Omni-Refinement Attention Network for Lane Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- We propose a novel feature fusion enhancement module (EnCA), which improves fusion quality through directional adaptive pooling and cross-layer integration.
- 2.
- We design an innovative feature extraction enhancement module (CSSA) that strengthens local representations via coordinated channel–spatial attention.
- 3.
- We conduct comprehensive experiments to validate the effectiveness of ORANet, achieving state-of-the-art results across multiple benchmark datasets.
2. Related Work
2.1. Segmentation-Based Methods
2.2. Row-Wise-Based Methods
2.3. Keypoint-Based Methods
2.4. Anchor-Based Methods
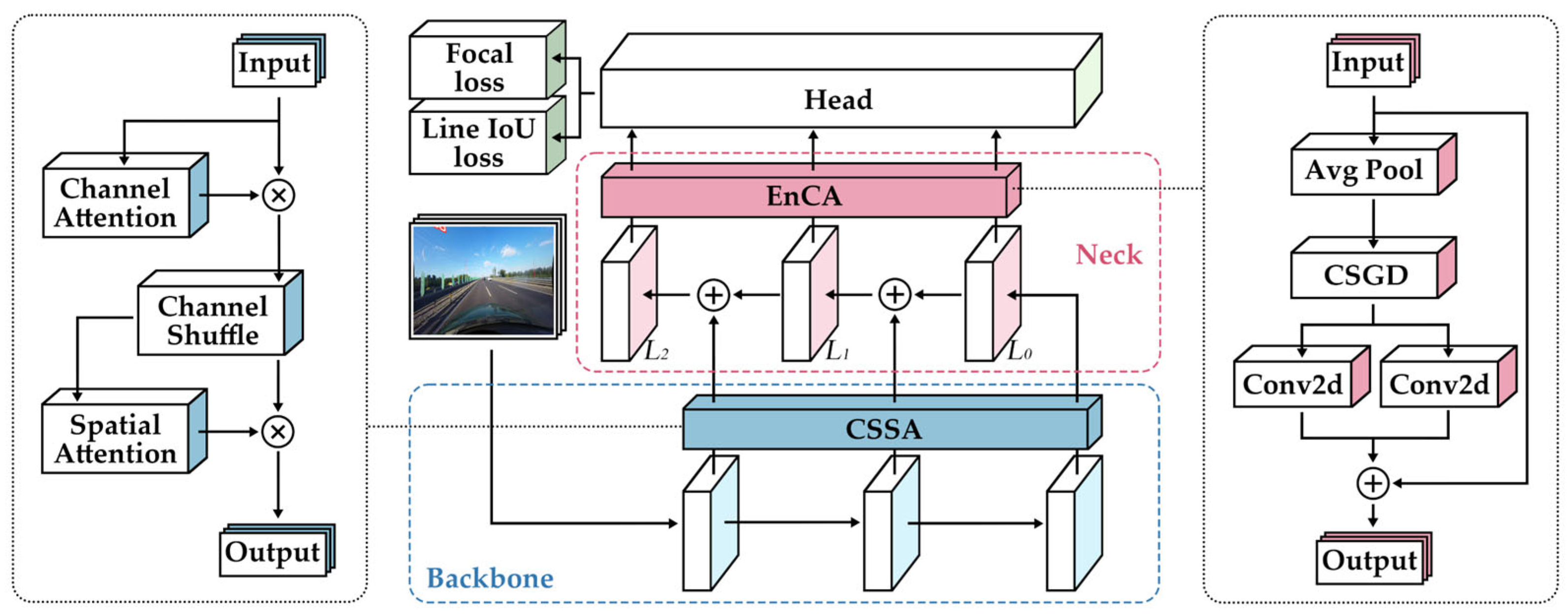
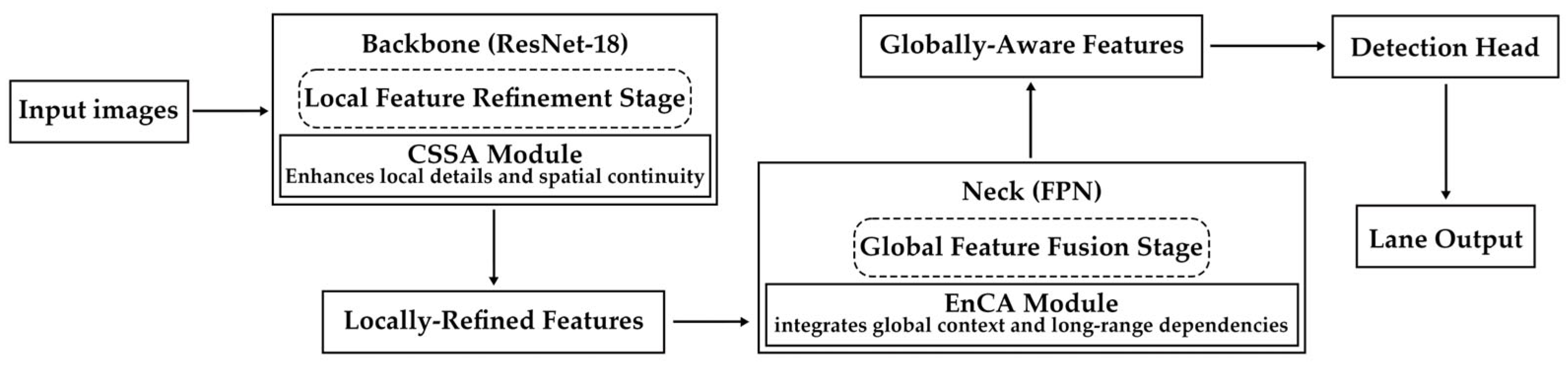
3. Approach
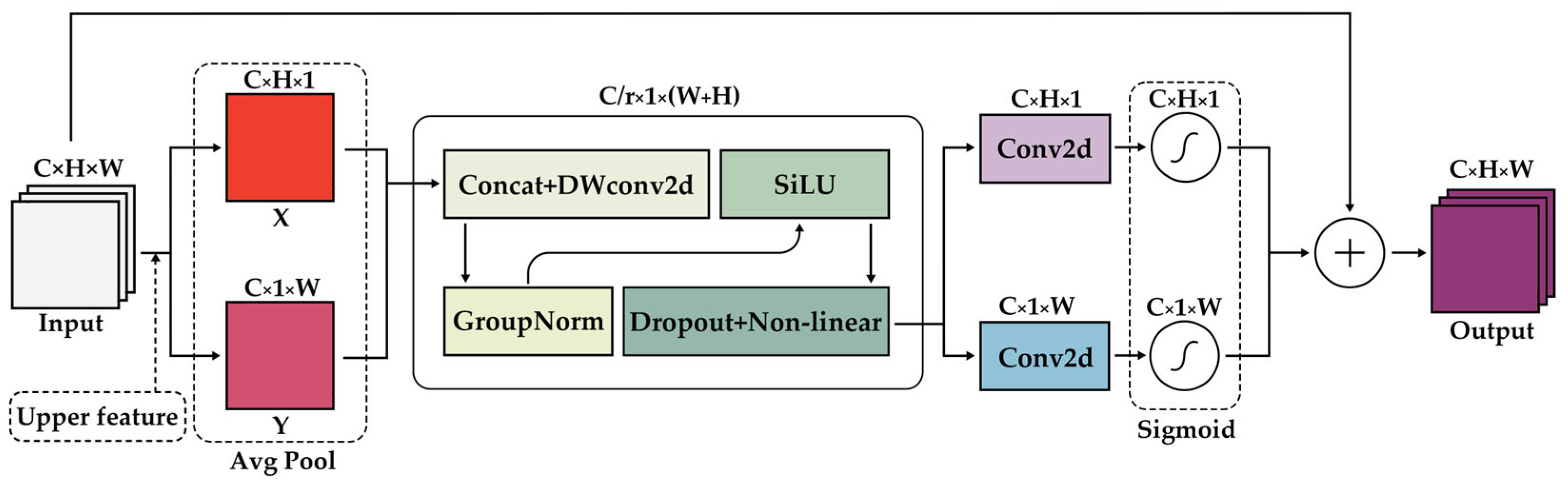
3.1. Enhanced Coordinate Attention (EnCA)
3.2. Channel Spatial Shuffle Attention (CSSA)
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.4. Quantitative Evalution
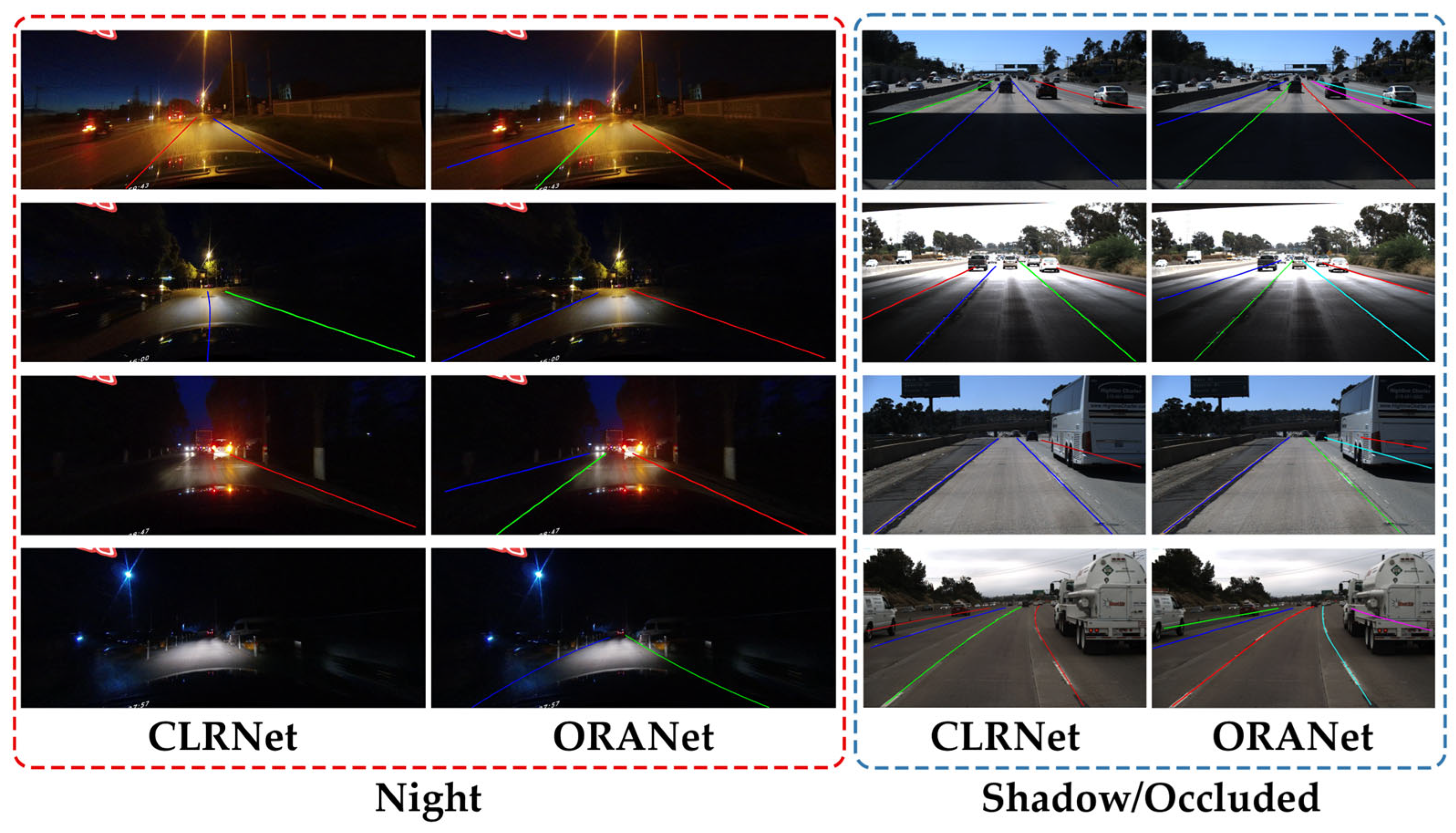
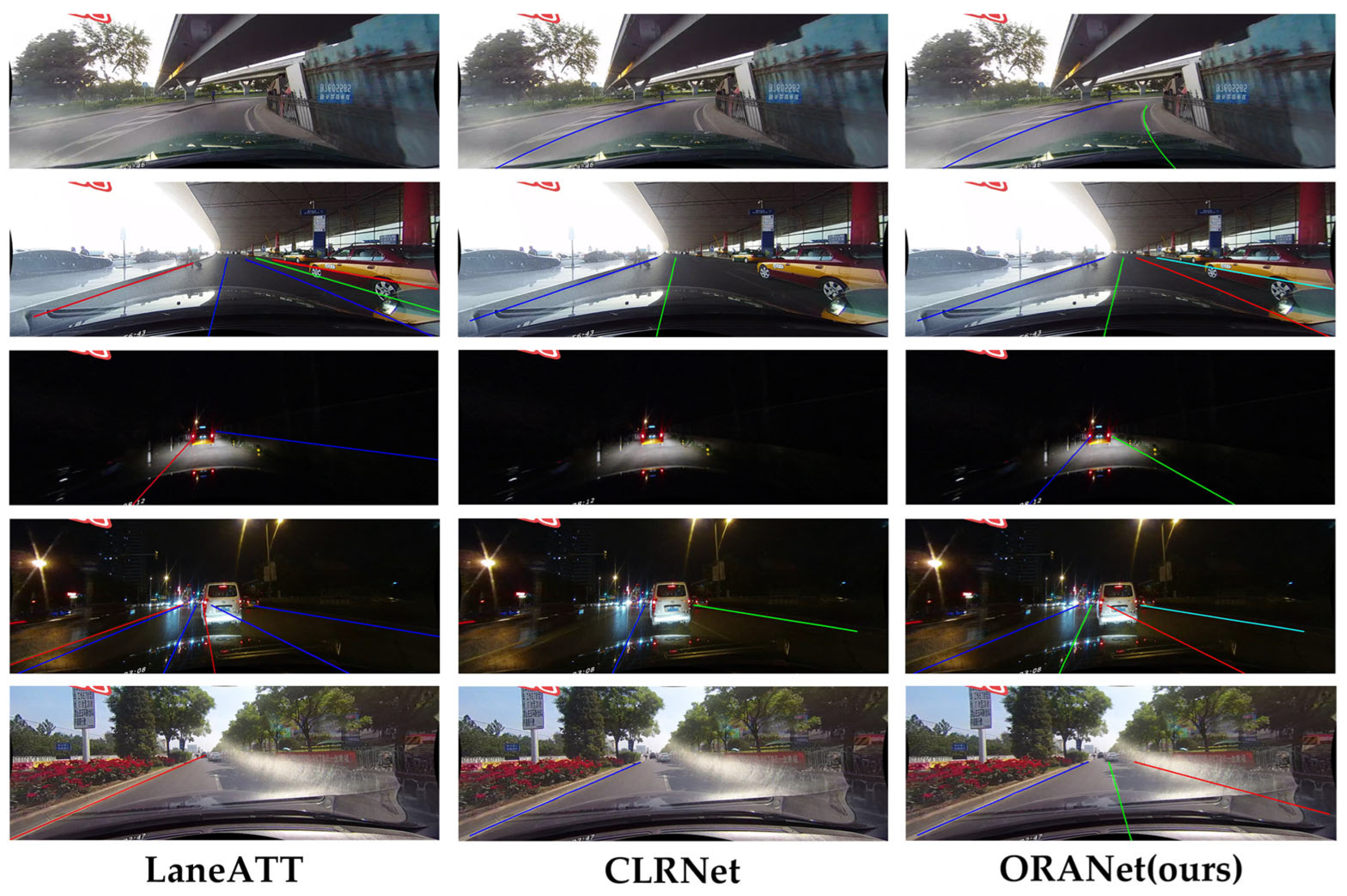
4.5. Qualitative Evalution
4.6. Ablation Study and Analysis
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rana, M.M.; Hossain, K. Connected and Autonomous Vehicles and Infrastructures: A Literature Review. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2023, 16, 264–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Pfeffer, P.E.; Edelmann, J. State of the Art: Ongoing Research in Assessment Methods for Lane Keeping Assistance Systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024, 9, 5853–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasebi, S.; Hayeri, Y.M.; Saghiri, A.M. A Literature Review of Energy Optimal Adaptive Cruise Control Algorithms. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 13636–13646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D. Color-Enhanced Lane Line Detection Algorithm Based on HSL Color Space. In Proceedings of the 2023 3rd International Conference on Computer Graphics, Image and Virtualization (ICCGIV 2023), Nanjing, China, 16–18 June 2023; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2023; Volume 12934, pp. 483–490. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. Lane Detection Method Based on Improved Hough Transform. Int. J. Simul. Process Model. 2023, 21, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaif, Z.; Abbadi, N.E. A Review of Machine Learning Techniques Utilised in Self-Driving Cars. Iraqi J. Comput. Sci. Math. 2024, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Ling, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, K.; Li, H.; Huang, X. InstLane Dataset and Geometry-Aware Network for Instance Segmentation of Lane Line Detection. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, X. Ultra Fast Structure-Aware Deep Lane Detection. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 276–291. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, W.; Yang, Z.; Cai, D.; He, X. CLRNet: Cross Layer Refinement Network for Lane Detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 888–897. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, H.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Stojanovic, V. Enhanced Feature Extraction YOLO Industrial Small Object Detection Algorithm Based on Receptive-Field Attention and Multi-Scale Features. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 35, 105023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Shi, J.; Luo, P.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Spatial as Deep: Spatial CNN for Traffic Scene Understanding. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2018, 32, 7276–7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Ma, Z.; Liu, C.; Loy, C.C. Learning Lightweight Lane Detection CNNs by Self Attention Distillation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–3 November 2019; pp. 1013–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Chaurasia, A.; Kim, S.; Culurciello, E. ENet: A Deep Neural Network Architecture for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.02147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Jia, P.; Wang, B.; Chen, L.; Jiang, K.; Yan, J.; Li, H. LaneSegNet: Map Learning with Lane Segment Perception for Autonomous Driving. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2312.16108. [Google Scholar]
