Drunk Driver Detection Using Multiple Non-Invasive Biosignals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
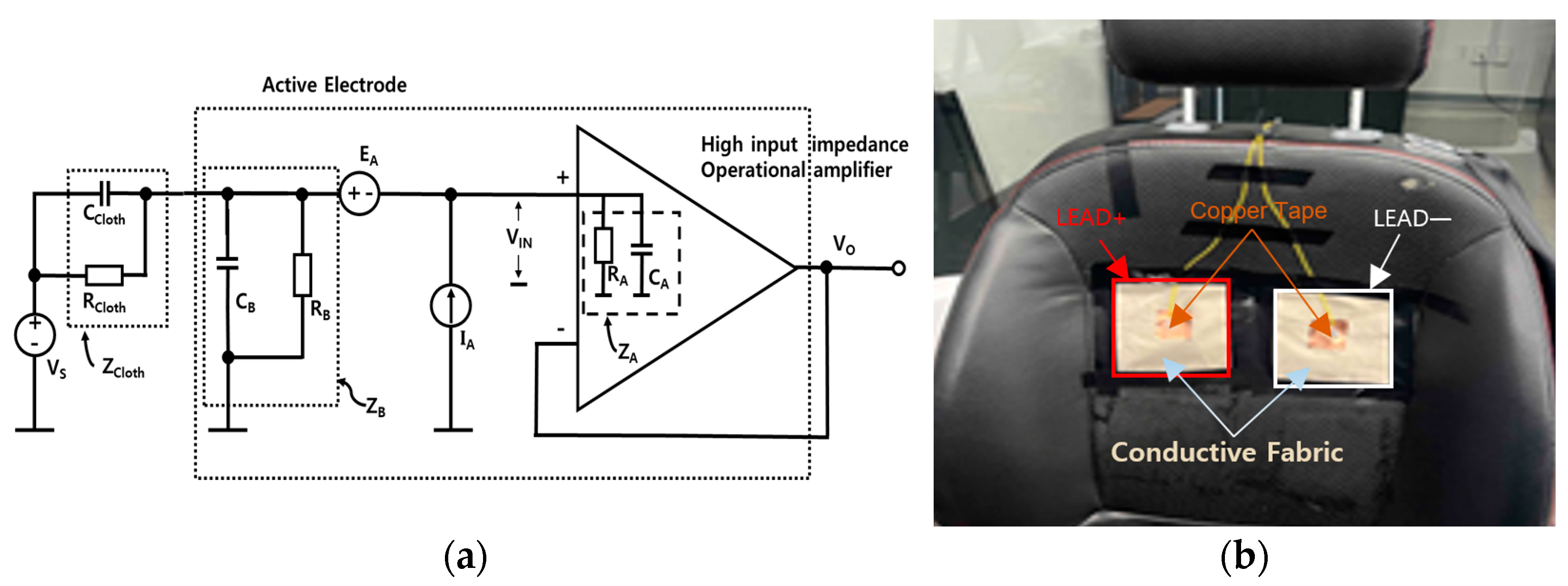
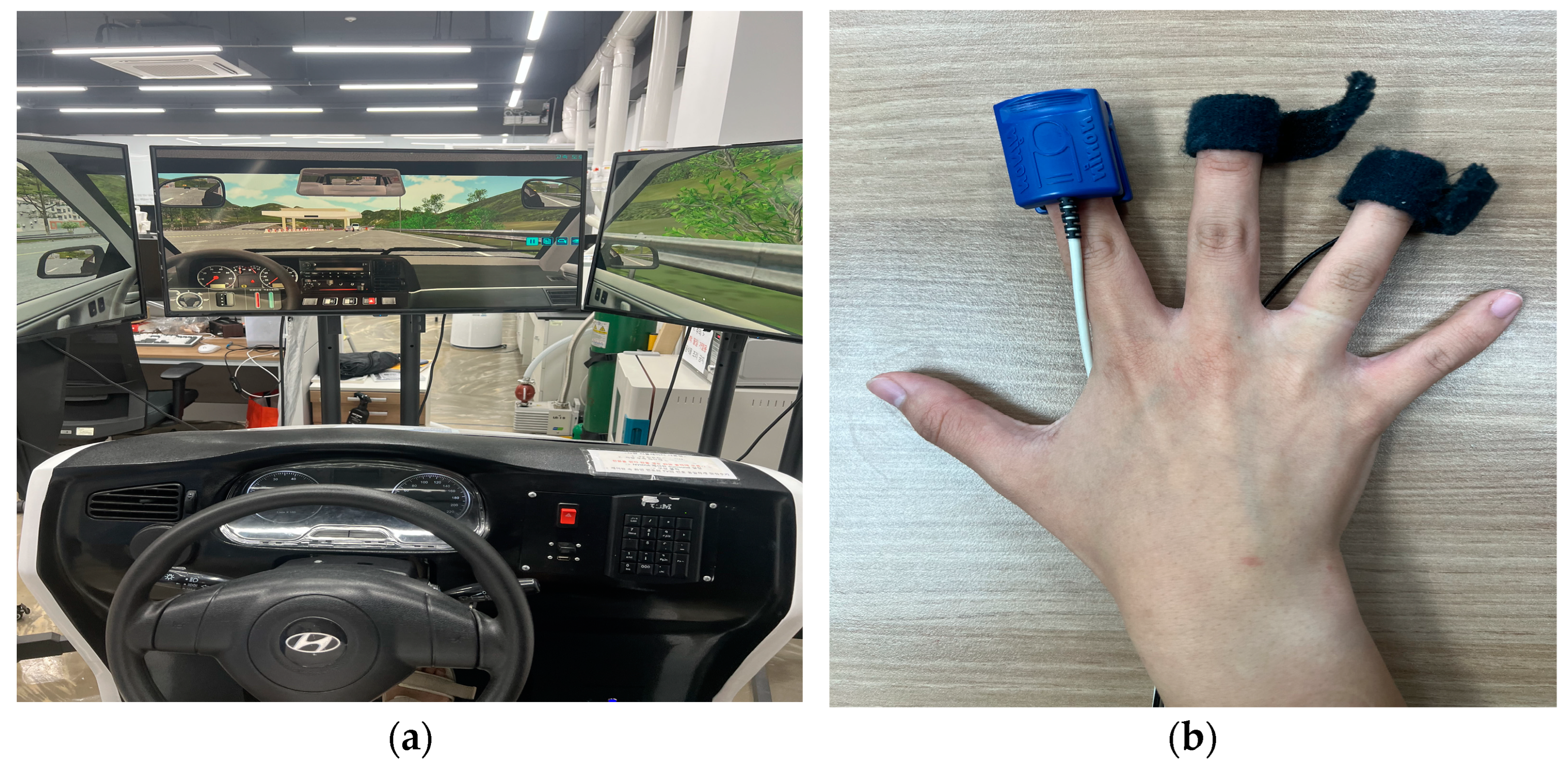
2.1. Biosignal Data Collection
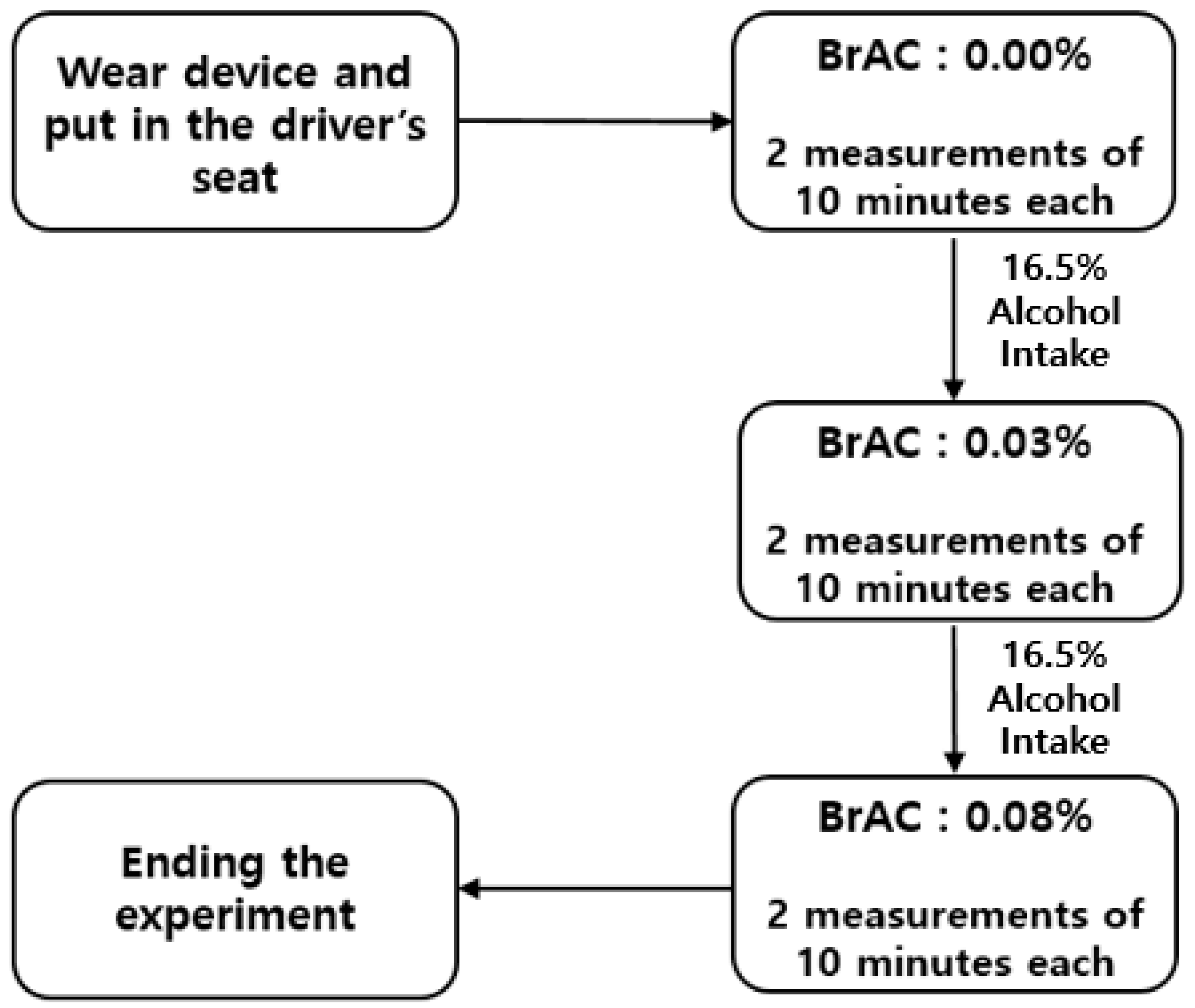
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Data Preprocessing
3. Results
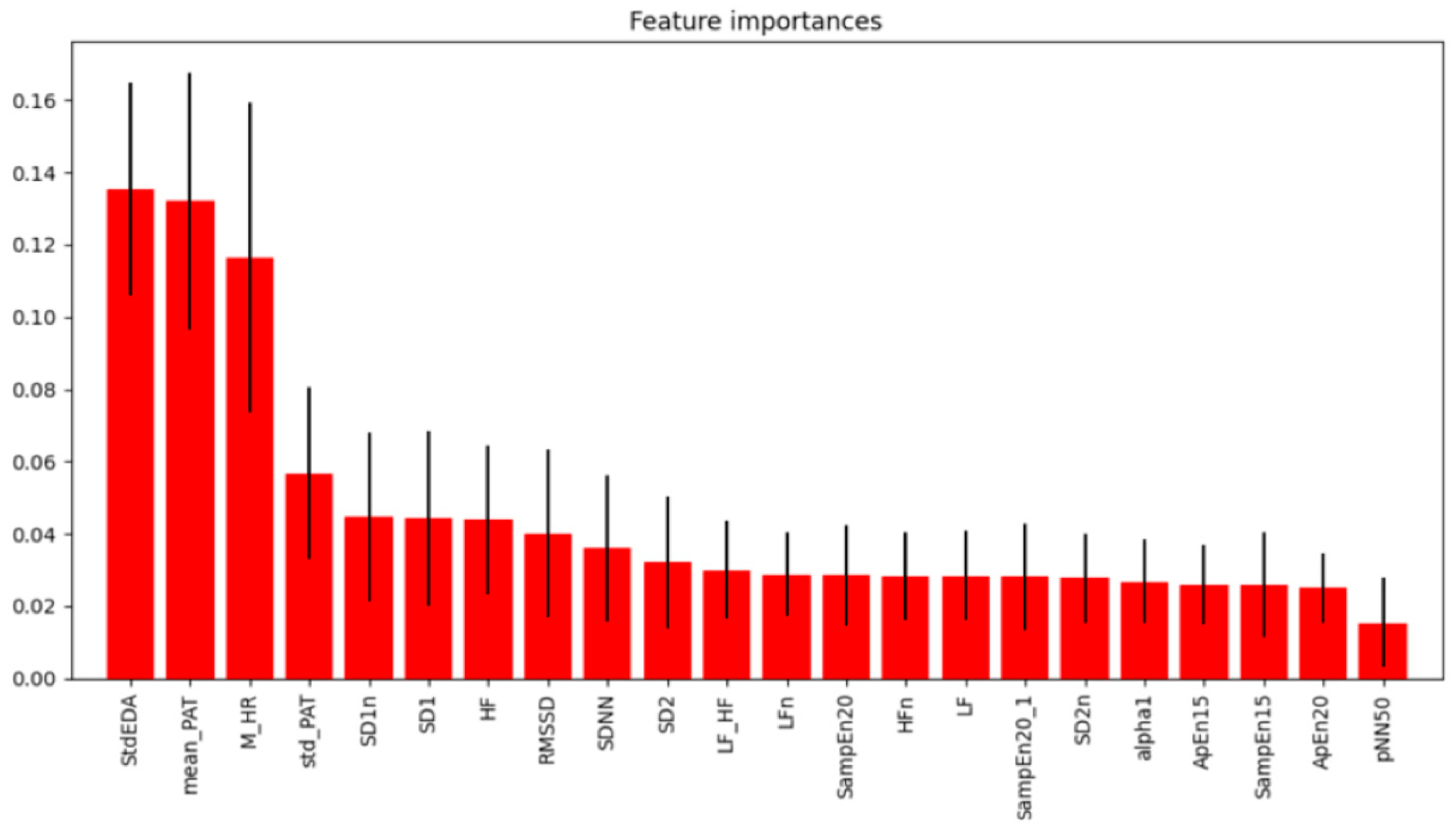
3.1. Analysis of HRV Characteristics and Other Biosignal Change Rates
3.2. Machine Learning Classification Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.; Yang, S. Development of a Classification Model for Driver’s Drowsiness and Waking Status Using Heart Rate Variability and Respiratory Features. J. Ergon. Soc. Korea 2016, 35, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.G.; Kim, K.K.; Park, S. ECG Measurement on a Chair without Conductive Contact. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 956–959. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Singh, M.; Kumar, P.; Bijalwan, A. An optimized approach using transfer learning to detect drunk driving. Sci. Program. 2022, 2022, 8775607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapthami, I.; Raju, V.V.N.; Vaithianathan, V.; Chinnasamy, P.; Kumaran, G.; Ayyasamy, R.K. IoT-based alcohol detection and vehicle control system. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Conference on Data Intelligence and Cognitive Informatics (ICDICI), Tirunelveli, India, 18–20 November 2024; pp. 262–266. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.-A.; Chan, C.-W.; Wiratama, B.S.; Chen, P.-L.; Wang, M.-H.; Chao, C.-J.; Saleh, W.; Huang, H.-C.; Pai, C.-W. Evaluating the effect of drunk driving on fatal injuries among vulnerable road users in Taiwan: A population-based study. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, E.J.; Moskowitz, H. Effects of Alcohol and Other Drugs on Driver Performance. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2004, 5, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penning, R.; Veldstra, J.L.; Daamen, A.P.; Olivier, B.; Verster, J.C. Drugs of Abuse, Driving, and Traffic Safety. Curr. Drug Abus. Rev. 2010, 3, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaluddin, N.A.; Mohamad Shuhaimi, N.S.; Hashim, W.; Ishak, S.Z. Driving Distractions Perceptions among Young Drivers in an Urban Area of Shah Alam. Environ.