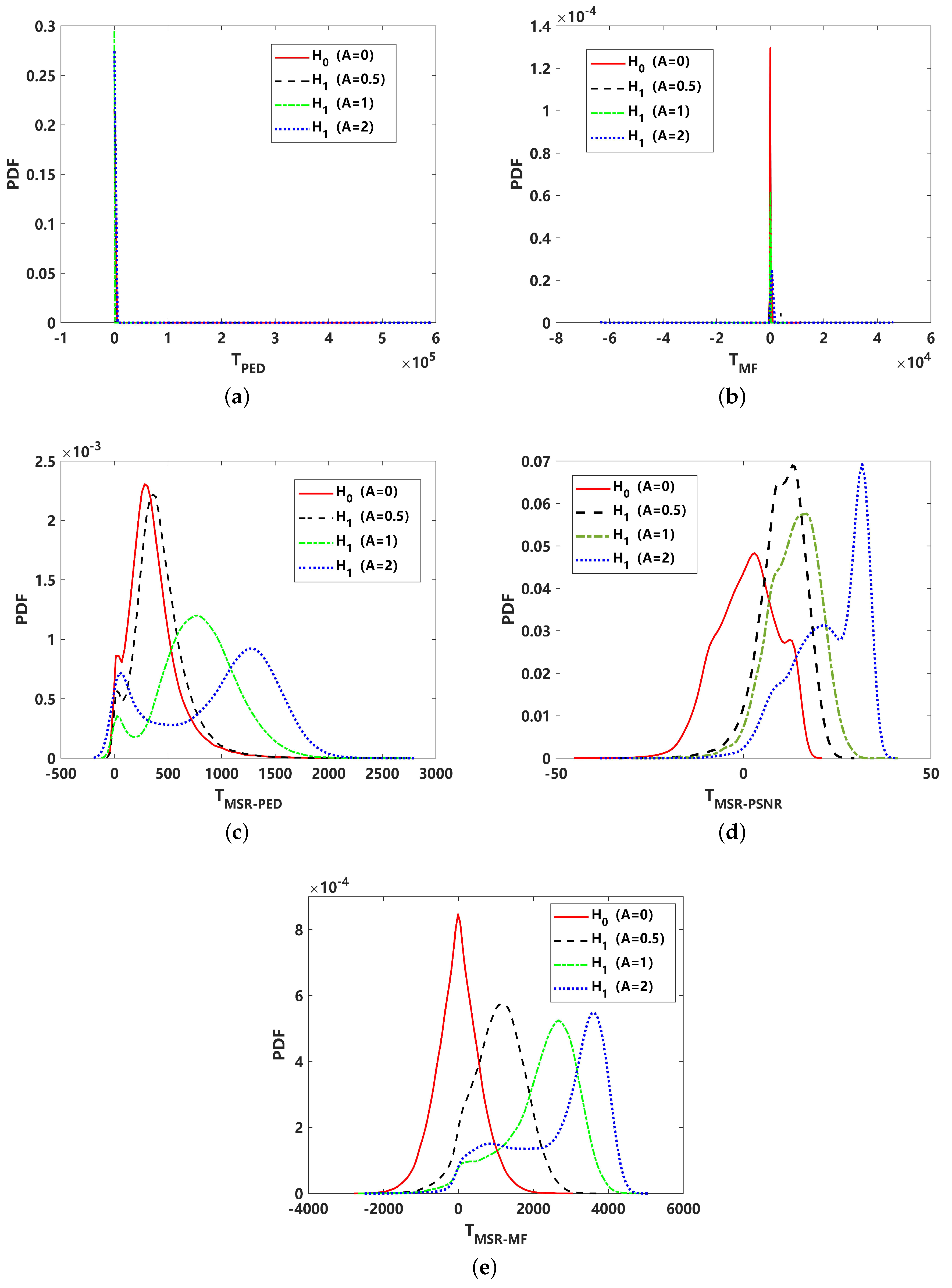
4.2. Detection Performance Analysis under Non-Gaussian Impulsive Noise ()
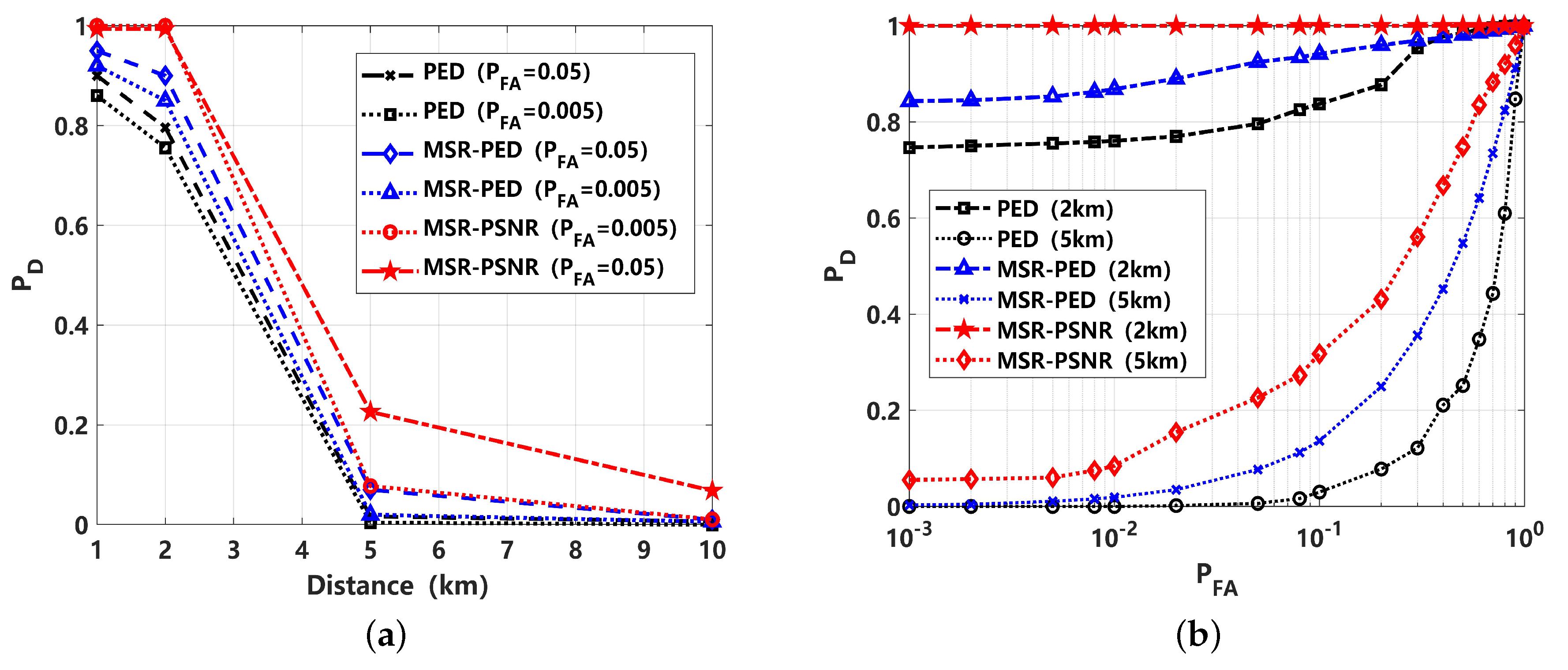
4.3. Detection Performance Analysis under Non-Gaussian Impulsive Noise ()
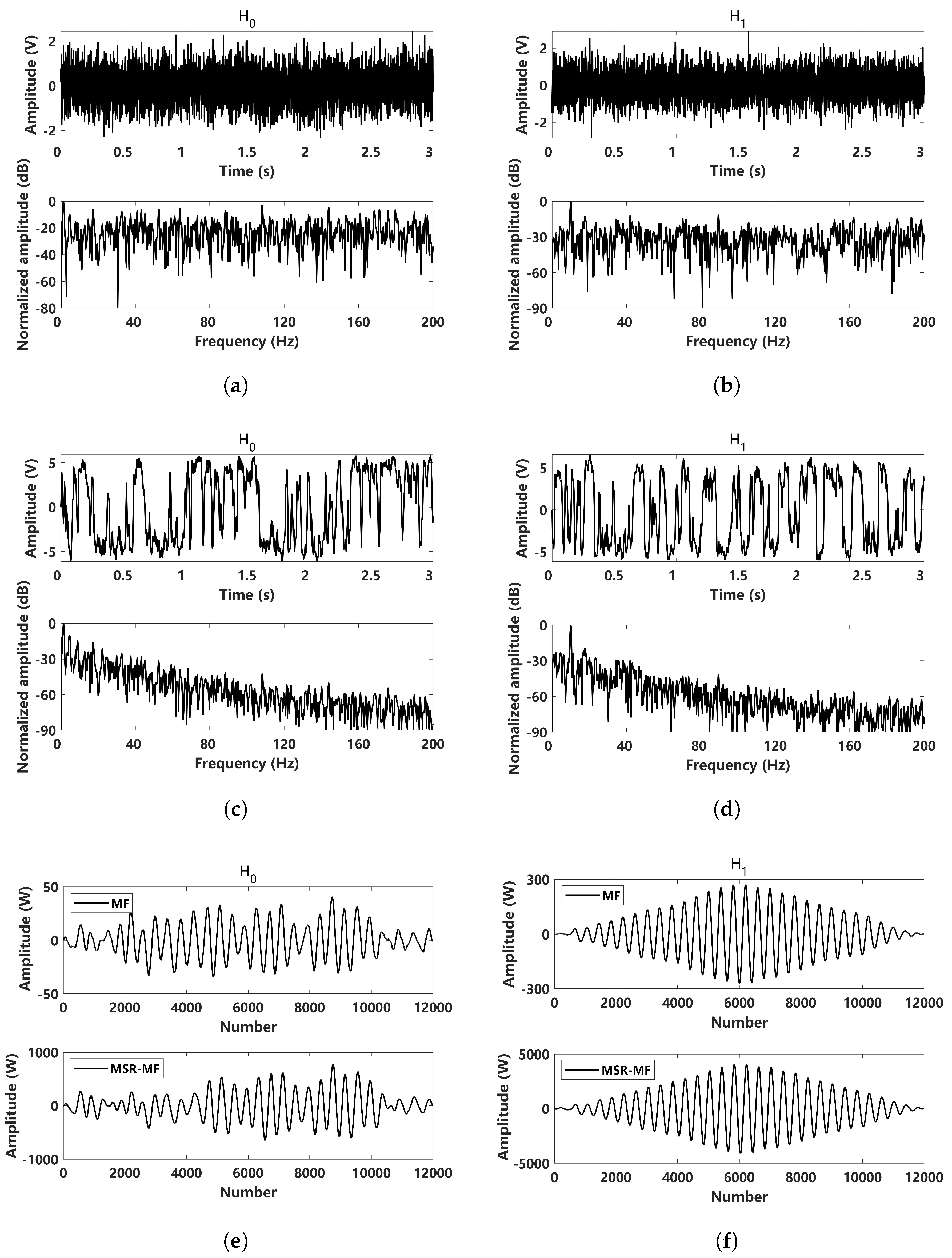
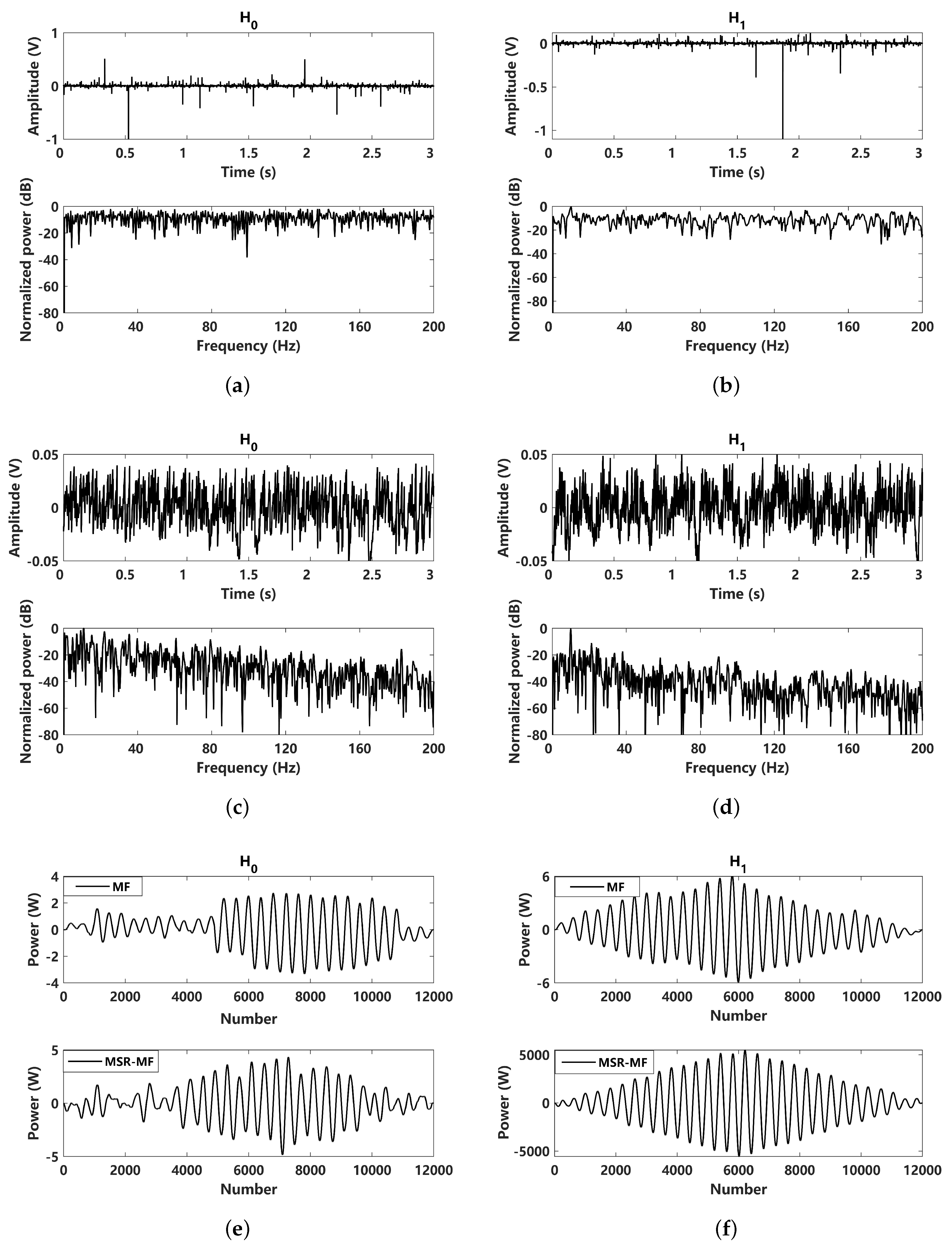
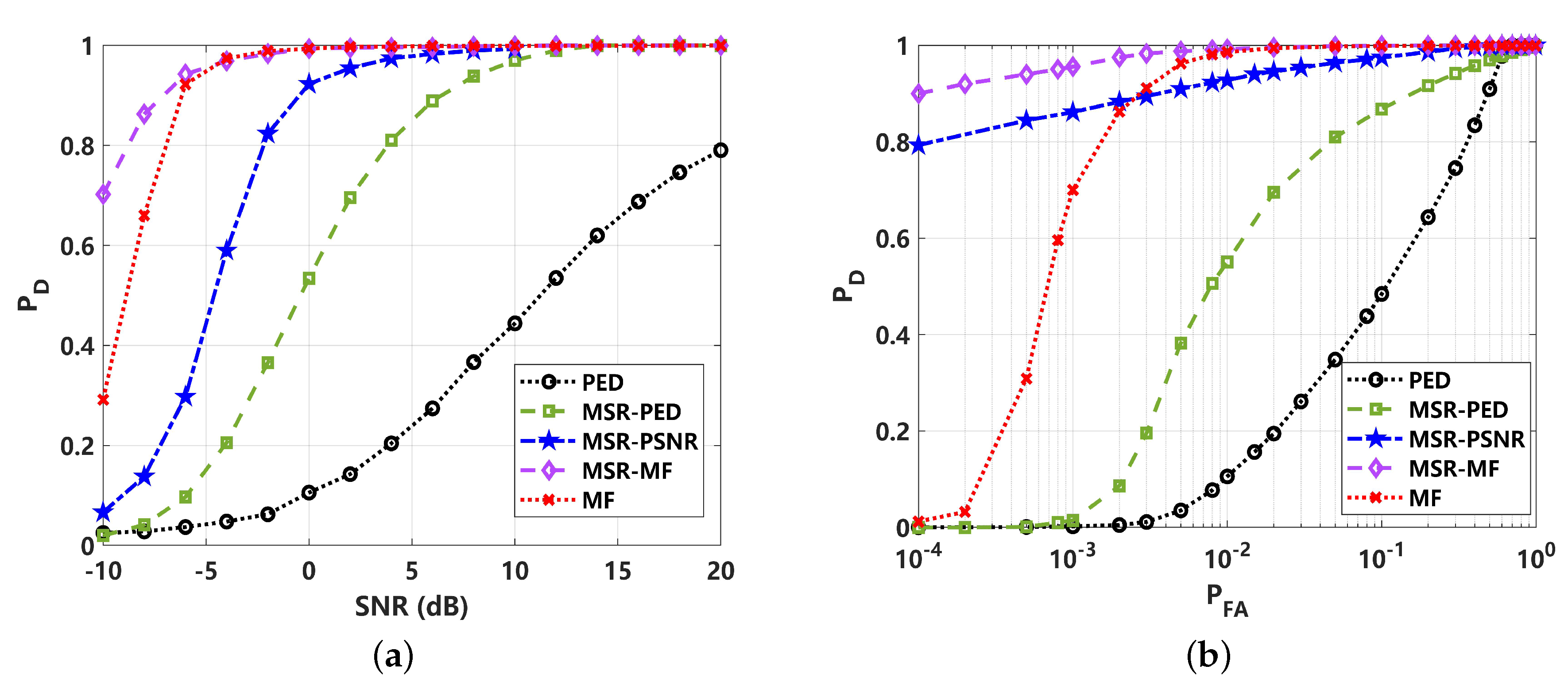
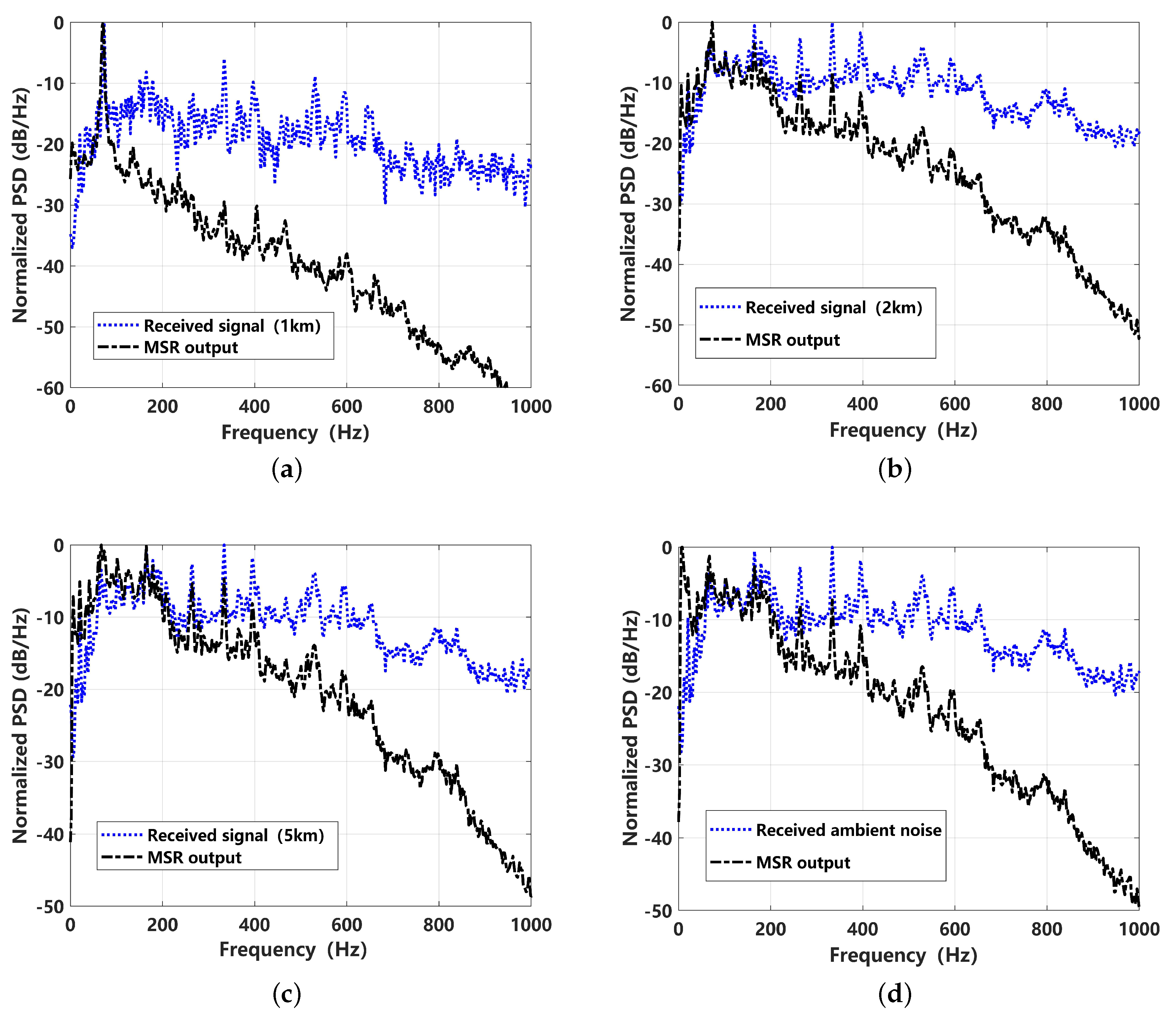
5. Experimental Verification
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Etter, P.C. Advanced applications for underwater acoustic modeling. Adv. Acoust. Vib. 2012, 2012, 214839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, G.L.; Zurk, L.M.; Jones, M.E.; Peterson, M.E. Extraction of small boat harmonic signatures from passive sonar. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 129, 3768–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, C.; Gupta, A. Ship detection using Neyman-Pearson criterion in marine environment. Ocean. Eng. 2017, 143, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Wang, X. Joint Detection and Reconstruction of Weak Spectral Lines under Non-Gaussian Impulsive Noise with Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, D. Mechanics of Underwater Noise; Pergamon Press: Los Altos, CA, USA, 1976; pp. 272–280. [Google Scholar]
- Urick, R.J. Principles of Underwater Sound; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 266–284. [Google Scholar]
