Cybersecurity Solutions for Industrial Internet of Things–Edge Computing Integration: Challenges, Threats, and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
- –
- RQ 1. What constitutes IIoT networks and which fundamental technologies facilitate their optimal operation?
- –
- RQ 2. In what ways does edge computing enhance the IIoT and what cybersecurity benefits are linked to its deployment?
- –
- RQ 3. Regarding CPS inside the IIoT, what are their effects on attacks?
- –
- RQ 4. How will edge computing secure CPS with IIoT strategies?
- –
- We developed a process for detecting new and relevant articles on the topic of interest.
- –
- We identified common IIoT layer attacks and penetration approaches.
- –
- We found common attacks and threats in IIoT edge computing.
- –
- We reviewed the cyberattack types over CPS and their impact on industry.
- –
- We broke down the real security techniques CPS in IIoT–edge computing and adopted them into a taxonomy.
- –
- A comparison study between our methodology and existing techniques in this area.
2. Related Work
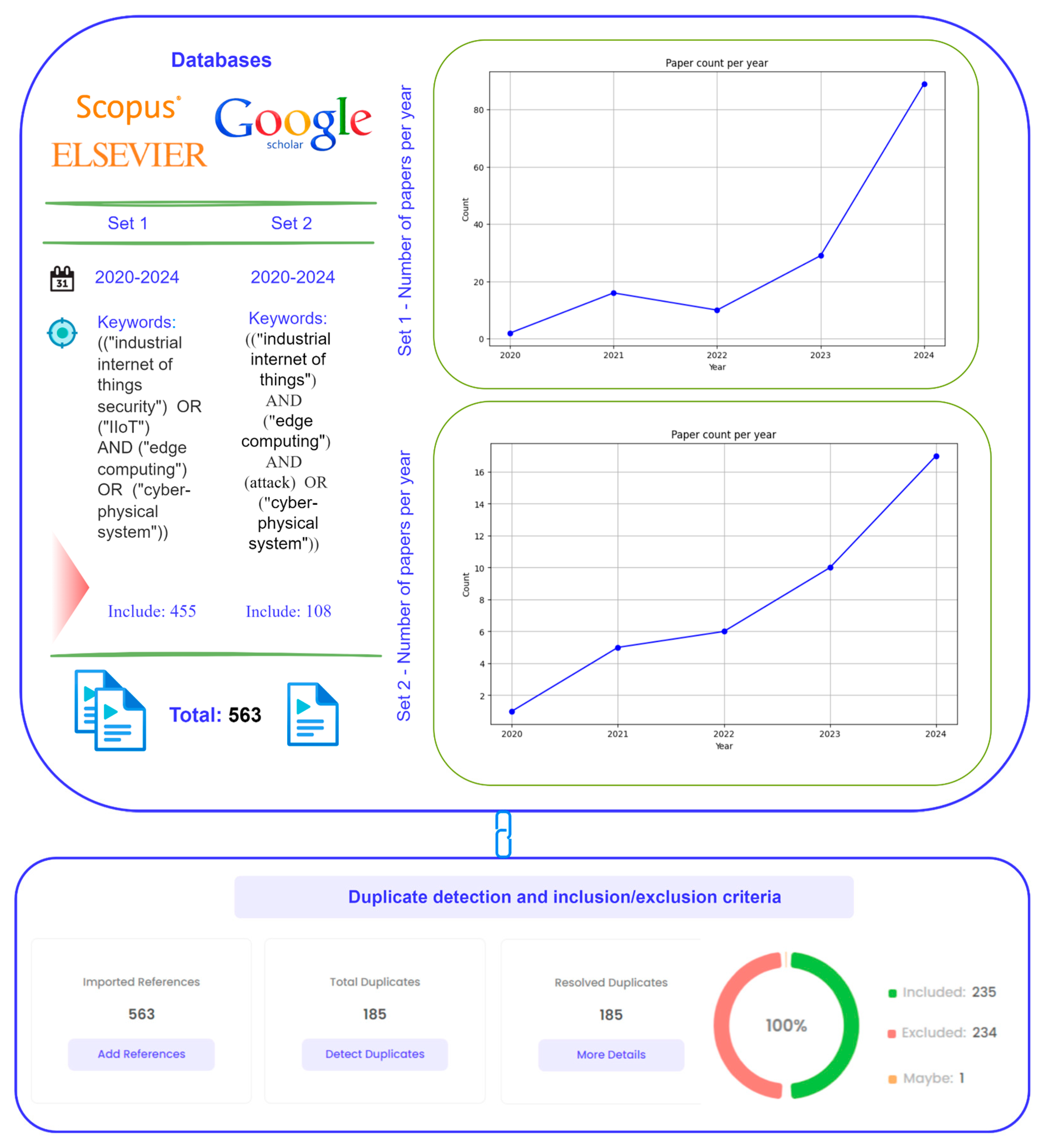
2.1. Methodology of Related Work
2.2. Related Work
3. Overview of Industrial Internet of Things
3.1. IIoT Industry
3.1.1. Implementation Examples
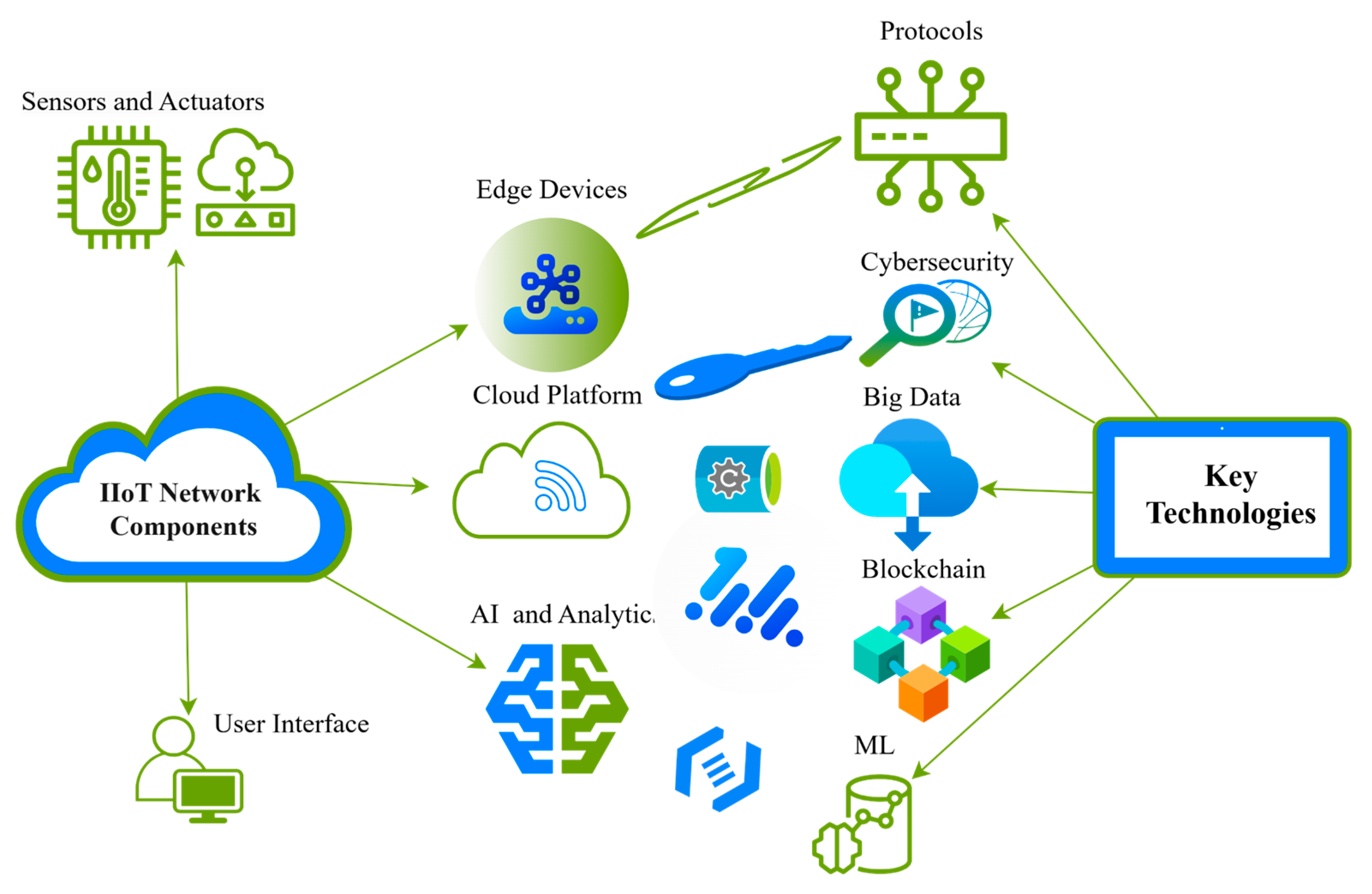
3.1.2. What Are IIoT Networks?
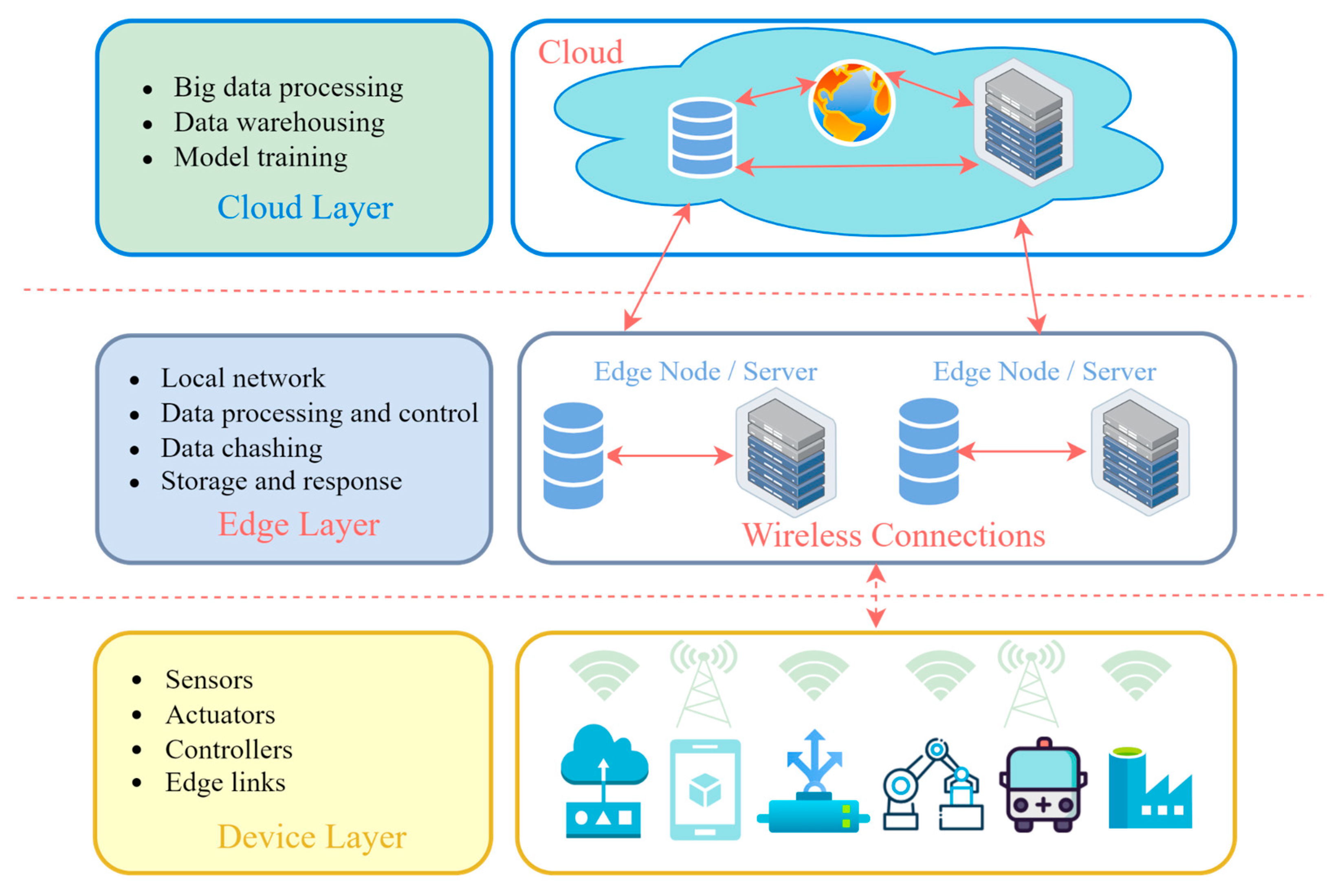
3.1.3. Structure and Components of IIoT Networks
3.1.4. Security and Data Management
3.2. IIoT Technology
3.2.1. Fifth-Generation and 6G Technologies
3.2.2. IIoT Sensors
3.2.3. Cloud and Edge Computing
3.2.4. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
3.3. IIoT Layers Attacks and Intrusion Methods
3.3.1. Application Layer Attacks
3.3.2. Processing Layer Attacks
3.3.3. Network Layer Attacks
3.3.4. Physical (Perception) Layer Attacks
| Authors | Type of Attacks | Effects | Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| [104] | Physical (perception) layer attacks:
|
|
|
| [105,106,107,108] | Network layer attacks:
|
|
|
| [109,110,111] | Processing layer attacks:
|
|
|
| [112] | Application layer attacks:
|
|
|
4. The Role of Edge Computing in the IIoT
4.1. Application of Edge Computing IIoT