-Behav. Proc. J. 2022, 7, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghpanahan, H.; Lewsey, J.; Mackay, D.F.; McIntosh, E.; Pell, J.; Jones, A.; Fitzgerald, N.; Robinson, M. An evaluation of the effects of lowering blood alcohol concentration limits for drivers on the rates of road traffic accidents and alcohol consumption: A natural experiment. Lancet 2019, 393, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, V.; Schumacher, A.; Sauber-Schatz, E. Alcohol-Impaired Driving among Adults—USA, 2014–2018. Inj. Prev. 2022, 28, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, K.; Lin, Z.; Gifford, M.; Svanström, L. Economics of Global Burden of Road Traffic Injuries and Their Relationship with Health System Variables. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Road Safety 2013: Supporting a Decade of Action; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Global Road Safety Partnership. Drinking and Driving: A Road Safety Manual for Decision-Makers and Practitioners; Global Road Safety Partnership: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Negussie, Y.; Geller, A.; Teutsch, S.M. (Eds.) Getting to Zero Alcohol-Impaired Driving Fatalities: A Comprehensive Approach to a Persistent Problem; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Exchange, A.G. Alabama Dui Attorney Blog. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 20, 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, B.; Schumacher, A.; Sauber-Schatz, E. Manipulation of Breath Alcohol Tests: Can Specific Techniques Alter Breath Alcohol Content? J. Emerg. Trauma Shock 2020, 13, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.G.; Chung, W.Y. Driver Alertness Monitoring Using Fusion of Facial Features and Bio-Signals. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 2416–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratama, B.G.; Ardiyanto, I.; Adji, T.B. A Review on Driver Drowsiness Based on Image, Bio-Signal, and Driver Behavior. In Proceedings of the 2017 3rd International Conference on Science and Technology-Computer (ICST), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 11–12 October 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.W.; Kim, S.J.; Cho, H.