Depression Recognition Using Daily Wearable-Derived Physiological Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Preparation
2.2. Feature Extraction
2.3. Statistical Analysis and Classification
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chodavadia, P.; Teo, I.; Poremski, D.; Fung, D.S.S.; Finkelstein, E.A. Prevalence and economic burden of depression and anxiety symptoms among Singaporean adults: Results from a 2022 web panel. BMC Psychiatry 2023, 23, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, C.; Valstar, M.F.; Morriss, R.K.; Crowe, J. Objective methods for reliable detection of concealed depression. Front. ICT 2015, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, P.D.; Vicnesh, J.; Lih, O.S.; Palmer, E.E.; Yamakawa, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Acharya, U.R. Artificial intelligence assisted tools for the detection of anxiety and depression leading to suicidal ideation in adolescents: A review. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2024, 18, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.; Abosuliman, S.S. Analyzing of optimal classifier selection for EEG signals of depression patients based on intelligent fuzzy decision support systems. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, U.R.; Sudarshan, V.K.; Adeli, H.; Santhosh, J.; Koh, J.E.; Puthankatti, S.D.; Adeli, A. A Novel Depression Diagnosis Index Using Nonlinear Features in EEG Signals. Eur. Neurol. 2015, 74, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wu, C.; Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Fu, S.; Wang, F.; Zhang, D. Quantitative personality predictions from a brief EEG recording. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2020, 13, 1514–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hu, X.; Long, X.; Tang, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, D. EEG responses to emotional videos can quantitatively predict big-five personality traits. Neurocomputing 2020, 415, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.; Yoon, J.; Kang, M.; Lee, D.; Park, E.; Han, J. Detecting depression on video logs using audiovisual features. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holko, M.; Litwin, T.R.; Munoz, F.; Theisz, K.I.; Salgin, L.; Jenks, N.P.; Holmes, B.W.; Watson-McGee, P.; Winford, E.; Sharma, Y. Wearable fitness tracker use in federally qualified health center patients: Strategies to improve the health of all of us using digital health devices. NPJ Digit. Med. 2022, 5, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, B.W.; Low, C.A.; Jacobson, N.; Areán, P.; Torous, J.; Allen, N.B. Guidelines for wrist-worn consumer wearable assessment of heart rate in biobehavioral research. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, M.E.; Aguilera, A. Mobile, social, and wearable computing and the evolution of psychological practice. Prof. Psychol. Res. Pract. 2012, 43, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, A.; Barbosa, M.; Morás, L.; Cazella, S.C.; Sgobbi, L.F.; Sene, I.; Marques, G. Occupational stress monitoring using biomarkers and smartwatches: A systematic review. Sensors 2022, 22, 6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shui, X.; Chen, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, D. Personality in daily life: Multi-situational physiological signals reflect big-five personality traits. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2023, 27, 2853–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, G.Y.; Loughnane, D.; Polley, C.; Jayarathna, T.; Breen, P.P. The apple watch for monitoring mental health–related physiological symptoms: Literature review. JMIR Ment. Health 2022, 9, e37354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, G.D.; Heinz, M.V.; Song, S.H.; Nemesure, M.D.; Jacobson, N.C. Using digital phenotyping to capture depression symptom variability: Detecting naturalistic variability in depression symptoms across one year using passively collected wearable movement and sleep data. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Alrazaq, A.; AlSaad, R.; Shuweihdi, F.; Ahmed, A.; Aziz, S.; Sheikh, J. Systematic review and meta-analysis of performance of wearable artificial intelligence in detecting and predicting depression. NPJ Digit. Med. 2023, 6, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.; Kim, J.; Mun, K.-R. Identifying depression in the elderly using gait accelerometry. In Proceedings of the 2022 44th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Glasgow, UK, 11–15 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.-G.; Ko, I.; Han, S. Depression level classification using machine learning classifiers based on actigraphy data. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 116622–116646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ruiz, J.G.; Galván-Tejada, C.E.; Zanella-Calzada, L.A.; Celaya-Padilla, J.M.; Galván-Tejada, J.I.; Gamboa-Rosales, H.; Luna-García, H.; Magallanes-Quintanar, R.; Soto-Murillo, M.A. Comparison of night, day and 24 h motor activity data for the classification of depressive episodes. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenza, G.; Citi, L.; Gentili, C.; Lanata, A.; Scilingo, E.P.; Barbieri, R. Characterization of depressive states in bipolar patients using wearable textile technology and instantaneous heart rate variability assessment. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2014, 19, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaleghi, A.; Shahi, K.; Saidi, M.; Babaee, N.; Kaveh, R.; Mohammadian, A. Linear and nonlinear analysis of multimodal physiological data for affective arousal recognition. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2024, 18, 2277–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Ramesh, J.; Ganguly, S.; Aburukba, R.; Sagahyroon, A.; Aloul, F. Evaluating multimodal wearable sensors for quantifying affective states and depression with neural networks. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 22788–22802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.P.; Lin, H.Y.; Lin, W.L.; Huang, A.C.W. Effects of stress, depression, and their interaction on heart rate, skin conductance, finger temperature, and respiratory rate: Sympathetic-parasympathetic hypothesis of stress and depression. J. Clin. Psychol. 2011, 67, 1080–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, X.; Lin, R.; Luo, Z.; Lin, B.; Mao, X.; Li, H.; Liu, R.; Zhang, D. Bodily electrodermal representations for affective computing. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2024, 15, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsue, S.; Yamamoto, T. Relationship between depression and movement quality in normal young adults. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2019, 31, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzammel, M.; Salam, H.; Othmani, A. End-to-end multimodal clinical depression recognition using deep neural networks: A comparative analysis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 211, 106433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.S.; Ahmed, N. A fast and minimal system to identify depression using smartphones: Explainable machine learning–based approach. JMIR Form. Res. 2023, 7, e28848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haderlein, J.F.; Peterson, A.D.; Burkitt, A.N.; Mareels, I.M.; Grayden, D.B. Autoregressive models for biomedical signal processing. In Proceedings of the 2023 45th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Sydney, Australia, 24–27 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Shui, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Hu, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, D. A dataset of daily ambulatory psychological and physiological recording for emotion research. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Xu, P.; Pei, X.; Wang, Q.; Yue, Y.; Han, C. Fatigue at the wheel: A non-visual approach to truck driver fatigue detection by multi-feature fusion. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2024, 199, 107511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Xu, M.; Xiao, X.; Xu, F.; Ming, D. Detection of dynamic changes of electrodermal activity to predict the classroom performance of college students. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2024, 18, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, B.; Tan, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y. Measurement of high-school students’ trait math anxiety using neurophysiological recordings during math exam. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 57460–57471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, F.; Liu, B.; Qi, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, D. Wearable neurophysiological recordings in middle-school classroom correlate with students’ academic performance. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doberenz, S.; Roth, W.T.; Wollburg, E.; Maslowski, N.I.; Kim, S. Methodological considerations in ambulatory skin conductance monitoring. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2011, 80, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, K.C.; Chandran, V.; Acharya, U.R.; Lim, C.M. Application of higher order statistics/spectra in biomedical signals—A review. Med. Eng. Phys. 2010, 32, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, A.; Bradshaw, B.; Landes, S.; Kammann, P.; Bois De Fer, B.; Lee, W.-N.; Lange, R. A novel digital approach to describe real world outcomes among patients with constipation. NPJ Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Gholaminejad, A.; Ding, G.; Gao, Y.; Han, J.; Keutzer, K. Personalized emotion recognition by personality-aware high-order learning of physiological signals. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2019, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, L.; Noohi, F.; Veziris, C.R.; Kosik, E.L.; Holley, S.R.; Lee, A.; Brown, J.A.; Roy, A.R.; Chow, T.E.; Allen, I. Dynamic autonomic nervous system states arise during emotions and manifest in basal physiology. Psychophysiology 2023, 60, e14218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portet, S. A primer on model selection using the Akaike Information Criterion. Infect. Dis. Model. 2020, 5, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, M.; Abdelwanis, M.; Maalouf, M.; Jelinek, H.F. Detecting depression severity using weighted random forest and oxidative stress biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Leemput, I.A.; Wichers, M.; Cramer, A.O.; Borsboom, D.; Tuerlinckx, F.; Kuppens, P.; Van Nes, E.H.; Viechtbauer, W.; Giltay, E.J.; Aggen, S.H. Critical slowing down as early warning for the onset and termination of depression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymkowicz, S.M.; Gerlach, A.R.; Homiack, D.; Taylor, W.D. Biological factors influencing depression in later life: Role of aging processes and treatment implications. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, S.; Wollschlaeger, D.; Dreimueller, N.; Engelmann, J.; Herzog, D.P.; Roll, S.C.; Tadić, A.; Lieb, K. Effects of age on depressive symptomatology and response to antidepressant treatment in patients with major depressive disorder aged 18 to 65 years. Compr. Psychiatry 2020, 99, 152170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smagula, S.F.; Zhang, G.; Gujral, S.; Covassin, N.; Li, J.; Taylor, W.D.; Reynolds, C.F.; Krafty, R.T. Association of 24-hour activity pattern phenotypes with depression symptoms and cognitive performance in aging. JAMA Psychiatry 2022, 79, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.E.; Di Biase, M.A.; Mosley, P.E.; Lupton, M.K.; Xia, Y.; Fripp, J.; Breakspear, M.; Cropley, V.; Zalesky, A. Evaluation of brain-body health in individuals with common neuropsychiatric disorders. JAMA Psychiatry 2023, 80, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzagalli, D.A.; Roberts, A.C. Prefrontal cortex and depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2022, 47, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singla, S.; Jhamb, S.; Singh, K.D.; Kumar, A. Depression affects autonomic system of the body? Yes, it does! J. Educ. Health Promot. 2020, 9, 217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perez, A.J.; Zeadally, S. Recent advances in wearable sensing technologies. Sensors 2021, 21, 6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, K.; Qian, K.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, X.; Hu, B. Depression recognition from EEG signals using an adaptive channel fusion method via improved focal loss. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2023, 27, 3234–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, P.; Li, S.; Zhao, Q.; Yin, Z.; Guan, W.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Liao, J. Construction of a resting EEG-based depression recognition model for college students and possible mechanisms of action of different types of exercise. BMC Psychiatry 2023, 23, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zitouni, M.S.; Lih Oh, S.; Vicnesh, J.; Khandoker, A.; Acharya, U.R. Automated recognition of major depressive disorder from cardiovascular and respiratory physiological signals. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 970993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohari, M.R.; Doggett, A.; Patte, K.A.; Ferro, M.A.; Dubin, J.A.; Hilario, C.; Leatherdale, S.T. Using random forest to identify correlates of depression symptoms among adolescents. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2024, 59, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniji, O.D.; Adeyemi, S.O.; Ajagbe, S.A. An improved bagging ensemble in predicting mental disorder using hybridized random forest-artificial neural network model. Informatica 2022, 46, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.K.; Hossain, T.; Safran, M.; Alfarhood, S.; Mridha, M.; Che, D. Ensemble of hybrid model based technique for early detecting of depression based on SVM and neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Zhao, S.; Hu, X. An ensemble classification model for depression based on wearable device sleep data. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2023, 28, 2602–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedor, S.; Lewis, R.; Pedrelli, P.; Mischoulon, D.; Curtiss, J.; Picard, R.W. Wearable technology in clinical practice for depressive disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2457–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.C.; Estepp, J.R.; Wilson, G.F.; Russell, C.A. The effects of day-to-day variability of physiological data on operator functional state classification. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Luo, X.; Chen, S.; Lyu, Y.; Ji, X.; Meng, Y.; Wang, D. Continuous Authentication via Wrist Photoplethysmogram: An Extensive Study. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2024, 24, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.Y.; Jang, E.H.; Choi, K.W.; Jeon, H.J.; Byun, S.; Sim, J.Y.; Choi, J.H.; Yu, H.Y. Skin conductance responses in Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) under mental arithmetic stress. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Yi, Y.; Liang, Z.; Yan, S. Hypergraph Neural Network for Multimodal Depression Recognition. Electronics 2024, 13, 4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, X.; Li, B.; Zhao, L.; Yan, D.; Yang, L. End-to-end depression recognition based on a one-dimensional convolution neural network model using two-lead ECG signal. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2022, 42, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leaning, I.E.; Ikani, N.; Savage, H.S.; Leow, A.; Beckmann, C.; Ruhé, H.G.; Marquand, A.F. From smartphone data to clinically relevant predictions: A systematic review of digital phenotyping methods in depression. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 158, 105541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

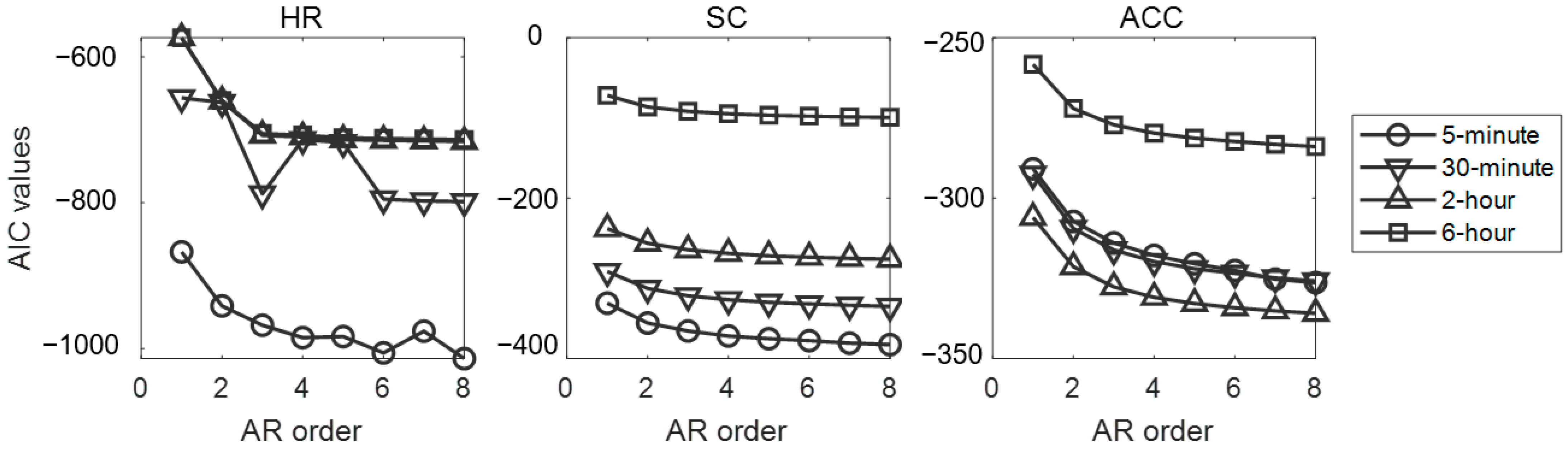
| Features | Heart Rate | Skin Conductance | Acceleration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t(115) | pFDR | t(115) | pFDR | t(115) | pFDR | ||
| Static | Mean | −0.05 | 0.963 | −0.59 | 0.673 | −3.10 | 0.007 |
| SD | −1.43 | 0.298 | −1.11 | 0.408 | 0.14 | 0.932 | |
| Skew | −0.68 | 0.655 | 0.56 | 0.673 | 2.75 | 0.021 | |
| Kurt | −0.68 | 0.655 | −3.17 | 0.001 | −1.10 | 0.408 | |
| Dynamic | AR1 | −2.89 | 0.022 | −3.69 | <0.001 | −5.82 | 0.001 |
| AR2 | 2.78 | 0.030 | −1.24 | 0.383 | −9.15 | <0.001 | |
| AR3 | −2.09 | 0.082 | −0.16 | 0.932 | −5.99 | 0.001 | |
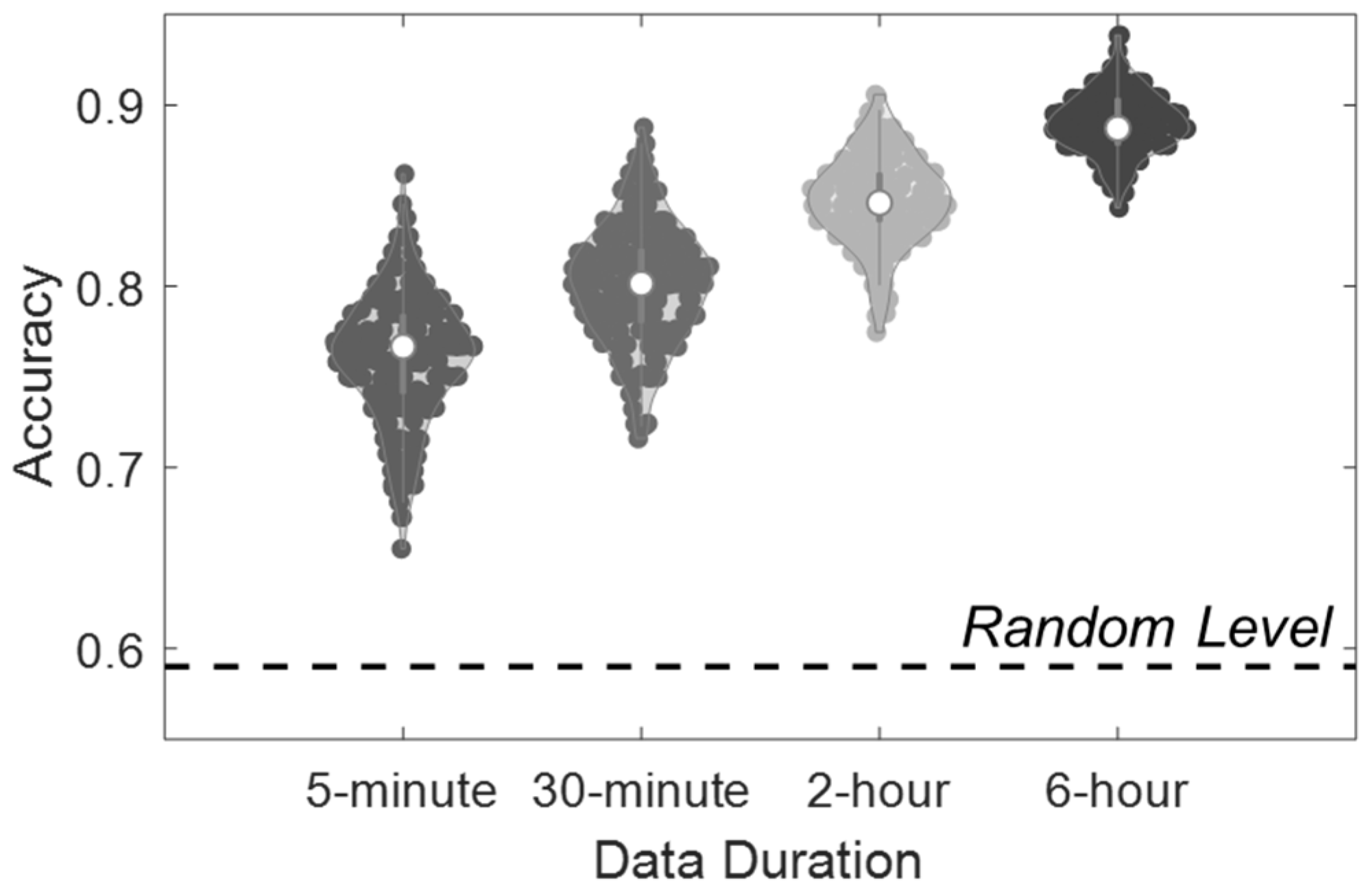
| Models | 5 min | 30 min | 2 h | 6 h | Random |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 76.0 (3.5) | 80.1 (3.2) | 84.7 (2.5) | 90.0 (1.7) | 49.7 (5.1) |
| SVM | 67.4 (4.4) | 67.0 (4.0) | 73.2 (3.5) | 74.1 (2.2) | 49.2 (4.5) |
| LDA | 64.6 (5.1) | 69.2 (4.7) | 77.0 (3.4) | 81.5 (2.3) | 52.1 (3.7) |
| KNN | 60.8 (4.9) | 64.6 (5.5) | 71.6 (3.7) | 76.1 (2.0) | 53.4 (2.6) |
| Selected Features | 5-min | 30-min | 2-h | 6-h | Random |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 76.0 (3.5) | 80.1 (3.2) | 84.7 (2.5) | 90.0 (1.7) | 49.7 (5.1) |
| Non-ACC | 70.4 (4.8) | 74.6 (4.4) | 77.0 (3.8) | 80.5 (2.4) | 50.4 (2.0) |
| Static | 75.8 (3.2) | 78.1 (3.1) | 80.6 (3.3) | 85.7 (1.5) | 49.9 (2.4) |
| Dynamic | 74.5 (3.7) | 77.3 (3.5) | 82.5 (2.9) | 89.3 (1.2) | 51.2 (2.3) |
| Non-ACC Dynamic | 68.4 (4.6) | 71.5 (4.3) | 74.5 (3.8) | 78.1 (2.3) | 52.3 (4.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shui, X.; Xu, H.; Tan, S.; Zhang, D. Depression Recognition Using Daily Wearable-Derived Physiological Data. Sensors 2025, 25, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020567
Shui X, Xu H, Tan S, Zhang D. Depression Recognition Using Daily Wearable-Derived Physiological Data. Sensors. 2025; 25(2):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020567
Chicago/Turabian StyleShui, Xinyu, Hao Xu, Shuping Tan, and Dan Zhang. 2025. "Depression Recognition Using Daily Wearable-Derived Physiological Data" Sensors 25, no. 2: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020567
APA StyleShui, X., Xu, H., Tan, S., & Zhang, D. (2025). Depression Recognition Using Daily Wearable-Derived Physiological Data. Sensors, 25(2), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020567






