Characterizing Surface Deformation of the Earthquake-Induced Daguangbao Landslide by Combining Satellite- and Ground-Based InSAR
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
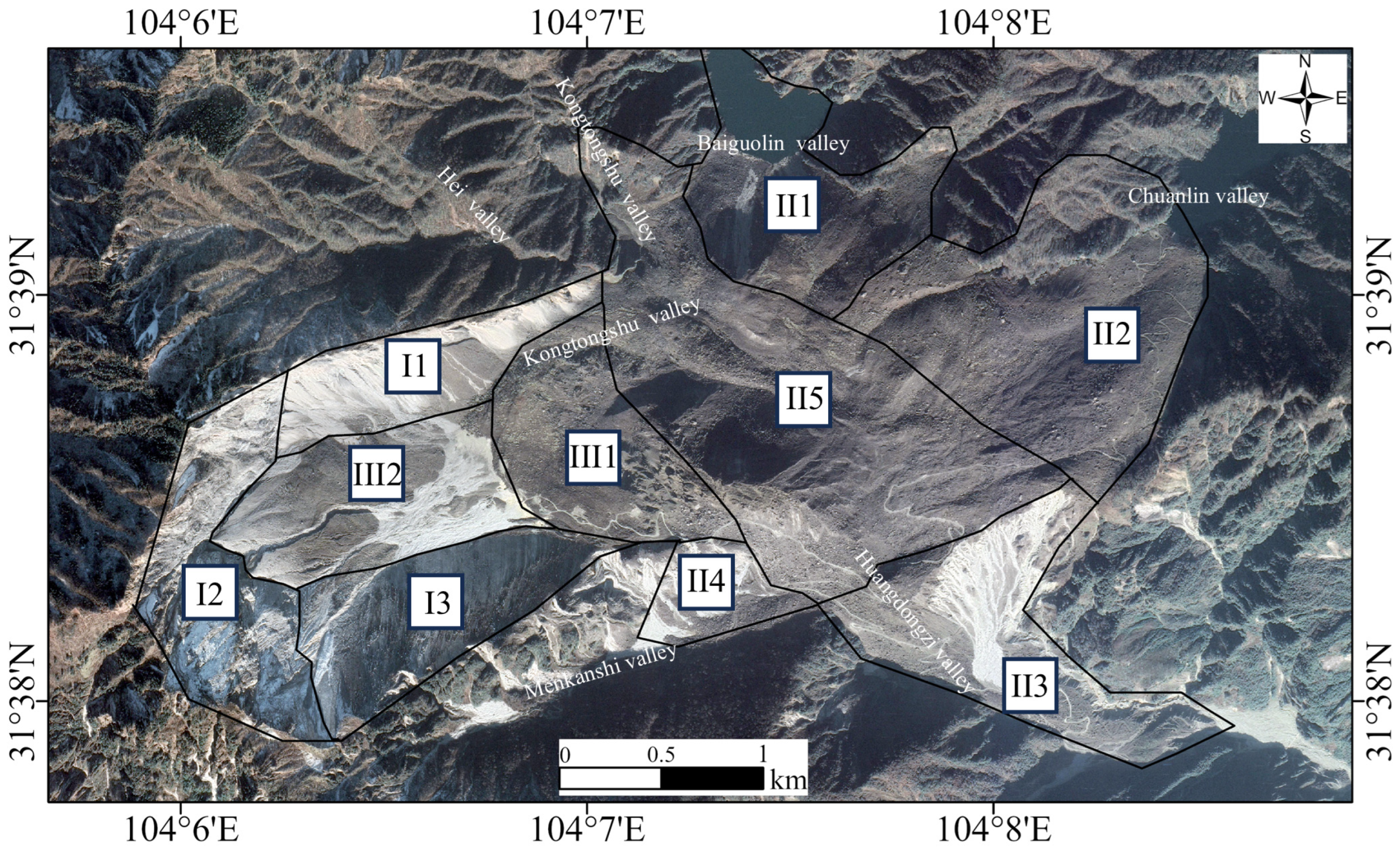
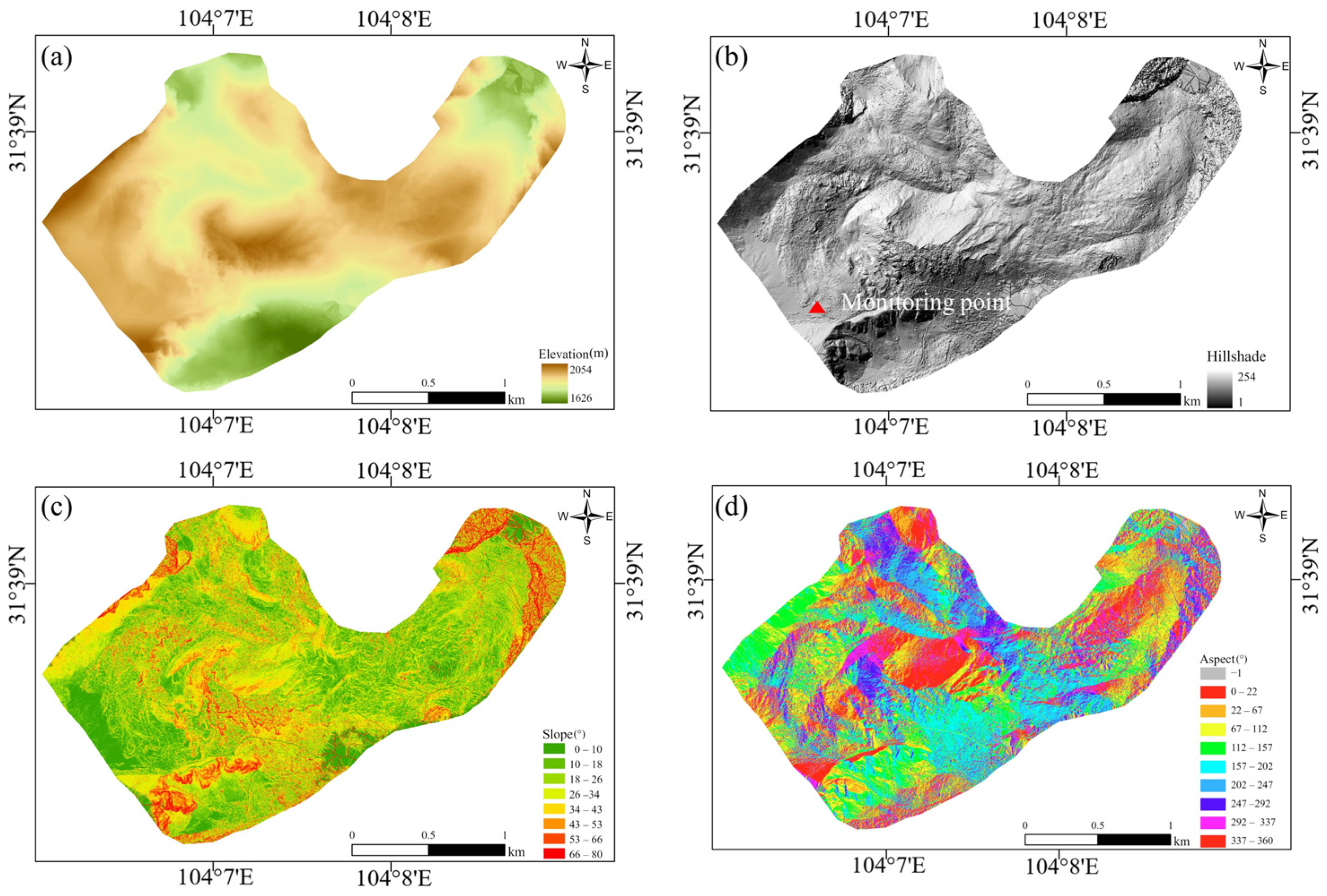
2.1. Study Area
2.2. SAR Datasets
2.3. GB-SAR Datasets
2.4. Ancillary Datasets
3. Methods
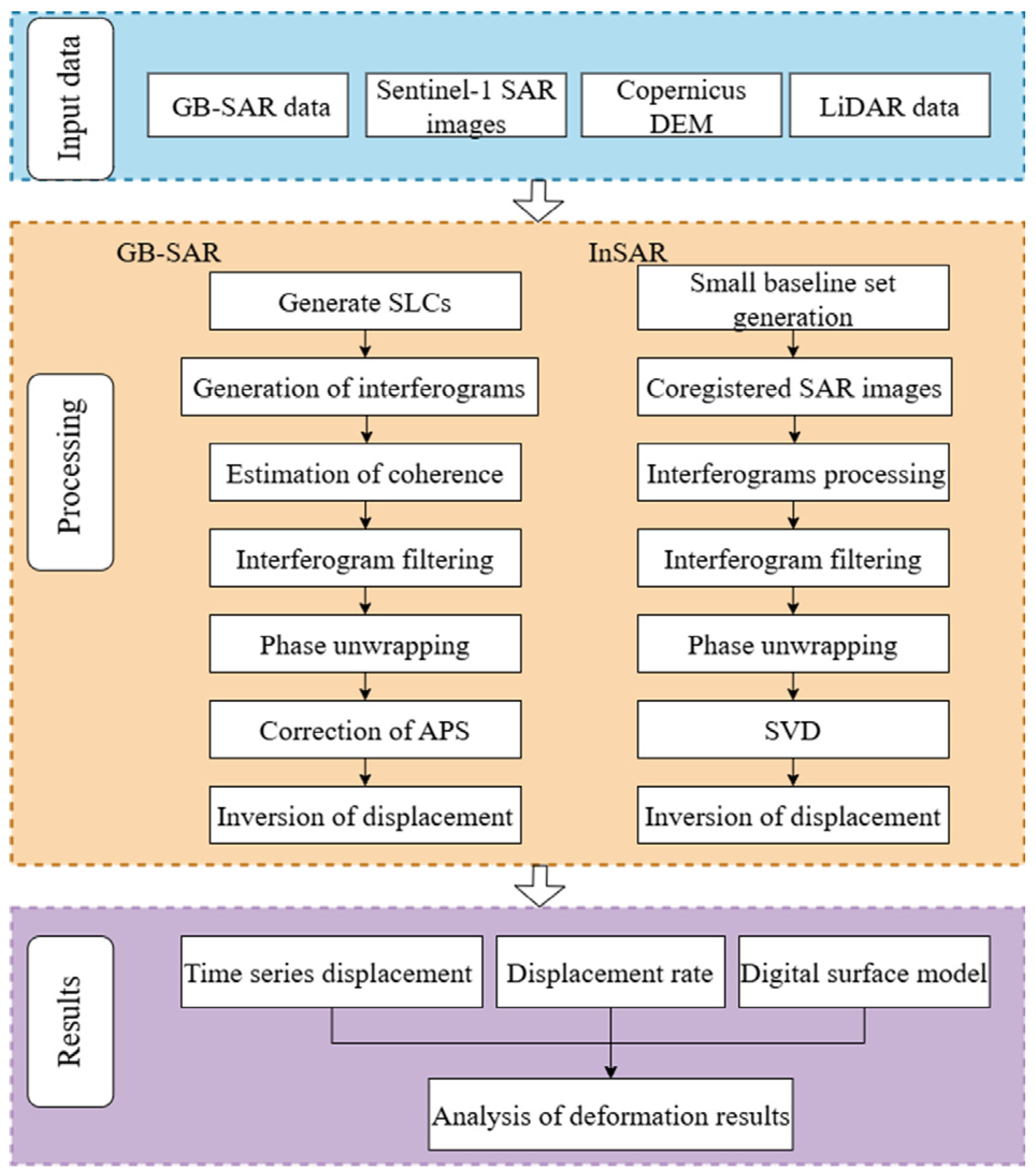
3.1. Satellite SAR Data Processing
3.2. GB-SAR Data Processing
3.3. Downslope Displacement Calculation
4. Results and Analysis
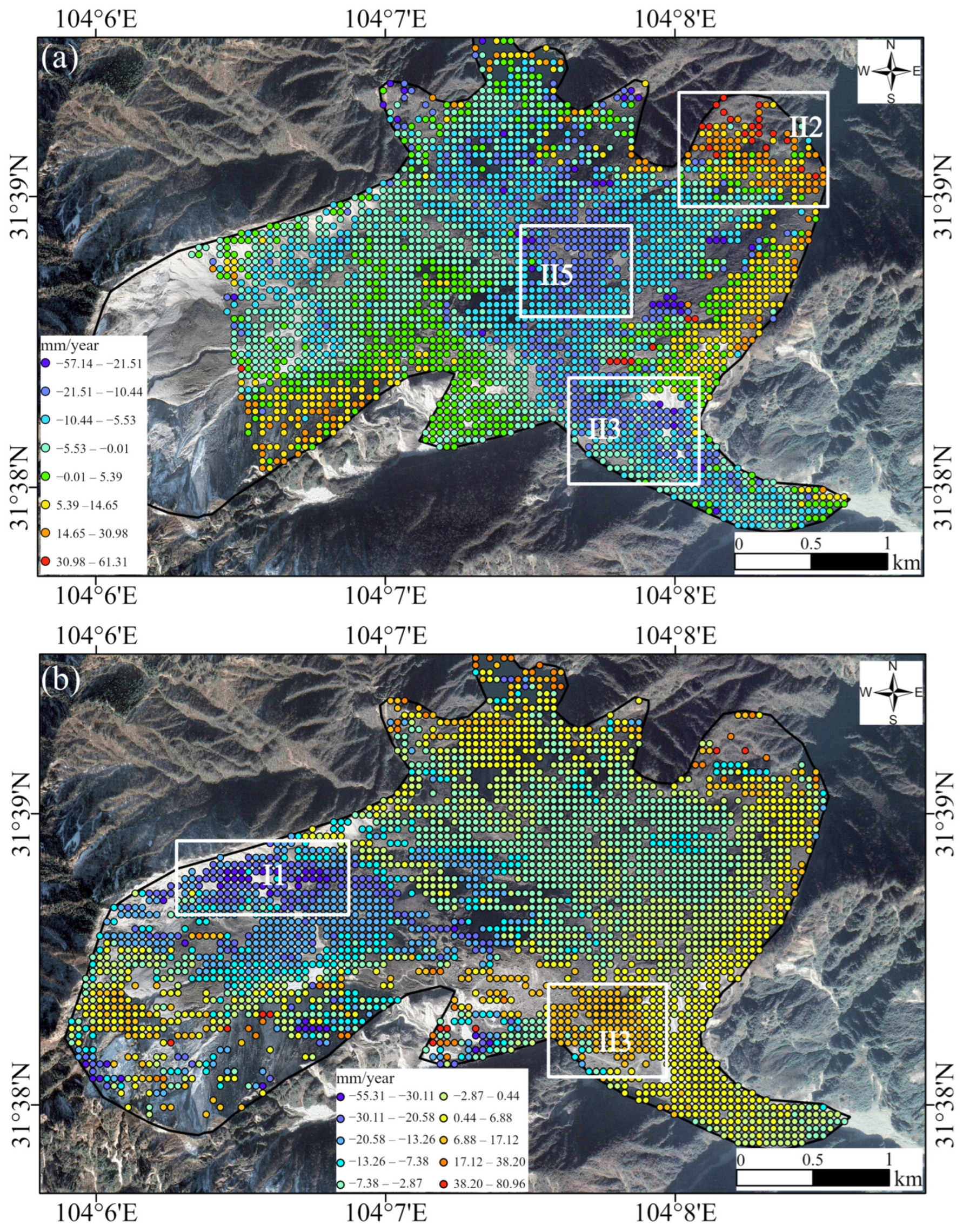
4.1. Satellite InSAR Measurement Results
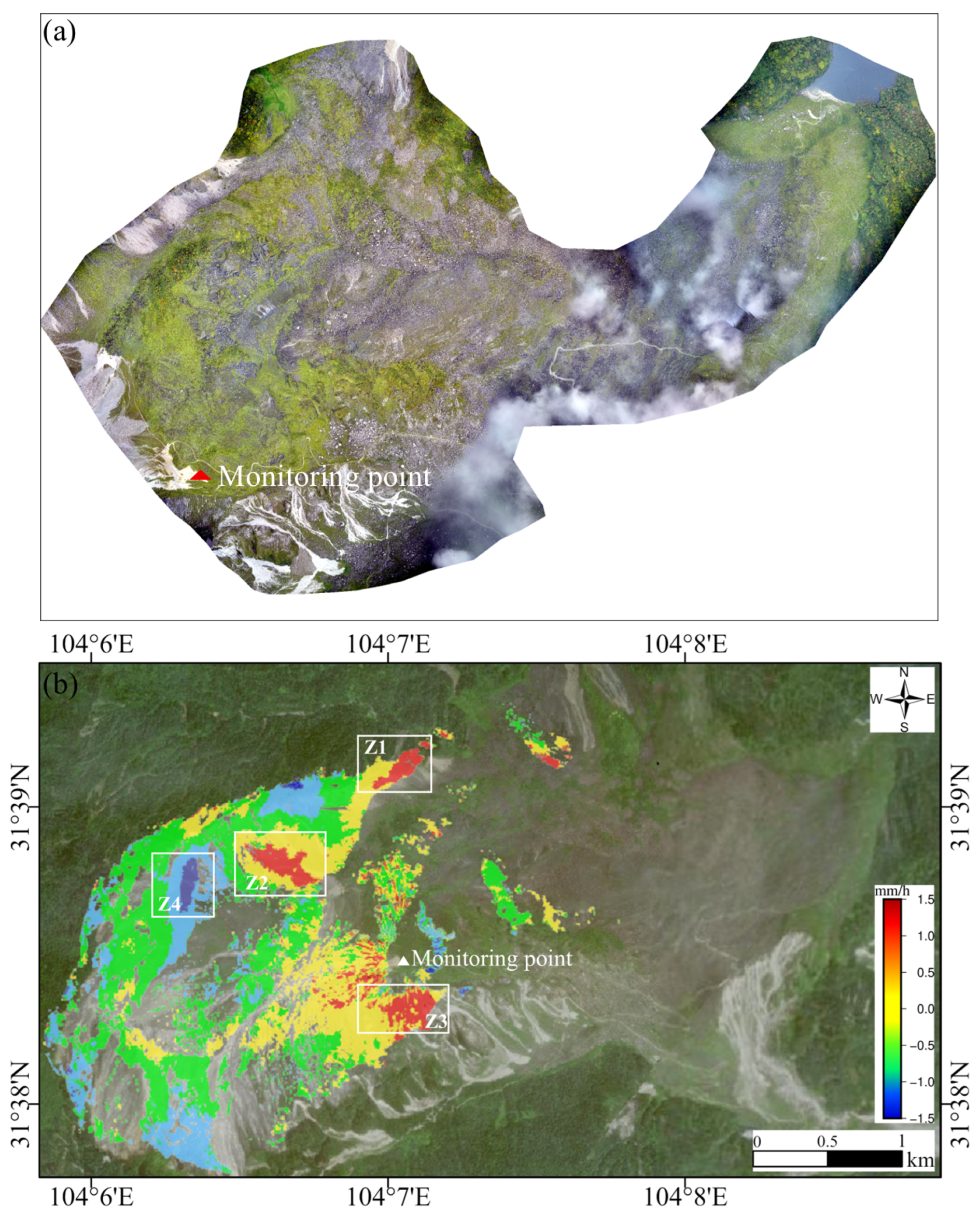
4.2. GB-SAR Measurement Results
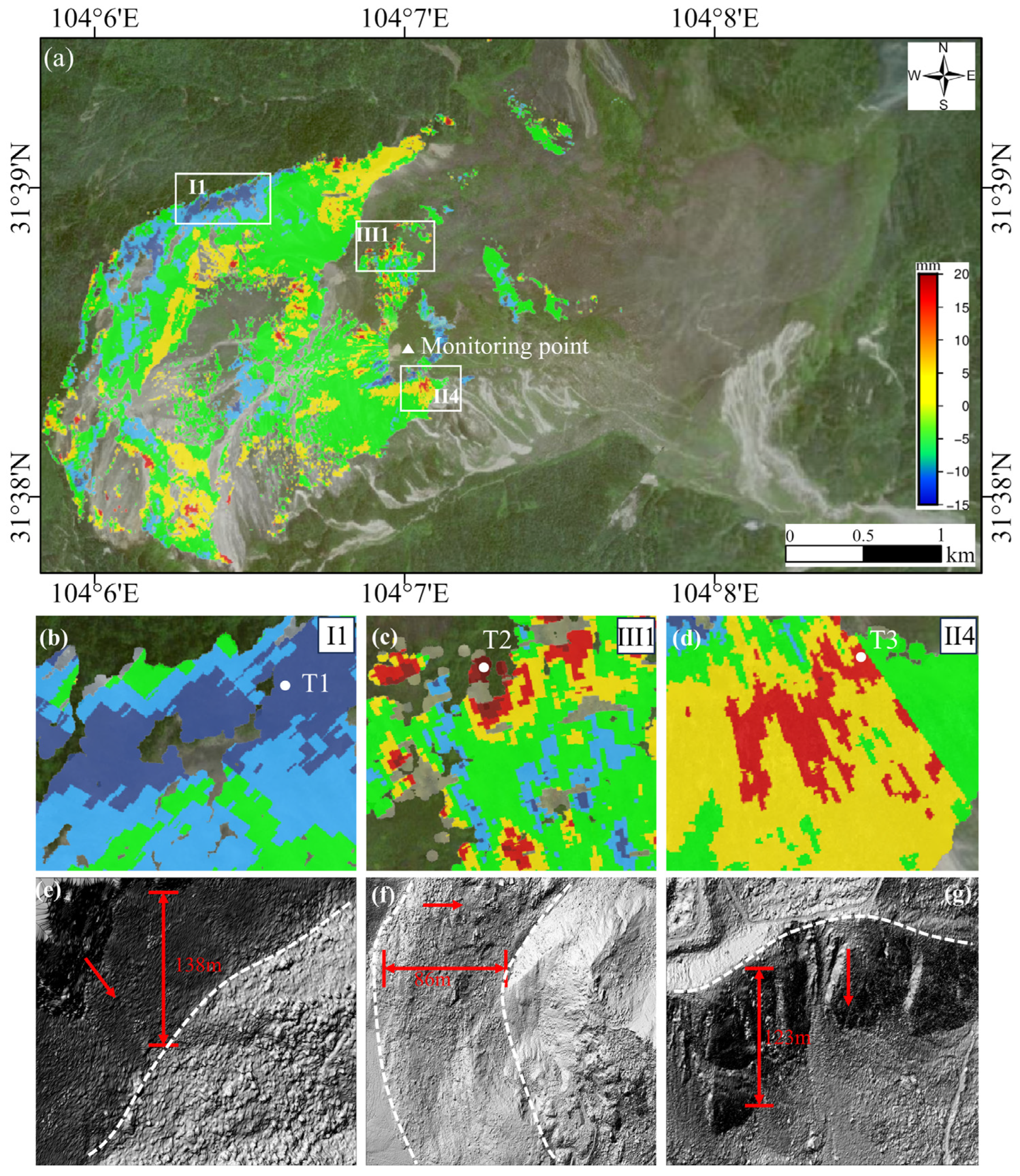
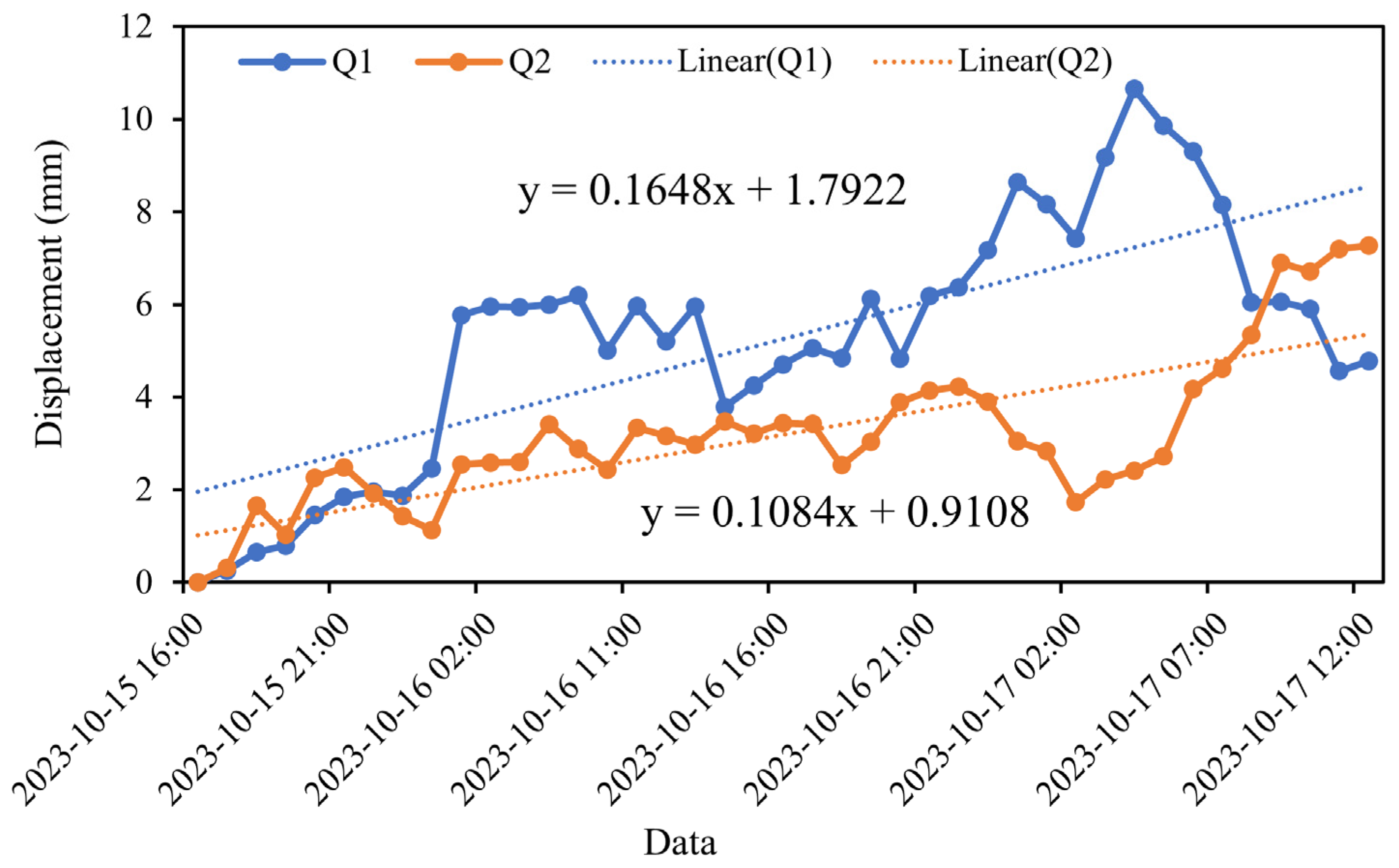
4.3. Downslope Displacements of DGBL
5. Discussion
5.1. Comparison of Satellite- and Ground-Based InSAR Measurements
5.2. Comparison with Existing DGBL InSAR Monitoring Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, R.; Li, W. Post-earthquake landsliding and long-term impacts in the Wenchuan earthquake area, China. Eng. Geol. 2014, 182, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, O.; Hovius, N.; Meunier, P.; Gorum, T.; Uchida, T. A seismologically consistent expression for the total area and volume of earthquake-triggered landsliding. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2016, 121, 640–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.Q.; Li, W.L. Analysis of the geo-hazards triggered by the 12 May 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2009, 68, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Xiong, C.; Wu, Q.; Xu, C.; Li, N.; Wu, N.A.; Cui, L. Dynamic response of the Daguangbao landslide triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake with a composite hypocenter. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2021, 12, 2170–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, B.; Song, Y.; Liang, J. Remote sensing research on Daguangbao gigantic rockslide triggered by Wenchuan earthquake. J. Eng. Geol. 2011, 19, 674–684. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Cheng, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, L. Quantification of mass wasting volume associated with the giant landslide Daguangbao induced by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake from persistent scatterer InSAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Li, Z.; Tomás, R.; Liu, G.; Yu, B.; Wang, X.; Cheng, H.; Chen, J.; Stockamp, J. Monitoring activity at the Daguangbao mega-landslide (China) using Sentinel-1 TOPS time series interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Wang, Y.; Ma, D.Y.; Jiang, R.Q.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, Z.W. Deformation Monitoring of Daguangbao Landslide Using Interferometric Point Target Analysis. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2021, 41, 1276–1281. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Wang, C.; Long, Y.; Yi, Z. Analysis of the Decadal Kinematic Characteristics of the Daguangbao Landslide Using Multiplatform Time Series InSAR Observations After the Wenchuan Earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2019JB019325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlà, T.; Tofani, V.; Lombardi, L.; Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Bertolo, D.; Thuegaz, P.; Casagli, N. Combination of GNSS, satellite InSAR, and GBInSAR remote sensing monitoring to improve the understanding of a large