Immunoglobulin G Determination in Human Serum and Milk Using an Immunosensor of New Conception Fitted with an Enzyme Probe as Transducer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1 Materials
2.2 Samples
2.3 Apparatus
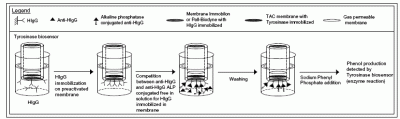
3. Methods
3.1 Construction of tyrosinase biosensor
3.2 Immobilization of tyrosinase in TAC membrane
3.3 Immobilization of tyrosinase in Pall-Biodyne membrane
3.4 Immobilization of tyrosinase in Immobilon Membrane
3.5 Optimization of the enzyme immobilization method
3.6 HIgG immobilization on Pall-Biodyne membrane
3.7 HIgG immobilization on Immobilon membrane
3.8 Immunosensor assembly
3.9 Determination of anti-HIgG with new immunosensor
3.10. Determination of HIgG with new immunosensor
3.11. Measures performed on the washing solutions
3.12. Measures performed on the Human serum and human milk
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Lodish, H.; Berk, A.; Zipursky, S.L.; Matsudaira, P.; Baltimore, D.; Darnell, J.E. Molecular Cell Biology, 4th Ed. ed; W. H. Freeman & Co: New York, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, J.M.; Tymoczko, J.L.; Stryer, L. Biochemistry, 3rd Ed. ed; W. H. Freeman and Co: New York, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Janeway, C.A.; Travers, P.; Walport, M.; Shlomchik, M. Immunobiology, 5th Ed. ed; Garland Publishing: New York and London, England, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhoff, M.E.; Rechnitz, G.A. Electrode-Based Enzyme Immunoassays usings urease conjugates. Method. Enzymol. 1980, 70, 439–454. [Google Scholar]
- Campanella, L.; Attioli, R.; Colapicchioni, C.; Tomassetti, M. New amperometric and potentiometric immunosensors for anti-human immunoglobulin G determinations. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 1999, 55, 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Campanella, L.; Martini, E.; Tomassetti, M. Immunochemical potentiometric method for HIgG and anti-HIgG determination, using a NH3 probe and immunoprecipitation as preconcentration procedure. Anal. Lett. 2007, 40, 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Campanella, L.; Martini, E.; Tomassetti, M. Determination of HIgG and anti-HIgG using a single potentiometric immunosensor and two different “competitive methods”: Application to the analysis of globulin G in human serum. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2008, 130, 520–530. [Google Scholar]
- Campanella, L.; Tomassetti, M.; Sammartino, M.P. Enzyme-entrapping membranes for enzyme sensors. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 1989, 16, 235–245. [Google Scholar]
- Mascini, M.; Mazzei, F. Amperometric sensor for pyruvate with immobilized pyruvate oxidase. Anal. Chim. Acta. 1987, 192, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Boyer, K.M.; Kendall, L.S.; Papierniak, C.K.; Klegerman, M.E.; Gotoff, S.P. Protective levels of human immunoglobulin G antibody to group B streptococcus type Ib. Infect. Immun. 1984, 45, 618–624. [Google Scholar]
- Skoog, D.A.; Leary, J.J. Principles of Instrumental Analysis, 4th Ed. ed; Edises srl: Napoli: Italy, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Muratsugu, M.; Kumasaka, K.; Tanaka, M.; Okushima, K.; Fukui, T. Detection of biotin-binding immunoglobulin G in human sera using avidin-coated multiwell microplates. J. Health Sci. 2001, 47, 424–428. [Google Scholar]
- French, M. Serum IgG subclasses in normal adults. Monograph. Allergy. 1986, 19, 100–150. [Google Scholar]