4.1.1. Architecture
4.1.2. Applications
4.1.3. Benefits
4.1.4. Security and Anomaly Detection
4.1.5. Challenges and Solutions
4.2. What Ways Can Edge Computing Enhance IIoT, and What Cybersecurity Benefits Does Its Implementation Offer?
4.2.1. Real-Time Data Processing
4.2.2. Augmented Cybersecurity Protocols
4.2.3. Real-Time Anomaly Detection and Security
4.2.4. AI Integration for Improved Security
4.3. Cybersecurity of Industrial Internet of Things–Fog Computing Systems
4.3.1. Access Control and Resource Management
4.3.2. Deep Learning for Intrusion Detection
4.3.3. Physical Layer Security
4.3.4. Zero Trust Architecture
4.3.5. Digital Twin-Managed Security
4.3.6. Blockchain-Enabled Security
4.3.7. Privacy
5. Integration of CPS with IIoT
5.1. Cyber-Physical Systems and Their Significance in Industrial Internet of Things
5.2. Application
5.3. Emerging Challenges
5.4. Overview of Existing Attacks in CPS IIoT
5.5. CPS Cybersecurity
6. Methods for Enhancing the Security of IIoT Cyber-Physical Systems Using Edge Computing
6.1. AI Methods
Federated Learning
6.2. Integration of IT/OT Security
6.3. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
6.4. Cryptography and Encryption
6.5. Edge Computing
7. Discussion and Recommendation
7.1. IIoT Attacks
7.2. Types of Cyber Attacks Against CPS
7.3. Analysis of Cybersecurity Approaches for Cyber-Physical Systems in IIoT–Edge Computing Integration
- -
- Integration of Cybersecurity and Physical Security—research frequently emphasizes cyberspace, neglecting the physical dimensions of CPS, which may result in vulnerabilities; a collaborative monitoring strategy for both domains can improve high detection accuracy [181].
- -
- Administration of Diverse Devices—contemporary solutions frequently do not satisfy the demands of IIoT devices, including real-time functionality and decentralization; implementing a zero trust architecture with network micro-segmentation can enhance management.
- -
- Identification of Uncommon Cyberattacks—the issue is intensified by the data imbalance in training datasets; advanced models, such as focal causal networks can proficiently rectify these imbalances, improving detection time [182].
