Dual-Branch Cross-Fusion Normalizing Flow for RGB-D Track Anomaly Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Introduction of a novel RGB-D anomaly detection method in combination with depth maps to take advantage of the shape information;
- Proposal of a dual-branch normalizing flow with cross-fusion strategy that fuses RGB images and depth maps;
- Introduction of the Mutual Perception module (MP) and Fusion Flow to improve the compatibility of RGB-D data;
- Achievement of advanced accuracy in TA dataset.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. 2D Anomaly Detection
2.1.1. Reconstruction-Based Methods
2.1.2. Embedding Similarity-Based Methods
2.1.3. Normalizing Flows-Based Methods
2.2. RGB-D Fusion Strategies
3. Method
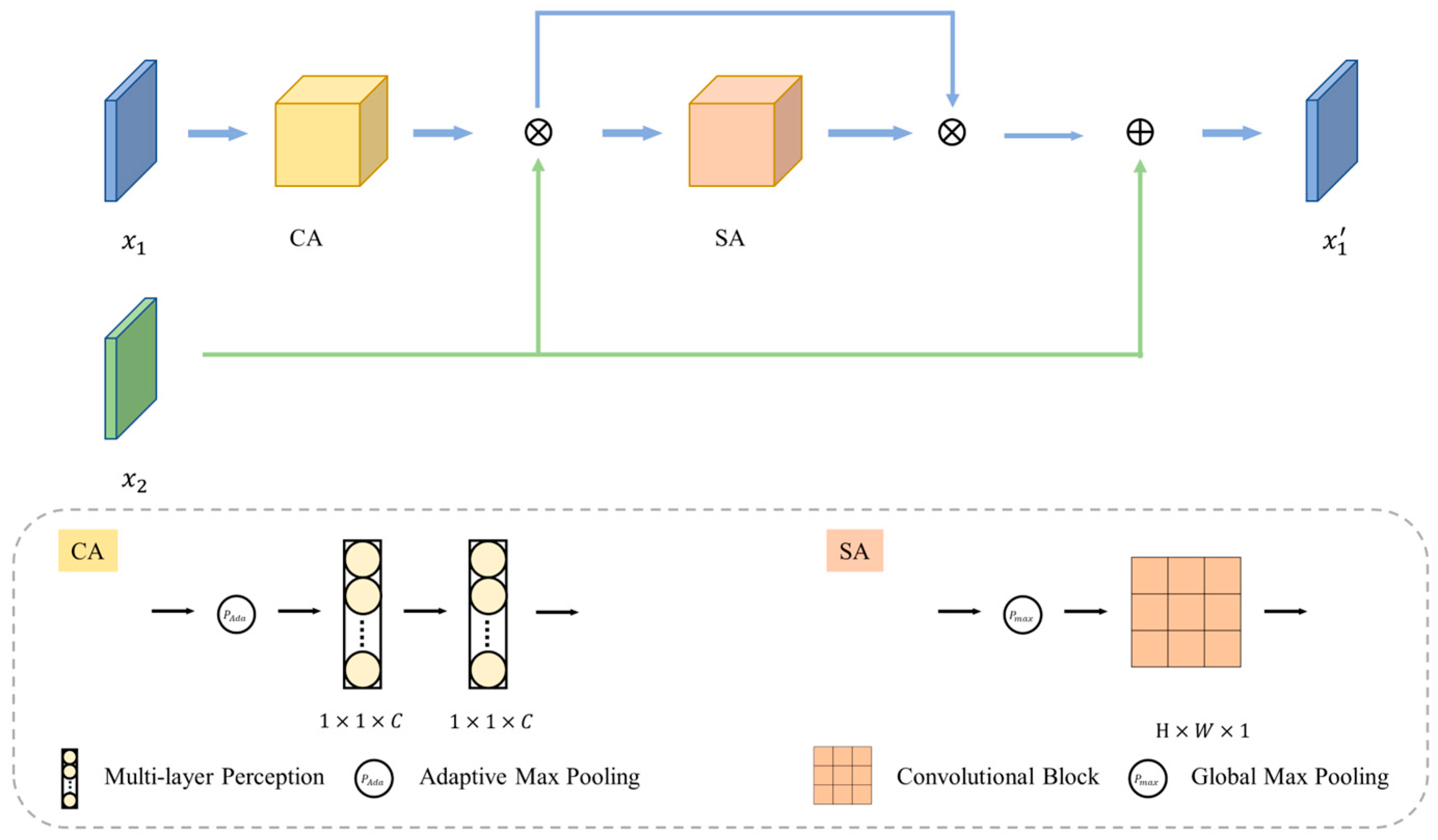
3.1. Mutual Perception Module (MP)
3.2. Feature Extraction
3.3. Fully Convolutional Normalizing Flow
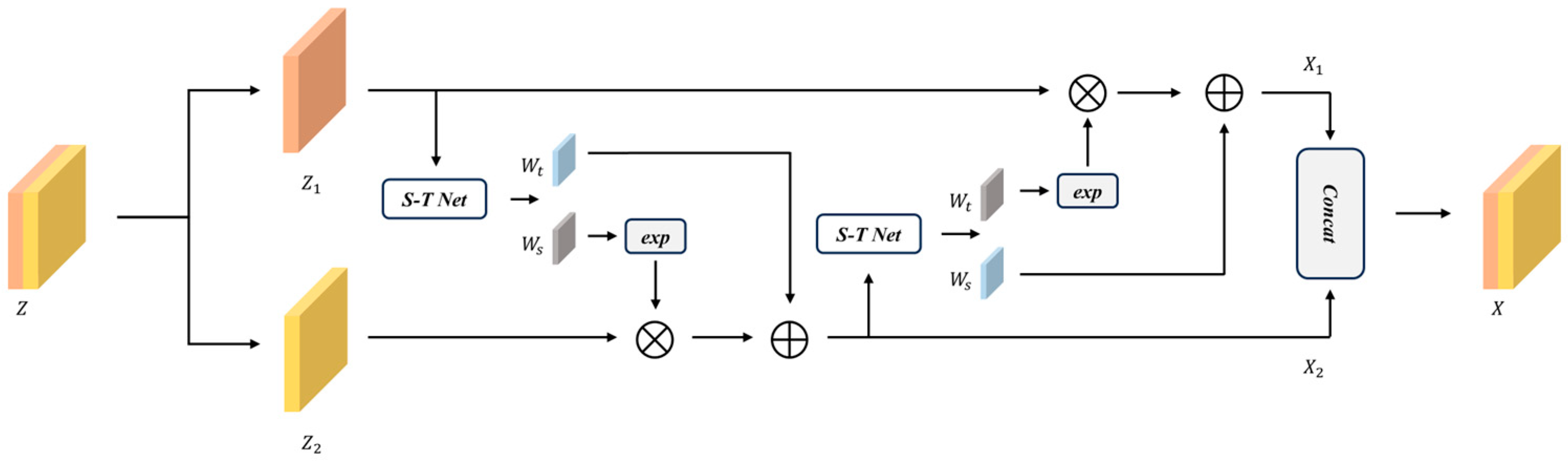
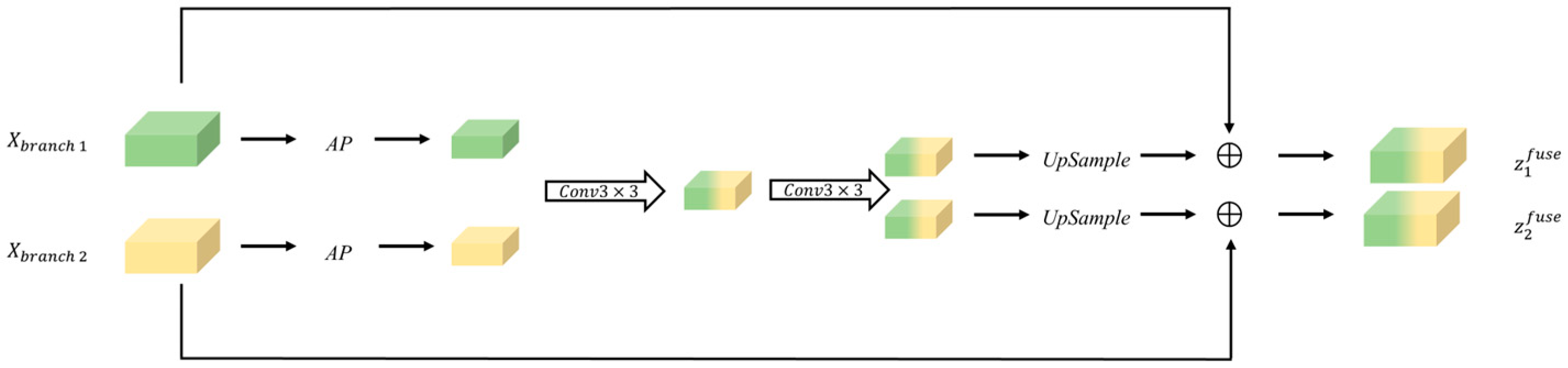
3.4. Fusion Flow
3.5. Learning Objective and Post Processing
4. Experiment
4.1. Datasets and Metrics
4.2. Experimental Details
4.3. Quantitative Comparison
4.4. Ablation Study
4.4.1. Influence of Different Modules
4.4.2. Influence of the Number of Normalizing Flow Blocks
4.4.3. Influence of Different Extractions
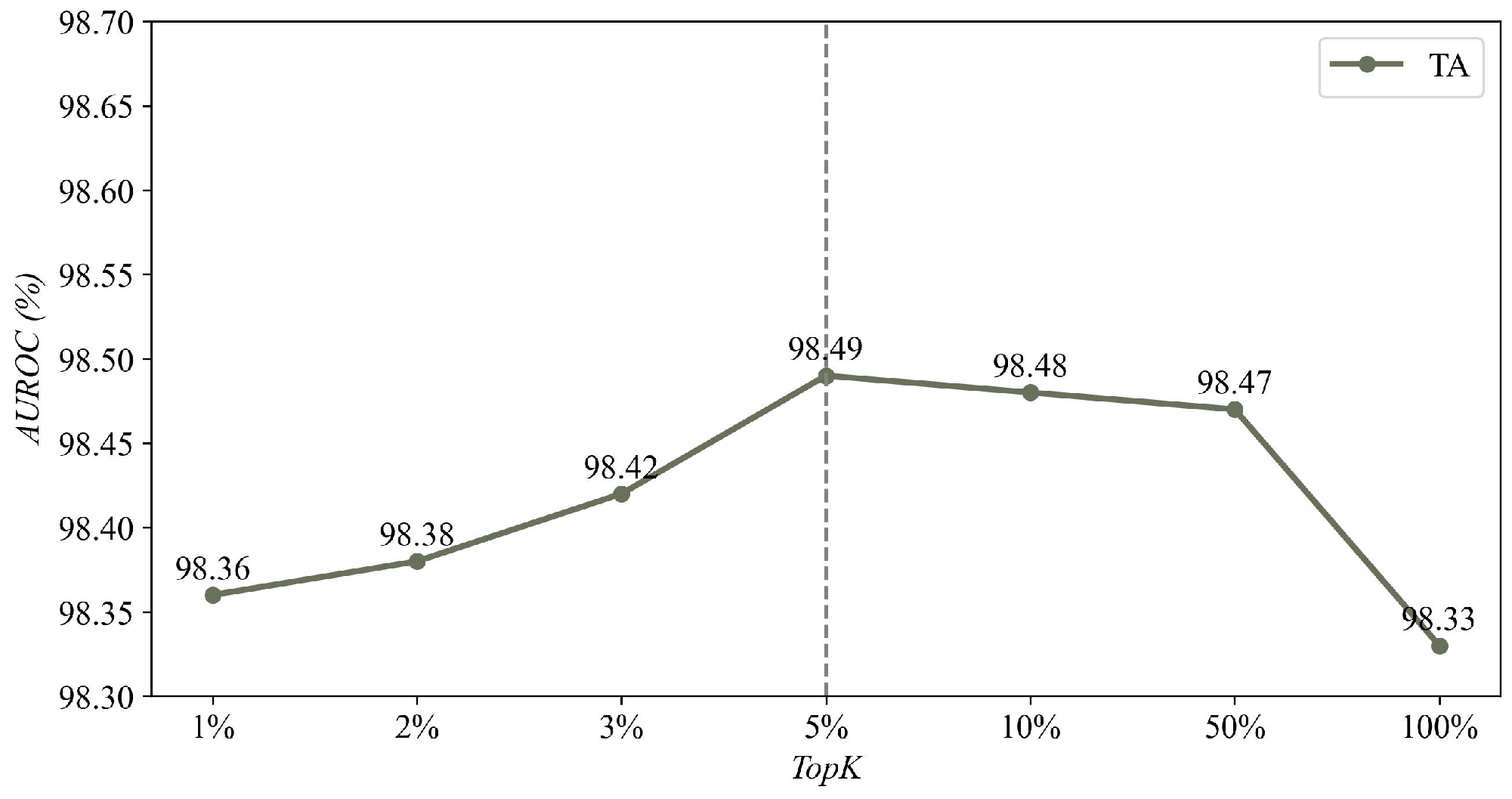
4.4.4. Influence of the K Sets in TopK:
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AE | Autoencoder |
| AUROC | Area Under Receiver Operator Curve |
| DCNF | Dual-Branch Cross-Fusion Normalizing Flow |
| TA | Track Anomaly |
