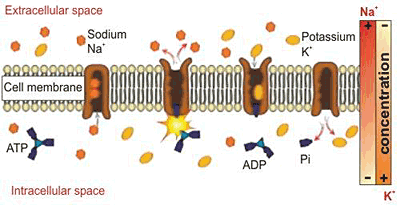
Na+,K+-ATPase as the Target Enzyme for Organic and Inorganic Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase activity
2.1. Specific inhibition by cardiac glycosides
2.2. Platinum-anticancer drugs
2.3. Metal ions
2.4. Toxic organic compounds
2.4.1. Herbicides
2.4.2. Insecticides
3. Principle of the application of Na+,K+-ATPase as a bioanalytical tool
3.1. Binding of Na+,K+-ATPase to microtiter plate coated with wheat germ agglutinin
3.2. Functional immobillization of biomembrane fragments on planar waveguids
3.3. Immobilization of brain Na+, K+-ATPase on nitrocellulose, glass fiber and polyvinylidene fluoride membranes
3.4. Immobilization of Na+,K+-ATPase on the surface of polystyrene microtiter plate
3.5. Immobilization of Na+, K+-ATPase on dextran surface
4. Signal detection
4.1. Methods for determination of Na+,K+-ATPase activity
4.1.1. Spectroscopic methods
4.1.2. HPLC methods
4.1.3. Coupled enzymatic methods
4.1.4. Fluorescence and bioluminescence methods
4.2. Na+, K+-ATPase based biosensors
4.2.1. Detection of various analytes by Na+,K+-ATPase assay
4.2.2. Resonant mirror biosensor
4.2.3. Evanescent wave fluorescence biosensor
4.2.4. Optical voltage assay of Na+,K+-ATPase
4.2.5. High-throughput screening assay for Na+, K+-ATPase using atomic absorption spectroscopy
Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Voet, D.; Voet, J.G. Biochemistry; John Wiley: New York, 1995; pp. 524–531. [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell, M. The role of hormone receptors and GTP-regulatory proteins in membrane transduction. Nature 1980, 284, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Xia, S.H. Mechanisms of regulation and function of G-protein-coupled receptor kinases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 7753–7757. [Google Scholar]
- Wackerhage, H.; Woods, N.M. Exercise-induced signal transduction and gene regulation in skeletal muscle. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2002, 1, 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, W.; Weiss, M. Digoxin Uptake, Receptor Heterogeneity and Inotropic Response in the Isolated Rat Heart: A Comprehensive Kinetic Model. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 302, 577–583. [Google Scholar]
- Hammes, S.R. The further redefining of steroid-mediated signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S A. 2003, 100, 2168–2170. [Google Scholar]
- Nambi, P.; Aiyar, N. G Protein-Coupled Receptors in Drug Discovery. ASSAY Drug Dev. Technol. 2003, 1, 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Skou, J.C.; Essman, M. The Na,K-ATPase. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 1992, 24, 249–261. [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen, P.L.; Hakansson, K.O.; Karlish, J.D. Structure and mechanism of Na+,K+-ATPase. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2003, 65, 817–849. [Google Scholar]
- Vasilets, L.A.; Schwarz, W. Structure–function relationships of cation binding in Na+/K+-ATPase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1993, 1154, 201–222. [Google Scholar]
- Scheiner-Bobis, G. The sodium pump, its molecular properties and mechanisms of ion transport. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 2424–2433. [Google Scholar]
- Lingrel, J.B.; Kuntzweiler, T. Na+,K+-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 19659–19662. [Google Scholar]
- Mercer, R.W. Structure of the Na+,K+-ATPase. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1993, 137, 139–168. [Google Scholar]
- Pressley, T.A. Structure and function of the Na+,K+ pump: ten years of molecular biology. Miner. Electrolyte Metab. 1996, 22, 264–271. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, D.C.; Forte, J.G. Functional significance of the β subunit for heterodimeric P-type ATPases. J. Exp. Biol. 1995, 198, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lutsenko, S.; Kaplan, J.H. An essential role for the extracellular domain of the Na+,K+-ATPase beta-subunit in cation occlusion. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 6737–6743. [Google Scholar]
- Beguin, P.; Wang, X.; Firsov, D.; Puoti, A.; Claeys, D.; Horisberger, J.D.; Geering, K. The gamma subunit is a specific component of the Na+,K+-ATPase and modulates its transport function. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 4250–4260. [Google Scholar]
- Minor, N.T.; Sha, Q.; Nichols, C.G.; Mercer, R.W. The gamma subunit of the Na+,K+-ATPase induces cation channel activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6521–6525. [Google Scholar]