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Z.; Gao, H.; Cong, X.; Wu, N.; Song, H.H. A Survey on Cyber–Physical Systems Security. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 21670–21686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, D.; Obaidat, M.S.; Vijayakumar, P. Edge-Assisted Intelligent Device Authentication in Cyber–Physical Systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 3057–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oks, S.J.; Jalowski, M.; Lechner, M.; Mirschberger, S.; Merklein, M.; Vogel-Heuser, B.; Möslein, K.M. Cyber-Physical Systems in the Context of Industry 4.0: A Review, Categorization, and Outlook. Inf. Syst. Front. 2022, 26, 1731–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Chen, J.; Lin, Y.; Zou, A.; Chen, C.; Guan, X.; Ma, Y. Smart Sensing and Communication Co-Design for IIoT-Based Control Systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 3994–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosen, A.S.M.S.; Sharma, P.K.; Ra, I.-H.; Cho, G.H. SPTM-EC: A Security and Privacy-Preserving Task Management in Edge Computing for IIoT. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 6330–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, G.B.; Selvarajan, S.; Ravi, A.K.; Sangeetha, K.; Khadidos, A.O.; Vatchala, S. An Analytical Framework for the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): Importance, Recent Challenges, and Enabling Technologies. In Industry Automation: The Technologies, Platforms and Use Cases; River Publishers: Nordjylland, Denmark, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Zumba, A.; Avila-Pesantez, D. Cybersecurity for Industrial IoT: Threats, Vulnerabilities, and Solutions: A Brief Review. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Congress on Information and Communication Technology (ICICT 2023), London, UK, 20–23 February 2023; Yang, X.S., Sherratt, R.S., Dey, N., Joshi, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems. Springer: Singapore, 2023; Volume 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalapathi, G.S.S.; Chamola, V.; Vaish, A.; Buyya, R. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) Applications of Edge and Fog Computing: A Review and Future Directions. In Fog/Edge Computing for Security, Privacy, and Applications; Chang, W., Wu, J., Eds.; Advances in Information Security; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, F.W.; Redchuk, A. Artificial Intelligence as a Process Optimization Driver under Industry 4.0 Framework and the Role of IIoT: A Bibliometric Analysis. J. Ind. Integr. Manag. 2022, 9, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Chen, L.; He, K.; Xia, J.; Fan, L.; Nallanathan, A. Computational Intelligence and Deep Learning for Next-Generation Edge-Enabled Industrial IoT. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2023, 10, 2881–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, B.T.; Idrees, A.K. Edge Computing for IoT. In Learning Techniques for the Internet of Things; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Enoch, O.S.; Umoga, U.J.; Obaigbena, A.; Jacks, B.S.; Ugwuanyi, D.E.; Daraojimba, A.I.; Lottu, O.A. Current State and Prospects of Edge Computing within the Internet of Things (IoT) Ecosystem. Int. J. Sci. Res. Arch. 2024, 11, 1863–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karyemsetty, N.; Narasimha, P.B.; Tejaswi, M.P.; Sivaji, V.N.; Kamal, C.L.V.; Samatha, B. Cybersecurity Fortification in Edge Computing through the Synergy of Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 7th International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud), Kirtipur, Nepal, 11–13 October 2023; pp. 1154–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Doghman, F.; Moustafa, N.; Khalil, I.; Sohrabi, N.; Tari, Z.; Zomaya, A.Y. AI-Enabled Secure Microservices in Edge Computing: Opportunities and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2023, 16, 1485–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomichev, D.S. Intelligent Communication for Internet of Things (IoRT). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Recent Innovations in Computing (ICRIC 2022), Samba, India, 13–14 May 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abosata, N.; Al-Rubaye, S.; Inalhan, G.; Emmanouilidis, C. Internet of Things for System Integrity: A Comprehensive Survey on Security, Attacks and Countermeasures for Industrial Applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Hu, J.; Wu, H.; Wu, J.; Yang, J.; Sheng, Q.; Dustdar, S. A Comprehensive Survey on Collaborative Data-Access Enablers in the IIoT. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 56, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Seo, Y.D.; Oh, S.-R.; Kim, Y.G. A Survey on Standards for Interoperability and Security in the Internet of Things. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1020–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luxmi, D.; Armstrong, E.; Newe, T. Industrial IoT, Cyber Threats, and Standards Landscape: Evaluation and Roadmap. Sensors 2021, 21, 3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behnke, I.; Austad, H. Real-Time Performance of Industrial IoT Communication Technologies: A Review. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 11, 7399–7410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Jan, M.A.; Rehman, A.U.; Mastorakis, S.; Alazab, M.; Watters, P. A Secured and Intelligent Communication Scheme for IIoT-enabled Pervasive Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 5128–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, A.; Asghar, M.Z. Cyber vulnerabilities detection system in logistics-based IoT data exchange. Egypt. Inform. J. 2024, 25, 100448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathee, G.; Ahmad, F.; Sandhu, R.; Kerrache, C.A.; Azad, M.A. On the design and implementation of a secure blockchain-based hybrid framework for Industrial Internet-of-Things. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.; Queralta, J.P.; Guan, J.; Awais, M.; Gia, T.N.; Bashir, A.K.; Kan, H.; Westerlund, T. Edge Computing to Secure IoT Data Ownership and Trade with the Ethereum Blockchain. Sensors 2020, 20, 3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainudin, A.; Putra, M.A.P.; Alief, R.N.; Kim, D.-S.; Lee, J.-M. Blockchain-aided Collaborative Threat Detection for Securing Digital Twin-based IIoT Networks. In Proceedings of the ICC 2024—IEEE International Conference on Communications, Denver, CO, USA, 9–13 June 2024; pp. 4656–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okfie, M.I.H.; Mishra, S. Anomaly Detection in IIoT Transactions using Machine Learning: A Lightweight Blockchain-based Approach. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2024, 14, 14645–14653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, A.; Myeong, S. Proactive Threat Hunting in Critical Infrastructure Protection through Hybrid Machine Learning Algorithm Application. Sensors 2024, 24, 4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.; Herrera, L.-C.; Donoso, Y.; Gutierrez, J.A. Survey on Intrusion Detection Systems Based on Machine Learning Techniques for the Protection of Critical Infrastructure. Sensors 2023, 23, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazra, A.; Alkhayyat, A.; Adhikari, M. Blockchain for cybersecurity in edge networks. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2022, 13, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Shao, H.; Su, Y.; Wang, C. Efficient heterogeneous signcryption scheme based on Edge Computing for Industrial Internet of Things. J. Syst. Archit. 2023, 136, 102836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayar, A.; Şener, U.; Kayabay, K.; Eren, P.E. Edge computing applications in industrial IoT: A literature review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on the Economics of Grids, Clouds, Systems, and Service, Izola, Slovenia, 13–15 September 2022; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 124–131. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Xue, C.; Wang, J.; Yun, Z.; Lin, N.; Han, S. A Survey on Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Testbeds for Connectivity Research. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.17485v2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehedi, S.T.; Anwar, A.; Rahman, Z.; Ahmed, K.; Islam, R. Dependable Intrusion Detection System for IoT: A Deep Transfer Learning Based Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalipour, A.; Murali, S. A Taxonomy of Machine-Learning-Based Intrusion Detection Systems for the Internet of Things: A Survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 9444–9466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaleh, S.S.; El Bachir Menai, M.; Al-Ahmadi, S. Federated Learning-Based Model to Lightweight IDSs for Heterogeneous IoT Networks: State-of-the-Art, Challenges, and Future Directions. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 134256–134272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohourian, A.; Dadkhah, S.; Molyneaux, H.; Neto, E.C.P.; Ghorbani, A.A. IoT-PRIDS: Leveraging packet representations for intrusion detection in IoT networks. Comput. Secur. 2024, 146, 104034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ding, Y.; Yu, G.; Zhong, Z.; Song, Y. Privacy-preserving dynamic auditing for regenerating code-based storage in cloud-fog-assisted IIoT. Internet Things 2024, 25, 101084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consul, P.; Budhiraja, I.; Garg, D.; Garg, S.; Kaddoum, G.; Hassan, M.M. SFL-TUM: Energy efficient SFRL method for large scale AI model’s task offloading in UAV-assisted MEC networks. Veh. Commun. 2024, 48, 100790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, H.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, H.; Sun, L. Cascading Threat Analysis of IoT Devices in Trigger-Action Platforms. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 12240–12251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainudin, A.; Ahakonye, L.A.C.; Akter, R.; Kim, D.-S.; Lee, J.-M. An Efficient Hybrid-DNN for DDoS Detection and Classification in Software-Defined IIoT Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 8491–8504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houda, Z.A.E.; Brik, B.; Ksentini, A.; Khoukhi, L.; Guizani, M. When Federated Learning Meets Game Theory: A Cooperative Framework to Secure IIoT Applications on Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 7988–7997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellappan, V.; Mahendran, A.; Subramanian, M.; Jotheeswaran, J.; Khadidos, A.O.; Khadidos, A.O.; Selvarajan, S. Sliding principal component and dynamic reward reinforcement learning based IIoT attack detection. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, T.; Xiong, J.; Bhuiyan, M.Z.A.; Ma, J.; Peng, C. A blockchain-based machine learning framework for edge services in IIoT. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 18, 1918–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tan, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, P. A Blockchain-Reinforced Federated Intrusion Detection Architecture for IIoT. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 26793–26805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, H.; Alazab, M.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Han, Z.; Su, C. Blockchain-Based Reliable and Efficient Certificateless Signature for IIoT Devices. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 7059–7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou El Houda, Z.; Brik, B.; Ksentini, A. Securing IIoT applications in 6G and beyond using adaptive ensemble learning and zero-touch multi-resource provisioning. Comput. Commun. 2024, 216, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouedi, O.; Piamrat, K. Toward a Scalable and Energy-Efficient Framework for Industrial Cloud-Edge-IoT Continuum. IEEE Internet Things Mag. 2024, 7, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassini, K.; Khalis, S.; Habibi, O.; Chemmakha, M.; Lazaar, M. An end-to-end learning approach for enhancing intrusion detection in Industrial-Internet of Things. Knowl. Based Syst. 2024, 294, 111785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandanwar, H.; Katarya, R. Deep learning enabled intrusion detection system for Industrial IOT environment. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 249, 123808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayan, H.; Nunes, M.; Rana, O.; Burnap, P.; Perera, C. Cybersecurity of industrial cyber-physical systems: A review. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 54, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Bin Alam, S.; Hoque, M.; Lameesa, A.; Afrin, S.; Farah, T.; Kabir, M.; Shafiullah, G.; Muyeen, S. Industrial Internet of Things enabled technologies, challenges, and future directions. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 110, 108847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayalaxmi, P.L.S.; Saha, R.; Kumar, G.; Kim, T.H. Machine and deep learning amalgamation for feature extraction in Industrial Internet-of-Things. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 97, 107610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.R.; Kawade, M.M.; Bharti, G.K.; Laxmaiah, G. Implementation of Intelligent CPS for Integrating the Industry and Manufacturing Process. In AI-Driven IoT Systems for Industry 4.0; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 273–288. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Shi, Z.; Liu, X. Imperceptible Adversarial Attack with Multigranular Spatiotemporal Attention for Video Action Recognition. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 17785–17796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hawawreh, M.; Hossain, M.S. Digital twin-driven secured edge-private cloud Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) framework. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2024, 226, 103888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, E.V.N.; Kranthi, M.; Sailaja, S.; Sesadri, U.; Koka, S.N.; Reddy, P.C.S. An Adaptive Intrusion Detection System in Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2024 1st International Conference on Innovative Sustainable Technologies for Energy, Mechatronics, and Smart Systems (ISTEMS), Dehradun, India, 26–27 April 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Visveshwarappa, M. Opportunities and Challenges of Digital Connectivity for Industrial Internet of Things. In AI-Driven IoT Systems for Industry 4.0; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Ma, M.; Wang, H. ASAP-IIOT: An Anonymous Secure Authentication Protocol for Industrial Internet of Things. Sensors 2024, 24, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, A. Distributed Systems, Web Technology, Cloud Computing and IoT Utilization for Sustainable Asset Management based on AI-driven Predictive Maintenance in Enterprise Systems. J. Inf. Technol. Inform. 2024, 3, 39–59. [Google Scholar]
- Selvarajan, S.; Srivastava, G.; Khadidos, A.O.; Khadidos, A.O.; Baza, M.; Alshehri, A.; Lin, J.C.W. An artificial intelligence lightweight blockchain security model for security and privacy in IIoT systems. J. Cloud Comput. 2023, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levshun, D.; Kotenko, I. A survey on artificial intelligence techniques for security event correlation: Models, challenges, and opportunities. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 8547–8590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, W.; Yun, L.; Zhiyi, L.; Jinlong, S.; Guan, G. A Distributed Sensor System Based on Cloud-Edge-End Network for Industrial Internet of Things. Future Internet 2023, 15, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sharma, S.; Sahu, A.; Sharma, A. Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Cities. Int. Res. J. Adv. Eng. Manag. 2024, 2, 2526–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, M.; Goyal, A.; Choudhary, A. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): A vivid perspective. In Inventive Systems and Control, Proceedings of the ICISC 2021, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 1–3 December 2021; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 939–949. [Google Scholar]
- Manogaran, G.; Alazab, M.; Shakeel, P.M.; Hsu, C.H. Blockchain assisted secure data sharing model for Internet of Things based smart industries. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2021, 71, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.C.; Ding, M.; Pathirana, P.N.; Seneviratne, A.; Li, J.; Niyato, D.; Poor, H.V. Federated learning for industrial internet of things in future industries. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2021, 28, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munirathinam, S. Industry 4.0: Industrial internet of things (IIoT). In Advances in Computers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 117, pp. 129–164. [Google Scholar]
- Pingli, D.; Muthu, B.A.; Kadry, S.N. Industrial internet of things for smart manufacturing applications using hierarchical trustful resource assignment. Work 2021, 68, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, N.; Padmapriya, V.; Kumar, N.; Rawat, M.; Singh, A. IoT for the Industry & Business. In Futuristic Trends in IOT; IIP Series: Karnataka, India, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awaisi, K.S.; Ye, Q.; Sampalli, S. A Survey of Industrial AIoT: Opportunities, Challenges, and Directions. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 96946–96996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, A. Internet of Things in Agricultural Innovation and Security. In Internet of Things for Sustainable Community Development: Wireless Communications, Sensing, and Systems; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 71–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zvarivadza, T.; Onifade, M.; Dayo-Olupona, O.; Said, K.O.; Githiria, J.M.; Genc, B.; Celik, T. On the Impact of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)-Mining Sector Perspectives. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2024, 38, 771–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaina, H.; Picallo, I.; Lopez-Iturri, P.; Biurrun, A.; Vazquez-Alejos, A.; Azpilicueta, L.; Socorro-Leranoz, B.; Falcone, F. IIoT Low-Cost ZigBee-Based WSN Implementation for Enhanced Production Efficiency in a Solar Protection Curtains Manufacturing Workshop. Sensors 2024, 24, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J. Drone Technology for Precision Agriculture: Advancements and Optimization Strategies. Highlights Sci. Eng. Technol. 2024, 111, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassine, A.L.I.A.; El Harmouzi, N. Industrial Policies in the 21st Century: The 4th Generation of Industrial Revolutions. Int. J. Account. Financ. Audit. Manag. Econ. 2024, 5, 335–350. [Google Scholar]
