Classification of Grades of Subchondral Sclerosis from Knee Radiographic Images Using Artificial Intelligence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Labeling
2.2. Training Environment and Data Preprocessing
2.3. Subchondral Sclerosis Classification Models and Statistical Analysis
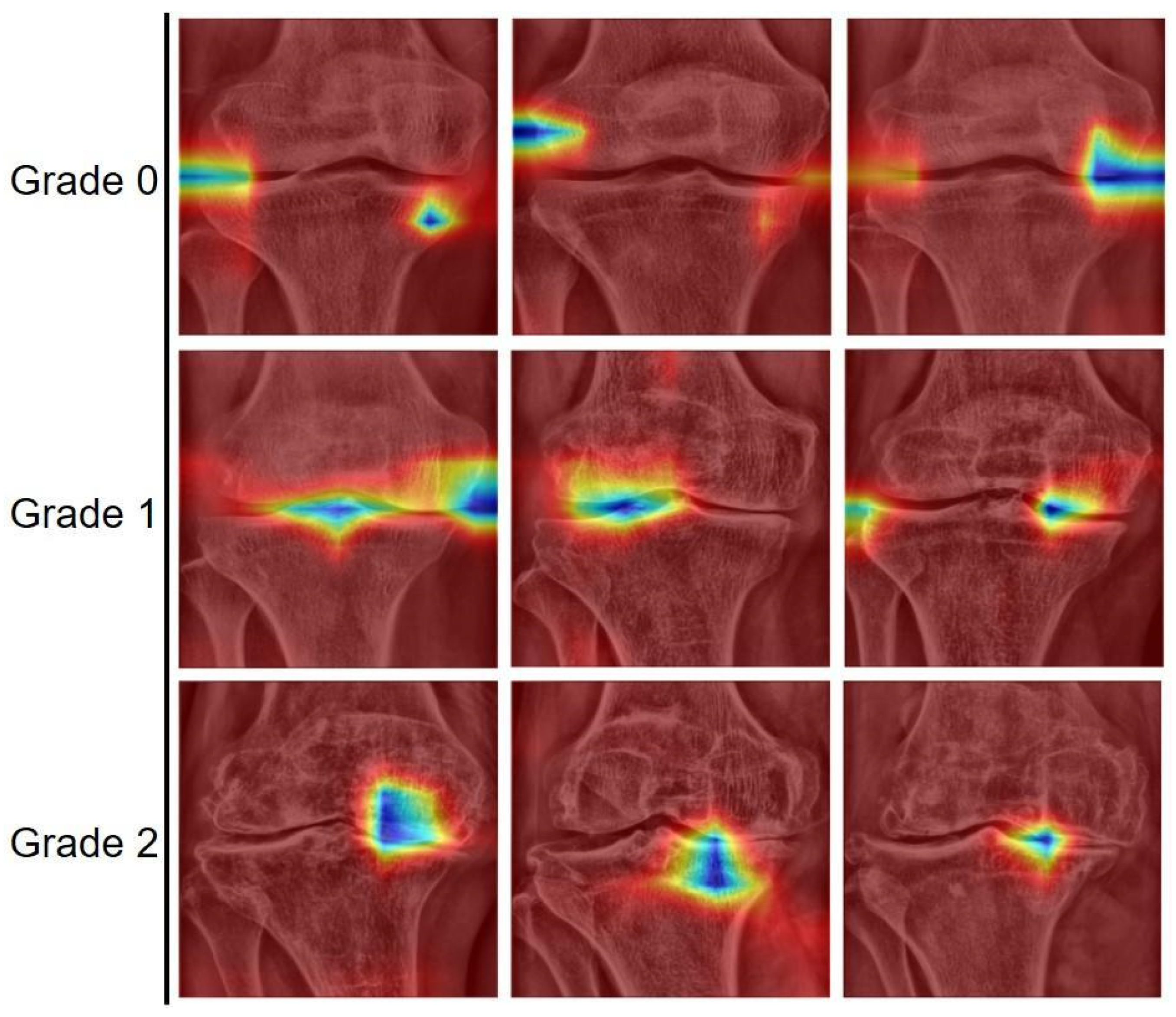
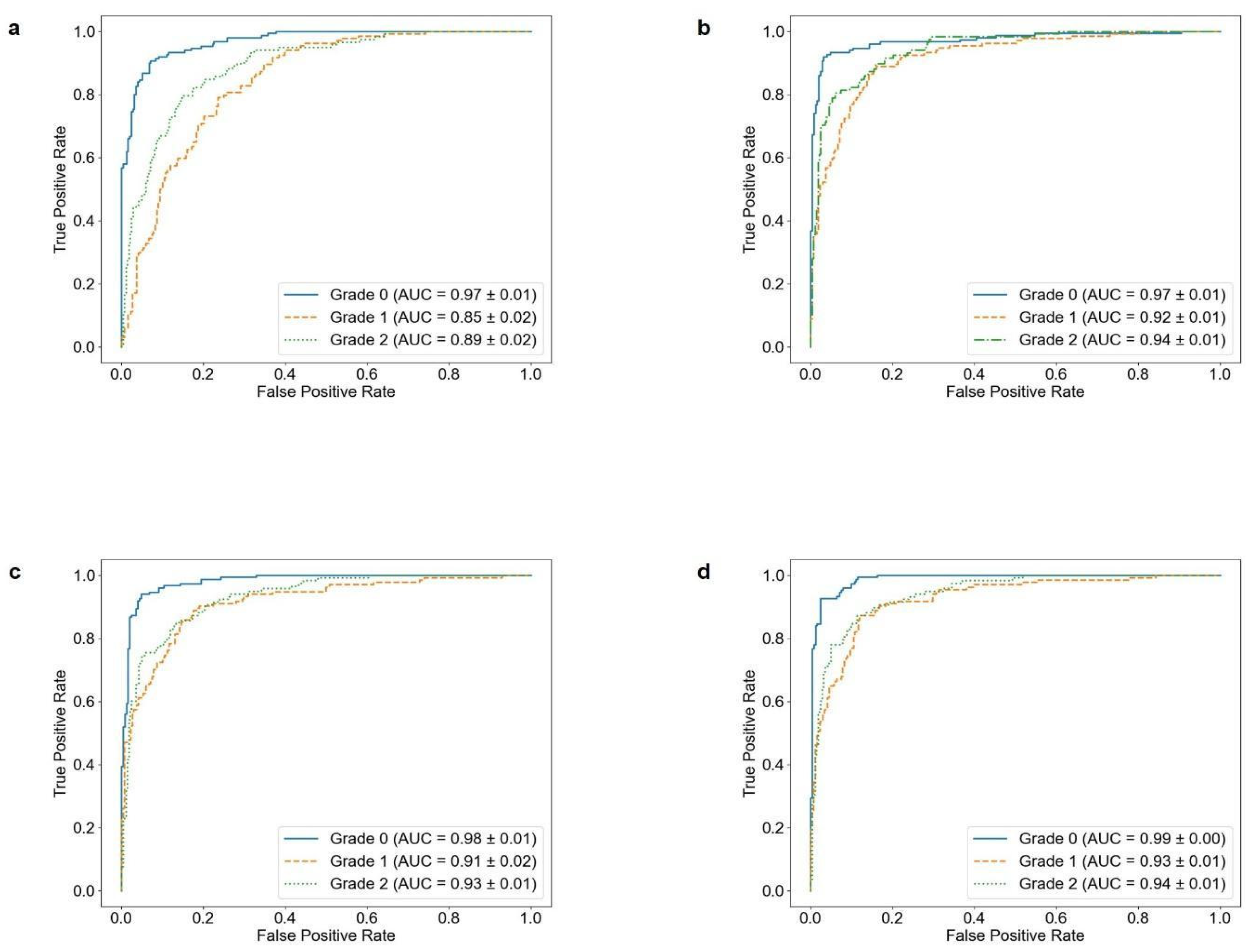
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Naghavi, M.; Lozano, R.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; Aboyans, V.; et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2163–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safiri, S.; Kolahi, A.-A.; Smith, E.; Hill, C.; Bettampadi, D.; Mansournia, M.A.; Hoy, D.; Ashrafi-Asgarabad, A.; Sepidarkish, M.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; et al. Global, regional and national burden of osteoarthritis 1990–2017: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, A.; Li, H.; Wang, D.; Zhong, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H. Global, regional prevalence, incidence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis in population-based studies. eClinicalMedicine 2020, 29–30, 100587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felson, D.T.; Naimark, A.; Anderson, J.; Kazis, L.; Castelli, W.; Meenan, R.F. The prevalence of knee osteoarthritis in the elderly. The Framingham Osteoarthritis Study. Arthritis Rheum. Off. J. Am. Coll. Rheumatol. 1987, 30, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagge, E.; Bjelle, A.; Valkenburg, H.A.; Svanborg, A. Prevalence of radiographic osteoarthritis in two elderly European populations. Rheumatol. Int. 1992, 12, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiese, K. Picking a bone with WISP1 (CCN4): New strategies against degenerative joint disease. J. Transl. Sci. 2016, 2, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, C.P.; Singh, P.; Chaturvedi, S.; Pruthi, K.K.; Vij, A. Epidemiology of knee osteoarthritis in India and related factors. Indian J. Orthop. 2016, 50, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, S.; Akbarian, E.; Lind, A.; Razavian, A.S.; Gordon, M. Automating classification of osteoarthritis according to Kellgren-Lawrence in the knee using deep learning in an unfiltered adult population. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsiadlo, P.; Wolski, M.; Stachowiak, G.W. Automated selection of trabecular bone regions in knee radiographs. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 1870–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Gao, L.; Shi, X.; Allen, K.; Yang, L. Fully automatic knee osteoarthritis severity grading using deep neural networks with a novel ordinal loss. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2019, 75, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, R.; Deng, Y.; Chen, K.; Jiang, T. A preliminary examination of the diagnostic value of deep learning in hip osteoarthritis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.C.; Kim, S.W.; Chae, D.S.; Yoo, S.K. Analysis of Feature Importance for Knee Osteoarthritis Severity Classification Using Machine Learning. J. Inst. Electron. Inf. Eng. 2020, 57, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiecicki, A.; Li, N.; O’Donnell, J.; Said, N.; Yang, J.; Mather, R.C.; Jiranek, W.A.; Mazurowski, M.A. Deep learning-based algorithm for assessment of knee osteoarthritis severity in radiographs matches performance of radiologists. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 133, 104334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylichenko, A.; Demyanenko, Y. Automatic grading of knee osteoarthritis from plain radiographs using densely connected convolutional networks. In Recent Trends in Analysis of Images, Social Networks and Texts, Proceedings of the 9th International Conference, AIST 2020, Skolkovo, Moscow, Russia, 15–16 October 2020; Revised Supplementary Proceedings 9; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiulpin, A.; Thevenot, J.; Rahtu, E.; Lehenkari, P.; Saarakkala, S. Automatic Knee Osteoarthritis Diagnosis from Plain Radiographs: A Deep Learning-Based Approach. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patron, A.; Annala, L.; Lainiala, O.; Paloneva, J.; Äyrämö, S. Method for Automatic Assessment of Spiking of Tibial Tubercles Associated with Knee Osteoarthritis. SSRN 2025, ssrn:4155105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Schacky, C.E.; Sohn, J.H.; Liu, F.; Ozhinsky, E.; Jungmann, P.M.; Nardo, L.; Posadzy, M.; Foreman, S.C.; Nevitt, M.C.; Link, T.M.; et al. Development and Validation of a Multitask Deep Learning Model for Severity Grading of Hip Osteoarthritis Features on Radiographs. Radiology 2020, 295, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.S.; Rajasekaran, M.P. Automatic detection and classification of knee osteoarthritis using deep learning approach. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.S.; Yon, C.-J.; Lee, D.; Lee, J.J.; Kang, C.H.; Kang, S.-B.; Lee, N.-K.; Chang, C.B. Assessment of a novel deep learning-based software developed for automatic feature extraction and grading of radiographic knee osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornale, S.S.; Patravali, P.U.; Hiremath, P.S. Early Detection of Osteoarthritis based on Cartilage Thickness in Knee X-ray Images. Int. J. Image Graph. Signal Process. 