- Scheiner-Bobis, G.; Fahlbusch, K.; Schoner, W. Demonstration of cooperating subunits in working (Na++K+)-ATPase by the use of the MgATP complex analogue cobalt tetrammine ATP. J. Biochem. 1987, 168, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Scheiner-Bobis, G.; Buxbaum, E.; Schoner, W. The Na+, K+-Pump, Part A: Molecular Aspects; Skou, J.C., Nørby, J.G., Maunsbach, A.B., Esmann, M., Eds.; Alan. R. Liss, Inc.: New York, 1988; pp. 219–226. [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren, M.; Wagg, J.; Bezanilla, F.; Rakowski, R.F.; De Weer, P.; Gadsby, D.C. Three distinct and sequential steps in the release of sodium ions by the Na+/K+-ATPase. Nature 2000, 403, 898–901. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, J.H. Biochemistry of Na+,K+-ATPase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 511–535. [Google Scholar]
- Levenson, R. Isoforms of the Na+,K+-ATPase: family members in search of function. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1994, 123, 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Lingrel, J.B.; Orlowsky, J.; Shull, M.M.; Price, E.M. Molecular genetics of Na+,K+-ATPase. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1990, 38, 37–89. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, G.; Mercer, R.W. Isozymes of the Na+,K+-ATPase: heterogeneity in structure, diversity in function. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 1998, 275, 633–650. [Google Scholar]
- Crambert, G.; Hasler, U.; Beggah, A.T.; Yu, C.; Modyanov, N.N.; Horisberger, J.D.; Lelièvre, L.; Geering, K. Transport and Pharmacological Properties of Nine Different Human Na+,K+-ATPase Isozymes. J Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 1976–1986. [Google Scholar]
- Crambert, G.; Schaer, D.; Roy, S.; Geering, K. New molecular determinants controlling the accessibility of ouabain to its binding site in human Na+,K+-ATPase alpha isoforms. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 65, 335–341. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, G. Na+,K+-ATPase subunit heterogeneity as a mechanism for tissue-specific ion regulation. Semin. Nephrol. 2005, 25, 292–303. [Google Scholar]
- Lingrel, J.; Williams, M.; Vorhees, C.; Moseley, A. Na+,K+-ATPase and the role of alpha isoforms in behavior. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2007, 39, 385–389. [Google Scholar]
- Lingrel, J.; Moseley, A.; Dostanic, I.; Cougnon, M.; He, S.; James, P.; Woo, A.; O'Connor, K.; Neumann, J. Functional roles of the alpha isoforms of the Na,K-ATPase. Ann. N Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 986, 354–359. [Google Scholar]
- Wagoner, K.; Sanchez, G.; Nguyen, A-N.; Enders, G.C.; Blanco, G. Different expression and activity of the α1 and α4 isoforms of the Na+,K+-ATPase during rat male germ cell ontogeny. Reproduction 2005, 130, 627–641. [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Ehmsen, J.; McDonough, A.A.; Farley, R.A.; Schwinger, R.H. Sodium pump isoform expression in heart failure: implication for treatment. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2002, 97, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, G. Na,K-ATPase subunit heterogeneity as a mechanism for tissuespecific ion regulation. Semin. Nephrol. 2005, 25, 292–303. [Google Scholar]
- Espineda, C.E.; Chang, J.H.; Twiss, J.; Rajasekaran, S.A.; Rajasekaran, A.K. Repression of Na,K-ATPase beta1-subunit by the transcription factor snail in carcinoma. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 1364–1373. [Google Scholar]
- Mijatovic, T.; Roland, I.; Van Quaquebeke, E.; Nilsson, B.; Mathieu, A.; Van Vynckt, F.; Darro, F.; Blanco, G.; Facchini, V.; Kiss, R. The alpha1 subunit of the sodium pump could represent a novel target to combat non-small cell lung cancers. J. Pathol. 2007, 212, 170–179. [Google Scholar]
- Mijatović, T.; Van Quaquebeke, E.; Delest, B.; Debeir, O.; Darro, F.; Kiss, R. Cardiotonic steroids on the road to anti-cancer therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1776, 32–57. [Google Scholar]
- Lefranc, F.; Mijatović, T.; Kondo, Y.; Sauvage, S.; Roland, I.; Krstić, D.; Vasić, V.; Gailly, P.; Kondo, S.; Blanco, G.; Kiss, R. Targeting the α1 subunit of the sodium pump to combat glioblastoma cells. Neurosurgery 2008, 62, 211–222. [Google Scholar]
- Mijatovic, T.; Ingrassia, L.; Facchini, V.; Kiss, R. Na+/K+-ATPase α subunits as new targets in anticancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2008, 12, 1403–1417. [Google Scholar]
- Inge, L.J.; Rajasekaran, S.A.; Yoshimoto, K.; Mischel, P.S.; McBride, W.; Landaw, E.; Rajasekaran, A.K. Evidence for a potential tumor suppressor role for the Na+,K+-ATPase beta1-subunit. Histol. Histopathol. 2008, 23, 459–467. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Askari, A. Na+/K+-ATPase as a signal transducer. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 2434–2439. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Cai, T. Na+-K+-ATPase-mediated signal transduction: From protein interaction to cellular function. Mol. Interv. 2003, 3, 157–168. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, O. Interaction of cardiac glycosides with (Na2+, K+)-activated ATPase. A biochemical link to digitalis-induced intropy. Pharmacol. Rev. 1984, 36, 143–163. [Google Scholar]
