Boundary Layer Control with a Plasma Actuator Utilizing a Large GND Mesh Electrode and Two HV Electrode Configurations †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
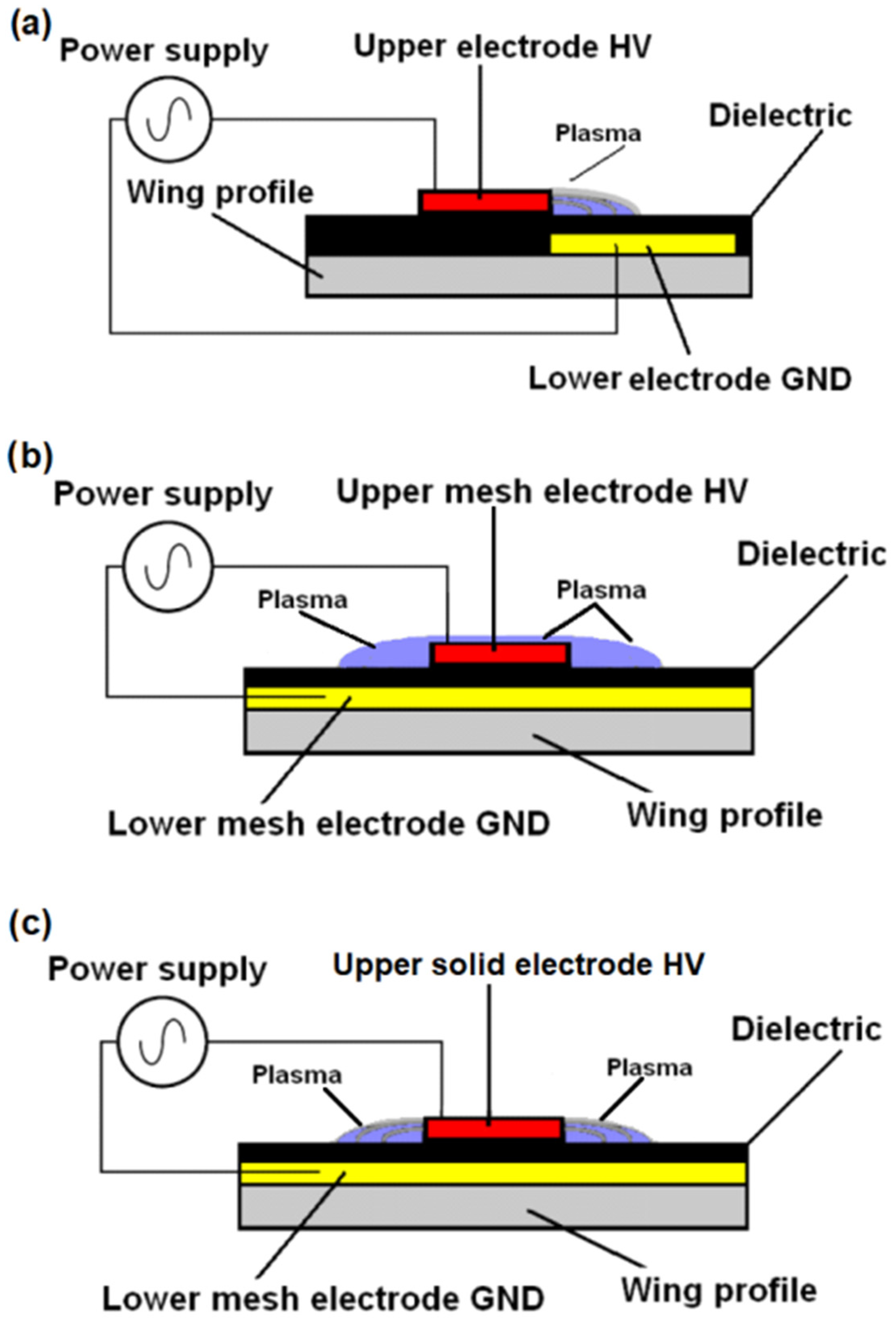
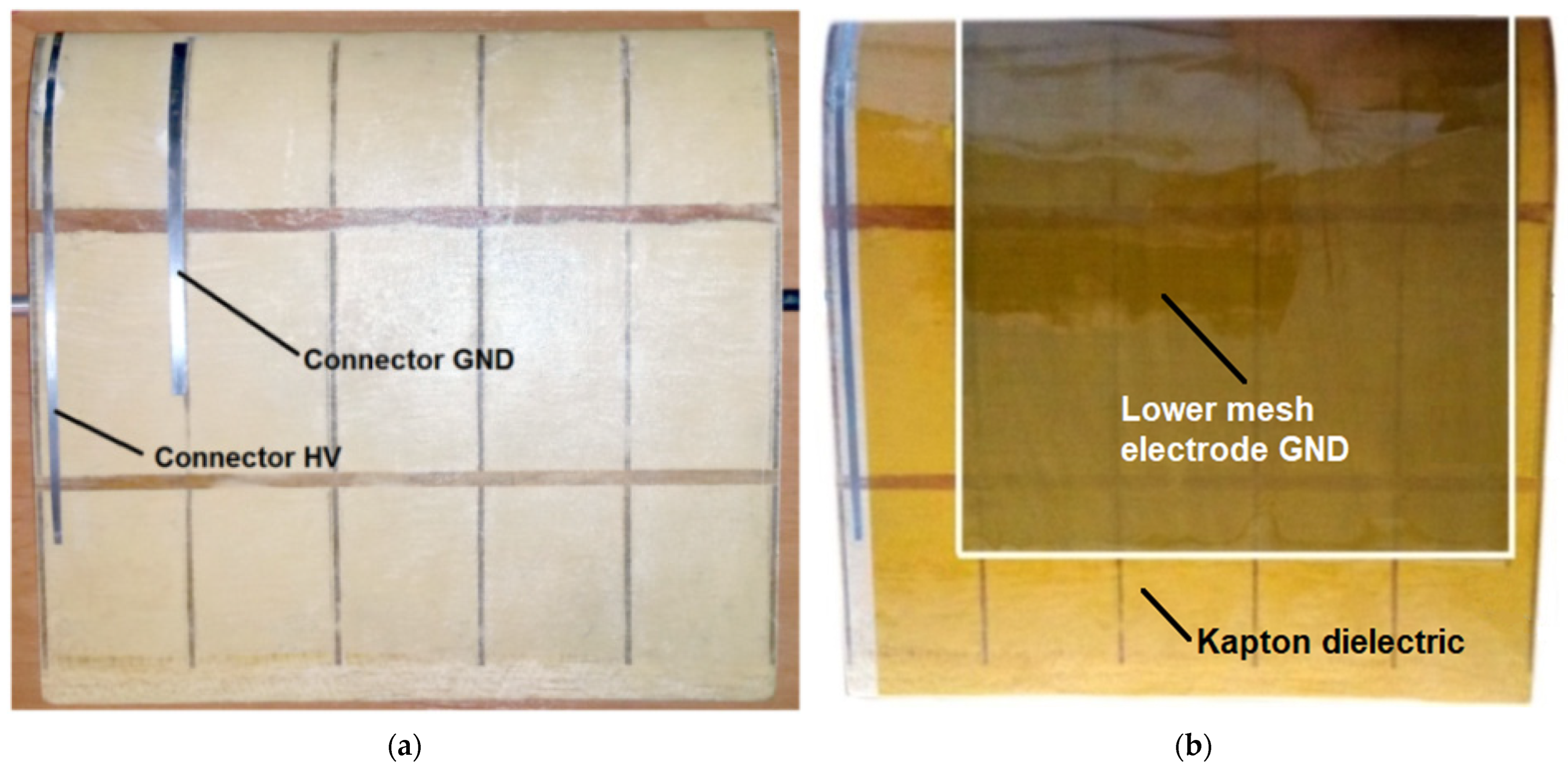
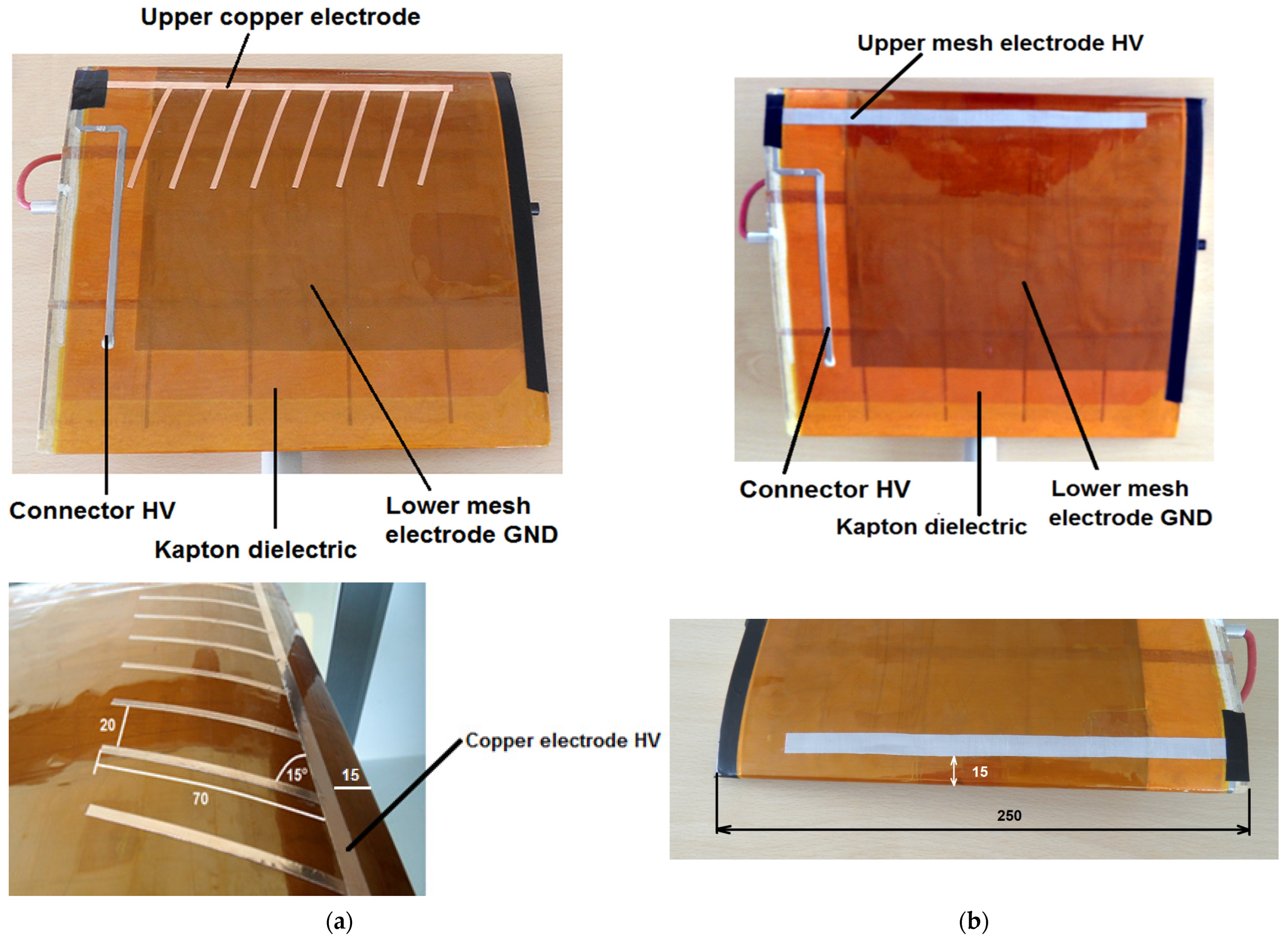
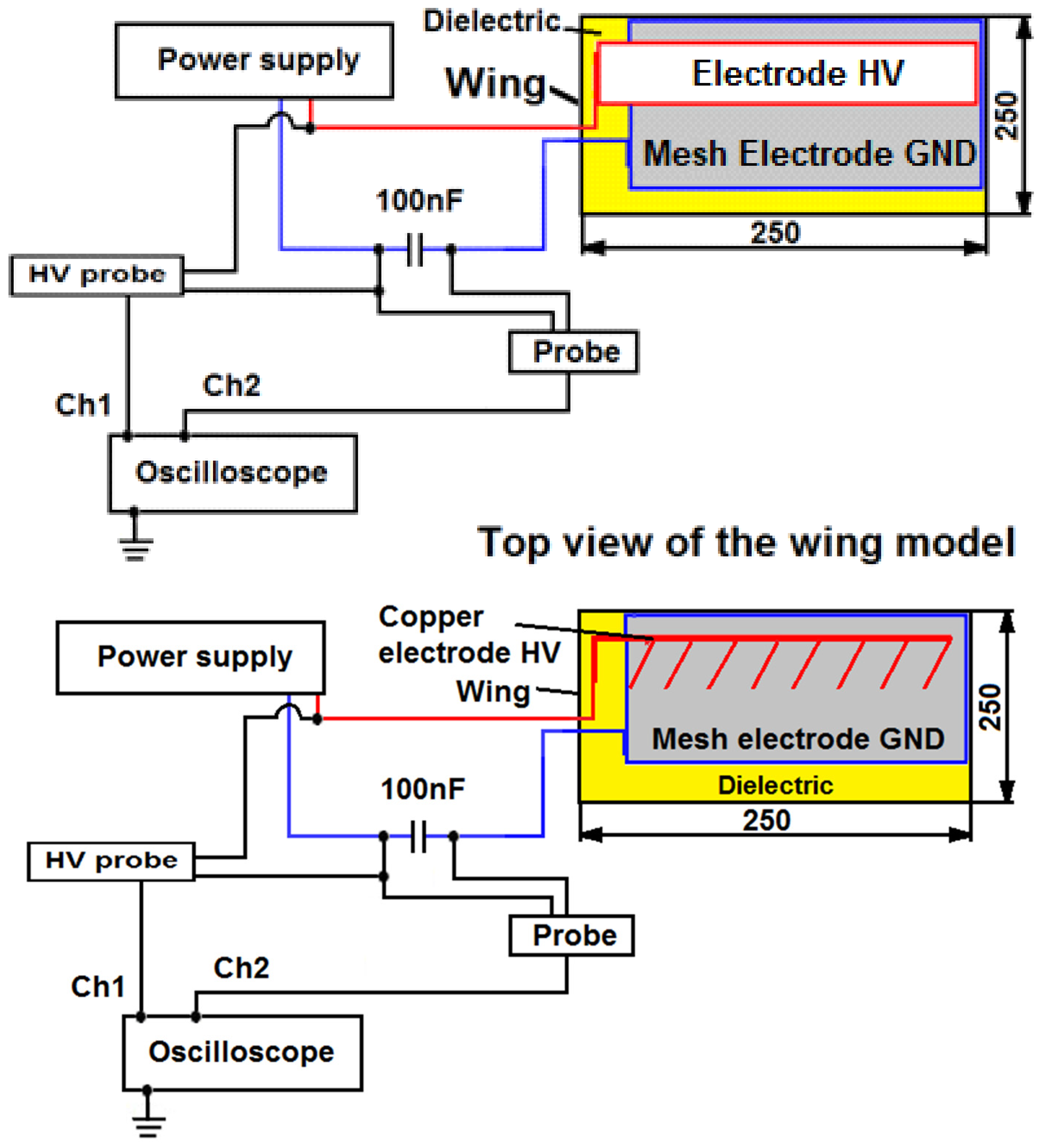
- Another research goal was to verify the expected high efficiency of the plasma actu-ator by using a large GND mesh electrode, which allows discharges to form at both edges of the copper HV electrode, and in the second case, directly through the HV mesh electrode.
- The efficiency of the plasma actuator powered at a frequency of 50 Hz was evaluated during the experiments.
- It was also checked whether the frequency of 50 Hz is optimal for powering the tested plasma actuator.
- The primary objective of the wind tunnel tests was to assess the effectiveness of the new plasma actuator design and determine the optimal geometry for the HV electrode in the DBD system.
- The experimental tests also served to verify the assumptions related to the oblique arrangement of the copper electrodes.
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
The Result Obtained for Plasma Actuator with Mesh Electrode GND and Oblique Copper Electrodes HV
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xue, C.-J.; Han, Y.; Qi, W.-G.; Dai, J.-H. Landing-Gear Drop-Test Rig Development and Application for Light Airplanes. J. Aircr. 