Unleashing the Potential of Pre-Trained Diffusion Models for Generalizable Person Re-Identification
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We investigate the feasibility of leveraging a pre-trained diffusion model as an expert to enhance generalizable feature learning for DG Re-ID by collaboratively training a discriminative Re-ID model and efficiently fine-tuning a generative diffusion model;
- We propose a simple yet effective correlation-aware conditioning scheme that combines the dark knowledge embedded in ID classification probabilities with learnable ID-wise prompts to guide the diffusion model, unleashing its generalization knowledge to the discriminative Re-ID model through gradient feedback;
- Extensive experiments on both single-source and multi-source DG Re-ID tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, achieving state-of-the-art performance. Additionally, plenty of ablation studies are conducted to provide a comprehensive analysis of the proposed method.
2. Related Work
2.1. Generative Diffusion Models
2.2. Diffusion Models for Representation Learning
2.3. Diffusion Models for Person Re-ID
2.4. Generalizable Person Re-ID
3. Diffusion Preliminaries
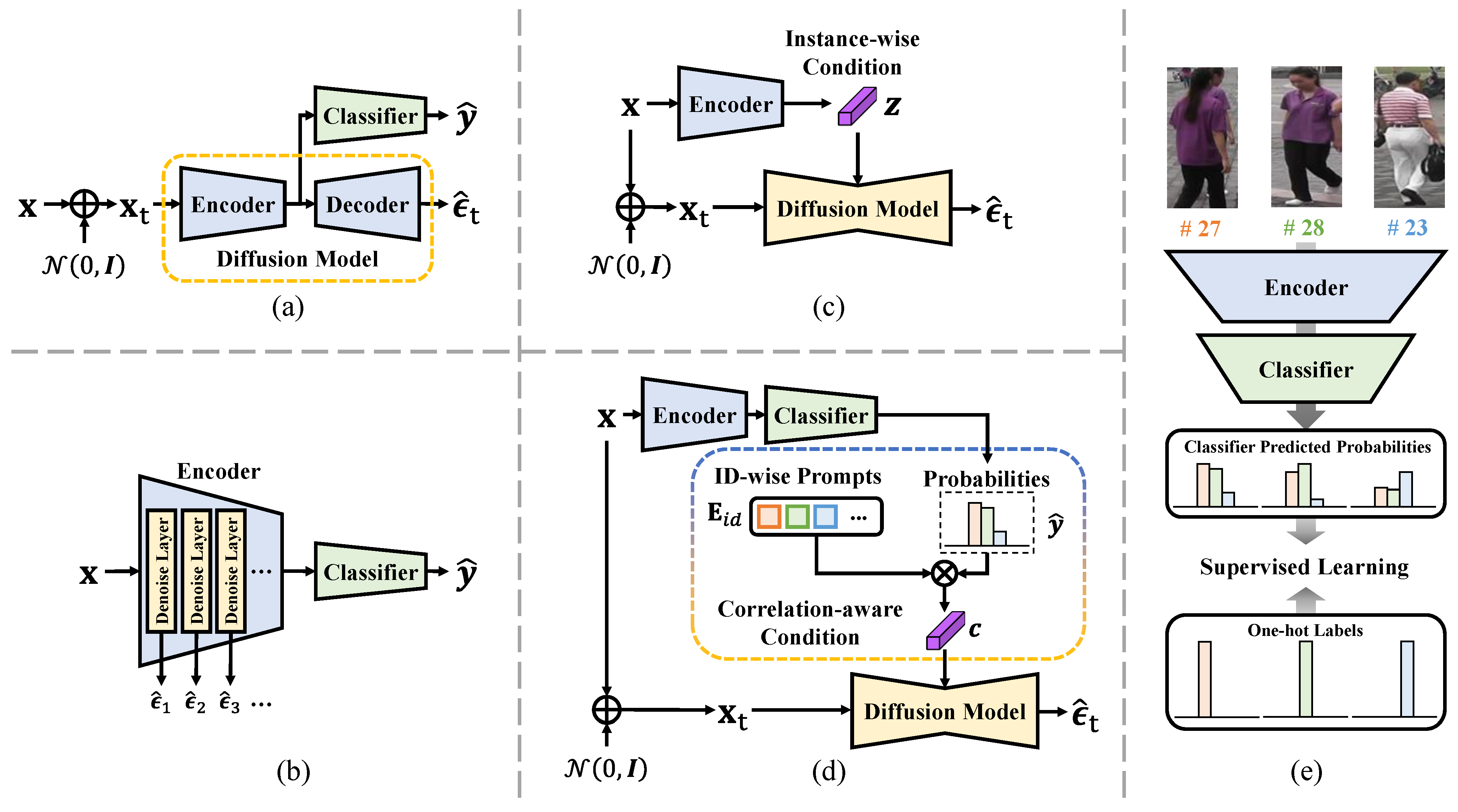
4. The Proposed Method
4.1. The Baseline Re-ID Model
4.2. The Generative Diffusion Model
4.3. The Correlation-Aware Conditioning Scheme
4.4. The Entire Training Loss
5. Experiments
5.1. Datasets and Evaluation Protocols
5.2. Implementation Details
5.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Arts
5.3.1. Single-Source DG Re-ID
5.3.2. Multi-Source DG Re-ID
5.4. Ablation Studies
5.4.1. Effectiveness of the CLIP-Based Re-ID Model
5.4.2. Effectiveness of the Diffusion Model Assistance
5.4.3. Ablations on Computational Overhead
5.4.4. Effectiveness of the Conditioning Scheme
5.4.5. Impact of the Hyper-Parameters
5.4.6. Impact of More Intricate Conditioning Schemes
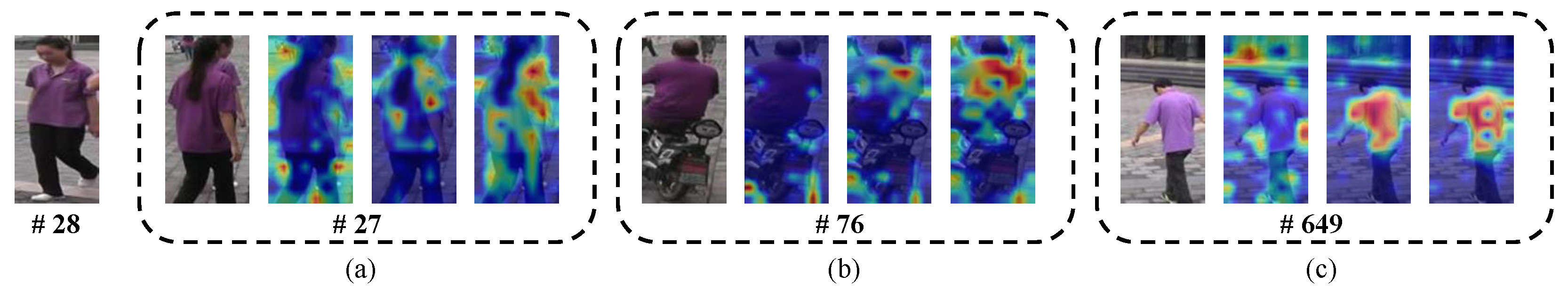
5.4.7. Visualization Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, H.; Gu, Y.; Liao, X.; Lai, S.; Jiang, W. Bag of tricks and a strong baseline for deep person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, Y.; Huang, W.; Liu, S.; Guo, P.; Zhang, Z.; Durrani, T.S. Person re-identification using local relation-aware graph convolutional network. Sensors 2023, 23, 8138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Liu, P.; Cao, X.; Liu, C. Dynamic Weighting Network for Person Re-Identification. Sensors 2023, 23, 5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhao, S.; Li, S.; Cheng, B.; Chen, J. Research on Person Re-Identification through Local and Global Attention Mechanisms and Combination Poolings. Sensors 2024, 24, 5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Luo, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, F.; Li, H.; Jiang, W. Transreid: Transformer-based object re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 15013–15022. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Lan, C.; Zeng, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L. Style normalization and restitution for generalizable person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 3143–3152. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Tan, T. Learning domain invariant representations for generalizable person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 32, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, T.; Yang, Y.; Ren, Z.; Wang, Z.; Hua, G. Calibrated domain-invariant learning for highly generalizable large scale re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Snowmass, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020; pp. 3589–3598. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Z.; Wei, L.; Xie, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Ai, H.; Tian, Q. Rethinking the distribution gap of person re-identification with camera-based batch normalization. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 140–157. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.; Kim, T.; Jeong, M.; Park, H.; Kim, C. Meta batch-instance normalization for generalizable person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 3425–3435. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, B.; Liu, L.; Gao, L.; Lin, G.; Yang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y. Dynamically transformed instance normalization network for generalizable person re-identification. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 285–301. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Huang, Z.; Li, L.; Zheng, K.; Zha, Z.J. Debiased batch normalization via gaussian process for generalizable person re-identification. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), Online, 22 February–1 March 2022; Volume 36, pp. 1729–1737. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Liang, J.; He, L.; Sun, Z. Mimic embedding via adaptive aggregation: Learning generalizable person re-identification. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 372–388. [Google Scholar]
- Han, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, C. One-Shot Unsupervised Cross-Domain Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 34, 1339–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, J. Invariance Learning under Uncertainty for Single Domain Generalization Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 5031911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Yang, F.; Luo, Z.; Lin, Y.; Li, S.; Sebe, N. Learning to generalize unseen domains via memory-based multi-source meta-learning for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 6277–6286. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, H.; Song, J.; Luo, X.; Zheng, F.; Li, W.; Shen, H.T. Meta distribution alignment for generalizable person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2487–2496. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, D. Style uncertainty based self-paced meta learning for generalizable person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 2107–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, E.P.; Shan, L.; Kot, A.C. Dex: Domain embedding expansion for generalized person re-identification. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), Online, 22–25 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, E.P.; Lin, S.; Kot, A.C. A unified deep semantic expansion framework for domain-generalized person re-identification. Neurocomputing 2024, 600, 128120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, M.A.; Ou, Y.; Li, T.; Jiang, G. Lightweight Multimodal Domain Generic Person Reidentification Metric for Person-Following Robots. Sensors 2023, 23, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.; Sun, L.; Yu, K.; Batmanghelich, K.; Jegelka, S.; Sra, S. Can contrastive learning avoid shortcut solutions? In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Online, 7 December 2021; Volume 34, pp. 4974–4986. [Google Scholar]
- Saharia, C.; Chan, W.; Saxena, S.; Li, L.; Whang, J.; Denton, E.L.; Ghasemipour, K.; Gontijo Lopes, R.; Karagol Ayan, B.; Salimans, T.; et al. Photorealistic text-to-image diffusion models with deep language understanding. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022; Volume 35, pp. 36479–36494. [Google Scholar]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 10684–10695. [Google Scholar]