- Doris, P.A. Endogenous inhibitors of the Na+,K+ pump. Miner. Electrolyte Metab. 1996, 22, 303–310. [Google Scholar]
- Prassas, I.; Diamandis, E.P. Novel therapeutic applications of cardiac glycosides. Natur. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 926–935. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, B.; Chaudhury, S. Thyroidal regulation of different isoforms of Na+,K+-ATPase in the primary cultures of neurons derived from fetal rat brain. Life Sci. 2002, 71, 1643–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Lima Santos, H.; Fortes Rigos, C.; Ciancaglini, P. Kinetics behaviors of Na+,K+-ATPase: Comparison of solubilized and DPPC:DPPE-liposome reconstituted enzyme. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmcol. 2006, 142, 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Rasić-Marković, A.; Krstić, D.; Vujović, Z.; Jakovljević, V.; Stanojlović, O.; Hrnčić, D.; Djurić, D.; Lončar-Stevanović, H. Modulations of rabbit erythrocyte ATPase activities induced by in vitro and in vivo exposure to ethanol. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 308, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, W.E.; Costa, L.G. Na+/K+-ATPase in rat brain and erythrocytes as a possible target and marker, respectively, for neurotoxicity: studies with chlordecone, organotins and mercury compounds. Toxicol. Lett. 1990, 51, 175–188. [Google Scholar]
- Cano, N.J.; Sabouraud, A.E.; Debray, M.; Scherrmann, J.M. Dose-dependent reversal of digoxin-inhibited activity of an in vitro Na+,K+-ATPase model by digoxin-specific antibody. Toxicol. Lett. 1996, 85, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Carfagna, M.A.; Ponsler, G.D.; Muhoberac, B.B. Inhibition of ATPase activity in rat synaptic plasma membranes by simultaneous exposure to metals. Chem-Biol. Interact. 1996, 100, 53–65. [Google Scholar]
- Lucchesi, P.A.; Sweadner, K.J. Postnatal changes in Na+,K+-ATPase isoform expression in rat cardiac ventricle. Conservation of biphasic ouabain affinity. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 9327–9331. [Google Scholar]
- Thévenod, F.; Friedmann, J.M. Cadmium-mediated oxidative stress in kidney proximal tubule cells induces degradation of Na+/K+-ATPase through proteasomal and endo-lysosomal proteolytic pathways. FASEB J. 1999, 13, 1751–1761. [Google Scholar]
- Thévenod, F. Nephrotoxicity and the proximal tubule. Insights from cadmium. Nephron Physiol. 2003, 93, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Duchnowicz, P.; Szczepaniak, P.; Koter, M. Erythrocyte membrane protein damage by phenoxyacetic herbicides and their metabolites. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2005, 82, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Melero, C.P.; Maderade, M.; Feliciano, A.S. A Short Review on Cardiotonic Steroids and Their Aminoguanidine Analogues. Molecules 2000, 5, 51–81. [Google Scholar]
- Esmann, M. ATPase and phosphatase activity of Na+,K+-ATPase: Molar and specific activity, protein determination. Methods Enzymol. 1988, 156, 105–115. [Google Scholar]
- Swann, A.C.; Steketee, J.D. Subacute noradrenergic agonists infusions in vivo increase Na+,K+-ATPase and ouabain binding in rat cerebral cortex. J. Neurochem. 1989, 52, 1598–1604. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, P.K. A Quick Assay for Na+-K+-ATPase Specific Activity. Z. Naturforsch. 2002, 57c, 562–564. [Google Scholar]
- Pullman, M.E.; Penefsky, H.S.; Datta, A.; Racker, E. Partial Resolution of the Enzymes Catalyzing Oxidative Phosphorylation. I. Purification and Properties of Soluble, Dinitrophenol-stimulated Adenosine Triphosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 1960, 235, 3322–3329. [Google Scholar]
- Debruyne, I. Inorganic Phosphate Determination: Colorimetric Assay Based on the Formation of a Rhodamine B-Phosphomolybdate Complex. Anal. Biochem. 1983, 130, 454–460. [Google Scholar]
- White, H.D. Special instrumentation and techniques for kinetic studies of contractile systems. Methods Enzymol. 1982, 85, 698–708. [Google Scholar]
- Stolz, M.; Lewitzki, E.; Mantele, W.; Barth, A.; Grell, E. Inhibition and partial reactions of Na+,K+-ATPase studied by Fourier Transform Infrared Difference Spectroscopy. Biopolymers 2006, 82, 368–372. [Google Scholar]
- Khaw, B.; Rammohan, R.; Abu-Taha, A. Bispecific Enzyme-Linked Signal-Enhanced Immunoassay with Subattomole Sensitivity. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2005, 3, 319–327. [Google Scholar]
- Doucet, A.; Katz, A.I.; Morel, F. Determination of Na-K-ATPase activity in single segments of the mammalian nephron. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 1979, 237, F105–F113. [Google Scholar]
- Pennial, R. An improved method for the determination of inorganic phosphate by the isobutanol-benzene extraction. Procedure. Anal. Biochem. 1966, 14, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- www.bioassaysys.com