- Varghese, N.; Shereef, S. Scope of Industrial Internet of Things in Manufacturing Industry: Challenges, Recent Trends and Applications. In Futuristic Trends in Artificial Intelligence; IIP Series: Karnataka, India, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopika, G.S.; Sree Krishna, M.; Rajasree, R.S.; Gnanavel, S.; Shankar, A. Industrial Internet of Things: Enhancement of Industries with Hyperautomation for Smart Manufacturing Machines. In Digital Twins in Industrial Production and Smart Manufacturing: An Understanding of Principles, Enhancers, and Obstacles; Willey: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 85–102. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Li, H.; Niu, K.; Shi, J.; Song, R. Application of Deep Learning-Based Intrusion Detection System (IDS) in Network Anomaly Traffic Detection. Appl. Comput. Eng. 2024, 86, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, M.; Nur, S. IoT Sensor Networks-Orchestrating Connectivity, Efficiency, and Intelligence Across Diverse Domains. Int. J. Innov. Res. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2024, 12, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbaja, C. Next-Generation Edge Computing: Leveraging AI-Driven IoT for Autonomous, Real-Time Decision Making and Cybersecurity. J. Artif. Intell. Gen. Sci. 2024, 5, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagachidambaresan, G.R.; Bharathi, N. Sensors for the Industrial Internet of Things. In Sensors and Protocols for Industry 4.0; Maker Innovations Series; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karacayılmaz, G.; Artuner, H. A Novel Approach Detection for IIoT Attacks via Artificial Intelligence. Clust. Comput. 2024, 27, 10467–10485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Xie, H. Internet of Things Data Processing and Analysis Based on Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the 2024 Second International Conference on Data Science and Information System (ICDSIS), Hassan, India, 17–18 May 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Dong, X.; Jia, N.; Zhang, W. Federated Learning-Oriented Edge Computing Framework for the IIoT. Sensors 2024, 24, 4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loseto, G.; Carretero, J.; Talia, D. A Cloud-Edge Artificial Intelligence Framework for Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the 2023 9th International Workshop on Advances in Sensors and Interfaces (IWASI), Monopoli (Bari), Italy, 8–9 June 2023; pp. 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcastro, L.; Carretero, J.; Talia, D. Edge-Cloud Solutions for Big Data Analysis and Distributed Machine Learning-1. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2024, 159, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Vinisha, V.; Rajkumar, M. A Study on Implementation of Artificial Intelligence Technologies in Business Automachine. Int. J. Adv. Res. Commer. Manag. Soc. Sci. 2024, 7, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini, P.; Diana, L.; Elhanashi, A.; Saponara, S. Overview of AI-Models and Tools in Embedded IIoT Applications. Electronics 2024, 13, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambiar, V.; Singh, S. Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in the Workplace: A Scoping Review. In Futuristic Trends in Management; IIP Series: Karnataka, India, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Wei, Z.; Li, B.; Zhang, R.; Song, L. Towards Ever-Evolution Network Threats: A Hierarchical Federated Class-Incremental Learning Approach for Network Intrusion Detection in IIoT. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 29864–29877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenofontos, C.; Zografopoulos, I.; Konstantinou, C.; Jolfaei, A.; Khan, M.K.; Choo, K.-K.R. Consumer, Commercial, and Industrial IoT (In)Security: Attack Taxonomy and Case Studies. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman, S.; Chen, B. Exposing Hidden Attackers in Industrial Control Systems Using Micro-Distortions. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 15, 2089–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, K.; Rane, S. AI in Industrial IoT Cybersecurity [Industrial and Governmental Activities. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2024, 19, 14–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saheed, Y.K.; Abdulganiyu, O.H.; Tchakoucht, T.A. Modified genetic algorithm and fine-tuned long short-term memory network for intrusion detection in the internet of things networks with edge capabilities. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 155, 111434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Tang, D.; Chen, J.; Liang, W.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Q. ERT-EDR: Online defense framework for TCP-targeted LDoS attacks in SDN. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 254, 124356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fawal, A.H.; Mansour, A.; Ammad Uddin, M.; Nasser, A. Securing IoT Networks from DDoS Attacks Using a Temporary Dynamic IP Strategy. Sensors 2024, 24, 4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A. Evolving Threat Landscape in IoT and IIoT Environments. In Smart and Agile Cybersecurity for IoT and IIoT Environments; Advances in Information Security, Privacy, and Ethic; IGI global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsimaa, J.; Korsimaa, J.; Weber, M.; Weber, M.; Salminen, P.; Salminen, P.; Mustonen, J.; Mustonen, J.; Iablonskyi, D.; Iablonskyi, D.; et al. Wireless and battery-operable IoT platform for cost-effective detection of fouling in industrial equipment. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Jing, T.; Gao, Q.; Mao, J.; Huo, Y.; Yang, Z. Multi-attribute weighted convolutional attention neural network for multiuser physical layer authentication in IIoT. Ad Hoc Netw. 2024, 163, 103593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Guan, Z.; Wu, L.; Du, X.; Guizani, M. A sentence-level text adversarial attack algorithm against IIoT based smart grid. Comput. Netw. 2021, 190, 107956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartiglia, M.; Costa, F.; Narayanan, S.; Bui, C.-V.H.; Ulusan, H.; Risi, N.; Haessig, G.; Hierlemann, A.; Cardes, F.; Indiveri, G. A 4096 channel event-based multielectrode array with asynchronous outputs compatible with neuromorphic processors. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, A.; Anumula, V.R.B.; Rajesh, G.; Narendra, V.; Challa, A.K. A Novel Efficient Intrusion Detection System in Cloud Using Hybrid Machine Learning Classifier. J. Comput. Sci. 2024, 4, 504–508. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, R.; Gu, D.; Tang, Q.; Huang, T.; Yu, F.R. Workflow Scheduling in Serverless Edge Computing for the Industrial Internet of Things: A Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 8242–8252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosam, F.; El-Sofany, S.; Abou El-Seoud, S.; Karam, O.H.; Bouallègue, B. Using Machine Learning Algorithms to Enhance IoT System Security. Dent. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hala, A.; Zayer, F.; Hadj, A.F.; Hamdi, B.; Baker, M.; Werghi, N.; Dias, J. Efficient and Lightweight In-memory Computing Architecture for Hardware Security. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2024, 190, 104898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, A.-H.; Khadeer Hussain, F. DDoS Attacks in IoT Networks: A Comprehensive Systematic Literature Review. World Wide Web 2021, 24, 971–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farraj, A.; Hammad, E. A Physical-Layer Security Cooperative Framework for Mitigating Interference and Eavesdropping Attacks in Internet of Things Environments. Sensors 2024, 24, 5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisdom, D.D.; Vincent, O.R.; Igulu, K.; Hyacinth, E.A.; Christian, A.U.; Oduntan, O.E.; Hauni, A.G. Industrial IoT Security Infrastructures and Threats. In Communication Technologies and Security Challenges in IoT; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 369–402. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, M.; Alnajim, S.; Habib, S.; Islam, M.; Thwin, S.M.; Alotaibi, F. A Comprehensive Survey of Cybersecurity Threats, Attacks, and Effective Countermeasures in Industrial Internet of Things. Technologies 2023, 11, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyeleko, A.H.; Feng, T. A Critical Overview of Industrial Internet of Things Security and Privacy Issues Using a Layer-Based Hacking Scenario. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 21917–21941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Roberts, H.; Mökander, J.; Tsamados, A.; Taddeo, M.; Floridi, L. The Case for a Broader Approach to AI Assurance: Addressing “Hidden” Harms in the Development of Artificial Intelligence. AI Soc. 2024, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Sun, W. Efficient Decentralized Optimization for Edge-Enabled Smart Manufacturing: A Federated Learning-Based Framework. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2024, 157, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zheng, M.; Jiang, L.; Gu, C.; Tan, R.; Cheng, P. Lightweight and Unobtrusive Data Obfuscation at IoT Edge for Remote Inference. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 9540–9551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogita, Y.; Raghav, R.; Kait, R. Edge Computing Empowering Distributed Computing at the Edge. In Emerging Trends in Cloud Computing Analytics, Scalability, and Service Models; Advances in Computational and Electrical Engineering; IGI global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, N.; Savaliya, M.; Patel, M.; Gautam, S.; Naik, R.R. Software Architecture Survey from an Edge Computing Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2024 1st International Conference on Cognitive, Green and Ubiquitous Computing (IC-CGU), Bhubaneswar, India, 1–2 March 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Makaya, C.; Grueneberg, K.; Ko, B.; Wood, D.; Desai, N.; Wang, X. EdgeSphere: A Three-Tier Architecture for Cognitive Edge Computing. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.16685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, D.B.; Rahimi, Z.; Jusoh, A.; Rashid, I.; Ismail, I.; Oliva, D.; Noryanti, M.; Sadiq, M.; Sait, K.A.; Al-Utaibi, T.I.; et al. Artificial Intelligence and Edge Computing for Machine Maintenance-Review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; An, J.; Sun, B.; Chen, D.; Bai, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y. Empowering intelligent manufacturing with edge computing: A portable diagnosis and distance localization approach for bearing faults. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2024, 59, 102246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Lyu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Jin, Y. IM-IAD: Industrial image anomaly detection benchmark in manufacturing. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2024, 54, 2720–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anarbayevich, A.R. Harnessing edge computing for enhanced security and efficiency in IOT networks. Am. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2024, 4, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulana, R.; Kaabouch, N. Combining Edge Computing-Assisted Internet of Things Security with Artificial Intelligence: Applications, Challenges, and Opportunities. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, F.; Awad, L.; Rafea, H.; Abdulrahman, A.; Jasim, A.; Ata, O. Enhancing IIoT security with machine learning and deep learning for intrusion detection. Malays. J. Comput. Sci. 2024, 37, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldikar, S.V.; Kader, O.F.M.A.; Yekollu, R.K. Edge Computing and Federated Learning for Real-Time Anomaly Detection in Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), Lalitpur, Nepal, 24–26 April 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, S.; Kumar, A.; Tyagi, N.; Chavan, S.S.; Machinathu, S.P.; Gangadharan, S. Towards intelligent industrial systems: A comprehensive survey of sensor fusion techniques in IIoT. Meas. Sens. 2024, 32, 100944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa, A.; Majd, N.E. Edge Computing Network Intrusion Detection System in IoT Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2024 33rd International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks (ICCCN), Big Island, HI, USA, 29–31 July 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shabnam, K.; Thompson, A.F.-B.; Tiwari, S. Cyber Security in Internet of Things-Based Edge Computing. In Emerging Technologies and Security in Cloud Computing; Advances in Information Security Privacy, and Ethics; IGI global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, R.E.; Andrade, W.J.; de Mello Henequim, C.; Lazzaretti, A.E.; Junior, A.D.S.B.; Loures, E.D.F.R.; Santos, E.A.P.; Reynoso-Meza, G. An industrial edge computing architecture for Local Digital Twin. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 193, 110257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrag, M.A.; Friha, O.; Maglaras, L.; Janicke, H.; Shu, L. Federated deep learning for cyber security in the internet of things: Concepts, applications, and experimental analysis. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 138509–138542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, W.B.; Othmen, S.; Hamdi, M.; Khdhir, R.; Hamam, H. Fog computing network security based on resources management. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2023, 2023, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanasi, C.; Russo, S.; Colajanni, M. Flexible zero trust architecture for the cybersecurity of industrial IoT infrastructures. Ad Hoc Netw. 2024, 156, 103414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hawawreh, M.; Sitnikova, E.; Aboutorab, N. X-IIoTID: A connectivity-agnostic and device-agnostic intrusion data set for industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 3962–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Yan, B.; Yang, T.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wang, W. Security-Enhanced Operational Architecture for Decentralized Industrial Internet of Things: A Blockchain-Based Approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 11073–11086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Tyagi SK, S.; Suryadevara, N.K.; Piuri, V.; Scotti, F.; Zeadally, S. Artificial intelligence-based sensors for next generation IoT applications: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 24920–24932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoi, G.; Sahu, R.K.; Oram, E.; Jhanjhi, N.Z. Risk Assessment and Security of Industrial Internet of Things Network Using Advanced Machine Learning. In Machine Learning for Cyber Physical System: Advances and Challenges; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 267–285. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, Z.; Yi, X.; Khalil, I.; Anwar, A.; Pal, S. Blockchain-Based and Fuzzy Logic-Enabled False Data Discovery for the Intelligent Autonomous Vehicular System. In Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Advanced Security on Software and Systems, Melbourne, Australia, 10–14 July 2023; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, M.K.; Chimsom, C. CPS: Role, Characteristics, Architectures and Future Potentials. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 200, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, H.; Zheng, Q.; Elhabob, R.; Kumar, S.; Kumari, S.; Xiong, H. Efficient plaintext checkable identity-based signcryption in cyber-physical systems towards IIoT. Eur. Trans. Telecommun. 2024, 35, e4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudresha, S.J.; Gopinath, H.R.; Kumar, G.R.; Shruthi, S.; Kalpana, S. A cyber–physical systems perspective on smart grids. In Futuristic Trends in Artificial Intelligence; IIP Series: Karnataka, India, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, M.; Kumar, I.; Khurshid, A.A. Changing Roles of Intelligent Robotics and Machinery Control Systems as Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) in the Industry 4.0 Framework. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Communication, Security and Artificial Intelligence (ICCSAI), Greater Noida, India, 23–25 November 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhapsekar, R.U.; O’Shea, N.; Davy, S.; Kilbane, D.; Abraham, L. An Edge-Centric Industrial IoT Solution for Smart Dairy Processing. IEEE Internet Things Mag. 2024, 7, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecílio, J.; Souto, A. Security Issues in Industrial Internet-of-Things: Threats, Attacks and Solutions. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 & IoT (MetroInd4.0 & IoT), Firenze, Italy, 29–31 May 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 458–463. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, W.; Shen, J. Security Control of Cyber–Physical Systems under Cyber Attacks: A Survey. Sensors 2024, 24, 3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiernan, B.-M.; Al Mallah, R.; Dagdougui, H. A Novel Bifurcation Method for Observation Perturbation Attacks on Reinforcement Learning Agents: Load Altering Attacks on a Cyber Physical Power System. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.05182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, P.; Rasteh, A.; Karri, R.; Khorrami, F. Tracking Real-time Anomalies in Cyber-Physical Systems Through Dynamic Behavioral Analysis. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.12438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buja, A.; Apostolova, M.; Luma, A. A model proposal for enhancing cyber security in industrial IoT environments. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2024, 6, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, H.; Zheng, Q.; Elhabob, R.; Kumar, S.; Yeh, K.-H.; Kumari, S.; Xiong, H. Proxy re-encryption with plaintext checkable encryption for integrating digital twins into IIoT. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2024, 116, 109164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atheeq, C.; Sultana, R.; Sabahath, S.A.; Mohammed MA, K. Advancing IoT Cybersecurity: Adaptive Threat Identification with Deep Learning in Cyber-Physical Systems. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2024, 14, 13559–13566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnar, P.; Bhirud, S. Security analysis of cyber-physical system using digital forensic incident response. Cyber Secur. Appl. 2023, 2, 100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konatham, B.R. A Secure and Efficient IIoT Anomaly Detection Approach Using a Hybrid Deep Learning Technique. Master’s Thesis, Wright State University, Dayton, OH, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.A. The Role of Blockchain Technology in Enhancing Cybersecurity. Int. J. Sci. Res. Eng. Manag. 2024, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, A.; Kim, T.W.; Singh, A.K.; Kang, J.; Park, J.-H. SecureIIoT Environment: Federated Learning Empowered Approach for Securing IIoT From Data Breach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 6406–6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Basset, M.; Moustafa, N.; Hawash, H. Privacy-preserved cyberattack detection in Industrial Edge of Things (IEoT): A blockchain-orchestrated federated learning approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 7920–7934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahli, N.; Benmohamed, M.; Bourennane, E.B. Security for industrial automation and control systems. Concept. Et Prod. Intégrées/Integr. Desing Prod. (CPI’13) 2013, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhole, M.; Kastner, W.; Sauter, T. IT Security Solutions for IT/OT Integration: Identifying Gaps and Opportunities. In Proceedings of the2024 IEEE 29th International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA), Padova, Italy, 10–13 September 2024; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulaziz, A.; Ullah, I.; Ahanger, T.A.; Atiquzzaman, M. Ensemble technique of intrusion detection for IoT-edge platform. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, A.; Chaturvedi, V.; Shafique, M. ViT4Mal: Lightweight Vision Transformer for Malware Detection on Edge Devices. ACM Trans. Embed. Comput. Syst. 2023, 22, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENISA Threat Landscape 2024 Identifies Availability Ransomware and Data Attacks as Key Cybersecurity Threats. Industrial Cyber. Available online: https://industrialcyber.co/reports/enisa-threat-landscape-2024-identifies-availability-ransomware-data-attacks-as-key-cybersecurity-threats/ (accessed on 9 November 2024).