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, K.H.; Kwon, H.Y. Prediction of Alcohol Consumption Based on Biosignals and Assessment of Driving Ability According to Alcohol Consumption. J. Biomed. Eng. Res. 2022, 43, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, S.; Kwon, S.; Park, J.; Lee, S.; Jung, Y. Driver Drowsiness Detection via PPG Biosignals by Using Multimodal Head Support. In Proceedings of the 2017 4th International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT), Barcelona, Spain, 5–7 April 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Alguindigue, J.; Sarkar, S.; Rajesh, R.; Sharmin, S.; Roberts, J.; Subba, S. Biosignals Monitoring for Driver Drowsiness Detection Using Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, I.C.; Lee, W.S.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, K. Development of Bio-Signal Measurement System for Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Convergence Information Technology (ICCIT 2007), Gyeongju, Republic of Korea, 21–23 November 2007; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 2033–2037. [Google Scholar]
- Alabi, O.O.; Adeaga, O.A.; Ajagbe, S.A.; Adekunle, E.O.; Adigun, M.O. Design and Implementation of an Alcohol Detection Driver System. Int. J. Reconfigurable Embed. Syst. 2024, 13, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Nandal, R. A Review Paper on Drunk Driving Detection System Using IoT & ML Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2022 5th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Technologies (CCICT), Sonepat, India, 8–9 July 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M.; Wen, P.; Song, B.; Li, Y. Detection of Alcoholic EEG Signals Based on Whole Brain Connectivity and Convolutional Neural Networks. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 79, 104242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.F.; Yang, C.Y.; Wu, Y.F. SVM-Based Classification Method to Identify Alcohol Consumption Using ECG and PPG Monitoring. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2018, 22, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barter, F.; Tanner, A. Autonomic Neuropathy in an Alcoholic Population. Postgrad. Med. J. 1987, 63, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M. Driver Drowsiness Detection Using Non-Intrusive Electrocardiogram and Steering Wheel Angle Signals. Master’s Thesis, Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, C.; Zhang, J.; Su, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, W. Driver fatigue detection using heart rate variability features from 2-minute electrocardiogram signals while accounting for sex differences. Sensors 2024, 24, 4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.C.-H.; Wang, C.-Y.; Li, H.-H.; Chiu, C.-D. Drunk driving detection using two-stage deep neural network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 116564–116571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yao, W.; Lu, B.; Fu, R. ECG-based real-time drivers’ fatigue detection using a novel elastic dry electrode. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnecke, J.M.; Ganapathy, N.; Koch, E.; Dietzel, A.; Flormann, M.; Henze, R.; Deserno, T.M. Printed and flexible ECG electrodes attached to the steering wheel for continuous health monitoring during driving. Sensors 2022, 22, 4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, G.; Wang, H.; Su, K.; Wang, X.; Teng, S.; Liu, P.X. Non-interference driving fatigue detection system based on intelligent steering wheel. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Kim, S.H. ECG measurement system for vehicle implementation and heart disease classification using machine learning. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 17968–17982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škorić, T. Stress level detection based on the capacitive electrocardiogram signals of driving subjects. Sensors 2023, 23, 9158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.L.; van Roon, A.; Riese, H.; Thio, C.; Oostenbroek, E.; Westrik, I.; de Geus, E.J.; Gansevoort, R.; Lefrandt, J.; Nolte, I.M.; et al. Validity of (Ultra-) Short Recordings for Heart Rate Variability Measurements. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minea, M.; Dumitrescu, C.M.; Costea, I.M. Advanced e-Call Support Based on Non-Intrusive Driver Condition Monitoring for Connected and Autonomous Vehicles. Sensors 2021, 21, 8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidikova, M.; Martinek, R.; Kawala-Sterniuk, A.; Ladrova, M.; Jaros, R.; Danys, L.; Simonik, P. Vital Sign Monitoring in Car Seats Based on Electrocardiography, Ballistocardiography and Seismocardiography: A Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonhardt, S.; Leicht, L.; Teichmann, D. Unobtrusive Vital Sign Monitoring in Automotive Environments—A Review. Sensors 2018, 18, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, H.J.; Chung, G.S.; Kim, K.K.; Park, K.S. Nonintrusive Biological Signal Monitoring in a Car to Evaluate a Driver’s Stress and Health State. Telemed. J. e-Health 2009, 15, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babusiak, B.; Martinek, R.; Jaros, R.; Adamec, Z.; Ladrova, M.; Krejcar, O. Design of Smart Steering Wheel for Unobtrusive Health and Drowsiness Monitoring. Sensors 2021, 21, 5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amidei, A.; Cucchiara, R.; Borghi, G.; Costantini, G.; Vezzani, R. Unobtrusive Multimodal Monitoring of Physiological Signals for Driver State Analysis. IEEE Sens. J. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Gong, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, J. Smart Steering Sleeve (S3): A Non-Intrusive and Integrative Sensing Platform for Driver Physiological Monitoring. Sensors 2022, 22, 7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Heo, J.; Lee, W.K.; Lim, Y.G.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, K.S. Flexible Capacitive Electrodes for Minimizing Motion Artifacts in Ambulatory Electrocardiograms. Sensors 2014, 14, 14732–14743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.K.; Lim, Y.K.; Park, K.S. Common Mode Noise Cancellation for Electrically Non-Contact ECG Measurement System on a Chair. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conference, Shanghai, China, 1–4 September 2005; pp. 5881–5883. [Google Scholar]