- Arveson, P.T.; Vendittis, D.J. Radiated noise characteristics of a modern cargo ship. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000, 107, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephen, R.A.; Bolmer, S.T.; Dzieciuch, M.A.; Worcester, P.F.; Andrew, R.K.; Buck, L.J.; Mercer, J.A.; Colosi, J.A.; Howe, B.M. Deep seafloor arrivals: An unexplained set of arrivals in long-range ocean acoustic propagation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 126, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoni, J.; Hanson, D. Detection of surface ships from interception of cyclostationary signature with the cyclic modulation coherence. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2012, 37, 478–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.W.; Cheng, G.L.; Chen, Y.N.; Zhang, M.M. On the porpogation mechanism of ship seismic wave and its application in mine fuze. Acta Armamentarii 2017, 38, 319. [Google Scholar]
- Trabattoni, A.; Barruol, G.; Dréo, R.; Boudraa, A. Ship detection and tracking from single ocean-bottom seismic and hydroacoustic stations. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 153, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertilone, D.C.; Killeen, D.S. Statistics of biological noise and performance of generalized energy detectors for passive detection. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2001, 26, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, H.; Shen, X.; He, K. Parameter matched stochastic resonance with damping for passive sonar detection. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 458, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Chi, C.; Liang, G. Sparsity-driven adaptive enhancement of underwater acoustic tonals for passive sonars. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 147, 2192–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; He, K.; Shen, X.; Ma, S.; Wang, H.; Qiao, C. Adaptive intrawell matched stochastic resonance with a potential constraint aided line enhancer for passive sonars. Sensors 2020, 20, 3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izacard, G.; Bernstein, B.; Fernandez-Granda, C. A learning-based framework for line-spectra super-resolution. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 3632–3636. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ma, Y. DeepLofargram: A deep learning based fluctuating dim frequency line detection and recovery. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 148, 2182–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikias, C.L.; Shao, M. Signal Processing with Alpha-Stable Distributions and Applications; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Andrew, R.K.; Howe, B.M.; Mercer, J.A.; Dzieciuch, M.A. Ocean ambient sound: Comparing the 1960s with the 1990s for a receiver off the California coast. Acoust. Res. Lett. Online 2002, 3, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Yan, S.; Shi, W.; Yang, X.; Guo, Y.; Gulliver, T.A. A novel underwater acoustic signal denoising algorithm for Gaussian/non-Gaussian impulsive noise. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 70, 429–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haining, H.; Yu, L. Underwater acoustic detection: Current status and future trends. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2019, 34, 264–271. [Google Scholar]
- Roch, M.A.; Soldevilla, M.S.; Burtenshaw, J.C.; Henderson, E.E.; Hildebrand, J.A. Gaussian mixture model classification of odontocetes in the Southern California Bight and the Gulf of California. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 121, 1737–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Chitre, M. Modeling colored impulsive noise by Markov chains and alpha-stable processes. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2015-Genova, Genova, Italy, 18–21 May 2015; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Jonathan, P.; Ewans, K. Statistical modelling of extreme ocean environments for marine design: A review. Ocean. Eng. 2013, 62, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassam, S.A. Signal Detection in Non-Gaussian Noise; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Goh, B.M.K.; Lim, H.S. Sequential algorithms for sample myriad and weighted myriad filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 60, 6047–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsihrintzis, G.A.; Nikias, C.L. Performance of optimum and suboptimum receivers in the presence of impulsive noise modeled as an alpha-stable process. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1995, 43, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammaitoni, L.; Hänggi, P.; Jung, P.; Marchesoni, F. Stochastic resonance. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1998, 70, 223–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Lei, Y.; Li, N. Applications of stochastic resonance to machinery fault detection: A review and tutorial. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 122, 502–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; He, Q.; Wang, J. A review of stochastic resonance in rotating machine fault detection. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 116, 230–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, H.; Shen, X.; Jiang, Z. Effects of Second-Order Matched Stochastic Resonance for Weak Signal Detection. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 46505–46515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Shen, X.; He, K.; Wang, H. Nonlinear filtering effects of intrawell matched stochastic resonance with barrier constrainted duffing system for ship radiated line signature extraction. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 141, 110428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zozor, S.; Amblard, P.O. On the use of stochastic resonance in sine detection. Signal Process. 2002, 82, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zozor, S.; Amblard, P.O. Stochastic resonance in locally optimal detectors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2003, 51, 3177–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Varshney, P.K.; Kay, S.M.; Michels, J.H. Theory of the stochastic resonance effect in signal detection: Part I—Fixed detectors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2007, 55, 3172–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hari, V.; Anand, G.; Premkumar, A.B.; Madhukumar, A. Design and performance analysis of a signal detector based on suprathreshold stochastic resonance. Signal Process. 2012, 92, 1745–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, F.; Chapeau-Blondeau, F.; Abbott, D. Stochastic resonance with colored noise for neural signal detection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Pan, Y.; Duan, F. SNR gain enhancement in a generalized matched filter using artificial optimal noise. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 155, 111741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Duan, F.; Bao, R.; Li, J. Stochastic resonance with tuning system parameters: The application of bistable systems in signal processing. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2002, 13, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ren, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Li, S. Adaptive bistable stochastic resonance aided spectrum sensing. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2014, 13, 4014–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; He, Q.; Kong, F. Effects of underdamped step-varying second-order stochastic resonance for weak signal detection. Digit. Signal Process. 2015, 36, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Lei, Y.; Lin, J.; Jia, F. An adaptive unsaturated bistable stochastic resonance method and its application in mechanical fault diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 84, 731–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Duan, D. Multi-parameter-adjusting stochastic resonance in a standard tri-stable system and its application in incipient fault diagnosis. Nonlinear Dyn. 2019, 96, 2069–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, D.C.; Du, L.C.; Wang, C.J. The