| MP | Mutual Perception module |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| kNN | k-Nearest Neighbor |
| NF | Normalizing Flow |
| RN-18 | ResNet-18 |
| RN-50 | ResNet-50 |
| WRN-20 | WideResNet-50 |
References
- Liu, J.; Song, K.; Feng, M.; Yan, Y.; Tu, Z.; Zhu, L. Semi-supervised anomaly detection with dual prototypes autoencoder for industrial surface inspection. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2021, 136, 106324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Li, B.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, B.; Shi, Y.; Jin, L.; Jin, X. Anomaly-prior guided inpainting for industrial visual anomaly detection. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 170, 110296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, L.; Wang, N. Anodfdnet: A deep feature difference network for anomaly detection. J. Sens. 2022, 2022, 3538541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, K.; Pemula, L.; Zepeda, J.; Schölkopf, B.; Brox, T.; Gehler, P. Towards total recall in industrial anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 21–24 June 2022; pp. 14318–14328. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, G.; Shen, C.; Cao, L.; Hengel, A.V.D. Deep learning for anomaly detection: A review. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2021, 54, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Song, K.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Tong, L.; Chen, S.; Yan, Y. NFCF: Industrial Surface Anomaly Detection with Normalizing Flow Cross-Fitting Network. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2023, 168, 107655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, R.; Qi, Z.; Shi, Y. Visual anomaly detection for images: A systematic survey. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 199, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N.; Hoshen, Y. Sub-image anomaly detection with deep pyramid correspondences. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.02357. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Fan, D.P.; Cheng, M.M.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. RGB-D salient object detection: A survey. Comput. Vis. Media 2021, 7, 37–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, X.; Song, J.; Shen, F.; Shen, H.T. MSFlow: Multiscale Flow-Based Framework for Unsupervised Anomaly Detection. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 36, 2437–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, P.; Fauser, M.; Sattlegger, D.; Steger, C. MVTec AD—A comprehensive real-world dataset for unsupervised anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9592–9600. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, P.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Luo, L. Normalizing Flow-Based Industrial Complex Background Anomaly Detection. J. Sens. 2023, 2023, 6690190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcay, S.; Atapour-Abarghouei, A.; Breckon, T.P. Ganomaly: Semi-supervised anomaly detection via adversarial training. In Computer Vision–ACCV 2018: 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision; Perth, Australia, 2–6 December 2018, Revised Selected Papers; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume Part III 14, pp. 622–637. [Google Scholar]