- Romanowicz, M.; Schmidt, J.E.; Bostwick, J.M.; Mrazek, D.A.; Karpyak, V.M. Changes in heart rate variability associated with acute alcohol consumption: Current knowledge and implications for practice and research. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 1092–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepoli, M.F.; Capucci, A.; Mazzola, P. The Role of Autonomic Nervous System in Cardiac Arrhythmias. Eur. Heart J. 2001, 22, 225–237. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.K.; Tsang, K.F.; Chi, H.R.; Hung, F.H. A Precise Drunk Driving Detection Using Weighted Kernel Based on Electrocardiogram. Sensors 2016, 16, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Features | Summary |
|---|---|
| M_HR | 5 min average heart rate |
| SDNN | Standard deviation of heart rate variability |
| RMSSD | Root mean square of successive RR interval differences |
| pNN50 | Proportion of RR intervals that differ by more than 50 ms |
| LF | Power in the low-frequency band |
| LFn | Relative power in the low-frequency band |
| HF | Power in the high-frequency band |
| HFn | Relative power in the high-frequency band |
| LF_HF | Ratio of low-frequency to high-frequency power |
| SD1 | Measure of short-term heart rate variability |
| SD2 | Measure of long-term heart rate variability |
| SD1n | SD1 normalized by total variability |
| SD2n | SD2 normalized by total variability |
| alpha1 | Center frequency of the low-frequency band |
| ApEn15 | Measure of irregularity for 15-point embedding |
| ApEn20 | Measure of irregularity for 20-point embedding |
| SampEn15 | Sample entropy for 15-point data |
| SampEn20 | Sample entropy for 20-point data |
| SampEn20_1 | Sample entropy for 20-point data (version 1) |
| mean_PAT | Average pulse arrival time |
| Std_PAT | Standard deviation of pulse arrival time |
| std_EDA | Standard deviation of skin conductance |
| Feature | BrAC (0.00%) | BrAC (0.03%) | BrAC (0.08%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M_HR | 80.30 ± 6.31 | 90.74 ± 9.11 | 88.46±8.50 |
| SDNN | 39.29 ± 17.35 | 35.38 ± 35.96 | 32.50 ± 26.61 |
| RMSSD | 30.21 ± 18.34 | 34.37 ± 55.12 | 27.24 ± 39.06 |
| pNN50 | 5.10 ± 6.53 | 2.066 ± 4.06 | 2.47 ± 5.55 |
| LF | 0.001 ± 0.004 | 0.001 ± 0.003 | 0.001 ± 0.002 |
| LFn | 63.8 ± 21.89 | 62.94 ± 20.42 | 66.14 ± 22.11 |
| HF | 0.001 ± 0.008 | 0.001 ± 0.005 | 0.001 ± 0.003 |
| HFn | 36.10 ± 21.89 | 37.06 ± 20.42 | 33.86 ± 22.11 |