landslide in high alpine environment. Geomorphology 2019, 335, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrigno, F.; Gigli, G.; Fanti, R.; Intrieri, E.; Casagli, N. GB-InSAR monitoring and observational method for landslide emergency management: The Montaguto earthflow (AV, Italy). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 17, 845–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagli, N.; Frodella, W.; Morelli, S.; Tofani, V.; Ciampalini, A.; Intrieri, E.; Raspini, F.; Rossi, G.; Tanteri, L.; Lu, P. Spaceborne, UAV and ground-based remote sensing techniques for landslide mapping, monitoring and early warning. Geoenviron. Disasters 2017, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Pei, X.; Fan, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Li, B. The characteristics and failure mechanism of the largest landslide triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake, May 12, 2008, China. Landslides 2012, 9, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Huang, D.; Cen, D. Numerical modelling of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake-triggered Daguangbao landslide using a velocity and displacement dependent friction law. Eng. Geol. 2016, 215, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Pei, X.; Huang, R. Effects of geological and tectonic characteristics on the earthquake-triggered Daguangbao landslide, China. Landslides 2018, 15, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Yang, Q.; Pei, X.; Huang, R.; Zhang, W. Geological and morphological study of the Daguangbao landslide triggered by the Ms. 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake, China. Geomorphology 2020, 370, 107394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Xiangjun, P.; Shenghua, C.; Shanyong, W.; Xiaochao, Z.; Yufei, L. On the initiation mechanism of the Daguangbao landslide triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan (Ms 7.9) earthquake. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 137, 106272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Chen, Z.; Zhan, J.; Chen, C.; Gao, S.; Kong, F.; Xia, X. Morphological evolution and flow conduction characteristics of fracture channels in fractured sandstone under cyclic loading and unloading. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2023, 33, 1527–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, N.; Luo, X.; Shen, P.; Xie, L.; Liu, G.; Wei, F.; Jiang, K.; Xu, W. An enhanced spectral diversity coregistration method for dual-polarimetric Sentinel-1A/B TOPS data. Geod. Geodyn. 2023, 14, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Meng, X.; Zhang, X. SRTM DEM and its application advances. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 3875–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okolie, C.J.; Smit, J.L. A systematic review and meta-analysis of Digital elevation model (DEM) fusion: Pre-processing, methods and applications. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 188, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Gui, R.; Hu, J.; Fu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, K.; Liu, L. InSAR Digital Elevation Model Void-Filling Method Based on Incorporating Elevation Outlier Detection. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monserrat, O.; Crosetto, M.; Luzi, G. A review of ground-based SAR interferometry for deformation measurement. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 93, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, S.; Liu, H.; Song, Y. Ground-based differential interferometry SAR: A review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2020, 8, 43–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiebes, B.; Tomelleri, E.; Mejia-Aguilar, A.; Rabanser, M.; Schlögel, R.; Mulas, M.; Corsini, A. Assessment of the 2006 to 2015 Corvara landslide evolution using a UAV-derived DSM and orthophoto. In Landslides and Engineered Slopes. Experience, Theory and Practice; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 1897–1902. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J.; Dong, X.; Li, M.; Xu, Q.; Liao, M. Detection and characterization of slow-moving landslides in the 2017 Jiuzhaigou earthquake area by combining satellite SAR observations and airborne Lidar DSM. Eng. Geol. 2022, 305, 106730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Chu, T.; Tissot, P.; Wu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H. Integrated coastal subsidence analysis using InSAR, LiDAR, and land cover data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 282, 113297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya, K.; Chaoying, Z.; Qin, Z.; Zhong, L.; Bin, L. Application of InSAR Techniques to an Analysis of the Guanling Landslide. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Qi, X.; Peng, B.; Wang, J. Optimized Landslide Susceptibility Mapping and Modelling Using the SBAS-InSAR Coupling Model. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Z.; Cui, H.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, Q. Surface deformation extraction from small baseline subset synthetic aperture radar interferometry (SBAS-InSAR) using coherence-optimized baseline combinations. GISci. Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, P.A.; Gurrola, E.M.; Agram, P.; Cohen, J.; Lavalle, M.; Riel, B.V.; Fattahi, H.; Aivazis, M.A.; Simons, M.; Buckley, S.M. The InSAR scientific computing environment 3.0: A flexible framework for NISAR operational and user-led science processing. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018-2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 4897–4900. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z. A modified Goldstein filter for interferogram denoising of interferometric imaging radar altimeter based on multiple quality-guided graphs. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0308636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.; Wegmüller, U.; Strozzi, T.; Wiesmann, A. Gamma SAR and interferometric processing software. In Proceedings of the Ers-Envisat Symposium, Gothenburg, Sweden, 16–20 October 2001; Volume 1620. [Google Scholar]
- Yunjun, Z.; Fattahi, H.; Amelung, F. Small baseline InSAR time series analysis: Unwrapping error correction and noise reduction. Comput. Geosci. 2019, 133, 104331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Ding, L.; Hu, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, T. The performance of LS and SVD methods for SBAS InSAR deformation model solutions. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 8547–8572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Li, Z.; Du, J.; Han, B.; Chen, B.; Li, Y.; Peng, J. Post-Event Surface Deformation of the 2018 Baige Landslide Revealed by Ground-Based and Spaceborne Radar Observations. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Hu, C.; Tian, W.; Zhao, Z. A grid partition method for atmospheric phase compensation in GB-SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5206713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, B.; Vincent, S.; Pathan, S.; Benitez, S.R.G. Machine learning based landslide susceptibility mapping models and GB-SAR based landslide deformation monitoring systems: Growth and evolution. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2023, 29, 100905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Wu, T.; Cai, J.; Zhu, X.; Hao, J. Quantification of permafrost creep provides kinematic evidence for classifying a puzzling periglacial landform. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2021, 46, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Millar, C.I.; Westfall, R.D.; Zebker, H.A. Surface motion of active rock glaciers in the Sierra Nevada, California, USA: Inventory and a case study using InSAR. Cryosphere 2013, 7, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.C.; Shirzaei, M.; Nadeau, R.M.; Bürgmann, R. Slow and Go: Pulsing slip rates on the creeping section of the San Andreas Fault. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 5940–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Liu, G.; Jia, H.; Zhang, B.; Wu, R.; Fu, Y.; Xiang, W.; Mao, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R. A new algorithm for landslide dynamic monitoring with high temporal resolution by Kalman filter integration of multiplatform time-series InSAR processing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 110, 102812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Suo, Z.; Qi, L.; Tang, F.; Guo, H.; Tao, H. A Reliable Observation Point Selection Method for GB-SAR in Low-Coherence Areas. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Satellite | Orbit Direction | Incident Angle (°) | Heading Angle (°) | Number of Images | Acquisition Dates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-1A | Ascending (P128) | 44.2 | −12.8 | 80 | 20210110–20231226 |