- Litwin, S.D.; Zehr, B.D.; Insel, R.A. Selective concentration of IgD class-specific antibodies in human milk. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1990, 80, 263–267. [Google Scholar]
- Asensi, M.T.; Martínez-Costa, C.; Buesa, J. Anti-rotavirus antibodies in human milk: quantification and neutralizing activity. J. Pediatr. Gastr. Nutr. 2006, 42, 560–567. [Google Scholar]
- Gasparoni, A.; Avanzini, A.; Ravagni Probizer, F.; Chirico, G.; Rondini, G.; Severi, F. IgG subclasses compared in maternal and cord serum and breast milk. Arch. Dis. Child. 1992, 67(1 Spec No), 41–43. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, P.L.; Mirtle, C.L.; Harvie, A.; McClelland, D.B. Milk protein concentrations in neonatal milk (witch's milk). Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1980, 39, 695–697. [Google Scholar]
- Mickleson, K.N.; Moriarty, K.M. Immunoglobulin levels in human colostrum and milk. J. Pediatr. Gastr. Nutr. 1982, 1, 381–384. [Google Scholar]
- Ogra, S.S.; Ogra, P.L. Immunologic aspects of human colostrum and milk. Distribution characteristics and concentrations of immunoglobulins at different times after the onset of lactation. J. Pediatr. 1978, 92, 546–549. [Google Scholar]
- Ly, Y.; Yamazaki, H. Detection of human blood by cloth-based enzyme immunoassay of immunoglobulin G. Biotechnol. Tech. 1995, 9, 677–680. [Google Scholar]
- Collin, R.; Prosser, C.; McLaren, R.; Thomson, M.; Malcolm, D. A Development and validation of a nephelometric immunoassay for IgG in milk. J. Dairy Res. 2002, 69, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Tedeschi, L.; Domenici, C.; Ahluwalia, A.; Baldini, F.; Mencaglia, A. Antibody immobilisation on fibre optic TIRF sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 19, 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, M.; Ozawa, F.; Sugimoto, W.; Aso, S. Miniature surface-plasmon resonance immunosensors-rapid and repetitive procedure. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2002, 372, 301–304. [Google Scholar]Dahint, R.; Bender, F.; Morhard, F. Operation of acoustic plate mode immunosensors in complex biological media. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 3150–3156. [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton, R.M.; Mottram, T.T.; Hart, J.P. Development of a screen-printed carbon electrochemical immunosensor for picomolar concentrations of estradiol in human serum extracts. J. Biochem. Bioph. Meth. 2005, 63, 201–12. [Google Scholar]
- Okochi, M.; Ohta, H.; Tanaka, T.; Matsunaga, T. Electrochemical probe for on-chip type flow immunoassay: immunoglobulin G labeled with ferrocenecarboaldehyde. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 90, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Munge, B.; Patel, V.; Jensen, G.; Bhirde, A.; Gong, J.D.; Kim, S.N.; Gillespie, J.; Gutkind, J.S.; Papadimitrakopoulos, F.; Rusling, J.F. Carbon nanotube amplification strategies for highly sensitive immunodetection of cancer biomarkers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 11199–11205. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.; Chew, F.T.; Li, S.F. Piezoelectric quartz crystal based label-free analysis for allergy disease. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2000, 15, 629–639. [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi, K.; Muguruma, H.; Karube, I. A novel method of immobilizing antibodies on a quartz crystal microbalance using plasma-polymerized films for immunosensors. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar]
- Aizawa, M. Immunosensors. Philos. T. Roy. Soc. B 1987, 316, 121–34. [Google Scholar]