- Baranchuk, D.; Voynov, A.; Rubachev, I.; Khrulkov, V.; Babenko, A. Label-Efficient Semantic Segmentation with Diffusion Models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Virtual, 25 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Shih, S.M.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Ji, S. Your vit is secretly a hybrid discriminative-generative diffusion model. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.07791. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson, D.A.; Zoran, D.; Malinowski, M.; Lampinen, A.K.; Jaegle, A.; McClelland, J.L.; Matthey, L.; Hill, F.; Lerchner, A. Soda: Bottleneck diffusion models for representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 23115–23127. [Google Scholar]
- Jaini, P.; Clark, K.; Geirhos, R. Intriguing properties of generative classifiers. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.16779. [Google Scholar]
- Fuest, M.; Ma, P.; Gui, M.; Fischer, J.S.; Hu, V.T.; Ommer, B. Diffusion models and representation learning: A survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.00783. [Google Scholar]
- Deja, K.; Trzciński, T.; Tomczak, J.M. Learning data representations with joint diffusion models. In Proceedings of the Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, Turin, Italy, 18–22 September 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 543–559. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, G.; Huang, X.; Sang, J. DenoiseReID: Denoising Model for Representation Learning of Person Re-Identification. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.08773. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, F.; Tang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. Diffusion feedback helps clip see better. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.20171. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G. Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.02531. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, E.J.; Shen, Y.; Wallis, P.; Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. Lora: Low-rank adaptation of large language models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.09685. [Google Scholar]
- Biderman, D.; Portes, J.; Ortiz, J.J.G.; Paul, M.; Greengard, P.; Jennings, C.; King, D.; Havens, S.; Chiley, V.; Frankle, J.; et al. LoRA Learns Less and Forgets Less. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.09673. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Virtual, 6–12 December 2020; Volume 33, pp. 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Meng, C.; Ermon, S. Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Virtual, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Peebles, W.; Xie, S. Scalable diffusion models with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 4195–4205. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, W.; Yang, H.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y. Denoising diffusion autoencoders are unified self-supervised learners. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 15802–15812. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). PMLR, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.C.; Prabhudesai, M.; Duggal, S.; Brown, E.; Pathak, D. Your diffusion model is secretly a zero-shot classifier. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 2206–2217. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, K.; Jaini, P. Text-to-image diffusion models are zero shot classifiers. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vancouver, BC, USA, 10–15 December 2024; Volume 36. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L. Vi-diff: Unpaired visible-infrared translation diffusion model for single modality labeled visible-infrared person re-identification. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.04122. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Hu, G.; Zhao, C. Diverse Person: Customize Your Own Dataset for Text-Based Person Search. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 4943–4951. [Google Scholar]