2019, 11, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subha, B.; Jeyakumar, V.; Deepa, S.N. Gaussian Aquila optimizer based dual convolutional neural networks for identification and grading of osteoarthritis using knee joint images. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.S.; Hasanaath, A.A.; Latif, G.; Bashar, A. Knee Osteoarthritis Detection and Severity Classification Using Residual Neural Networks on Preprocessed X-ray Images. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahum, R.; Irtaza, A.; El-Meligy, M.A.; Sharaf, M.; Tlili, I.; Butt, S.; Mahmood, A.; Awais, M.; El-Sherbeeny, A.M. A Robust Framework for Severity Detection of Knee Osteoarthritis Using an Efficient Deep Learning Model. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2023, 37, 2352010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhang, R. A novel computer-assisted diagnosis method of knee osteoarthritis based on multivariate information and deep learning model. Digit. Signal Process. 2022, 133, 103863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boniatis, I.; Costaridou, L.; Cavouras, D.; Kalatzis, I.; Panagiotopoulos, E.; Panayiotakis, G. Osteoarthritis severity of the hip by computer-aided grading of radiographic images. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2006, 44, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, M.; Lu, S.; Chung, J.H.; Hassan, S.; Elsissy, J.; Schneiderman, B.A. Diagnosing the Severity of Knee Osteoarthritis Using Regression Scores from Artificial Intelligence Convolution Neural Networks. Orthopedics 2024, 47, E247–E254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, D.J.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet 2019, 393, 1745–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, C.; Cushnaghan, J.; Kirwan, J.; Dieppe, P.; Rogers, J.; McAlindon, T.; McCrae, F. Radiographic assessment of the knee joint in osteoarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1992, 51, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Qi, W.; Shuang, L. Medical X-ray image enhancement based on wavelet domain homomorphic filtering and CLAHE. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Robots & Intelligent System (ICRIS), Zhangjiajie, China, 27–28 August 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.; Singh, A.K.; Ghrera, S.; Elhoseny, M. An approach for de-noising and contrast enhancement of retinal fundus image using CLAHE. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 110, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniyappan, S.; Allirani, A.; Saraswathi, S. A novel approach for image enhancement by using contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization method. In Proceedings of the 2013 Fourth International Conference on Computing, Communications and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Tiruchengode, India, 4–6 July 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.; Maheshwari, S.; Agarwal, A. Contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization based enhancement for real time video system. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), Delhi, India, 24–27 September 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 2392–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Zhou, C.; Ruan, Y.; Li, Y. MobileNetV2 model for image classification. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd International Conference on Information Technology and Computer Application (ITCA), Guangzhou, China, 18–20 December 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revathi, S.A.; Babu, B.S. Enhanced image classification with integrating DenseNet121 with Mixup augmentation and attention mechanisms for knee OA. In Proceedings of the 2024 Second International Conference on Advanced Computing & Communication Technologies (ICACCTech), Sonipat, India, 16–17 November 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, N.; Anower, M.S.; Hassan, R. Automated diagnosis of pneumonia from classification of chest x-ray images using EfficientNet. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for Sustainable Development (ICICT4SD), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 27–28 February 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Wei, X.C.; Zhou, J.M.; Wei, L. The Age-Related Changes in Cartilage and Osteoarthritis. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 916530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Bang, C.H.; Song, G.G.; Kim, C.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, S.J. Knee osteoarthritis and menopausal hormone therapy in postmenopausal women: A nationwide cross-sectional study. Menopause 2019, 26, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Subchondral Sclerosis Grade | Train | Validation | Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample, n | Ratio, % | Sample, n | Ratio, % | Sample, n | Ratio, % | |
| Grade 0 | 1178 | 36.64 | 142 | 35.32 | 150 | 37.31 |
| Grade 1 | 1011 | 31.45 | 137 | 34.08 | 134 | 33.33 |
| Grade 2 | 1026 | 31.91 | 123 | 30.60 | 118 | 29.36 |
| Total | 3215 | 100 | 402 | 100 | 402 | 100 |
| Grade 0 | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Total (Men, Women) | Proportion (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20s | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 (0, 4) | 1.00 |
| 30s | 8 | 0 | 0 | 8 (4, 4) | 2.01 |
| 40s | 15 | 1 | 0 | 16 (2, 14) | 4.02 |