- Bergman, L.; Cohen, N.; Hoshen, Y. Deep nearest neighbor anomaly detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.10445. [Google Scholar]
- Defard, T.; Setkov, A.; Loesch, A.; Audigier, R. Padim: A patch distribution modeling framework for anomaly detection and localization. In International Conference on Pattern Recognition; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 475–489. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, R.A.; Urmonov, O.; Kim, H. Two-stage coarse-to-fine image anomaly segmentation and detection model. Image Vis. Comput. 2023, 139, 104817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, L.; Sohl-Dickstein, J.; Bengio, S. Density estimation using real nvp. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1605.08803. [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph, M.; Wandt, B.; Rosenhahn, B. Same same but differnet: Semi-supervised defect detection with normalizing flows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Virtual, 5–9 January 2021; pp. 1907–1916. [Google Scholar]
- Gudovskiy, D.; Ishizaka, S.; Kozuka, K. Cflow-ad: Real-time unsupervised anomaly detection with localization via conditional normalizing flows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, C.; Nguyen, T.V.; Katti, H.; Yadati, K.; Kankanhalli, M.; Yan, S. Depth matters: Influence of depth cues on visual saliency. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2012: 12th European Conference on Computer Vision; Florence, Italy, 7–13 October 2012, Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Proceedings; Volume Part II 12, pp. 101–115. [Google Scholar]
- Desingh, K.; Krishna, K.M.; Rajan, D.; Jawahar, C.V. Depth really Matters: Improving Visual Salient Region Detection with Depth. In Proceedings of the BMVC, Bristol, UK, 9–13 September 2013; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Gong, X.; Yu, L.; Zhou, W.; Ying Yang, M. Exploiting global priors for RGB-D saliency detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Li, B.; Xiong, W.; Hu, W.; Ji, R. RGBD salient object detection: A benchmark and algorithms. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference; Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014, Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Proceedings; Volume Part III 13, pp. 92–109. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, N.; Yan, C.; Li, X. CNNs-based RGB-D saliency detection via cross-view transfer and multiview fusion. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 48, 3171–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Gong, X. Adaptive fusion for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 55277–55284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Gobichettipalayam, S.; Tamadazte, B.; Allibert, G.; Paudel, D.P.; Demonceaux, C. Robust rgb-d fusion for saliency detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Prague, Czech Republic, 12–16 September 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 403–413. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Schirrmeister, R.; Zhou, Y.; Ball, T.; Zhang, D. Understanding anomaly detection with deep invertible networks through hierarchies of distributions and features. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 21038–21049. [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph, M.; Wehrbein, T.; Rosenhahn, B.; Wandt, B. Fully convolutional cross-scale-flows for image-based defect detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 1088–1097. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann, P.; Fauser, M.; Sattlegger, D.; Steger, C. Uninformed students: Student-teacher anomaly detection with discriminative latent embeddings. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 4183–4192. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Song, B.C. Cfa: Coupled-hypersphere-based feature adaptation for target-oriented anomaly localization. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 78446–78454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

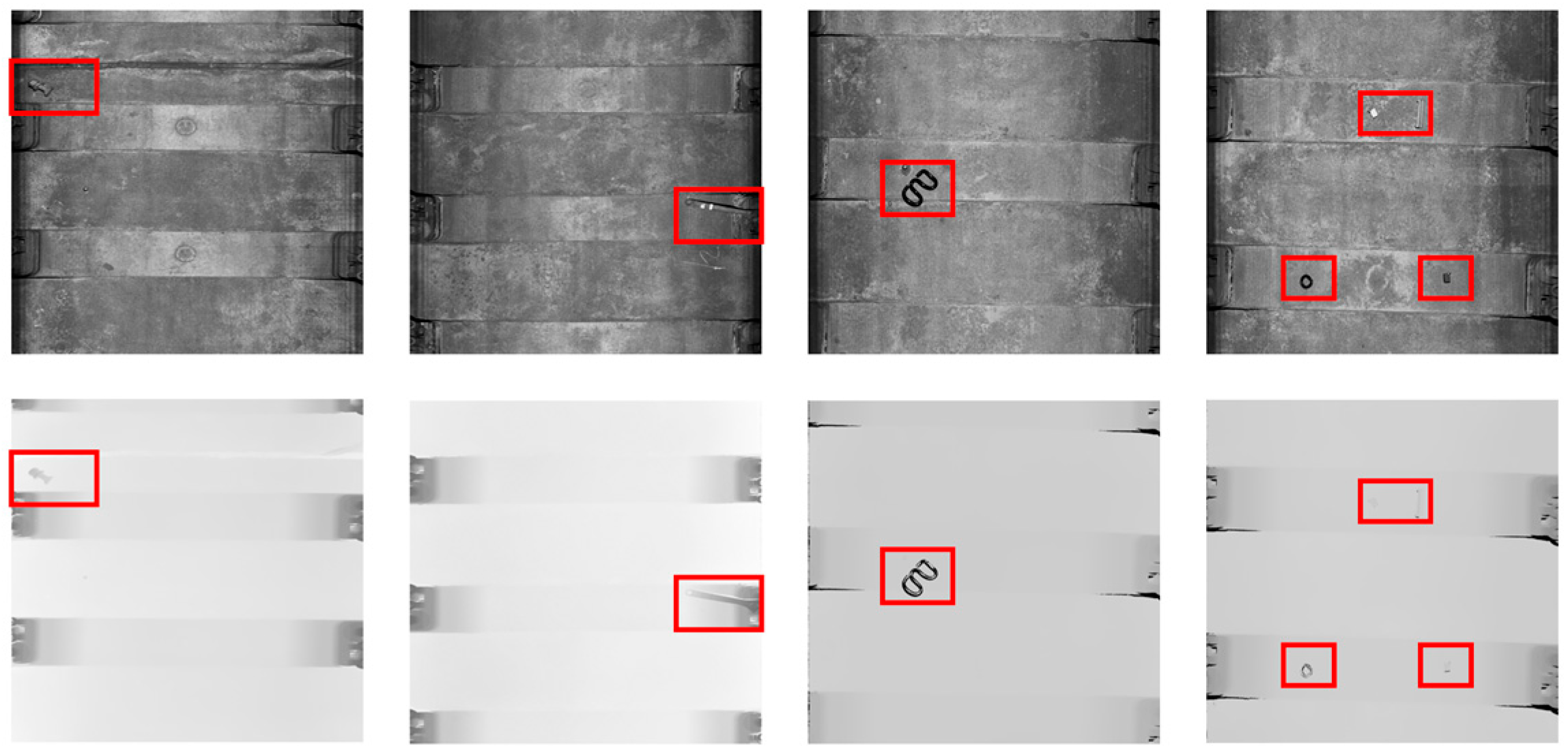

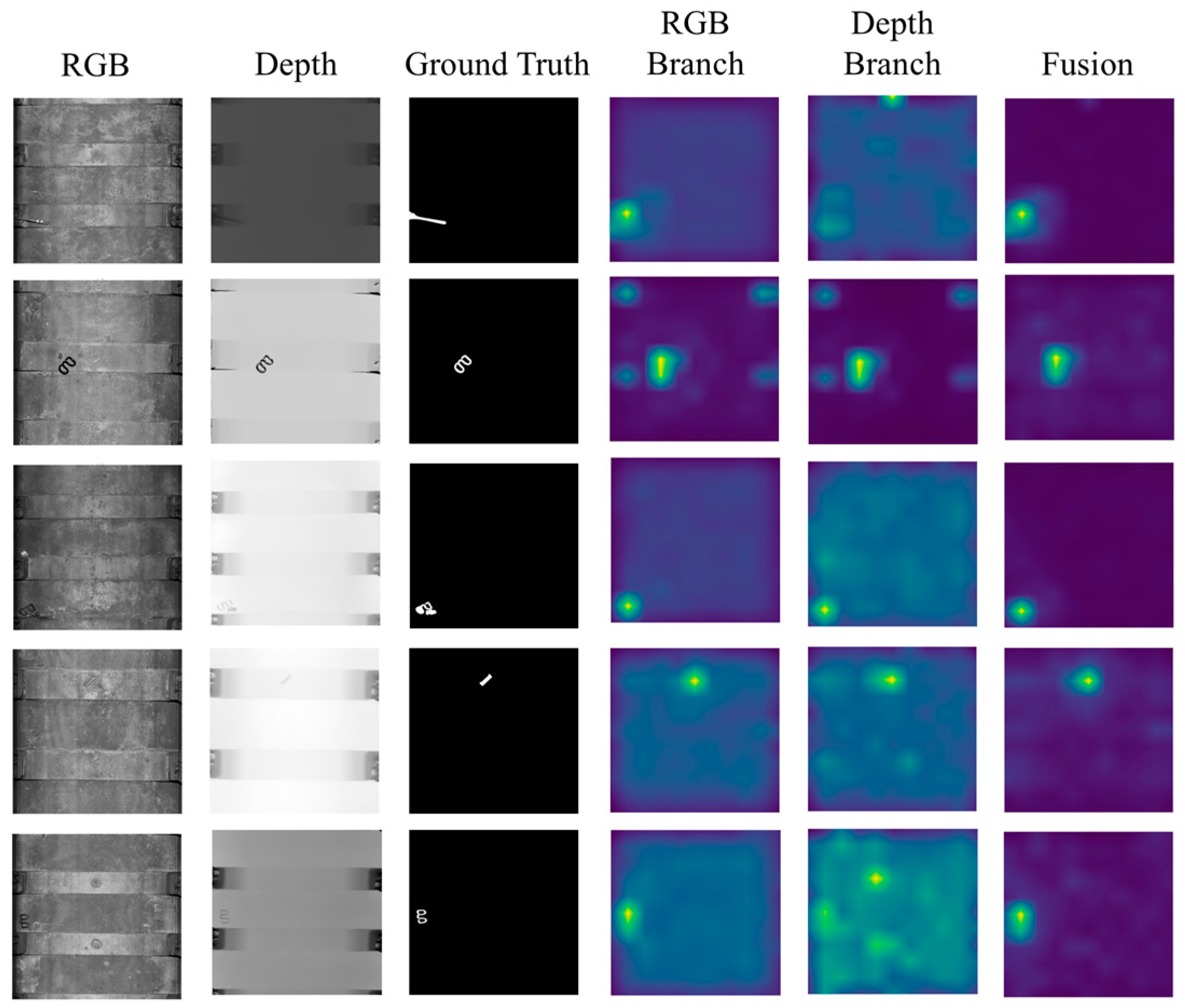
| Method | GANomaly [13] | PaDiM [15] | CFA [31] | CFlow [19] | MSFlow [10] | DCNF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUROC | 80.30 | 91.70 | 94.28 | 93.12 | 94.75 | 98.49 |
| Method | DCNF (RGB) | DCNF (Depth) | DCNF |
|---|---|---|---|
| AUROC | 97.02 | 95.94 | 98.49 |