- Bhunia, A.K.; Khan, S.; Cholakkal, H.; Anwer, R.M.; Laaksonen, J.; Shah, M.; Khan, F.S. Person image synthesis via denoising diffusion model. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 5968–5976. [Google Scholar]
- Asperti, A.; Fiorilla, S.; Orsini, L. A generative approach to person reidentification. Sensors 2024, 24, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.; Kong, J.; Jiang, M.; Lu, M.; Mian, A. Unsupervised Learning of Intrinsic Semantics With Diffusion Model for Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2024, 33, 6705–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Luo, M.; Dang, Z.; Dai, G.; Chang, X.; Wang, J. PSDiff: Diffusion Model for Person Search with Iterative and Collaborative Refinement. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Tong, Z.; Duan, L.Y. Generalizable person re-identification with relevance-aware mixture of experts. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 16145–16154. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Dou, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X. Domain generalization person re-identification via style adaptation learning. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2024, 15, 4733–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. Identity-seeking self-supervised representation learning for generalizable person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 15847–15858. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, S.; Gao, J.; Guan, M.; Ruan, J.; Zhou, C.; Liu, T.; Qian, D.; Fu, Y. Learning robust visual-semantic embedding for generalizable person re-identification. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.09498. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, S.; Chen, H.; Ran, W.; Yu, Z.; Liu, T.; Qian, D.; Fu, Y. Deep multimodal fusion for generalizable person re-identification. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.00933. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.; Wang, G.; Yuan, W.; Zhu, S.; Tan, P. Cluster contrast for unsupervised person re-identification. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV), Macao, China, 4–8 December 2022; pp. 1142–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Phuong, M.; Lampert, C. Towards understanding knowledge distillation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 5142–5151. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, R.; Kornblith, S.; Hinton, G.E. When does label smoothing help? In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Chau, L.p.; Kot, A.C. Embracing the dark knowledge: Domain generalization using regularized knowledge distillation. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACM MM), Virtual, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 2595–2604. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, N.; Yan, S.; Tang, H.; Tang, J.; Zhang, L. Multi-view information integration and propagation for occluded person re-identification. Inf. Fusion 2024, 104, 102201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Shen, L.; Tian, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Tian, Q. Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1116–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y. Unlabeled samples generated by gan improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3754–3762. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Zhang, S.; Gao, W.; Tian, Q. Person transfer gan to bridge domain gap for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.; Zheng, L.; Cao, D.; Li, S. Re-ranking person re-identification with k-reciprocal encoding. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1318–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.; Zheng, L.; Kang, G.; Li, S.; Yang, Y. Random erasing data augmentation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 13001–13008. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Hermans, A.; Beyer, L.; Leibe, B. In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.07737. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, S.; Shao, L. Transmatcher: Deep image matching through transformers for generalizable person re-identification. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Online, 6–14 December 2021; Volume 34, pp. 1992–2003. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, S.; Shao, L. Interpretable and generalizable person re-identification with query-adaptive convolution and temporal lifting. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 456–474. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, S.; Shao, L. Graph sampling based deep metric learning for generalizable person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 7359–7368. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Song, J.; Ni, H.; Shen, H.T. Style-controllable generalized person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACM MM), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 7912–7921. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, H.; Li, Y.; Gao, L.; Shen, H.T.; Song, J. Part-aware transformer for generalizable person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 11280–11289. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Peng, W. Multiple integration model for single-source domain generalizable person re-identification. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2024, 98, 104037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Wang, S. Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 480–496. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, X. Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACM MM), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 274–282. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Yang, Y.; Cavallaro, A.; Xiang, T. Omni-scale feature learning for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3702–3712. [Google Scholar]
- Elfwing, S.; Uchibe, E.; Doya, K. Sigmoid-weighted linear units for neural network function approximation in reinforcement learning. Neural Netw. 2018, 107, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). PMLR, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; Volume 37, pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]

| Dataset | Cameras | IDs | Train | Query | Gallery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Market1501 [60] | 6 | 1501 | 12,936 | 3368 | 15,913 |
| DukeMTMC-reID [61] | 8 | 1812 | 16,522 | 2228 | 17,661 |
| MSMT17 [62] | 15 | 4101 | 32,621 | 11,659 | 82,161 |
| CUHK03-NP [63] | 2 | 1467 | 7365 | 1400 | 5332 |
| Model | MA→D | MA→MS | MA→C3 | D→MA | D→MS | D→C3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP | R1 | mAP | R1 | mAP | R1 | mAP | R1 | mAP | R1 | mAP | R1 | |
| SNR [6] | 33.6 | 55.1 | - | - | - | - | 33.9 | 66.7 | - | - | - | - |
