Measuring Iron Oxide Composites with a Custom-Made Scanning Magnetic Microscope
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
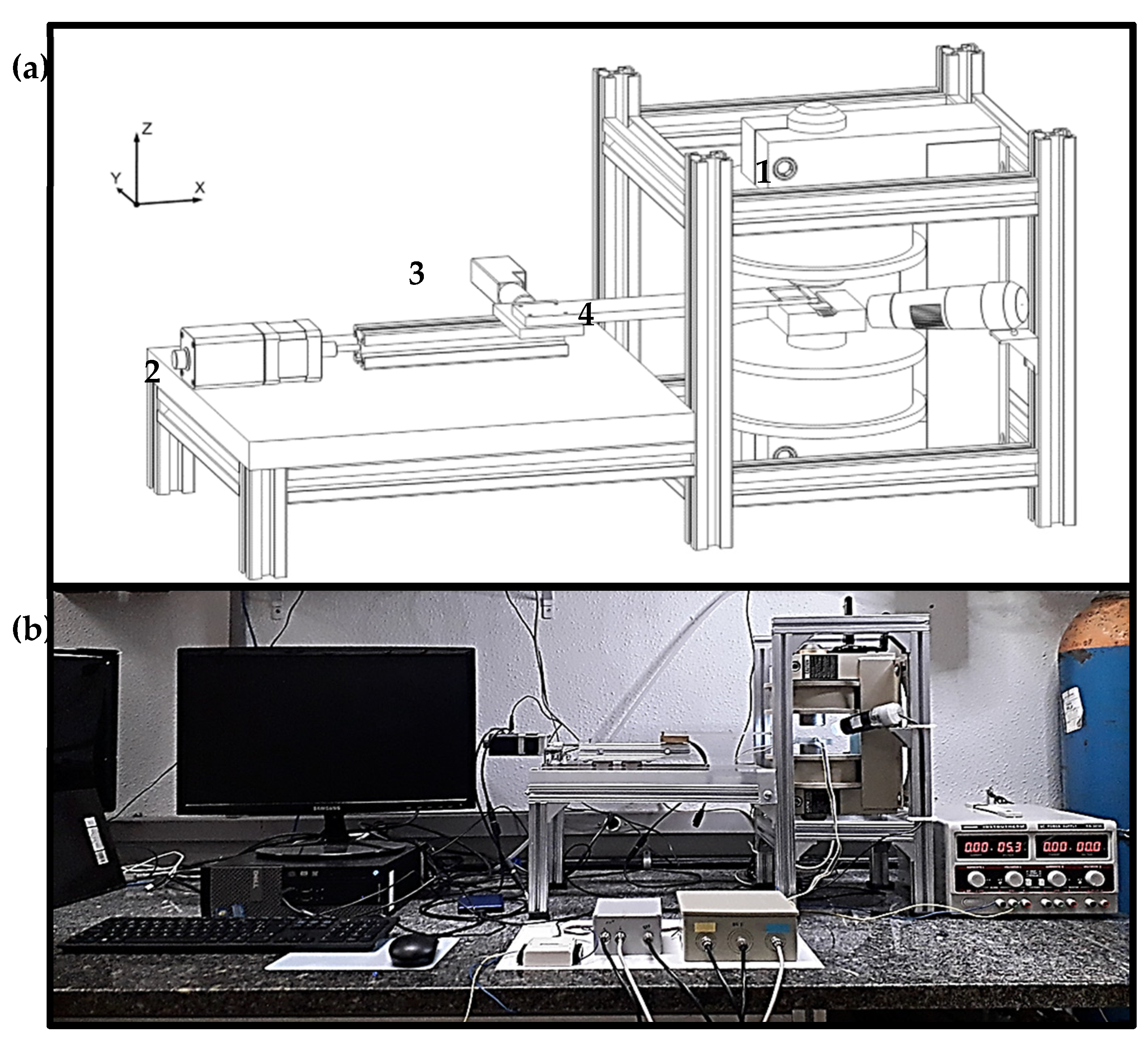
2.1. Structure of the Microscope
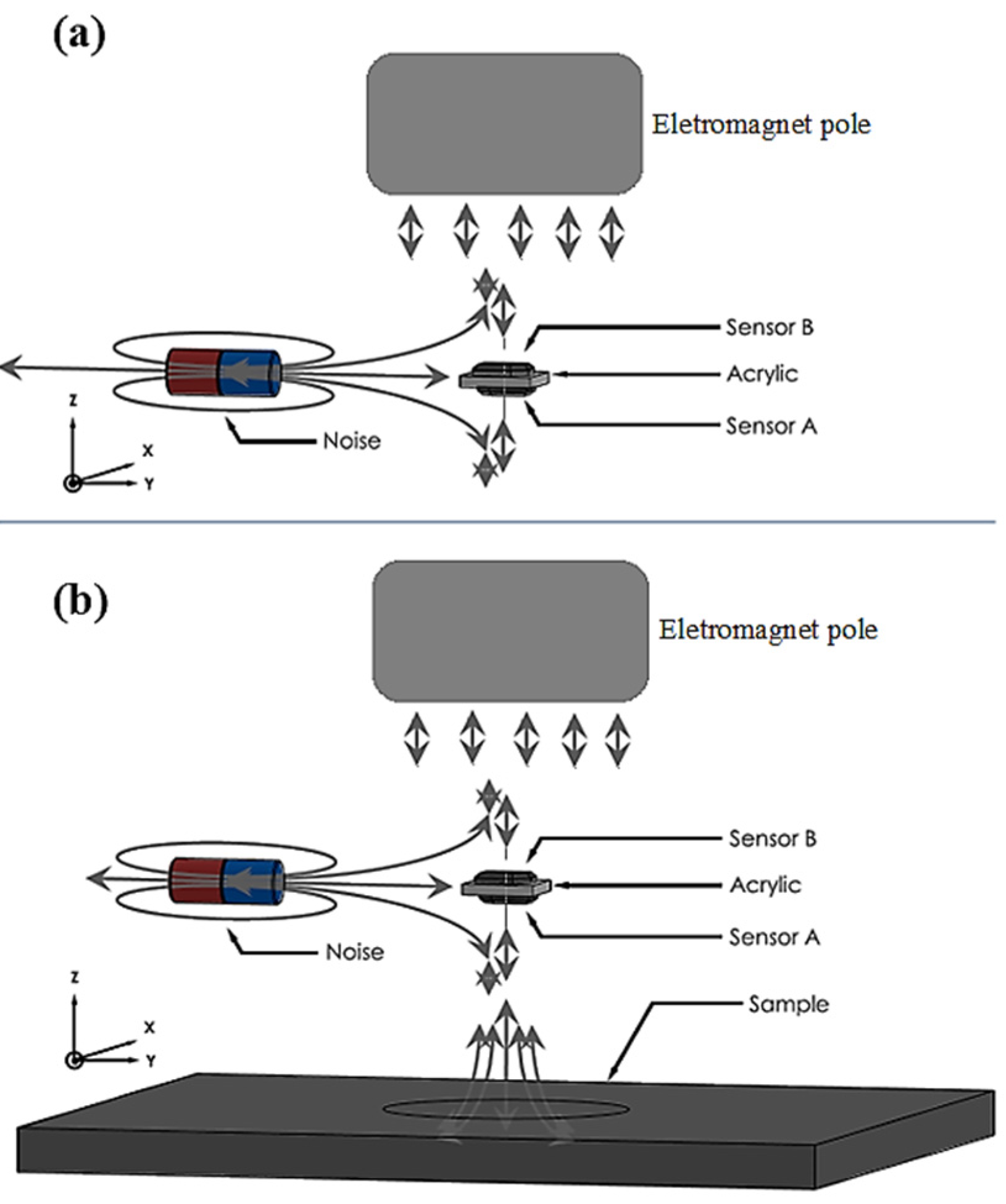
2.2. Readout Electronic System
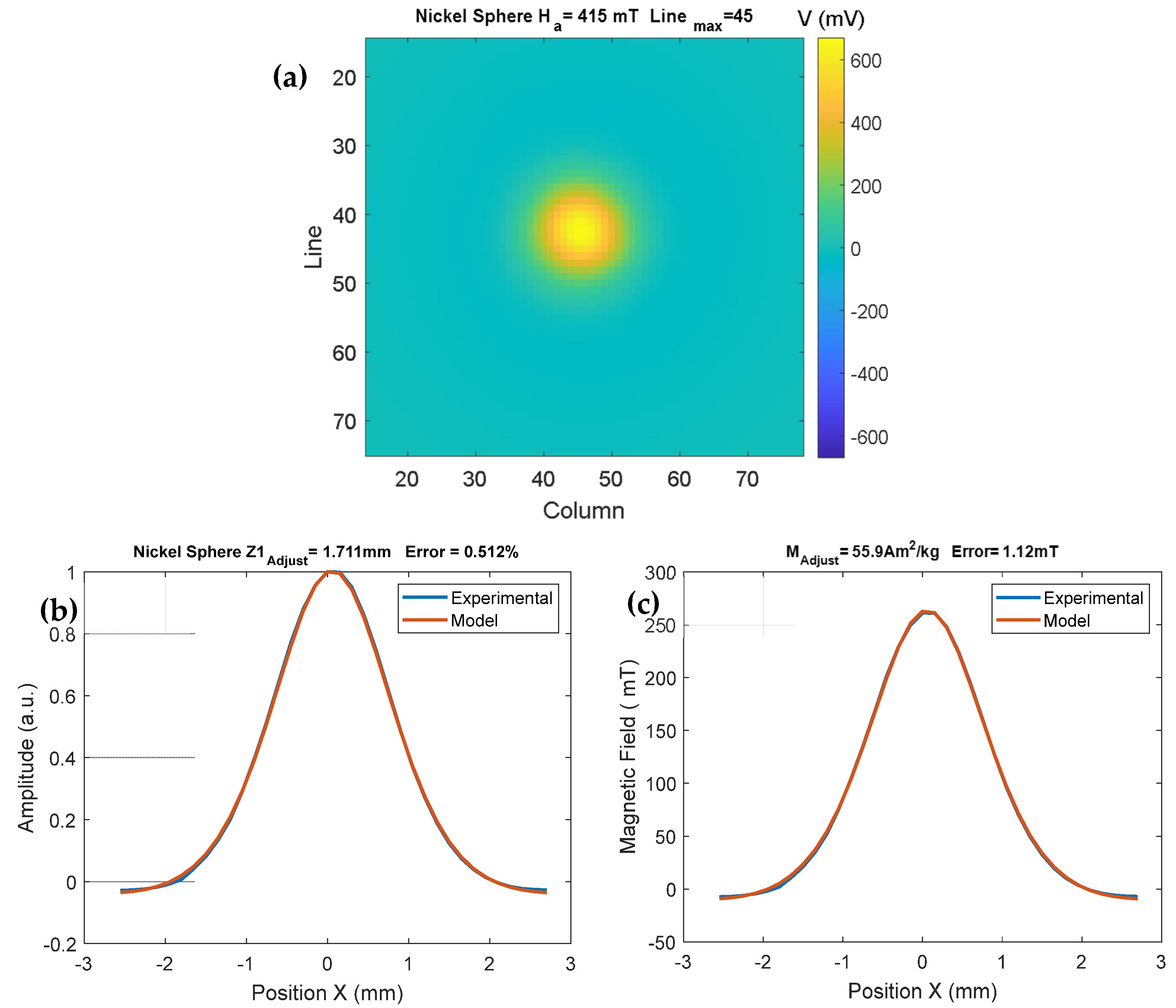
2.3. Calibration
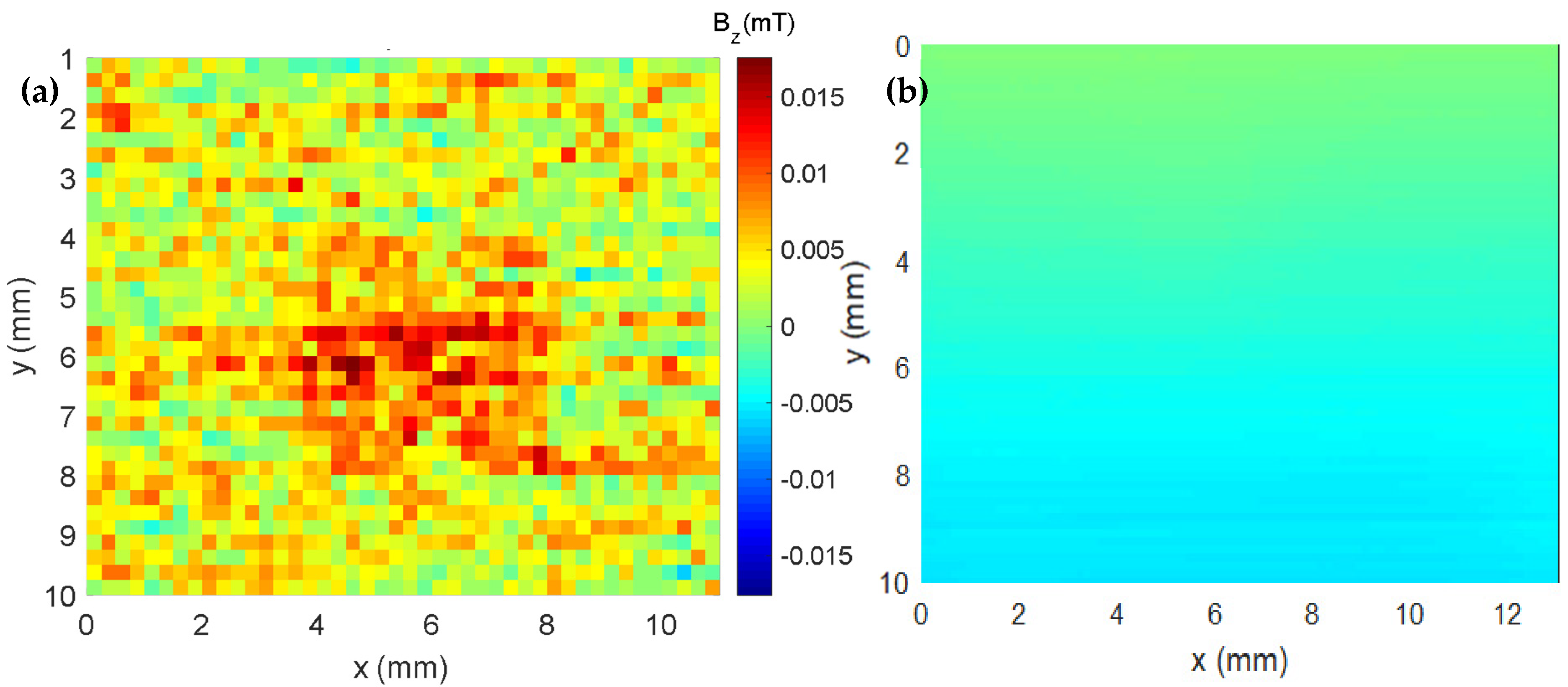
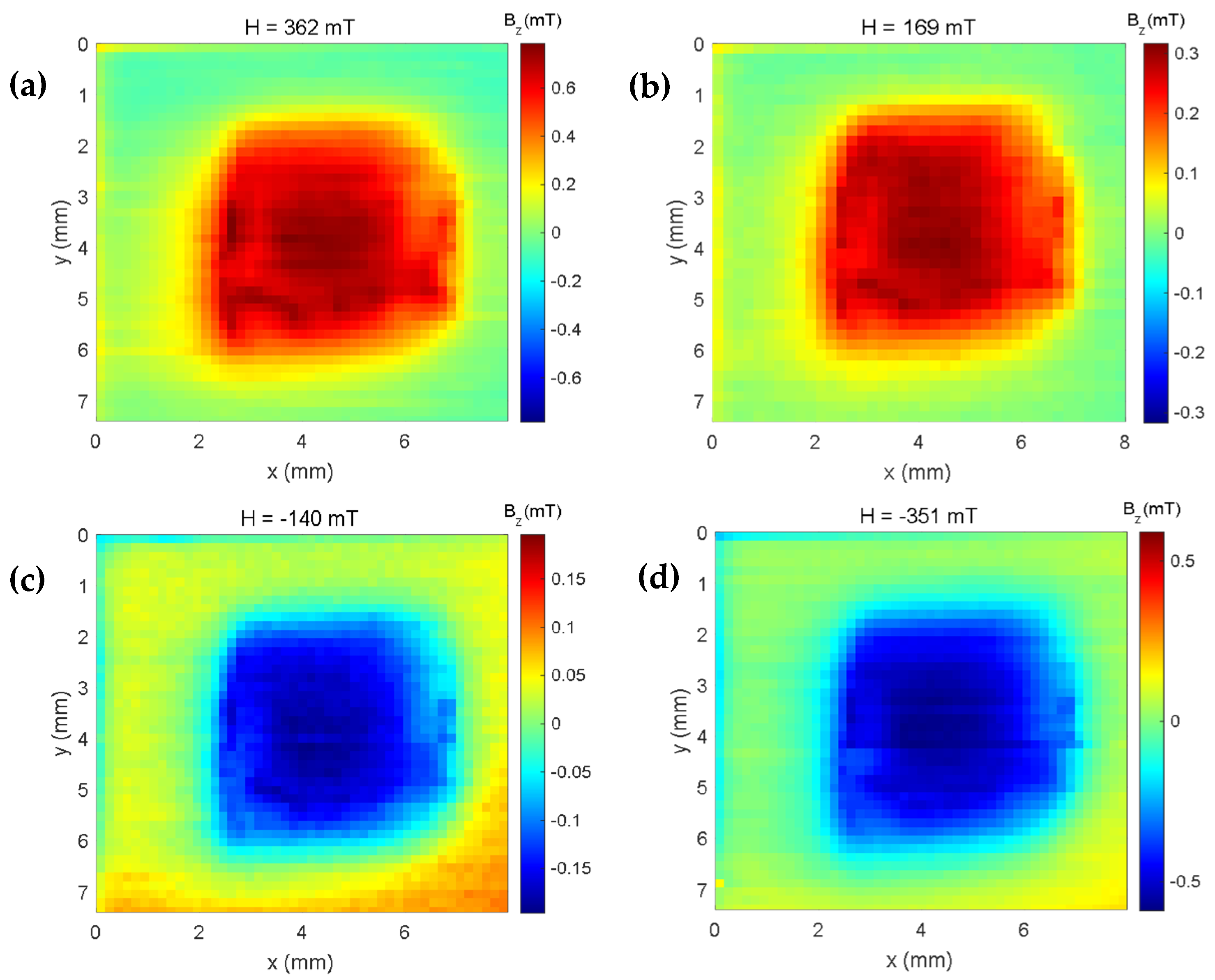
3. Synthesis of Iron Oxide Composites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zverev, V.I.; Pyatakov, A.P.; Shtil, A.A.; Tishin, A.M. Novel applications of magnetic materials and technologies for medicine. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 459, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safronov, A.P.; Beketov, I.V.; Tyukova, I.S.; Medvedev, A.I.; Samatov, O.M.; Murzakaev, A.M. Magneticnanoparticles for biophysical applications synthesized by high-power physical dispersion. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 383, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudoshnikov, S.; Tarasov, V.; Liubimov, B.; Odintsov, V.; Venediktov, S.; Nozdrin, A. Scanning magnetic microscope based on magnetoimpedance sensor for measuring of local magnetic fields. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 510, 166938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, J.F.; Reis, A.L.; Yokoyama, E.; Medina, C.D.; Osorio, G.F.; Luz-Lima, C.; De Falco, A.; Lima, C.D.; Silva, J.F.; Sinimbu, L.I.; et al. Construction of a Hall effect scanning magnetic microscope using permanent magnets for characterization of rock samples. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 569, 170304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, J.F.D.F.; Reis, A.L.A.; Oliveira, V.C., Jr.; Santos, A.F.; Luz-Lima, C.; Yokoyama, E.; Mendoza, L.A.F.; Pereira, J.M.B.; Bruno, A.C. Characterizing Complex Mineral Structures in Thin Sections of Geological Samples with a Scanning Hall Effect Microscope. Sensors 2019, 19, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foner, S. Versatile and sensitive vibrating-sample magnetometer. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1959, 30, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, L.; Luo, G.; Yu, M.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Yang, P.; Lin, Q.; Jiang, Z. The Micro-Fabrication and Performance Analysis of Non-Magnetic Heating Chip for Miniaturized Serf Atomic Magnetometer. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 557, 169495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarskiy, D.A.; Mironov, V.L.; Skorokhodo, E.V.; Fraerman, A.A. Impact of magnetic resonance force microscope probe on gyrotropic mode of magnetic vortex oscillations. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 552, 169152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, H.; Kohashi, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Kuwahara, M. Improvement of type-I method for observing magnetic contrast using scanning electron microscope under tilting-deceleration condition. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 546, 168733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Auerbach, N.; Roy, I.; Bocarsly, M.; Huber, M.E.; Barick, B.; Pariari, A.; Hücker, M.; Lim, Z.S.; Ariando, A.; et al. Scanning SQUID-on-tip microscope in a top-loading cryogen-free dilution refrigerator. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2023, 94, 053706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Dominguez, V.; Quesada, A.; Guzmán-Mínguez, J.C.; Moreno, L.; Lere, M.; Spottorno, J.; Giacomone, F.; Fernández, J.F.; Hernando, A.; García, M.A. A simple vibrating sample magnetometer for macroscopic samples. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 034707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Pérez, M.J.; Gella, D.; Müller, B.; Morosh, V.; Wölbing, R.; Sesé, J.; Kieler, O.; Kleiner, R.; Koelle, D. Three-axis vector nano superconducting quantum interference device. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8308–8315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, J.M.; Lusche, R.; Ventura, J.; Fermento, R.; Carpinteiro, F.; Araujo, J.P.; Sousa, J.B.; Cardoso, S.; Freitas, P.P. Versatile, high sensitivity, and automatized angular dependent vectorial Kerr magnetometer for the analysis of nanostructured materials. Review of Scientific Instruments. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2011, 82, 043902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokeakh, A.I.; Artyomov, M.Y. Precision Hall effect magnetometer. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2023, 94, 034702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Saitoh, E.; Miyajima, H.; Masuda, H. Scanning Hall probe microscopy with high resolution of magnetic field image. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 282, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachser, R.; Hütner, J.; Schwalb, C.H.; Huth, M. Granular Hall sensors for scanning probe microscopy. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, J.M.; Sosa, V. Alternative method to calculate the magnetic field of permanent magnets with azimuthal symmetry. Rev. Mex. De Fis. E 2013, 59, 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- van Bladel, J. Electromagnetic Fields, 2nd ed.; Wiley-IEEE Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Ma, J.; Zeng, Z.; Li, J.; Feng, H.; Rui, X.; Zhang, H.; Huang, X. Remanent magnetization of steel plates after being magnetized by moving magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 578, 170818. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, E.B.; Cherniak, D.J.; Nichols, C.I.; Weiss, B.P. Pb diffusion in magnetite: Dating magnetite crystallization and the timing of remanent magnetization in banded iron formation. Chem. Geol. 2023, 640, 121748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

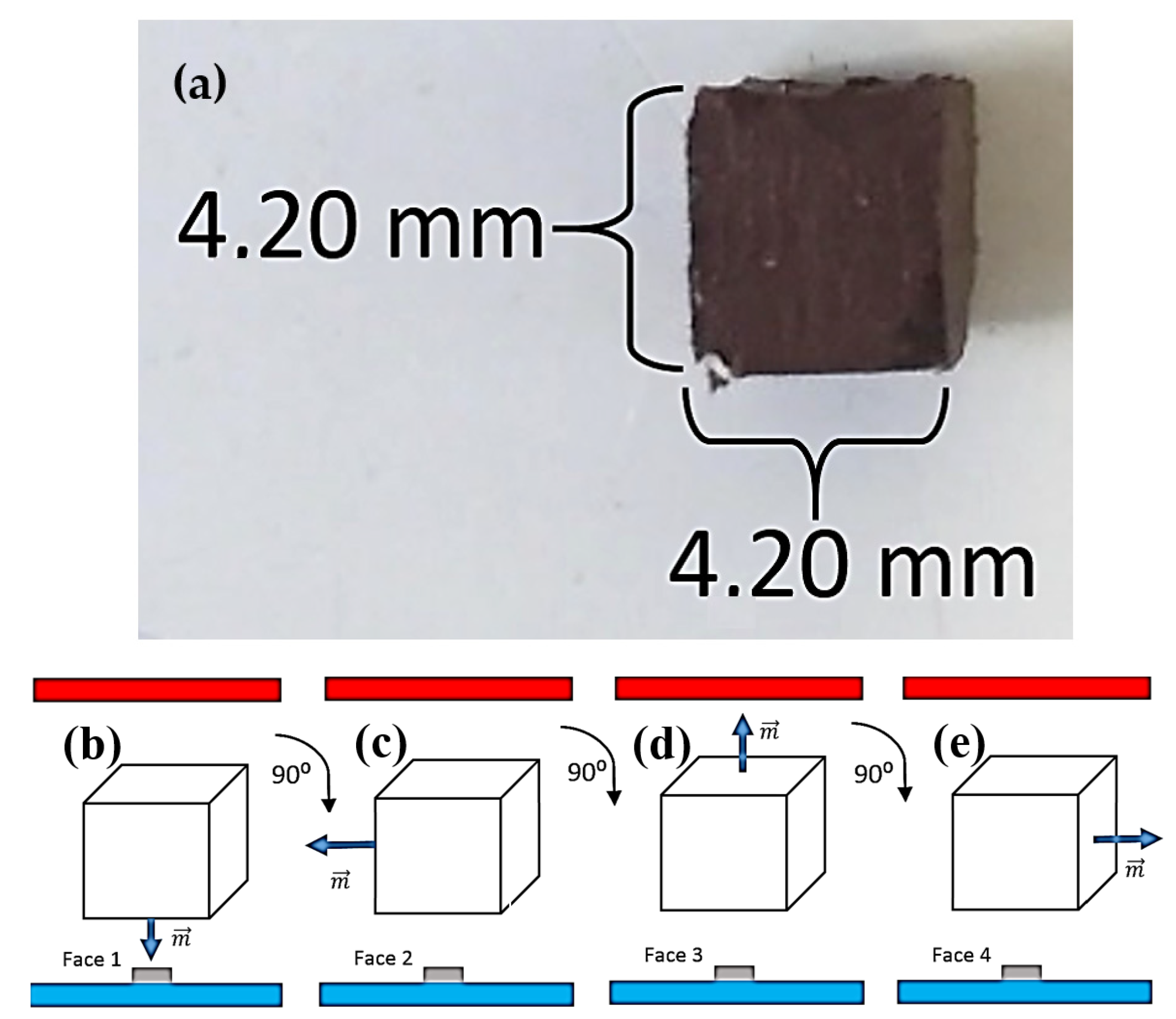

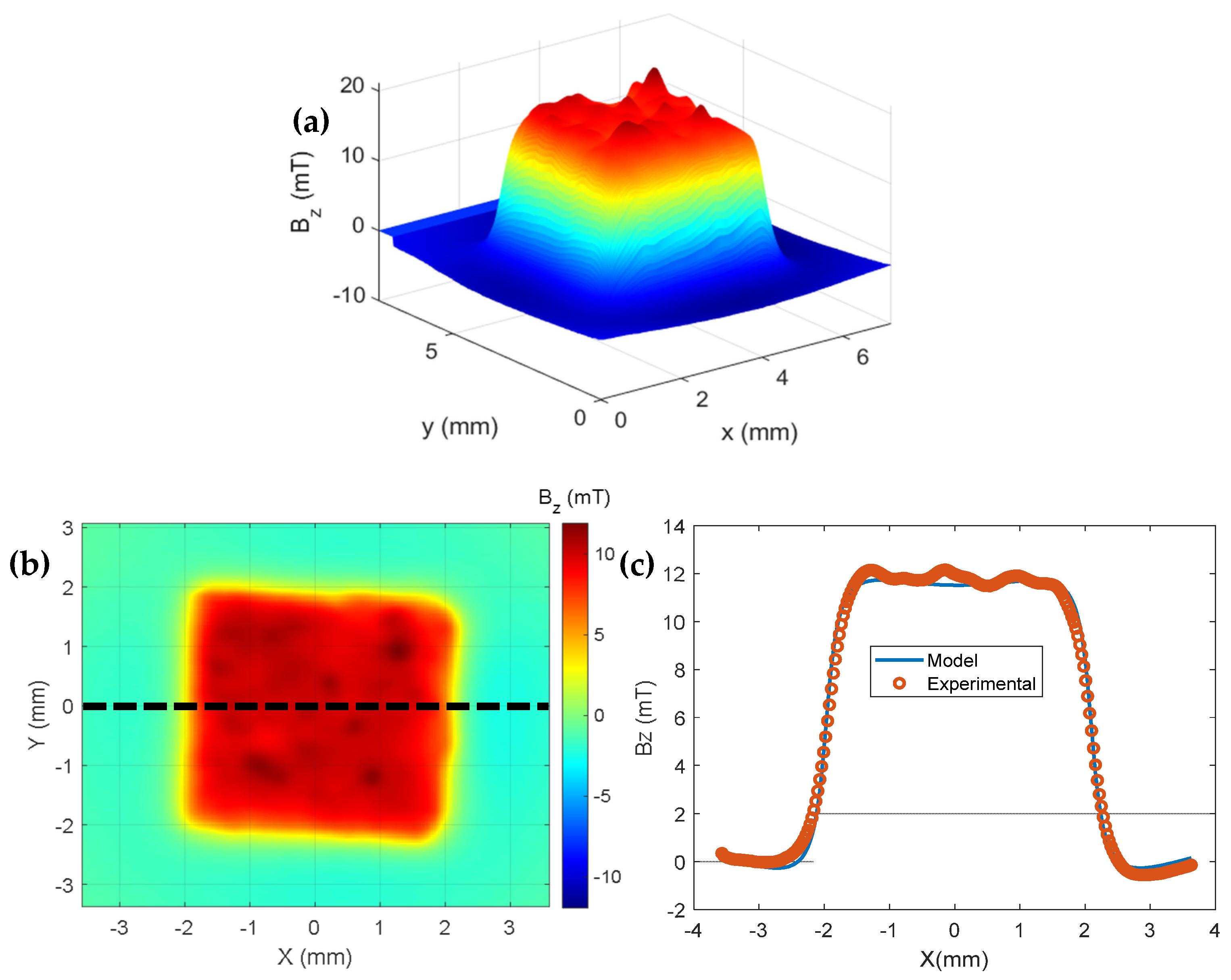
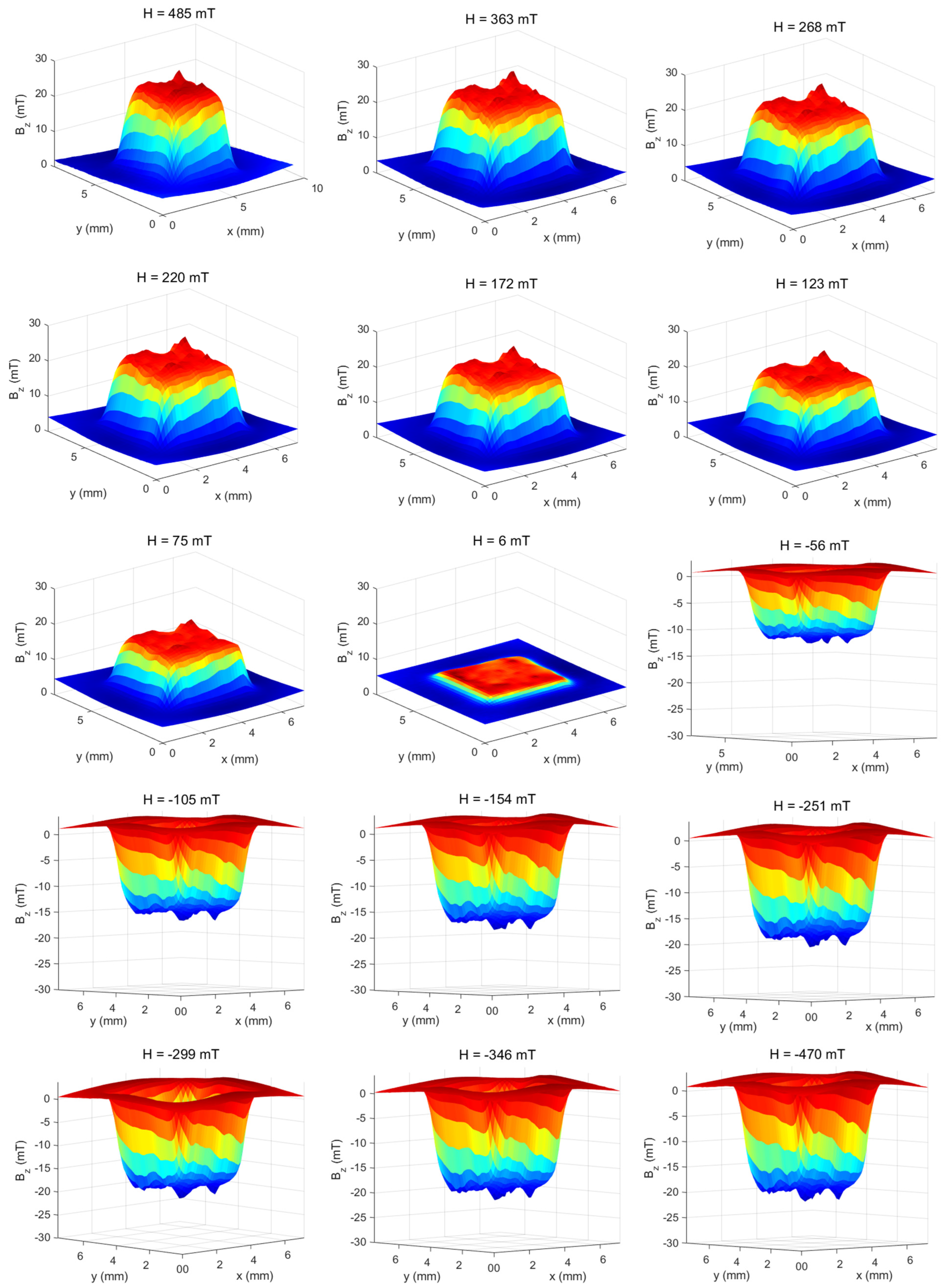
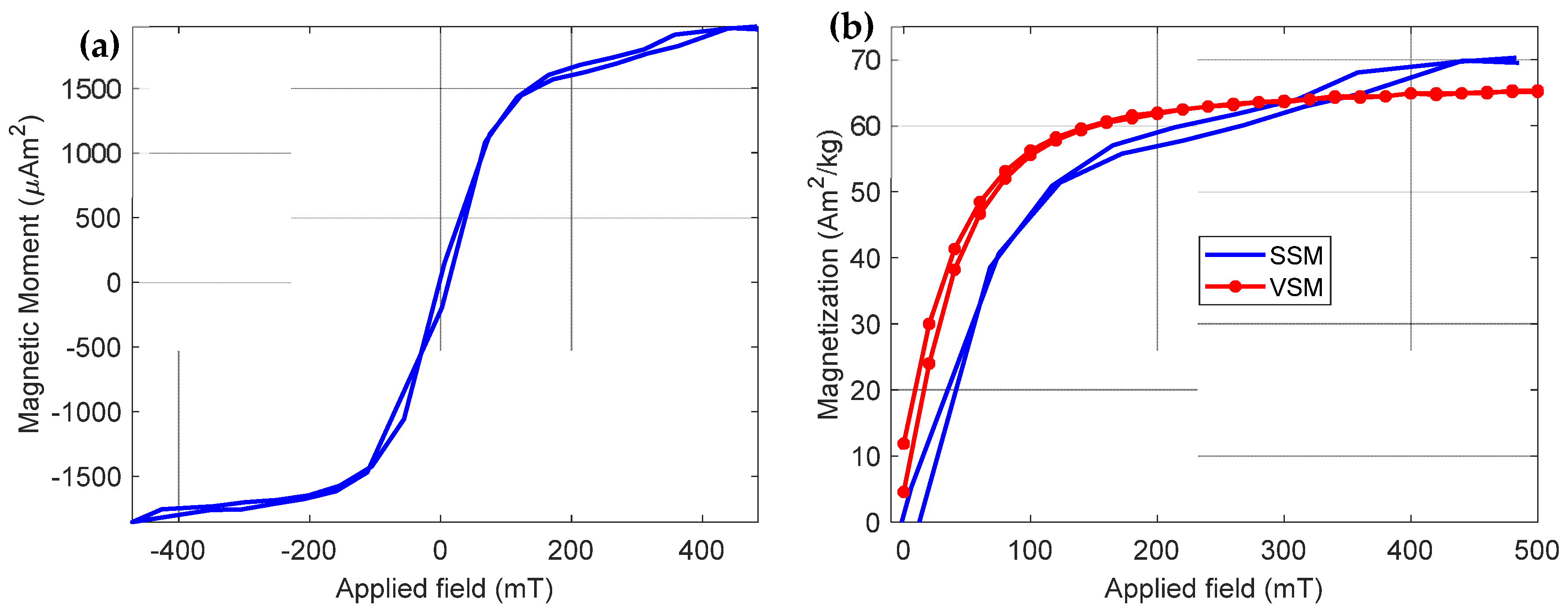
| Sample | Microparticles + Epoxy Cube Mass (mg) | Microparticle Mass | Epoxy Mass (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 70.0 | 0 | 70 |
| 1 | 95.9 | 38.1 mg | 57.8 |
| 2 | 90.7 | 31.4 mg | 59.3 |
| 3 | 83.5 | 28.1 mg | 55.4 |
| 4 | 86.5 | 8.83 mg | 77.7 |
| 5 | 81.9 | 2.36 mg | 79.5 |
| 6 | 72.3 | 695 µg | 71.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medina, C.D.; Mendoza, L.A.F.; Luz-Lima, C.; Bruno, A.C.; Araujo, J.F.D.F. Measuring Iron Oxide Composites with a Custom-Made Scanning Magnetic Microscope. Sensors 2025, 25, 2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082594
Medina CD, Mendoza LAF, Luz-Lima C, Bruno AC, Araujo JFDF. Measuring Iron Oxide Composites with a Custom-Made Scanning Magnetic Microscope. Sensors. 2025; 25(8):2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082594
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedina, Christian D., Leonardo A. F. Mendoza, Cleânio Luz-Lima, Antonio C. Bruno, and Jefferson F. D. F. Araujo. 2025. "Measuring Iron Oxide Composites with a Custom-Made Scanning Magnetic Microscope" Sensors 25, no. 8: 2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082594
APA StyleMedina, C. D., Mendoza, L. A. F., Luz-Lima, C., Bruno, A. C., & Araujo, J. F. D. F. (2025). Measuring Iron Oxide Composites with a Custom-Made Scanning Magnetic Microscope. Sensors, 25(8), 2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082594