- Krstić, D.; Krinulović, K.; Spasojević-Tišma, V.; Joksić, G.; Momić, T.; Vasić, V. Effects of digoxin and gitoxin on the enzymatic activity and kinetic paramethers of Na+,K+-ATPase. J. Enz. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2004, 19, 409–415. [Google Scholar]
- Nenchay, B.R. Inhibition of adenosine triphosphatases by gold. Arthritis. Rheum. 1980, 23, 464–470. [Google Scholar]
- Nayeemunnisa, B.P.M. Effect of methyl parathion on Na+-K+ and Mg2+ adenosine triphosphatase activity in developing central nervous system in rats. Ind. J. Exp. Biol. 1993, 31, 785–787. [Google Scholar]
- Cantley, L.C. Effects of pyridoxal phosphate treatment on the (Na+,K+)-ATPase. Curr. Top. Bioenerg. 1981, 11, 201–237. [Google Scholar]
- Balzan, S.; D'urso, G.; Ghione, S.; Martinelli, A.; Montali, U. Selectiv inhibition of human erythrocyte Na+,K+-ATPase cardiac glycoside and by mammalian digitalis like factor. Life Sci. 2000, 67, 1921–1928. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, R.; Gray, P.; Andrews, J. Digitalis: Its mode of action, receptor, and structure-activity relationship. Adv. Drug Res. 1990, 19, 312–562. [Google Scholar]
- Almotrefi, A.A.; Basco, C.; Moorji, A.; Dzimiri, N. Class I antiarrhytmic drug effects on uabain binding to quinea pig cardiac Na+,K+-ATPase. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1999, 77, 866–870. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.W.; Ho, C.S.; Swaminathan, R. The chronic effecs of long-term digoxin administration on a Na+/K+-ATPase activity in rat tissue. Int. J. Cardiol. 1993, 40, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Krstic, D.; Tomic, N.; Krinulovic, K.; Vasic, V. Effects of potassium modulations on digoxin – induced inhibition of porcine cerebral cortex Na,K-ATPase. Iugoslav. Physiol. Pharmacol. Acta 2003, 39(1), 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, J.; Lloyd, B.L.; Taylor, R.R. The Influence of Heart Rate on Digoxin-induced Inhibition of Myocardial Na+-K+-ATPase Activity in the Dog. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2007, 8, 283–286. [Google Scholar]
- Qing-Feng, T.; Soszynski, P.A.; Hollenberg, N.K.; Graves, S.W. Specificity of the volume-sensitive sodium pump inhibitor isolated from human peritoneal dialysate in chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 1996, 49, 420–429. [Google Scholar]
- Horvat, A.; Momić, T.; Banjac, A.; Petrović, S.; Nikezić, G.; Demajo, M. Selective inhibition of brain Na,K-ATPase by drugs. Physiol. Res. 2006, 55, 325–338. [Google Scholar]
- Post, R.I.; Merit, C.R.; Kosolving, C.R.; Albbright, C.D. Membrane adenosine triphosphatase as a participant in the active transport of sodium and potasium in the erythrocyte. J. Biol. Chem. 1960, 235, 1796–1802. [Google Scholar]
- Peković, S.; Nedeljković, N.; Nikezić, G.; Horvat, A.; Stojiljković, M.; Rakić, L.; Martinović, J.V. Biochemical characterization of the hippocampal and striatal Na,K-ATPase reveals striking differences in kinetic properties. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 1997, 16, 227–240. [Google Scholar]
- Acuna Castroviejo, D.; Del Aguila, C.M.; Fernandez, B.; Gomar, M.D.; Castillo, J.L. Characterization of ouabain high-affinity binding to rat cerebral cortex. Modulation by melatonin. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 226, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzoni, M.R.; Martini, C.; Lucacchini, A. [3H]ouabain binding to ox brain membranes: characterization of a high-affinity binding site. Neurochem. Int. 1990, 16, 193–197. [Google Scholar]
- Teiple, J.; Koshland, D.E. The significance of intermediary plateau regions in enzyme saturation curves. Biochemistry 1969, 8, 4656–4663. [Google Scholar]
- Molinoff, P.B.; Wolfe, B.B.; Weiland, G.A. Quantitative analysis of drug receptor interactions. II. Determination of the properties of receptor subtypes. Life Sci. 1981, 29, 427–443. [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen, P.L. Purification and characterization of (Na+ plus K+)-ATPase. IV. Estimation of the purity and of the molecular weight and polypeptide content per enzyme unit in preparations from the outer medulla of rabbit kidney. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1974, 356, 53–67. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, A.; Lindenmayer, G.E.; Allen, J.C. The Sodium-Potassium Adenosine Triphosphatase: Pharmacological, Physiological and Biochemical Aspects. Pharmacol. Rev. 1975, 27, 3–134. [Google Scholar]
- Wallick, E.T.; Schwartz, A. Interaction of cardiac glycosides with Na+,K+-ATPase. Methods Enzymol. 1998, 156, 201–213. [Google Scholar]
- Burt, S.K.; Mackay, D.; Hagler, A.T. Computer-aided Drug Design: Methods and Applications; Perun, T.J., Propts, C.L., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, 1989; pp. 55–91. [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld, W.; Schonfeld, R.; Menke, K.H.; Weiland, J.; Repke, K.R.H. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1986, 35, 3221–3231.