2012, 49, 2064–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S. Structural reliability analysis and uncertainties-based collaborative design and optimization of turbine blades using surrogate model. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2018, 42, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Yi, G.; Dong, L.; Gang, M.; Hao, G.; Qun, L.; Ji, X. Design and static testing of wing structure of a composite four-seater electric aircraft. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2020, 27, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yunxia, C.; Rui, K. A study of aircraft landing gear testing system on PHM. In Proceedings of the Prognostics and System Health Managment Confernece, Shenzhen, China, 24–25 May 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninian, D.; Dakka, S.M. Design, Development and Testing of Shape ShiftingWing Model. Aerospace 2017, 4, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.W.; Zhao, X. Effect of Plasma Actuator on Flow Field. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2022, 141, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, I. Mechanical Tests of Aircraft Structural Components. J. R. Aeronaut. Soc. 2016, 36, 673–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnapowski, E.; Pytka, J.; Józwik, J.; Michałowska, J. Wind Tunnel Testing of Mesh Electrodes Plasma Actuator. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 7th International Workshop on Metrology for AeroSpace (MetroAeroSpace), Pisa, Italy, 22–24 June 2020; pp. 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnapowski, E. Review of Selected Methods for Increasing the Aerodynamic Force of the Wing. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2019, 13, b60–b67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhu, D.; Attoui, M.; Deng, Z.; Tang, J.; Jiang, J. Comparison of nanoparticle generation by two plasma techniques: Dielectric barrier discharge and spark discharge. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnapowski, E.; Gnapowski, S.; Pytka, J. The impact of dielectrics on the electricalcapacity, concentration, efficiency ozonegeneration for the plasma reactor with meshelectrodes. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2018, 20, 085505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messanelli, F.; Belan, M. Ionic wind measurements on multi-tip plasma actuators. EPJ Web Conf. 2016, 114, 02073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seraudie, A.; Aubert, E.; Naudé, N.; Cambronne, J. Effect of Plasma Actuators on a Flat Plate Laminar Boundary Layer in Subsonic Conditions. In Proceedings of the 3rd AIAA Flow Control Conference, Fluid Dynamics and Co-located Conferences, San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–8 June 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Do, H.; Choi, H. Drag reduction on a three-dimensional model vehicle using a wire-to-plate DBD plasma actuator. Exp. Fluids 2020, 61, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnapowski, E.; Pytka, J.; Józwik, J.; Laskowski, J.; Michałowska, J. Wind Tunnel Testing of Plasma Actuator with Two Mesh Electrodes to Boundary Layer Control at High Angle of Attack. Sensors 2021, 21, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, Z.; Hu, X.; Guo, P.