| Sentinel-1A/B | Descending (P62) | 37.6 | 192.8 | 111 | 20210105–20231221 |
| Monitoring Accuracy (mm) | Maximum Viewing Angle (°) | Acquisition Interval (min) | Acting Distance (km) | Pixel Size | Total Observation Time (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 360° × 60° | 6 | 5 | 0.3 m × 1° | 45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Cai, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Fan, J.; Yao, Y.; Deng, B. Characterizing Surface Deformation of the Earthquake-Induced Daguangbao Landslide by Combining Satellite- and Ground-Based InSAR. Sensors 2025, 25, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25010066
Wang X, Zhang W, Cai J, Wang X, Wu Z, Fan J, Yao Y, Deng B. Characterizing Surface Deformation of the Earthquake-Induced Daguangbao Landslide by Combining Satellite- and Ground-Based InSAR. Sensors. 2025; 25(1):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25010066
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaomeng, Wenjun Zhang, Jialun Cai, Xiaowen Wang, Zhouhang Wu, Jing Fan, Yitong Yao, and Binlin Deng. 2025. "Characterizing Surface Deformation of the Earthquake-Induced Daguangbao Landslide by Combining Satellite- and Ground-Based InSAR" Sensors 25, no. 1: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25010066
APA StyleWang, X., Zhang, W., Cai, J., Wang, X., Wu, Z., Fan, J., Yao, Y., & Deng, B. (2025). Characterizing Surface Deformation of the Earthquake-Induced Daguangbao Landslide by Combining Satellite- and Ground-Based InSAR. Sensors, 25(1), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25010066