- Nowatari, M.; Kawakami, M.; Hatsuse, H.; Matsuura, N. Radioimmunoassay for the complement-activating component of. Ra-reactive factor. J. Clin. Ligand Assay 1997, 20, 240–245. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Sánchez, C.; González-García, M.B.; Costa-García, A. AC voltammetric carbon paste-based enzyme immunosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2000, 14, 917–924. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Mernaugh, R.L.; Yan, H.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, X. Engineered recombinant single-chain fragment variable antibody for immunosensors. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 6834–6842. [Google Scholar]








| Methods | Determination anti-HIgG by means of new immunosensor, that uses as transducer a tyrosinase enzyme electrode. Geometry of the test: competition for the HIgG, immobilized on the membrane, between the anti-HIgG conjugated with the alkaline phosphatase and not conjugated, both free in solution. | |
|---|---|---|
| Membrane Employed | Pall-Biodyne | Immobilon |
| Regression equation (Y= a.u., X= mM) level of confidence (1- α) = 0.95 | Y = -2.01 (±0.63) logX-10.46 (±2.09) (n – v) = 8 ; (t = 2.31) | Y = -0.86 (±0.14) logX-4.66 (±1.84) (n – v) = 7 ; (t = 2.36) |
| Linear range (mM) | (0.52-37) × 10-7 | (0.52 – 23) × 10-7 |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.9887 | 0.9872 |
| Pooled SD% | 5.5 | 5.8 |
| Limit of detection (LOD) (mM) | 0.25 × 10-7 | 0.35 × 10-7 |
| Repeatability of the Measurement RSD %(n = 5) | 6.6 | 7.2 |
| Methods | Determination HIgG by means of new immunosensor, that uses as transducer a tyrosinase enzyme electrode. Geometry of the test: competition for the free in solution anti-HIgG conjugated with the alkaline phosphatase, between the HIgG immobilized on the membrane and HIgG free in solution. | |
|---|---|---|
| Membrane Employed | Pall-Biodyne | Immobilon |
| Regression equation (Y=a.u., X= mM) level of confidence (1- α) = 0.95 | Y = -1.19 (±0.26) log X-6.27 (±1.23) (n - v) = 6 ; (t = 2.45) | Y = -1.16 (±0.16) log X-6.40 (±1.54) (n - v) = 7 ; (t = 2.36) |
| Linear range (mM) | (0.52 - 37) × 10-7 | (0.52 - 13) × 10-7 |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.9785 | 0.9770 |
| Pooled SD% | 5.8 | 6.1 |
| Limit of detection (LOD) (mM) | 0.25 × 10-7 | 0.26 × 10-7 |
| Repeatability of the Measurement RSD (n = 5) | 6.8 | 7.4 |
| Methods | Determination of anti-HIgG by means of tyrosinase biosensor, on the washing solution, after immunocomplex formation on the immunosensor membrane | Determination of HIgG by means of tyrosinase biosensor, on the washing solution, after immunocomplex formation on the immunosensor membrane | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Membrane Employed | Pall-Biodyne | Immobilon | Pall-Biodyne | Immobilon |
| Regression equation (X= mM, Y= u.a) level of confidence (1- α) = 0.95 | Y = 0.85 (±0.08) logX + 6.1 (±1.2) (n – v)= 8; (t = 2.31) | Y = 0.36 (±0.05) logX + 4.7 (±0.9) (n – v)= 7; (t = 2.36) | Y = 1.27 (±0.8) logX + 9.9 (±1.5) (n – v)= 8; (t = 2.31) | Y = 0.54 (±0.04) logX + 4.3 (±1.1) (n – v)= 7; (t = 2.36) |
| Linear range (mM) | (0.52 - 13) × 10-7 | (0.52 – 13) × 10-7 | (0.52 - 13) × 10-7 | (0.52 – 10) × 10-7 |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.9756 | 0.9625 | 0.9755 | 0.9784 |
| Pooled SD% | 6.7 | 7.7 | 7.0 | 7.8 |
| Limit of detection (LOD) (mM) | 0.25 × 10-7 | 0.25 × 10-8 | 0.25 × 10-8 | 0.35 × 10-8 |
| Repeatability of the Measurement RSD% (n=5) | 6.9 | 7.3 | 6.8 | 7.2 |