| CBN [9] | - | - | 9.5 | 25.3 | - | - | - | - | 9.5 | 25.3 | - | - |
| QAConv [69] | 28.7 | 48.8 | 7.0 | 22.6 | - | - | 27.2 | 58.6 | 8.9 | 29.0 | - | - |
| TransMatcher ‡ [68] | - | - | 18.4 | 47.3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| MetaBIN [10] | 33.1 | 55.2 | - | - | - | - | 35.9 | 69.2 | - | - | - | - |
| DTIN-Net [11] | 36.1 | 57.0 | - | - | - | - | 37.4 | 69.8 | - | - | - | - |
| QAConv-GS [70] | - | - | 15.0 | 41.2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| MDA † [17] | 34.4 | 56.7 | 11.8 | 33.5 | - | - | 38.0 | 70.3 | - | - | - | - |
| Li et al. [71] | - | - | 21.8 | 47.5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SuA-SpML [18] | 34.8 | 55.5 | 11.1 | 30.1 | - | - | 36.3 | 65.8 | 13.6 | 37.8 | - | - |
| DIR-ReID [7] | 33.0 | 54.5 | - | - | - | - | 35.2 | 68.2 | - | - | - | - |
| GN [14] | 34.0 | 52.3 | 10.3 | 28.6 | 14.5 | 14.4 | 34.3 | 64.3 | 12.3 | 33.8 | 10.3 | 10.2 |
| GN+SNR [14] | 34.7 | 55.4 | - | - | 15.2 | 15.1 | 36.9 | 68.5 | - | - | 11.5 | 11.0 |
| PAT [72] | - | - | 18.2 | 42.8 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| LDU [15] | 38.0 | 59.5 | 13.5 | 35.7 | 18.2 | 18.5 | 42.3 | 73.2 | 16.7 | 44.2 | 14.2 | 14.2 |
| MTI [73] | 36.4 | 57.8 | - | - | 16.2 | 16.3 | 38.2 | 70.5 | - | - | 13.3 | 13.3 |
| Baseline (ours) | 47.8 | 67.3 | 22.0 | 50.1 | 30.0 | 30.4 | 41.7 | 70.5 | 19.0 | 46.9 | 22.1 | 23.1 |
| DCAC (ours) | 49.5 | 69.1 | 23.4 | 52.1 | 32.5 | 33.2 | 42.3 | 71.5 | 19.7 | 47.4 | 23.0 | 23.5 |
| Model | MS→MA | MS→D | MS→C3 | C3→MA | C3→D | C3→MS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP | R1 | mAP | R1 | mAP | R1 | mAP | R1 | mAP | R1 | mAP | R1 | |
| PCB [74] | 26.7 | 52.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| MGN [75] | 25.1 | 48.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| OSNet-IBN [76] | 37.2 | 66.5 | 45.6 | 67.4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SNR [6] | 41.4 | 70.1 | 50.0 | 69.2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CBN [9] | 45.0 | 73.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| TransMatcher ‡ [68] | 52.0 | 80.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| QAConv-GS [70] | 46.7 | 75.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| MDA † [17] | 53.0 | 79.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| GN [14] | - | - | - | - | - | - | 40.6 | 67.6 | 31.2 | 50.0 | 11.9 | 33.4 |
| GN+SNR [14] | 37.5 | 68.0 | 45.4 | 66.2 | 18.3 | 17.4 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| LDU [15] | 44.8 | 74.6 | 48.9 | 69.2 | 21.3 | 21.3 | 37.5 | 68.1 | 29.5 | 51.8 | 12.6 | 36.9 |
| MTI [73] | 42.7 | 72.9 | 47.7 | 67.5 | 16.0 | 15.4 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Baseline (ours) | 51.0 | 76.5 | 57.1 | 73.8 | 32.7 | 32.9 | 39.6 | 66.2 | 41.4 | 62.7 | 16.6 | 45.2 |
| DCAC (ours) | 52.1 | 77.9 | 58.4 | 75.0 | 34.1 | 34.4 | 42.0 | 68.6 | 43.2 | 64.8 | 17.8 | 47.3 |
| Model | Target: MA | Target: D | Target: MS | Target: C3 | Average | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP | R1 | mAP | R1 | mAP | R1 | mAP | R1 | mAP | R1 | |
| QAConv50 [69] | 39.5 | 68.6 | 43.4 | 64.9 | 10.0 | 29.9 | 19.2 | 22.9 | 28.0 | 46.6 |
| M3L [16] | 48.1 | 74.5 | 50.5 | 69.4 | 12.9 | 33.0 | 29.9 | 30.7 | 35.4 | 51.9 |
| M3LIBN [16] | 50.2 | 75.9 | 51.1 | 69.2 | 14.7 | 36.9 | 32.1 | 33.1 | 37.0 | 53.8 |
| RaMoE [50] | 56.5 | 82.0 | 56.9 | 73.6 | 13.5 | 34.1 | 35.5 | 36.6 | 40.6 | 56.6 |
| PAT [72] | 51.7 | 75.2 | 56.5 | 71.8 | 21.6 | 45.6 | 31.5 | 31.1 | 40.3 | 55.9 |
| DEX [19] | 55.2 | 81.5 | 55.0 | 73.7 | 18.7 | 43.5 | 33.8 | 36.7 | 40.7 | 58.9 |
| UDSX [20] | 60.4 | 85.7 | 55.8 | 74.7 | 20.2 | 47.6 | 37.2 | 38.9 | 43.4 | 61.7 |