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. Separation Flow Control of a Generic Ground Vehicle Using an SDBD Plasma Actuator. Energies 2019, 12, 3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Wang, C.C. Bulk flow modification with horseshoe and serpentine plasma actuators. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 032004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendt, A.; Podliński, J.; Mizeraczyk, J. Multi DBD plasma actuator for flow separation control around NACA0012 and NACA0015 airfoil models. Przegląd Elektrotech. 2012, 88, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Leroy, A.; Audier, P.; Podlinski, J.; Berendt, A.; Hong, D.; Mizeraczyk, J. Enhancement of lift and drag performances of NACA0012 airfoil by multi-DBD plasma actuator with additional floating interelectrodes. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Electrohydrodynamics, Gdańsk, Poland, 23–26 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gnapowski, E. Effect of Mesh Electrodes Geometry on the Ozone Concentration in the Presence of Micanite Dielectric. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2018, 12, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogelschatz, U.; Eliasson, B.; Egli, W. From ozone generators to at television screens: History and future potential of dielectric-barrier discharges. Pure Appl. Chem. 1999, 71, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Li, J.; Niu, Z.; Liang, H.; Zhao, G.; Hua, W. Aerodynamic performance enhancement of a flying wing using nanosecond pulsed DBD plasma actuator. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2015, 28, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverkamp, R.G.; Miller, B.B.; Free, K.W. Ozone Production in a High Frequency Dielectric Barrier Discharge Generator. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2002, 24, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.T.; Kong, M.G. Frequency range of stable dielectric-barrier discharges in atmospheric He and N/sub2/. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2004, 32, 1709–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnapowski, E.; Gnapowski, S. Changes in the power discharge in a plasma reactor using porous versus solid dielectric barriers and meshes electrodes. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2016, 44, 2079–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, S.; Kogoma, M.; Uehara, M.; Kimura, Y. Appearance of stable glow discharge in air, argon, oxygen and nitrogen at atmospheric pressure using a 50 Hz source. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1993, 26, 889.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, K.; Ninomiya, Y.; Fujii, K.; Oyama, A. Airfoil Flow Experiment on the Duty Cycle of DBD Plasma Actuator. In Proceedings of the 47th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Aerospace Sciences Meetings, Orlando, FL, USA, 5–8 January 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangyin, Z.; Yinghong, L.; Hua, L.; Menghu, H.; Yun, W. Flow separation control on swept wing with nanosecond pulse driven DBD plasma actuators. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2015, 28, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.P.; Ng, T.T.; Vasudevan, S.; Corke, T.C.; Post, M.L.; McLaughlin, T.E.; Suchomel, C.F. Scaling Effects of an Aerodynamic Plasma Actuator. J. Aircr. 2008, 45, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yan, H.; Jin, Y.; Ren, C. Plasma Actuator Performance Driven by Dual-Power Supply Voltage—AC High Voltage Superimposed with Pulse Bias Voltage. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2017, 45, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Hong, D.; Pouvesle, J.; Boucinha, V.; Weber, R.; Leroy, A. Study of a DBD plasma actuator dedicated to airflow separation control. In Proceedings of the IEEE 35th International Conference on Plasma Science, Karlsruhe, Germany, 15–19 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Corke, T.C.; Thomas, F.O. Plasma Actuators for Separation Control of Low-Pressure Turbine Blades. AIAA J. 2012, 44, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, H.; Shiraishi, T. Experimental Characterization of Dual-Grounded Tri-Electrode Plasma Actuator. AIAA J. 2015, 53, 3157–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuong, L.N.; Dieu, N.; Tran, O.; Doan, V.; Duc, D. Influence of oxygen concentration, feed gas flow rate and air humidity on the output of ozone produced by corona discharge. Vietnam J. Chem. 2019, 57, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayanan, V.; Balakrishnan, A.; Mahendran, N. Effects of Temperature and Flow Rates of Ozone Generator on the DBD by Varying Various Electrical Parameters. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2012, 9, 1496–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetyaningrum, A.; Kusumaningtyas, D.; Suseno, P.; Ratnawati, R. Effect of pH and Gas Flow Rate on Ozone Mass Transfer of Κ-Carrageenan Solution in Bubble Column Reactor. Reakt. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 18, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Mizuno, Y.; Blajan, M. Basic Study on Flow Control by Using Plasma Actuator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 3472–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobiev, A.; Rennie, R.M.; Jumper, E.J. Lift Enhancement by Plasma Actuators at Low Reynolds Numbers. J. Aircr. 2013, 50, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, Y.-N.; Kim, I.-T.; Cho, G. Discharge Characteristics and Plasma Erosion of Various Dielectric Materials in the Dielectric Barrier Discharges. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


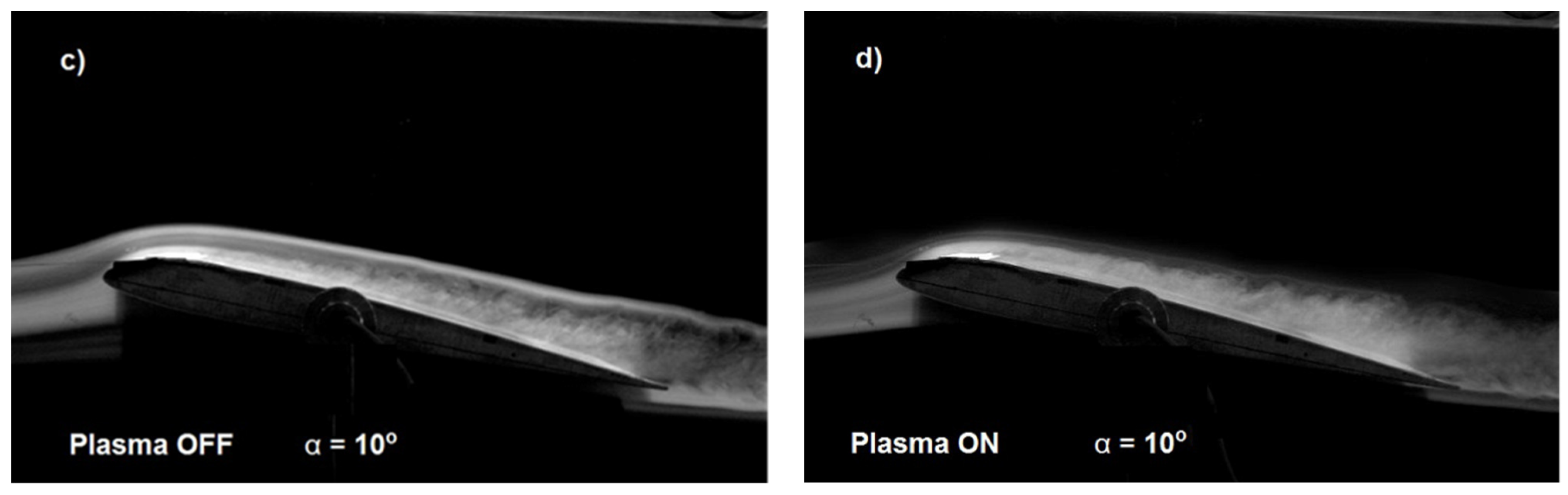

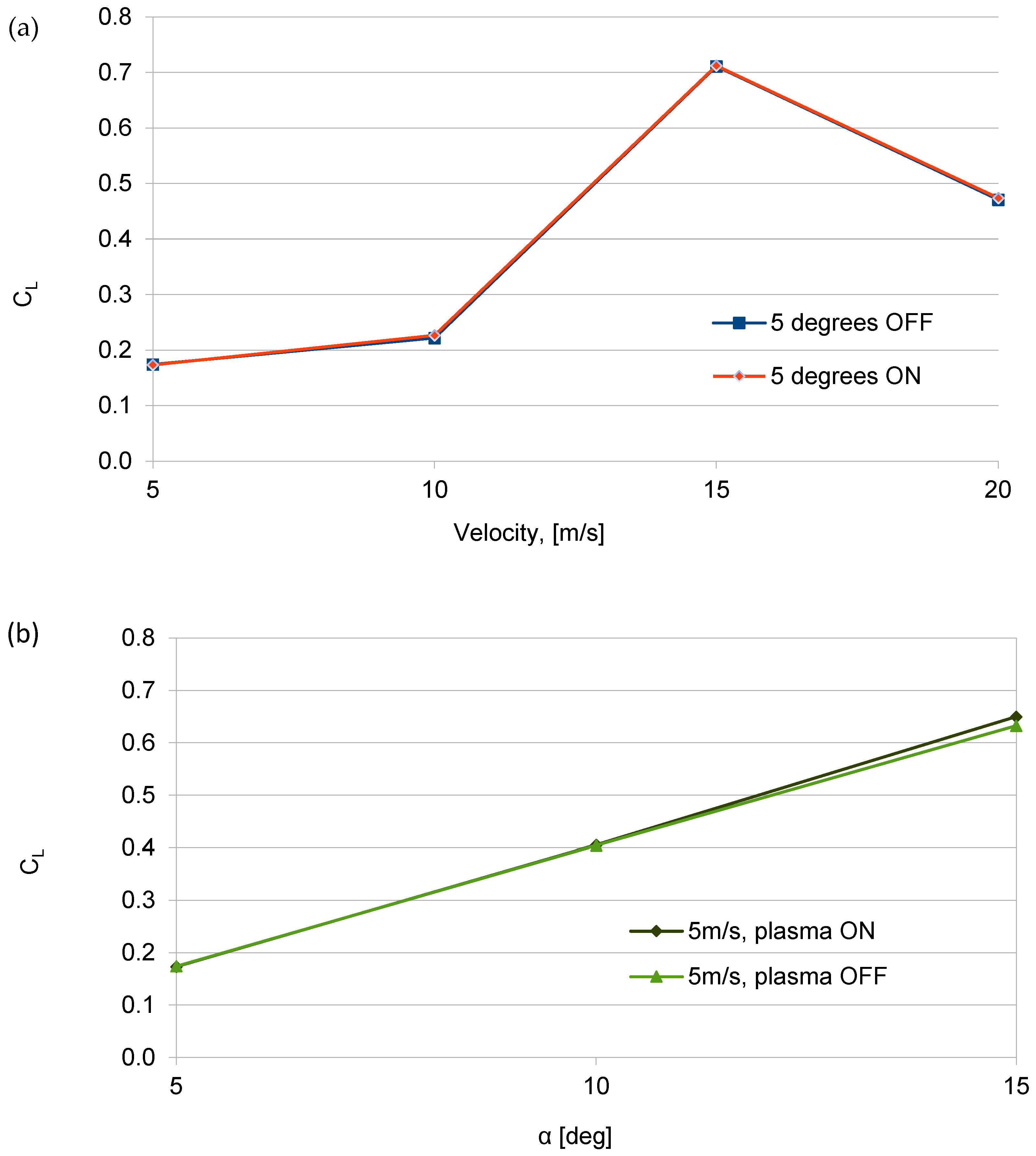
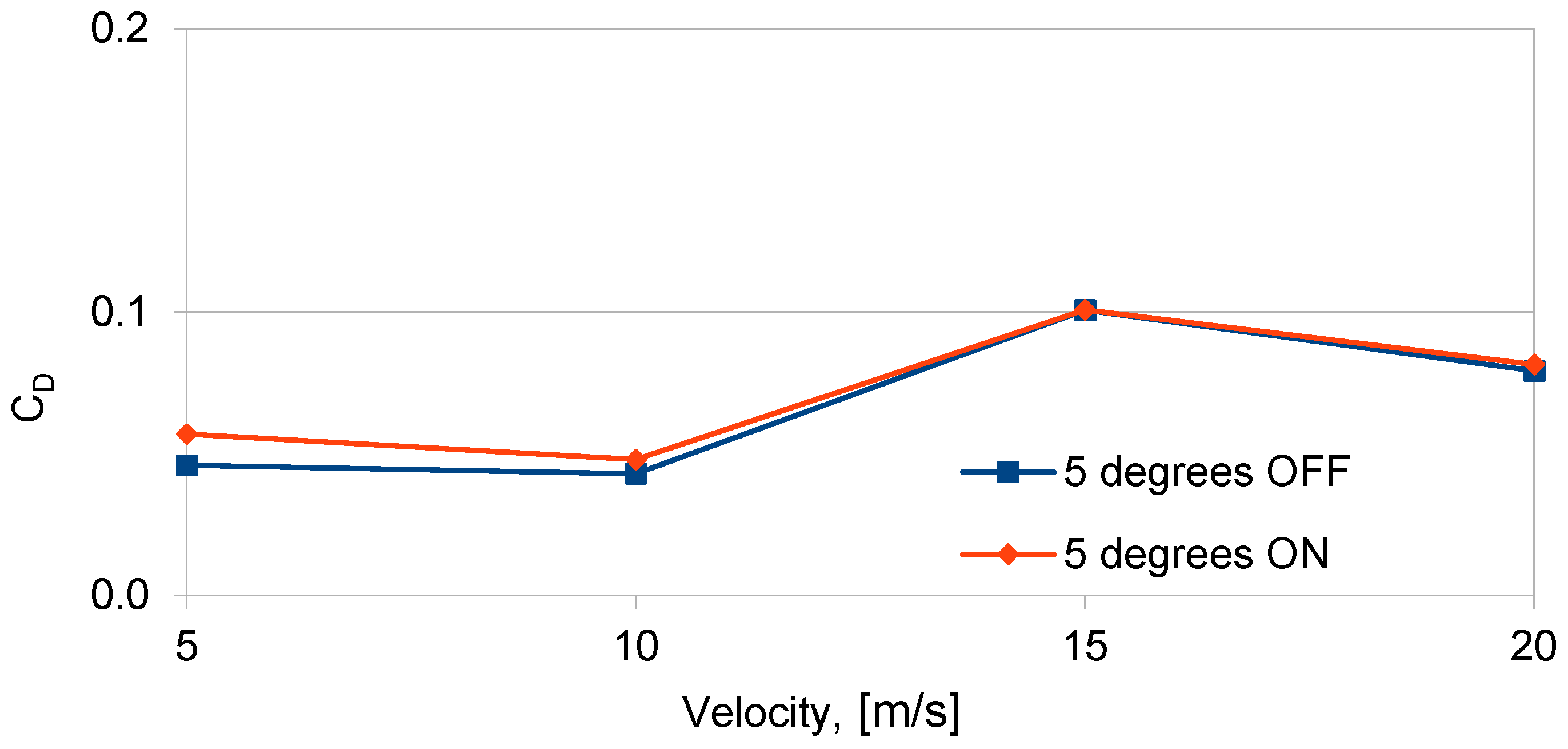
| V (m/s) | Normal Force (N) | Axial Force (N) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma Actuator | ||||
| OFF | ON | OFF | ON | |
| 5 | 0.40 | 0.48 | 0.03 | 0.09 |