| LF_HF | 3.87 ± 5.84 | 4.075 ± 7.79 | 4.51 ± 6.58 |
| SD1 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.025 ± 0.04 | 0.02 ± 0.03 |
| SD2 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.042 ± 0.03 | 0.040 ± 0.03 |
| SD1n | 28.08 ± 15.04 | 36.93 ± 61.71 | 28.17 ± 43.37 |
| SD2n | 66.31 ± 25.86 | 62.16 ± 51.92 | 58.31 ± 39.22 |
| alpha1 | 1.09 ± 0.32 | 1.10 ± 0.39 | 1.15 ± 0.40 |
| ApEn15 | 0.20 ± 0.11 | 0.280 ± 0.15 | 0.27 ± 0.16 |
| ApEn20 | 0.32 ± 0.12 | 0.39 ± 0.14 | 0.38 ± 0.16 |
| SampEn15 | 2.20 ± 0.52 | 1.90 ± 0.71 | 1.99 ± 0.65 |
| SampEn20 | 1.88 ± 0.40 | 1.64 ± 0.61 | 1.71 ± 0.57 |
| SampEn20_1 | 1.88 ± 0.40 | 1.64 ± 0.61 | 1.71 ± 0.57 |
| mean_PAT | 0.43 ± 0.17 | 0.80 ± 0.80 | 0.60 ± 0.52 |
| Std_PAT | 0.03 ± 0.09 | 0.28 ± 0.50 | 0.16 ± 0.33 |
| std_EDA | 0.13 ± 0.18 | 0.13 ± 0.12 | 0.07 ± 0.10 |
| Machine Learning Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | 0.51 | 0.57 | 0.53 | 0.5 |
| RF | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.85 |
| K-NN | 0.64 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.57 |
| XGBoost | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 |
| SGD | 0.54 | 0.61 | 0.58 | 0.53 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.54 | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.56 |
| Gradient Boosting | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 |
| MLP | 0.58 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.64 |
| LDA | 0.53 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 |
| Bagging | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 |
| Voting | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.72 | 0.72 |
| DNN | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.71 |
| Machine Learning Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | 0.49 | 0.55 | 0.51 | 0.47 |
| RF | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 |
| K-NN | 0.71 | 0.76 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| XGBoost | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.88 |
| SGD | 0.5 | 0.49 | 0.55 | 0.47 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.52 | 0.51 |
| Gradient Boosting | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 |
| MLP | 0.56 | 0.66 | 0.65 | 0.65 |
| LDA | 0.54 | 0.56 | 0.53 | 0.52 |