- AI, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, F. AF-ICNet Semantic Segmentation Method for Unstructured Scenes Based onSmall Target Category Attention Mechanism and Feature Fusion. Acta Photonica Sin. 2023, 52, 0110001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, P.; Li, X. Ultra Fast Deep Lane Detection With Hybrid Anchor Driven Ordinal Classification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 46, 2555–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Zhu, S.; Tan, P. CondLaneNet: A Top-To-Down Lane Detection Framework Based on Conditional Convolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 3773–3782. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Wu, W.; Chen, C.; Yang, T.; Zhu, S.; Shen, J.; Kehtarnavaz, N.; Shah, M. Deep Learning-Based Human Pose Estimation: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 56, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.; Lee, Y.; Azam, S.; Munir, F.; Jeon, M.; Pedrycz, W. Key Points Estimation and Point Instance Segmentation Approach for Lane Detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 8949–8958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Jin, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, W. Focus on Local: Detecting Lane Marker From Bottom Up via Key Point. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Online, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 14122–14130. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Zhu, X.; Yu, C.; Li, W.; Ma, Y.; Jin, R.; Ren, X.; Ren, D.; Wang, M.; Yang, W. GANet: Goal Area Network for Motion Forecasting. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2209.09723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shen, C.; Shao, W.; Xing, T.; Hu, R.; Xu, P.; Chai, H.; Xue, R. CANet: Curved Guide Line Network with Adaptive Decoder for Lane Detection. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023—2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Terven, J.; Córdova-Esparza, D.