| Method | GANomaly | PaDiM | CFA | CFlow | MSFlow | DCNF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recall | 83.40 | 90.81 | 94.30 | 93.99 | 92.93 | 96.47 |
| Method | DCNF (RGB) | DCNF (Depth) | DCNF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recall | 94.13 | 93.85 | 96.47 |
| MP | Fusion Flow | TA |
|---|---|---|
| × | × | 97.26 |
| × | √ | 97.76 |
| √ | × | 98.08 |
| √ | √ | 98.49 |
| n | 2 | 5 | 8 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUROC | 97.76 | 97.87 | 98.49 | 98.49 |
| Method | GANomaly | PaDiM | CFA | CFlow | MSFlow | DCNF (RN-18) | DCNF (RN-50) | DCNF (WRN-50) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA | 80.3 | 91.7 | 94.28 | 93.12 | 94.75 | 97.79 | 98.13 | 98.49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.; Wen, P.; Li, J.; Luo, L. Dual-Branch Cross-Fusion Normalizing Flow for RGB-D Track Anomaly Detection. Sensors 2025, 25, 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082631
Gao X, Wen P, Li J, Luo L. Dual-Branch Cross-Fusion Normalizing Flow for RGB-D Track Anomaly Detection. Sensors. 2025; 25(8):2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082631
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xiaorong, Pengxu Wen, Jinlong Li, and Lin Luo. 2025. "Dual-Branch Cross-Fusion Normalizing Flow for RGB-D Track Anomaly Detection" Sensors 25, no. 8: 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082631
APA StyleGao, X., Wen, P., Li, J., & Luo, L. (2025). Dual-Branch Cross-Fusion Normalizing Flow for RGB-D Track Anomaly Detection. Sensors, 25(8), 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082631