- Jortani, S.A.; Helm, R.A.; Valdes, R., Jr. Inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase by oleandrin and oleandrigenin, and their detection by digoxin immunoassay. Clin. Chem. 1996, 42, 1654–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Laricchia-Robbio, L.; Balzan, S.; Ghione, S.; Montali, U.; Revoltella, R.P. Detection of digitalis compounds using a surface plasmon resonance-based biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1998, 13, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Goto, A.; Yamada, K.; Yagi, N.; Yoshioka, M.; Sugimoto, T. Physiology and pharmacology of endogenous digitalis-like factors. Pharmacol. Rev. 1992, 44, 377–399. [Google Scholar]
- Hamlyn, J.M.; Hamilton, B.P.; Manunta, P. Endogenous ouabain, sodium balance and blood pressure: a review and a hypothesis. J. Hypertens. 1996, 14, 151–168. [Google Scholar]
- Van Quaquebeke, E.; Mahieu, T.; Dumont, P.; Dewelle, J.; Ribaucour, F.; Simon, G.; Sébastien Sauvage, S.; Gaussin, J.; Tuti, J.; El Yazidi, M.; Van Vynckt, F.; Mijatovic, T.; Lefranc, F.; Darro, F.; Kiss, R. 2,2,2-Trichloro-N-({2-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-1,3-dioxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo [de] isoquinolin- 5-yl}carbamoyl)acetamide (UNBS3157), a Novel Nonhematotoxic Naphthalimide Derivative with Potent Antitumor Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 4122–4134. [Google Scholar]
- Mijatovic, T.; Lefranc, F.; Van Quaquebeke, E.; Van Vynckt, F.; Darro, F.; Kiss, R. UNBS1450: A new hemi-synthetic cardenolide with promising anti-cancer activity. Drug. Dev. Res. 2007, 68, 164–173. [Google Scholar]
- Jakupec, M.A.; Galanski, M.; Keppler, B.K. Tumour-inhibiting platinum complekses-state of the art and future perspectives. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 146, 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Eastman, A. Cisplatin. Chemistry and Biochemistry of a Leading Anticancer Drug, the Mechanism of Action of Cisplatin: From Adducts to Apoptosis; Lippert, B., Ed.; V.H.C.A., Wiley-VCH: Zurich, 1999; pp. 111–134. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, S.K. A histochemical approach to the mechanism of action of cisplatin and its analogues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1993, 41, 1053–1073. [Google Scholar]
- Gullo, J.J.; Litterst, C.L.; Maguire, P.J.; Sikic, B.I.; Hoth, D.F.; Woolley, P.V. Pharmacokinetics and protein binding of cis-dichlorodiammine platinum (II) administered as a one hour or as a twenty hour infusion. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1985, 5, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Krinulović, K.; Bugarčić, Ž.; Vrvić, M.; Krstić, D.; Vasić, V. Prevention and recovery of (μ3-diethylentriamino)-chloro-palladium(II)-chloride induced inhibition of Na/K-ATPase by SH containing ligands – L-cysteine and glutathione. Toxicol. In Vitro 2006, 20, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Krinulović, K.S.; Vasić, V.M. Interaction of some Pd (II) complexes with Na+/K+-ATPase: Inhibition, kinetics, prevention and recovery. J. Enz. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2006, 21, 459–465. [Google Scholar]
- Vasić, V.; Krinulović, K.; Krstić, D.; Momić, T.; Horvat, A. ATPases as multi-response sensing system for various organic and inorganic analytes. Monatsh. Chem. 2004, 135, 605–614. [Google Scholar]
- Vujsić, Lj.; Krstić, D.; Krinulović, K.; Vasić, V. The influence of transition and heavy metal ions on ATP-ases activity in rat synaptic plasma membranes. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2004, 69, 541–547. [Google Scholar]
- Vasić, V.; Jovanović, D.; Horvat, A.; Momić, T.; Nikezić, G. Effect of Cd and Hg on the activity of Na,K-ATPase and Mg-ATPase adsorbed on polystirene Microtiter Plates. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 300, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Vasić, V.; Živanović, M.; Čakar, M.; Savić, J.; Nedeljković, J.; Bugarčić, Ž. Influence of acidity on the reaction between [PdCl(dien)] and L-cysteine or GSH in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate micelles. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2005, 18, 441–447. [Google Scholar]
- Sakakibara, N.; Suzuki, K.; Kaneta, H.; Yoshimura, Y.; Deyama, Y.; Matsumoto, A.; Fukuda, H. Inhibition of Na, K-ATPase by cisplatin and its recovery by 2-mercaptoethanol in human squamous cell carcinoma cells. Anti-cancer Drugs 1999, 10, 203–211. [Google Scholar]
- Neault, J.F.; Benkirane, A.; Malonga, H.; Tajmir-Riahi, H.A. Interaction of cisplatin drug with Na+,K+-ATPase: drug binding mode and protein secondary structure. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2001, 86, 603–609. [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto, S.; Kawazoe, Y.; Ikeno, M.; Saitoh, M.; Nakano, Y.; Nishi, Y.; Fukushima, S.; Takuchi, Y. Role of Na+, K+-ATPase α1 subunit in the intracellular accumulation of cisplatin. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2006, 57, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Sastre, J.; Sahuquillo, A.; Vidal, M.; Rauret, G. Determination of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in environmental samples: microwave-assisted total digestion versus aqua regia and nitric acid extraction. Anal. Chem. Acta 2002, 462, 59–72. [Google Scholar]