| Bagging | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 |
| Voting | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.79 |
| DNN | 0.78 | 0.77 | 0.78 | 0.77 |
| Machine Learning Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | 0.48 | 0.60 | 0.52 | 0.48 |
| RF | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.81 |
| K-NN | 0.66 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.68 |
| XGBoost | 0.81 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.79 |
| SGD | 0.50 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.50 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.53 | 0.52 |
| Gradient Boosting | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| MLP | 0.53 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.56 |
| LDA | 0.52 | 0.54 | 0.53 | 0.51 |
| Bagging | 0.81 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 |
| Voting | 0.76 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.77 |
| DNN | 0.61 | 0.63 | 0.61 | 0.6 |
| Study | Classification Models | Inputs | Number of Classifications | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [18] | SVM | ECG, PPG, Car data | 2 (Normal, Drunk) | 95% |
| [48] | Weighted Kernel SVM | ECG | 2 (Normal, Drunk) | 87.52% |
| Proposed work | 12 machine learning methods | CCECG, PPG, EDA | 3 (Normal, Light, and Heavy Drunk) | 88% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.H.; Son, H.W.; Lee, T.M.; Baek, H.J. Drunk Driver Detection Using Multiple Non-Invasive Biosignals. Sensors 2025, 25, 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25051281
Kim SH, Son HW, Lee TM, Baek HJ. Drunk Driver Detection Using Multiple Non-Invasive Biosignals. Sensors. 2025; 25(5):1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25051281
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sang Hyuk, Hyo Won Son, Tae Mu Lee, and Hyun Jae Baek. 2025. "Drunk Driver Detection Using Multiple Non-Invasive Biosignals" Sensors 25, no. 5: 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25051281
APA StyleKim, S. H., Son, H. W., Lee, T. M., & Baek, H. J. (2025). Drunk Driver Detection Using Multiple Non-Invasive Biosignals. Sensors, 25(5), 1281. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25051281