| 50s | 42 | 11 | 7 | 60 (17, 43) | 15.10 |
| 60s | 43 | 42 | 44 | 129 (21, 108) | 32.39 |
| 70s | 31 | 68 | 54 | 153 (19, 134) | 38.53 |
| 80s | 6 | 11 | 11 | 28 (3, 25) | 7.04 |
| 90s | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 (1, 3) | 1.00 |
| Total | 150 | 134 | 118 | 402 | 100 |
| Model | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Accuracy (%) | AUC * | p-Value ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-Layer CNN | 73.38 ± 1.38 | 87.12 ± 0.70 | 73.81 ± 1.54 | 89.52 ± 0.46 | <0.05 |
| DenseNet121 | 82.98 ± 1.55 | 91.75 ± 0.78 | 83.31 ± 1.62 | 94.68 ± 0.84 | |
| MobileNetV2 | 83.41 ± 1.20 | 91.98 ± 0.61 | 83.78 ± 1.22 | 94.45 ± 0.71 | |
| EfficientNetB0 | 84.27 ± 1.03 | 92.46 ± 0.49 | 84.70 ± 0.98 | 95.17 ± 0.41 |
| 3-Layer CNN | DenseNet121 | MobileNetV2 | EfficientNetB0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-Layer CNN | 1.00 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| DenseNet121 | <0.001 | 1.00 | 0.8741 | 0.1523 |
| MobileNetV2 | <0.001 | 0.8741 | 1.00 | 0.4892 |
| EfficientNetB0 | <0.001 | 0.1523 | 0.4892 | 1.00 |
| Category | Grade 0 | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Accuracy (%) | p-Value * | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detected | Total | Detected | Total | Detected | Total | ||||
| Age Group | Group A (20s–50s) | 63 | 69 | 10 | 12 | 4 | 7 | 0.77 ± 0.09 | <0.05 |
| Group B (60s–90s) | 77 | 81 | 90 | 122 | 92 | 111 | 0.84 ± 0.04 | ||
| Sex | Group C (Men) | 37 | 38 | 8 | 12 | 12 | 17 | 0.78 ± 0.10 | <0.05 |
| Group D (Women) | 103 | 112 | 92 | 122 | 84 | 101 | 0.84 ± 0.04 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-B.; Kim, Y.J.; Jung, J.-Y.; Kim, K.G. Classification of Grades of Subchondral Sclerosis from Knee Radiographic Images Using Artificial Intelligence. Sensors 2025, 25, 2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082535
Kim S-B, Kim YJ, Jung J-Y, Kim KG. Classification of Grades of Subchondral Sclerosis from Knee Radiographic Images Using Artificial Intelligence. Sensors. 2025; 25(8):2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082535
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Soo-Been, Young Jae Kim, Joon-Yong Jung, and Kwang Gi Kim. 2025. "Classification of Grades of Subchondral Sclerosis from Knee Radiographic Images Using Artificial Intelligence" Sensors 25, no. 8: 2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082535
APA StyleKim, S.-B., Kim, Y. J., Jung, J.-Y., & Kim, K. G. (2025). Classification of Grades of Subchondral Sclerosis from Knee Radiographic Images Using Artificial Intelligence. Sensors, 25(8), 2535. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082535