effects of time delay on stochastic resonance in a bistable system with correlated noises. J. Stat. Phys. 2009, 137, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Ding, X.; Han, D. Study on multi-frequency weak signal detection method based on stochastic resonance tuning by multi-scale noise. Measurement 2014, 47, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yang, H. Lévy noise induced stochastic resonance in an FHN model. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2016, 59, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.N.; Kang, Y.M. Stochastic resonance in underdamped periodic potential systems with alpha stable Lévy noise. Phys. Lett. A 2018, 382, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, H.; Shen, X.; Dong, H. Stochastic resonance for underwater vlf weak signal detection under lévy noise background. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Xiamen, China, 22–25 October 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, S. Fundamentals of Statistical Processing, Volume I: Estimation Theory; PTR Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1993; pp. 83–182. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Feng, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, W.; Duan, J. Lévy noise-induced stochastic resonance in a bistable system. Eur. Phys. J. B 2013, 86, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, B.; Wiesenfeld, K. Theory of stochastic resonance. Phys. Rev. A 1989, 39, 4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.Q. Theory and Methods for Weak Characteristic Signal Detection with Stochastic Resonance; National Defense Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacic, I.; Brennan, M.J. The Duffing Equation: Nonlinear Oscillators and Their Behaviour; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Stocks, N.G. Suprathreshold stochastic resonance in multilevel threshold systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, S.; Imkeller, P.; Pavlyukevich, I.; Peithmann, D. Stochastic Resonance; American Mathematical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Volume 194. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, H.; Ma, S.; Suo, J.; Zhu, Z. Matched Stochastic Resonance Enhanced Underwater Passive Sonar Detection under Non-Gaussian Impulsive Background Noise. Sensors 2024, 24, 2943. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24092943
Dong H, Ma S, Suo J, Zhu Z. Matched Stochastic Resonance Enhanced Underwater Passive Sonar Detection under Non-Gaussian Impulsive Background Noise. Sensors. 2024; 24(9):2943. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24092943
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Haitao, Shilei Ma, Jian Suo, and Zhigang Zhu. 2024. "Matched Stochastic Resonance Enhanced Underwater Passive Sonar Detection under Non-Gaussian Impulsive Background Noise" Sensors 24, no. 9: 2943. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24092943
APA StyleDong, H., Ma, S., Suo, J., & Zhu, Z. (2024). Matched Stochastic Resonance Enhanced Underwater Passive Sonar Detection under Non-Gaussian Impulsive Background Noise. Sensors, 24(9), 2943. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24092943