- Chetty, C.S.; Rajanna, B.; Rajanna, S. Inhibition of rat barain microsomal Na,K-ATPase and ouabain binding by mercuric chloride. Toxicol. Lett. 1990, 51, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Bose, S.; Mukhopadhyay, B.; Sarkar, D.; Das, D.; Bandyopadhyay, J.; Bose, R.; Majmudar, C.; Mondal, S.; Sen, S. Specific binding of inorganic mercury to Na+,K+-ATPase in rat liver plasma membrane and signal transduction. BioMetals 1997, 10, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Vasić, V.; Jovanović, D.; Krstić, D.; Nikezć, G.; Horvat, A.; Vujsić, Lj.; Nedeljković, N. Prevention and recovery of CuSO4-induced inhibition of Na+/K+-ATPase and Mg2+-ATPase in rat brain synaptosomes by EDTA. Toxicol. Lett. 1999, 110, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Schoot, B.M.; Van Emst-De Vries, S.E.; Van Haard, P.M.; DePont, J.J.; Bonting, S.L. Studies on (Na/K+)-activated ATPase. XLVI. Effect of cation-induced conformational changes in sulfhydryl group modification. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1980, 602, 144–154. [Google Scholar]
- Schoot, B.M.; DePont, J.J.; Bonting, S.L. Studies on (Na+/K+)-activated ATPase. XLVI. Evidence of two classes of essential sulfhydryl groups. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1978, 522, 602–613. [Google Scholar]
- Momić, T.; Vujčić, Z.; Vasić, V.; Horvat, A. Immobilization of Na+,K+-ATPase isolated from rat brain synaptic plasma membranes. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2002, 67, 809–817. [Google Scholar]
- Sillen, L.G.; Martell, A.E. Stability constants of metal-ion complexes; Special Publication No. 1, Chem. Soc.: London, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, B.R. Bioorganic chemistry of toxicity. Handbook on toxicity of Inorganic compounds; Seiler, H.G., Sigel, H., Siegel, A., Eds.; Dekker: New York, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Vasić, V.; Kojić, D.; Krinulović, K.; Čolović, M.; Vujačić, A.; Stojić, D. Time Dependent Inhibition of Na+/K+-ATPase Induced by Single and Simultaneous Exposure to Lead and Cadmium. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 81, 1402–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Saracci, R.; Kogevinas, M.; Bertazzi, P.A.; Bueno de Mesquita, B.H.; Coggon, D.; Green, L.M.; Kauppinen, T.; L'Abbé, K. A.; Littorin, M.; Lynge, E.; Mathews, J.D.; Neuberger, M.; Osman, J.; Pearce, N. Cancer mortality in workers exposed to chlorophenoxy herbicides and chlorophenols. Lancet 1991, 338, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Duchnowicz, P.; Szczepaniak, P.; Koter, M. Erytrocyte membrane protein damage by phenoxyacetic and their maetabolites. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol 2005, 82, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Suwalsky, M.; Benites, M.; Villena, F.; Aguilar, F.; Sotomayor, C.P. Interaction of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) with cell and model membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1285, 267–276. [Google Scholar]
- Giraud, F.; Claret, R.; Garay, R. Interaction of cholesterol with the Na pump in red blood cells. Nature 1976, 264, 646–648. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda, K.; Nishio, I.; Masuyama, Y. Triphosphatase in the regulation of membrane fluidity of erythrocyte in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 1997, 10, 1411–1414. [Google Scholar]
- Kimelberg, H.K.; Papahadjopoulos, D. Phospolipid requirements for (Na+/K+)-ATPase activity: head group specificity and fatty acid fluidity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1972, 282, 277–292. [Google Scholar]
- Rohn, T.T.; Hinds, T.R.; Vincenzi, F.F. Inhibition of Ca2+-pump and the Na+/K+-ATPase by iron-generated free radicals. Protection by 6,7-dimethyl-2,4-DI-1-1-pyrrolidinyl-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine sulfate (U-89842D), a potent, novel, antioxidant/free radical scavenger. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1996, 51, 471–476. [Google Scholar]
- Duchnowicz, P.; Koter, M.; Duda, W. Damage of erytrocyte by phenoxyacetic herbicides and their metabolites. Pest. Biochem. Physiol 2002, 74, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Ichikawa, K.; Utsumi, H. Quantitative analysis for the enhancment of hydroxyl radical generation by phenols during ozonation of water. Water Res. 1998, 11, 3261–3266. [Google Scholar]
- Cascorbi, I.; Foret, M. Interaction of xenobiotics on the glucose-transport system and the Na+/K+ ATPase of human skin fibroblasts. Ecotoxicol Environ. Saf. 1991, 1, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.C.; Keizer, R.F.; Ambrose, W.; Breese, G.R. Effects of 2,4,5– trichlorophenoxyacetic acid and quinolinic acid on 5-hydroxy-3-indoleacetic acid transport by the rabbit choroids plexus: pharmacology and electron microscopic chemistry. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1987, 3, 436–444. [Google Scholar]