-M.; Romero-González, J.-A. A Comprehensive Review of YOLO Architectures in Computer Vision: From YOLOv1 to YOLOv8 and YOLO-NAS. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2023, 5, 1680–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable Bag-of-Freebies Sets New State-of-the-Art for Real-Time Object Detectors. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Hosang, J.; Benenson, R.; Schiele, B. Learning Non-Maximum Suppression. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 6469–6477. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Line-CNN: End-to-End Traffic Line Detection With Line Proposal Unit. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabelini, L.; Berriel, R.; Paixão, T.M.; Badue, C.; De Souza, A.F.; Oliveira-Santos, T. Keep Your Eyes on the Lane: Real-Time Attention-Guided Lane Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 294–302. [Google Scholar]
- Zunair, H.; Khan, S.; Hamza, A.B. Rsud20K: A Dataset for Road Scene Understanding in Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 27–30 October 2024; pp. 708–714. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T.; Fang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, W.; Yang, Z.; Liu, H.; Cai, D. RESA: Recurrent Feature-Shift Aggregator for Lane Detection. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 3547–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Hao, Z.; Zhu, M.; Wang, J. An Efficient Lane Detection Network with Channel-Enhanced Coordinate Attention. Machines 2024, 12, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Huang, Q.; Du, C. Lane Detection Based on ECBAM_ASPP Model. Sensors 2024, 24, 8098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Seok Lee, H.; Myeong, H.; Yun, S.; Park, H.; Cho, J.; Hoon Kim, D. End-to-End Lane Marker Detection via Row-Wise Classification. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 4335–4343. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. SGDR: Stochastic Gradient Descent with Warm Restarts. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1608.03983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philion, J. FastDraw: Addressing the Long Tail of Lane Detection by Adapting a Sequential Prediction Network. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 11582–11591. [Google Scholar]