- Raza, A.; Memon, S.; Nizamani, M.A.; Hussain Shah, M. Machine Learning-Based Security Solutions for Critical Cyber-Physical Systems. In Proceedings of the 2022 10th International Symposium on Digital Forensics and Security (ISDFS), Istanbul, Turkey, 6–7 June 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahoun, A.H.; Arafa, M. Secure control design for nonlinear cyber–physical systems under DoS, replay, and deception cyber-attacks with multiple transmission channels. ISA Trans. 2022, 128, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sá, A.O.; Prado, C.B.; Flavio, M.L.; Carmo, L.F. Intelligent Attacks on Cyber-Physical Systems and Critical Infrastructures. In Modern Technologies Enabling Innovative Methods for Maritime Monitoring and Strengthening Resilience in Maritime Critical Infrastructures; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 332–351. [Google Scholar]
- Mtukushe, N.; Onaolapo, A.K.; Aluko, A.; Dorrell, D.G. Review of Cyberattack Implementation, Detection, and Mitigation Methods in Cyber-Physical Systems. Energies 2023, 16, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyarao, S.L.; Tummala, V.; Inapakurthi, R.K. A Two-stage Kalman Filter for Cyber-attack Detection in Automatic Generation Control System. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2022, 10, 50–59. [Google Scholar]
- Syrmakesis, A.D.; Alhelou, H.H.; Hatziargyriou, N.D. Novel SMO-Based Detection and Isolation of False Data Injection Attacks against Frequency Control Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2023, 39, 1434–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naha, A.; Teixeira, A.; Ahlen, A.; Dey, S. Quickest detection of deception attacks in networked control systems with physical watermarking. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.01466. [Google Scholar]
- Driss, M.; Almomani, I.; Ahmad, J. A federated learning framework for cyberattack detection in vehicular sensor networks. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 4221–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhelou, H.H.; Cuffe, P. A Dynamic-State-Estimator-Based Tolerance Control Method Against Cyberattack and Erroneous Measured Data for Power Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 18, 4990–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huma, Z.E.; Latif, S.; Ahmad, J.; Idrees, Z.; Ibrar, A.; Zou, Z.; Alqahtani, F.; Baothman, F. A hybrid deep random neural network for cyberattack detection in the industrial internet of things. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 55595–55605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, Z.A.; Singh, Y.; Singh, P.K.; Gonçalves, P.J.S. Defending the Defender: Adversarial Learning Based Defending Strategy for Learning Based Security Methods in Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS). Sensors 2023, 23, 5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchinezhad, S.; Haghighi, M.S.; Puig, V. Identification and analysis of stochastic deception attacks on cyber–physical systems. J. Frankl. Inst. 2024, 361, 106774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, J. CPS attack detection under limited local information in cyber security: An ensemble multi-node multi-class classification approach. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. 2024, 20, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirendra, S.; Sengar, S. An ECC based Secure Authentication Protocol for M2M Communication in Industrial IOT Edge Device. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2024, 12, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Li, Q.; Yousafzai, A. Blockchain and federated learning-based intrusion detection approaches for edge-enabled industrial IoT networks: A survey. Ad Hoc Netw. 2024, 152, 103320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampa, T.; Müller, C.K.; Großmann, D. Interlocking IT/OT security for edge cloud-enabled manufacturing. Ad Hoc Netw. 2024, 154, 103384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhou, J.; Ma, M. Anonymous Batch Message Authentication Aided by Edge Servers in Industrial Internet of Thing. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE World AI IoT Congress (AIIoT), Seattle, WA, USA, 29–31 May 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 584–590. [Google Scholar]
- Cambosuela, L.; Kaur, M.; Astya, R. The Vulnerabilities and Risks of Implementing Internet of Things (IoT) in Cyber Security. In Proceedings of the 2024 11th International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization (Trends and Future Directions) (ICRITO), Noida, India, 14–15 March 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, M.; Uddin, G. A Large-Scale Study of IoT Security Weaknesses and Vulnerabilites in the Wild. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 2024, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthi, E.; Williams, L.; Ieropoulos, V.; Spyridopoulos, T. Investigating Radio Frequency Vulnerabilities in the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT 2024, 5, 356–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, K.; Mozumder, M.A.I.; Joo, M.-I.; Kim, H.-C. BFLIDS: Blockchain-Driven Federated Learning for Intrusion Detection in IoMT Networks. Sensors 2024, 24, 4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Mao, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, S. Edge Server Enhanced Secure and Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning. Comput. Netw. 2024, 249, 110465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Kim, E.; Lee, C. A scalable blockchain-enabled federated learning architecture for edge computing. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0308991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacmarcik, A.; Prvulovic, M. Securing CPS Through Simultaneous Analog Side-Channel Monitoring of Cyber and Physical Domains. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 126717–126728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miryahyaei, M.; Fartash, M.; Akbari Torkestani, J. Focal Causal Temporal Convolutional Neural Networks: Advancing IIoT Security with Efficient Detection of Rare Cyber-Attacks. Sensors 2024, 24, 6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Authors | Year | Results | Key Issues | Not Considered |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [51] | 2022 | IDS for protecting industrial CPS reaching 98.45% accuracy | Integration of AI, edge computing, enhanced security measures, 5G, and digital twins | Long-term sustainability, human factors, security cost analysis, and the impact of emerging technologies like blockchain |
| [52] | 2023 | CPS architecture for IIoT security. Protecting devices from cyber threats and improving detection accuracy with neural networks | IIoT faces challenges like heavy traffic, diverse networks, and high computing demands | The impact of new technologies on IIoT security |
| [53] | 2024 | The potential of smart factories in enhancing the manufacturing sector | CPS integrates technologies, upgrades systems, and ensures data security | Cybersecurity measures |
| [54] | 2023 | Implementation of blockchain and edge in IIoT | Integration of RCL, REL, and cloud computing layers | Blockchain architectures |
| [55] | 2024 | IDS for detecting attacks in IIoT using digital twin and online learning | Detecting attacks | Scalability and adaptability |
| [56] | 2024 | Intelligent intrusion detection system using SVD and SMOTE to improve accuracy | Modern IDS have flaws that intelligent recognition methods can address | Attack types |
| [57] | 2024 | IIoT across various industries and the importance of Edge AI for digital connectivity | The need to improve digital connectivity in IIoT using Edge AI | Problems of digital connectivity through Edge AI |
| [58] | 2024 | Anonymous authentication protocol for IIoT users, effective against attacks | Design of secure protocols to ensure security in IIoT | Security issues due to open wireless networks |
| [59] | 2024 | Security and architecture of distributed digital twins for maintenance | Digital twins: limited standards need better implementation and feedback | Feedback mechanisms |
| [60] | 2023 | Key IIoT security issues: attacks, data breaches, and the importance of encryption | Malicious attacks and privacy concerns in IIoT | Comprehensive solutions of security and privacy |
| [61] | 2024 | Role of AI in detecting and preventing cyberattacks in IIoT, essential for enhancing cybersecurity through ML, behavioral analysis, and NLP for anomaly detection | Data quality limits, high development costs | User experience and usability in cybersecurity solutions |
| Authors | Year | Real-Time Data Processing | Cybersecurity | Attacks | AI | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [129] | 2021 | Data generation, architecture: cloud computing, network function visualization, blockchain, SDN, edge computing, and IoT/IIoT perception layers | - | DDos MITM information gathering malware | DT RF SVM KNN DNN | DNN achieves 94.67% for 15 classes and 96.01% for 6 classes, while DT scores 67.11% for 15 classes and 77.90% for 6 classes |
| [127] | 2023 |
| Security protocols that reduce data transmission risks to cloud servers and improve overall IoT application security | - | - | - |
| [125] | 2024 |
| Secure IDS | Malware DDoS MitM | kNN DT | 100% |
| [121] | 2024 | EC-IoT enhances real-time data processing by reducing latency and improving response time | Strategies for enhancing data and network security through the combination of EC-IoT and AI | - | - | - |
| [128] | 2024 | The Local Digital Twin (LDT) architecture at the edge enables real-time control. | - | - | ML | LDT on the assembly line in Brazil, using ML, improved productivity by 1.3–2.5% |