| (a) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Run of successive measures | Equation of the linear Regression (Y= a.u., X= mM of anti-HIgG) | Correlation coefficient |
| run 1 | y = -2.01 (± 0.2) log x- 10.5 (±2.1) | r2 = 0.9887 |
| run 2 | y = -2.05 (± 0.4) log x- 8.5 (± 1.6) | r2 = 0.9786 |
| run 3 | y = -1.18 (± 0.3) log x- 7.8 (± 1.4) | r2 = 0.9377 |
| (b) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Run of successive measures | Equation of the linear regression (Y= a.u., X= mM of anti-HIgG) | Correlation coefficient |
| run 1 | y = -0.86 (± 0.13) log x- 4.7 (± 1.8) | r2 = 0.9872 |
| run 2 | y = -0.77 (± 0.10) log x- 3.5 (± 1.2) | r2 = 0.9451 |
| run 3 | y = -0.48 (± 0.18) log x- 2.5 (± 1.6) | r2 = 0.9288 |
| Human serum | n= 5 RSD% ≤ 5 (a) | n= 5 RSD% ≤ 5 (b) | n= 5 RSD% ≤ 6 (c) | n= 5 RSD% ≤ 6 (d) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diluted 1:100,000 | 2.446 | 2.452 | +0.24 | 0.176 | 0.168 | -4.55 |
| Diluted 1:10,000 | 1.458 | 1.442 | -1.10 | 0.327 | 0.348 | -6.42 |
| Diluted 1:1,000 | 0.546 | 0.490 | -4.82 | 0.578 | 0.586 | -1.38 |
| Diluted 1:100 | 0.162 | 0.165 | +1.85 | 0.892 | 0.899 | -0.78 |
| Biological Matrix | Dilution | Final concentration immunoglobulin G in the diluted sample (mM) n=5; RSD%≤ 5 | Found concentration immunoglobulin G in the undiluted sample (mM) n= 5; RSD%≤ 5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human Serum | 1:10,000 | 2.30 × 10-8 | 2.30 × 10-4 |
| Human Serum | 1:1,000 | 1.95 × 10-7 | 1.95 × 10-4 |
| Human Serum | 1:100 | 2.48 × 10-6 | 2.48 × 10-4 |
| Human Milk | 1:1,000 | 2.03 × 10-7 | 2.03 × 10-4 |
| Human Milk | 1:100 | 1.82 × 10-6 | 1.82 × 10-4 |
| Biologica l Matrix | Dilution | Final concentration Immunoglobulin G in the diluted sample (mM) (n=5); RSD%≤ 5 | Added immunoglobulin G concentration (mM) | Experimental immunoglobulin G concentration (mM) (n= 5); RSD%≤ 5 | Recovery % immunoglobulin G concentration in the diluted sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human Serum | 1:1,000 | 1.95 × 10-7 | 3.50 × 10-7 | 5.58 × 10-7 | 102.4 |
| Human Serum | 1:100 | 24.8 × 10-7 | 3.50 × 10-7 | 29.21 × 10-7 | 103.2 |
| Human Milk | 1:1,000 | 2.03 × 10-7 | 12.7 × 10-7 | 14.8 × 10-7 | 99.5 |
| Human Milk | 1:100 | 13.2 × 10-7 | 12.7 × 10-7 | 25.2 × 10-7 | 97.3 |
© 2008 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Campanella, L.; Lelo, D.; Martini, E.; Tomassetti, M. Immunoglobulin G Determination in Human Serum and Milk Using an Immunosensor of New Conception Fitted with an Enzyme Probe as Transducer. Sensors 2008, 8, 6727-6746. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8106727
Campanella L, Lelo D, Martini E, Tomassetti M. Immunoglobulin G Determination in Human Serum and Milk Using an Immunosensor of New Conception Fitted with an Enzyme Probe as Transducer. Sensors. 2008; 8(10):6727-6746. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8106727
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampanella, Luigi, Dalina Lelo, Elisabetta Martini, and Mauro Tomassetti. 2008. "Immunoglobulin G Determination in Human Serum and Milk Using an Immunosensor of New Conception Fitted with an Enzyme Probe as Transducer" Sensors 8, no. 10: 6727-6746. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8106727
APA StyleCampanella, L., Lelo, D., Martini, E., & Tomassetti, M. (2008). Immunoglobulin G Determination in Human Serum and Milk Using an Immunosensor of New Conception Fitted with an Enzyme Probe as Transducer. Sensors, 8(10), 6727-6746. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8106727