- Abualsaud, H.; Liu, S.; Lu, D.B.; Situ, K.; Rangesh, A.; Trivedi, M.M. LaneAF: Robust Multi-Lane Detection With Affinity Fields. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 7477–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, K.; Luo, J.; Wei, X.; Wei, X. Structure Guided Lane Detection. In Proceedings of the Thirtieth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, Montreal, QC, Canada, 19–27 August 2021; International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence Organization: California, LA, USA; pp. 997–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Tabelini, L.; Berriel, R.; Paixão, T.M.; Badue, C.; De Souza, A.F.; Oliveira-Santos, T. PolyLaneNet: Lane Estimation via Deep Polynomial Regression. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 6150–6156. [Google Scholar]




| Category | Method | Dataset(s) | Backbone/Model | Feature Extraction Strategy | Evaluation Metrics | Validation/Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Segmentation-based | SCNN | CULane | VGG16 | Spatial CNN for shape priors | F1, IoU | Improves structural continuity but computationally heavy |
| ENet-SAD | CULane | ENet | Self-Attention Distillation | F1 | Lightweight, enhances shallow features but less robust under occlusion | |
| Row-wise-based | UFLD | TuSimple, CULane | ResNet | Row-wise classification, global features | Acc, FN, FP | Real-time speed, but limited local detail and sensitivity to tilt |
| CondLaneNet | CULane | ResNet | Dynamic convolution, conditional anchors | F1, Acc | Handles occlusion better but high complexity | |
| Keypoint-based | PINet | TuSimple | Hourglass | Keypoint estimation + clustering | Acc, FN, FP | Provides fine-grained lanes but requires costly post-processing |
| FOLOLane | TuSimple, CULane | ResNet | Keypoint heatmaps + geometric constraints | Acc, FN, FP | Strong localization, but computationally expensive | |