- Gevondyan, N.M.; Gevondyan, V.S.; Gavrilyeva, E.E.; Modyanov, N.N. Analysis of free sulfhydryl groups and disulfide bonds in Na+,K+-ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1989, 255, 265–268. [Google Scholar]
- Jinna, R.R.; Uzodinma, J.E.; Desaiah, D. Age related changes in rat brain ATPases during treatment with chlordecone. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 1989, 27, 199–208. [Google Scholar]
- Desaiah, D. Biochemical mechanisms of chlordecone neurotoxicity: A review. Neurotoxicology 1982, 3, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Rajanna, B.; Hobson, M. Influence of mercury on uptake of [3H]dopamine and [3H]norepinephrine by rat synaptosomes. Toxicol. Lett. 1985, 27, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ballatori, N.; Chenyang, S.; Boyer, J.L. Altered plasma ion permeability in mercury-induced cell injury, studies in hepatocytes of easmobranch Raja erinacea. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1988, 95, 279–291. [Google Scholar]
- Kostyniak, P.J.; Clarkson, T.W.; Cestero, R.V.; Freeman, R.B.; Abbasi, A.H. An extracorporeal complexing hemodialysis system for the treatment of methylmercury poisoning. I. In vitro studies of the effects of four complexing agents on the distribution and dialyzability of methylmercury in human blood. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1975, 192, 260–269. [Google Scholar]
- Dierkes-Tizek, U.; Glaser, U.; Oldiges, H.; Hetwer, H. Wirkung von Organophosphaten auf Herz –ATPasen von Ratten. Drug Res. 1984, 34, 671–678. [Google Scholar]
- Robineau, P.; Leclerq, Y.; Gerbi, A.; Berrebi-Bertrand, I.; Lelievre, L.G. An organophosphorus com pound,Vx, selectively inhibits the rat cardiac Na+, K+-ATPase α1 isoform. FEBS Lett. 1991, 281, 145–148. [Google Scholar]
- Imamura, T.; Hasegawa, L. Effects of an impurity of malathion and its structural analog on rat liver carboxylesterases and erythrocyte esterases. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 1984, 22, 312–320. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Sandhir, R.; Kiran, R. Erythrocyte antioxidant enzymes in toxicological evaluation of commonly used organophosphate pesticides. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 44, 580–583. [Google Scholar]
- Jarmillo-Juarez, F.; Rio Posadasdel, F.A.; Reyes, J.L.; Rodriguez, L.; Sanchez, E.I.; Cuellar, L.H. Effects of intrauterine exposure to parathion on the activity of renal ATPase in offspring. J. Appl. Toxicol. 1989, 9, 401–405. [Google Scholar]
- Blasiak, J. Allosteric inhibition of the (Na+/K+)-ATPase by Parathion and Methylparathion. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 1996, 54, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Riedel, B.; Christenson, G. Effect of selected water toxicants and other chemicals upon adenosine triphosphatase activity in vitro. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1979, 23, 365–368. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.F.; Siddiqui, M.K.J.; Jamil, K. Inhibition of Acetylcholinesterase and Different ATPases by a Novel Phosphorothionate (RPR-II) in Rat Brain. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2000, 47, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Desaiah, D. Comparative effects of chlordecone and mirex on rat cardiac ATPases and binding of H-catecholamines. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. 1980, 4, 237–248. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, S.K.; Desaiah, D. Effects of chlordecone and its structural analogs on p-nitrophenyl phosphatase. Toxicol. Lett. 1982, 12, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Desaiah, D. Interaction of chlordecone with biological membranes. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 1981, 8, 719–730. [Google Scholar]
- Hartimeier, W. Immobilisierte Biokatalysatoren; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Schwedt, G.; Stein, K. Immobilized enzymes as tools in food analysis. Z. Lebensm. Unters. Forsch. 1994, 199, 171–182. [Google Scholar]
- Grazú, V.; Abian, O.; Mateo, C.; Batista-Viera, F.; Fernández-Lafuente, R.; Guisán, J.M. Stabilization of enzymes by multipoint immobilization of thiolated proteins on new epoxy-thiol supports. Biotechnol. Bioengineer. 2005, 90, 597–605. [Google Scholar]
- Vamvakaki, V.; Chaniotakis, N.A. Immobilization of enzymes into nanocavities for the improvement of biosensor stability. Biosens. Bioelecton. 2007, 22, 2650–2655. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.C.; Kang, D.J. Molecular recognition and specific interactions for biosensing applications. Sensors 2008, 8, 6605–6641. [Google Scholar]
- Nagamune, H.; Urayama, O.; Hara, Y.; Ota, F.; Hirota, K.; Satomi, Y.; Seo, K.; Fukui, K.; Nakao, M. Directional immobilization of sodium- and potassium-activated ATPase to expose its cytoplasmic part to the liquid phase on microtiter plates by wheat germ agglutinin. Anal. Biochem. 1989, 180, 362–367. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlak, M.; Grell, E.; Schick, E.; Anselmetti, D.; Ehrat, M. Functional immobilization of biomembrane fragments on planar waveguides for the investigation of side-directed ligand binding by surface-confined fluorescence. Faraday Discuss. 1998, 111, 273–288. [Google Scholar]