| [117] | 2024 | The federated platform enables fast data processing, with ADMM algorithms cutting response time by up to 58% | The decentralized system secures data and, with IIoT, reduces latency and boosts security | - | ML FL | Edge algorithms reduced response time by 17.2% and 58%, maintaining accuracy. Testing on power plant data confirmed the effectiveness of FL |
| [128] | 2024 | Real-time data processing is crucial for applications requiring timely decision-making | ML and FL methods assist in detecting cyber threats | - | ML FL |
|
| Aspects | Categories |
|---|---|
| Sensors and AI | Improve performance |
| State indicators ensure data integrity | |
| Security and Integrity | Integration of heterogeneous networks and privacy protection |
| Blockchain + AI = data protection from threats | |
| Prevents critical malfunctions data integrity | |
| Cryptography | |
| Key Technologies | Sensors |
| Machine learning | |
| Blockchain, AI | |
| Applications | Motion control, resource distribution |
| Industry, robotics | |
| Agriculture, healthcare | |
| Smart grids, energy systems | |
| Network security | |
| Transport systems, smart grids | |
| Challenges | Trust management, secure routing protocols, integration of heterogeneous networks, and privacy protection |
| Cyberattacks | |
| Cybersecurity, privacy, compatibility | |
| Process control | |
| Cybersecurity threats, data privacy |
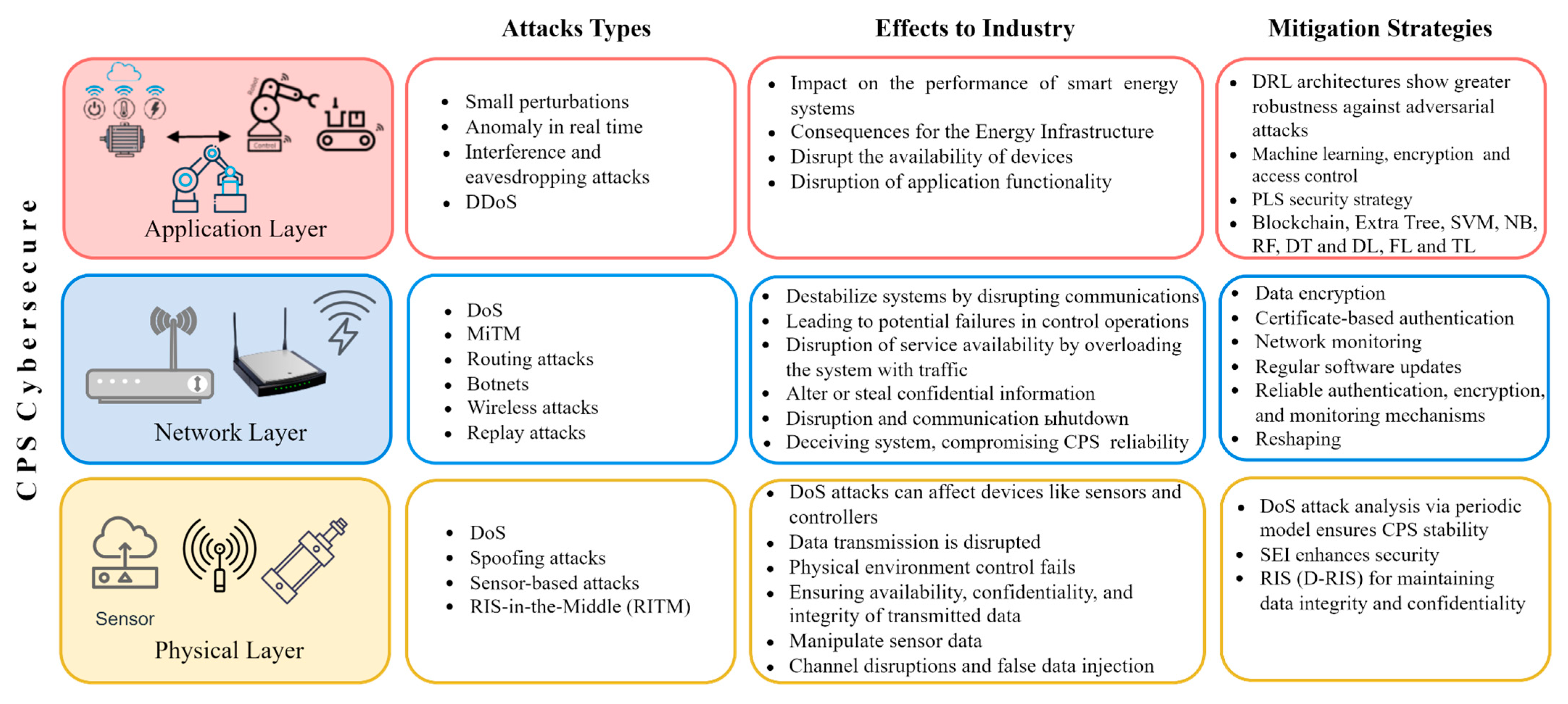
| Types of Attack | Effects to Industry | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| DoS | Destabilize systems by disrupting communications, leading to potential failures in control operations. Disruption of service availability by overloading the system with traffic | Network segmentation and access control limit the spread of attacks and prevent unauthorized access to critical system components |
| MiTM | Alter or steal confidential information | Strengthening authentication can prevent unauthorized access and reduce identity spoofing risks |
| Replay attacks | Deceiving the system, affecting the integrity and reliability of CPS operations | Reshaping will change traffic patterns, making it harder for adversaries to access sensitive user information and ultimately improving user privacy |
| Small perturbations | Impact on the performance of smart energy systems | Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) architectures exhibit greater robustness against adversarial attack |
| Traffic analysis attacks | Extract confidential information from network traffic | The development of a traffic reshaping method that could significantly prevent image-based attacks aimed at IoT traffic analysis |
| Eavesdropping and IP spoofing | Confidentiality and authenticity of communications | - |
| Anomaly in real time | Consequences for the energy infrastructure | |
| Interference and eavesdropping attacks | Disrupt the availability of Internet of Things (IoT) devices | PLS strategy |
| DoS, DDoS | Disruption of application functionality | Blockchain, Extra Tree, SVM, NB, RF, DT and DL, and FL and transfer learning |
| Spoofing attacks | Ensuring availability, confidentiality, and integrity of transmitted data | SEI (Specific Emitter Identification) enhances security |
| Sensor-based attacks | Manipulate sensor data | - |
| RIS-in-the-Middle (RITM) | Channel disruptions and false data injection | RIS (D-RIS) by using non-cooperative communication channels and maintaining data integrity and confidentiality |
| Attack Type | Affected Layers | Effect | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ransomware | Perception, Application, Data | Production halt, financial loss, reputation damage | Colonial Pipeline (2021) |
| DoS | Network, Application | Disruption of real-time monitoring, operational downtime DDoS attacks can halt production lines, causing significant downtime and financial losses | Smart grid outages A DDoS attack on an intelligent manufacturing system can disrupt the entire supply chain |
| Supply Chain Attacks | All layers | Long-term, hidden vulnerabilities in software/hardware | SolarWinds (2020) |
| Firmware Exploits | Perception, Application | Physical process manipulation, production shutdowns | Siemens PLC vulnerabilities |
| MitM | Network, Perception | Data alteration, faulty operations | Smart manufacturing data tampering |
| Authors | Attack Type | Detection Techniques | Detection Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| [162] | DoS | Kalman Filter | 90% |
| [163] | FDIA | Sliding Mode Observer Methods | 100% |
| [164] | DoS | Watermarking | 100% |
| [165] | Intrusion | FL, GRU, RF | 99% |
| [166] | Malware, password, phishing, SQL injection | Dynamic Estimator-Based Cyberattack Tolerant Control | 99% |
| [167] | Generic | A Hybrid Deep Random Neural Network | 98%, 99% |
| [168] | Evasion, data poisoning | RF, ANN, LTSM | 96%, 98% |
| [169] | Deception attacks | Markov Chain | - |
| [170] | DDoS, password, backdoor, SQL injection, ransomeware, port-scanning, uploading, vulnerability scanner | LR, RF, CNN, SVM, kNN | 100% |
| Research Field | Authors | Year | Contributions | Cybersecurity Methods | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ML DL FL | Blockchain | IDS | IT/ OT | Cryptography and Encryption | ||||
| IIoT CPS | [19] | 2021 | M2M communication in IIoT leverages advanced models like 5G, TSN Ethernet, and autonomous networks to improve manufacturing efficiency. It also tackles cyber threats and ensures data security through robust M2M connectivity | − | − | − | − | − |
| [45] | 2021 | Overview of the integrity of industrial IoT systems, classifying various attacks and security solutions: IoT/IIoT security solutions include communication protocols, networks, cryptography, and IDS | − | − | + | − | + | |
| [123] | 2024 | Data filtering, encryption, and decentralized processing strengthen IIoT systems against cyber threats | − | − | − | − | + | |
| [134] | 2024 | A real-time security system using digital twin technology and interactive ensemble ML to enhance attack detection in IIoT environments and tackle data-related issues | + | − | + | − | − | |
| [156] | 2024 | IoT-Defender, with MGA for feature selection and LSTM for cyberattack detection in IoT networks, aims to enhance IDS performance by optimizing relevant feature selection | + | − | + | − | − | |
| [171] | 2024 | A secure M2M authentication protocol in IIoT utilizing ECC-based cryptography to enhance security | − | − | − | + | ||
| [172] | 2024 | Blockchain-based IIoT architectures enhance security and privacy while developing a reputation-based behavioral punishment mechanism to improve security effectiveness | − | + | − | − | − | |
| [173] | 2023 | Network-level security for protecting production through virtualization, designed for legacy environments, aims to converge IT and OT domains to enhance scalability and security in manufacturing networks | − | − | − | + | − | |
| IIoT–Edge Computing | [5] | 2022 | A framework designed for the secure transmission, storage, and computation of IIoT tasks that combines edge computing with IIoT platforms. It employs simplified encryption and a modified ElGamal encryption method, along with digital signatures, to improve overall performance. | − | − | − | + | − |
| [122] | 2024 | FL platform that optimizes industrial data processing with minimal latency and security, addressing efficient data processing for manufacturers in smart production environments with edge technology support | + | − | − | − | − | |
| [153] | 2024 | AI improves diagnostic and predictive methods for industrial machines, addressing privacy issues, high latency, and low availability through edge-level computations | + | − | − | − | − | |
| [154] | 2024 | Blockchain-based FL enhances collaborative intrusion detection in IIoT environments by ensuring data privacy and reducing vulnerability to MITM attacks through a secure parameter verification scheme. The architecture improves intrusion detection accuracy | + | − | − | − | − | |
| [174] | 2023 | Security threats in the edge computing–IIoT environment include access control, encrypted communication, and authentication measures | − | − | − | − | + | |
| CPs IIoT–Edge Computing | Our paper | 2024 | Common attacks to IIoT–edge computing highlight various cyberattacks on CPS and their industrial impact. They underscore the importance of integrating IIoT–edge computing for protection against CPS IIoT cyberattacks. A taxonomy of main security methods for CPS IIoT–edge computing has been developed, comparing our approach with other sources in this research area | + | + | + | + | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhukabayeva, T.; Zholshiyeva, L.; Karabayev, N.; Khan, S.; Alnazzawi, N. Cybersecurity Solutions for Industrial Internet of Things–Edge Computing Integration: Challenges, Threats, and Future Directions. Sensors 2025, 25, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25010213
Zhukabayeva T, Zholshiyeva L, Karabayev N, Khan S, Alnazzawi N. Cybersecurity Solutions for Industrial Internet of Things–Edge Computing Integration: Challenges, Threats, and Future Directions. Sensors. 2025; 25(1):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25010213
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhukabayeva, Tamara, Lazzat Zholshiyeva, Nurdaulet Karabayev, Shafiullah Khan, and Noha Alnazzawi. 2025. "Cybersecurity Solutions for Industrial Internet of Things–Edge Computing Integration: Challenges, Threats, and Future Directions" Sensors 25, no. 1: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25010213
APA StyleZhukabayeva, T., Zholshiyeva, L., Karabayev, N., Khan, S., & Alnazzawi, N. (2025). Cybersecurity Solutions for Industrial Internet of Things–Edge Computing Integration: Challenges, Threats, and Future Directions. Sensors, 25(1), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25010213