| Anchor-based | LaneATT | TuSimple, CULane | ResNet | Anchor-based with attention | Acc, FN, FP | Improves anchor-based detection but struggles with occlusion and curvature |
| CLRNet | TuSimple, CULane | ResNet | Cross-layer refinement (FPN) | F1, Acc | Strong baseline, but lacks refined local feature extraction |
| Learning Rate | F1@50 Score | Convergence Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| 0.001 | 79.15 | Unstable |
| 0.0006 | 79.54 | Stable, but suboptima |
| 0.0003 (ours) | 79.58 | Optimal stability and performance |
| 0.0001 | 79.31 | Slow convergence |
| Method | Backbone | mF1 | F1@50 | F1@75 | Normal | Crowded | Shadow | No Line | Arrow | Curve | Cross | Night |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCNN [11] | VGG16 | 38.84 | 71.60 | 39.84 | 90.60 | 69.70 | 66.90 | 43.40 | 84.10 | 64.40 | 1990 | 66.10 |
| RESA [31] | ResNet34 | - | 74.50 | - | 91.90 | 72.40 | 72.00 | 46.30 | 88.10 | 68.60 | 1896 | 69.80 |
| FastDraw [37] | ResNet50 | 47.86 | 75.30 | 53.39 | 92.10 | 73.10 | 72.80 | 47.70 | 88.30 | 70.30 | 1503 | 69.90 |
| E2E [34] | ERFNet | - | 74.00 | - | 91.00 | 73.10 | 74.10 | 46.60 | 85.80 | 71.90 | 2022 | 67.90 |
| UFLD [8] | ResNet18 | 38.94 | 68.40 | 40.01 | 87.70 | 66.00 | 62.80 | 40.20 | 81.00 | 57.90 | 1743 | 62.10 |
| PINet [19] | Hourglass | 46.81 | 74.40 | 51.33 | 90.30 | 72.30 | 68.40 | 49.80 | 83.70 | 65.20 | 1427 | 67.70 |
| LaneATT [27] | ResNet18 | 47.35 | 75.13 | 51.29 | 91.17 | 72.71 | 68.03 | 49.13 | 87.82 | 63.75 | 1020 | 68.58 |
| LaneAF [38] | DLA34 | 50.42 | 77.41 | 56.79 | 91.80 | 75.61 | 79.12 | 51.38 | 86.88 | 72.70 | 1360 | 73.03 |
| SGNet [39] | ResNet18 | - | 76.12 | - | 91.42 | 74.05 | 72.17 | 50.16 | 87.13 | 67.02 | 1164 | 70.67 |
| CLRNet [9] | ResNet18 | 55.23 | 79.58 | 62.21 | 93.30 | 78.33 | 79.66 | 53.14 | 90.25 | 71.56 | 1321 | 75.11 |
| Ours | ResNet18 | 55.33 | 79.82 | 62.45 | 93.54 | 77.97 | 82.10 | 52.89 | 90.61 | 72.74 | 1333 | 75.59 |
| Method | Backbone | Acc (%) | FP (%) | FN (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCNN [11] | VGG16 | 96.53 | 6.17 | 1.80 |