| SALDG [51] | 57.6 | 82.3 | 52.0 | 71.2 | 18.1 | 46.5 | 32.4 | 34.5 | 40.0 | 58.6 |
| DCAC (Ours) | 56.7 | 80.0 | 58.9 | 75.4 | 27.5 | 56.7 | 42.5 | 43.6 | 46.4 | 63.9 |
| Model | PT | Trainable | MA→MS | MS→MA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP | R1 | mAP | R1 | ||||
| Baseline | - | - | - | 22.0 | 50.1 | 51.0 | 76.5 |
| DCAC (frozen) | ✓ | × | × | 21.3 | 49.7 | 50.8 | 76.5 |
| DCAC (LoRA adaptation) | ✓ | ✓ | × | 23.4 | 52.1 | 52.1 | 77.9 |
| DCAC (partial fine-tuning 1) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 22.1 | 50.3 | 47.1 | 74.6 |
| DCAC (partial fine-tuning 2) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 22.1 | 50.4 | 51.9 | 78.5 |
| DCAC (full fine-tuning) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 21.8 | 50.1 | 51.5 | 76.6 |
| DCAC (train from scratch) | × | ✓ | ✓ | 21.9 | 50.3 | 51.7 | 77.6 |
| Mode | Model | MA→MS | Time (ms) | TFLOPs | Memory (GB) | Parameters (M) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP | R1 | ||||||
| Training | Baseline | 22.0 | 50.1 | 140.3 | 1.46 | 7.58 | 85.94 |
| DCAC (Frozen) | 21.3 | 49.7 | 464.7 | 8.50 | 17.22 | 86.51 | |
| DCAC (LoRA adaptation) | 23.4 | 52.1 | 578.1 | 8.52 | 18.15 | 89.01 | |
| DCAC (Partial fine-tuning 1) | 22.1 | 50.3 | 647.1 | 8.50 | 23.92 | 599.37 | |
| DCAC (Partial fine-tuning 2) | 22.1 | 50.4 | 662.1 | 8.50 | 25.01 | 696.41 | |
| DCAC (Full fine-tuning) | 21.8 | 50.1 | 735.9 | 8.50 | 28.24 | 946.03 | |
| Inference | - | - | - | 40.3 | 1.46 | 2.27 | 85.55 |
| Conditioning Scheme | MA→MS | MS→MA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP | R1 | mAP | R1 | |
| Baseline | 22.0 | 50.1 | 51.0 | 76.5 |
| DCAC (Instance-wise) | 22.4 | 50.8 | 51.6 | 77.7 |
| DCAC (Class-wise) | 22.6 | 51.2 | 50.5 | 76.5 |
| DCAC (Correlation-aware) | 23.4 | 52.1 | 52.1 | 77.9 |
| Model | Market1501 | MSMT17 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP | R1 | mAP | R1 | |
| Baseline | 86.4 | 94.4 | 70.4 | 88.1 |
| DCAC (instance-wise) | 86.4 | 94.7 | 70.4 | 88.5 |
| DCAC (class-wise) | 86.6 | 94.5 | 70.6 | 88.2 |
| DCAC (correlation-aware) | 86.8 | 94.9 | 70.1 | 88.3 |
| Rank r | MA→MS | MS→MA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP | Rank-1 | mAP | Rank-1 | |
| 8 | 23.4 | 52.1 | 51.4 | 77.3 |
| 16 | 22.1 | 50.7 | 51.7 | 77.9 |
| 32 | 22.4 | 51.4 | 52.1 | 77.9 |
| 64 | 22.9 | 51.6 | 51.1 | 77.5 |
| Model | Transformations | MA→MS | MS→MA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiLU | BN | mAP | R1 | mAP | R1 | |
| Baseline | - | - | 22.0 | 50.1 | 51.0 | 76.5 |
| DCAC | × | × | 23.4 | 52.1 | 52.1 | 77.9 |
| + Non-linearity | ✓ | × | 22.4 | 50.8 | 50.4 | 76.9 |
| + BatchNorm | × | ✓ | 22.5 | 50.9 | 51.0 | 76.8 |
| + ConditionNet | ✓ | ✓ | 21.9 | 50.1 | 50.5 | 76.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Gong, X. Unleashing the Potential of Pre-Trained Diffusion Models for Generalizable Person Re-Identification. Sensors 2025, 25, 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020552
Li J, Gong X. Unleashing the Potential of Pre-Trained Diffusion Models for Generalizable Person Re-Identification. Sensors. 2025; 25(2):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020552
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiachen, and Xiaojin Gong. 2025. "Unleashing the Potential of Pre-Trained Diffusion Models for Generalizable Person Re-Identification" Sensors 25, no. 2: 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020552
APA StyleLi, J., & Gong, X. (2025). Unleashing the Potential of Pre-Trained Diffusion Models for Generalizable Person Re-Identification. Sensors, 25(2), 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020552