| 10 | 3.33 | 3.40 | 0.16 | 0.18 |
| 15 | 6.57 | 6.65 | 0.33 | 0.36 |
| 20 | 7.40 | 7.61 | 0.34 | 0.40 |
| V (m/s) | Normal Force (N) | Axial Force (N) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma Actuator | ||||
| OFF | ON | OFF | ON | |
| 5 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| 10 | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.07 | 0.08 |
| 15 | 6.18 | 6.19 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| 20 | 7.29 | 7.33 | 0.56 | 0.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gnapowski, E.; Gnapowski, S.; Tomiło, P. Boundary Layer Control with a Plasma Actuator Utilizing a Large GND Mesh Electrode and Two HV Electrode Configurations. Sensors 2025, 25, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25010105
Gnapowski E, Gnapowski S, Tomiło P. Boundary Layer Control with a Plasma Actuator Utilizing a Large GND Mesh Electrode and Two HV Electrode Configurations. Sensors. 2025; 25(1):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25010105
Chicago/Turabian StyleGnapowski, Ernest, Sebastian Gnapowski, and Paweł Tomiło. 2025. "Boundary Layer Control with a Plasma Actuator Utilizing a Large GND Mesh Electrode and Two HV Electrode Configurations" Sensors 25, no. 1: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25010105
APA StyleGnapowski, E., Gnapowski, S., & Tomiło, P. (2025). Boundary Layer Control with a Plasma Actuator Utilizing a Large GND Mesh Electrode and Two HV Electrode Configurations. Sensors, 25(1), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25010105