| RESA [31] | ResNet34 | 96.82 | 3.63 | 2.48 |
| PolyLaneNet [40] | EfficientNetB0 | 93.36 | 9.42 | 9.33 |
| E2E [34] | ERFNet | 96.02 | 3.21 | 4.28 |
| UFLD [8] | ResNet18 | 95.82 | 19.05 | 3.92 |
| UFLD [8] | ResNet34 | 95.86 | 18.91 | 3.75 |
| LaneATT [27] | ResNet18 | 95.57 | 3.56 | 3.01 |
| LaneATT [27] | ResNet34 | 95.63 | 3.53 | 2.92 |
| LaneATT [27] | ResNet122 | 96.10 | 5.64 | 2.17 |
| CLRNet [9] | ResNet18 | 96.84 | 2.28 | 1.92 |
| Ours | ResNet18 | 96.97 | 3.14 | 1.42 |
| Configuration | F1-CULane | Acc(%)-Tusimple |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline(CLRNet) | 79.58 | 96.84 |
| Baseline + CA | 79.54 | 96.86 |
| Baseline + EnCA | 79.63 | 96.92 |
| Baseline + CBAM | 79.60 | 96.87 |
| Baseline + CSSA | 79.71 | 96.89 |
| Baseline + EnCA + CSSA(Ours) | 79.82 | 96.97 |
| Module | Complexity Setting | F1-Score | Params(M) | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSSA | High(Ratio:C/2) | 79.79 | 23.5 | 21.5 | 105 |
| CSSA | Low(Ratio:C/8) | 79.41 | 18.5 | 16.7 | 137 |
| EnCA | High(Standard Conv) | 79.75 | 24.1 | 22.5 | 100 |
| None | Original | 79.58 | 19.8 | 17.4 | 129 |
| Both | Ours(C/4; DWConv) | 79.82 | 20.4 | 18.5 | 123 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Z.; Cao, B. Omni-Refinement Attention Network for Lane Detection. Sensors 2025, 25, 6150. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196150
Zhang B, Zhang L, Wang T, Wei Y, Chen Z, Cao B. Omni-Refinement Attention Network for Lane Detection. Sensors. 2025; 25(19):6150. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196150
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Boyuan, Lanchun Zhang, Tianbo Wang, Yingjun Wei, Ziyan Chen, and Bin Cao. 2025. "Omni-Refinement Attention Network for Lane Detection" Sensors 25, no. 19: 6150. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196150
APA StyleZhang, B., Zhang, L., Wang, T., Wei, Y., Chen, Z., & Cao, B. (2025). Omni-Refinement Attention Network for Lane Detection. Sensors, 25(19), 6150. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196150