- Linder, A.; Weiland, U.; Apell, H.U. Novel polymer substrates for SFM investigations of living cells, biological membranes, and proteins. J. Struct. Biol. 1999, 126, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplya, A.; Kravtsova, V.V.; Kravtsov, A.V. Inactivation of brain Na+,K+-ATPase catalytic subunit isoforms by sodium dodecyl sulfate. Membr. Cell Biol. 1997, 11, 87–99. [Google Scholar]
- Vale-Gonzalez, C.; Pazos, M.J.; Alfonso, A.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Study of neuronal effects of ouabain and palytoxin and their binding to Na,K-ATPases using an optical biosensor. Toxicon 2007, 50, 541–552. [Google Scholar]
- Shahedi, M.; Laborde, K.; Lelongt, B.; Oudar, O.; Sachs, C. A cytochemical procedure for determination of Na+,K+-ATPase activity in MDCK cells. Kidney Int. 1992, 41, 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- LeBel, D.; Poirier, G.G.; Beaudoin, A.R. A convenient method for the ATPase assay. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 85(1), 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, D.; Watts, A.; Pates, R.D.; Uhl, R. ESR Spin-label Studies of Lipid-Protein Interactions in Membranes. Biophys. J. 1982, 37, 265–274. [Google Scholar]
- Sudo, J.; Terui, J.; Iwase, H.; Kakuno, K. Assay of ATPase and Na+,K+-ATPase activity using high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of ADP derived from ATP. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2000, 744(1), 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Palma, F.; Ligi, F.; Soverchia, C.; Fioritti, A. HPLC method for measuring (Na+-K+) ATPase and (Ca+-Mg2+) ATPase in erythrocytes from different species of mammals. Boll. Soc. Ital. Biol. Sper. 1991, 67(8), 759–66. [Google Scholar]
- Savić, J.; Krinulović, K.; Momić, T.; Čolovic, M.; Vujačić, A. Application of ultra performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) for determination of Na,K-ATPase activity. Proceedings of the 9th international Conference on Fundamental and Applied aspects of Physical Chemistry; Antić Jovanović, A., Ed.; Society of Physical Chemists of Serbia: Belgrade,Serbia, 2008; pp. 36–38. [Google Scholar]
- Nedeljković, N.; Horvat, A. One-step Bioluminescence ATPase Assay for the Evaluation of Neurotoxic Effects of Metal Ions. Monatsh. Chem. 2007, 138, 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, M.R. A continuous Spectrophotometric assay for inorganic phosphate and for measuring phosphate release kinetics in biological systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1992, 89(11), 4884–4887. [Google Scholar]
- Henkel, R.D.; VandeBerg, J.L.; Walsh, R.A. A microassay for ATPase. Anal. Biochem. 1988, 169, 312–318. [Google Scholar]
- González-Romo, P.; Sánchez-Nieto, S.; Gavilanes-Ruíz, M. A Modified Colorimetric Method for the Determination of Orthophosphate in the Presence of High ATP Concentrations. Anal. Biochem. 1992, 200, 235–238. [Google Scholar]
- Hegyvary, C.; Jorgensen, P.L. Conformational changes of renal sodium plus potassium ion-transport adenosine triphosphatase labeled with fluorescein. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 6296–6303. [Google Scholar]
- Efendiev, R.; Das-Panja, K.; Cinelli, A.R.; Bertorello, A.M.; Pedemonte, C.H. Localization of intracellular compartments that exchange Na,K-ATPase molecules with the plasma membrane in a hormone-dependent manner. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 151, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen, B.; Birkelund, S.; Jorgensen, P.L. Trafficking of Na+,K+-ATPase Fused to Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein Is Mediated by Protein Kinase A or C. J. Membr. Biol. 2003, 191, 1432–1424. [Google Scholar]
- Samsonova, N.A.; Rozhanets, V.V. Enzymic micromethod of determining membrane Na, K-ATPase activity in the rat cerebral cortex. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 1978, 86, 507–509. [Google Scholar]
- Fortes, P.A.G. Anthroylouabain: a specific fluorescent probe for the cardiac glycoside receptor of the sodium-potassium ATPase. Biochemistry 1977, 16, 531–540. [Google Scholar]
- Fortes, P.A.G. A fluorometric method for the determination of functional Na+,K+-ATPase and cardiac glycoside receptors. Anal. Biochem. 1986, 158(2), 454–462. [Google Scholar]
- Karlish, S.J.D. Na+,K+-ATPase structure and Kinetics; Skou, J.C., Norby, J.G., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, 1979; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Grell, E.; Warmuth, R.; Ruf, H. Ionics and conformational transitions of Na+,K+-ATPase. Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl. 1992, 146, 213–221. [Google Scholar]
- Vasić, V.; Černigoj, U.; Krinulović, K.; Joksić, G.; Franko, M. Evaluation of photochemical degradation of digoxin by Na,K-ATPase assay. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 404–409. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, R.J.; Watts, H.J.; Lowe, C.R.; Buckle, P.E.; Yeung, D.K.T.M.; Pollard-Knight, D.V. Techniques in Protein Chemistry V; Academic Press: San Diego, 1994; pp. 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Taitt, C.R.; Anderson, G.P.; Ligler, F.S. Evanescent wave fluorescence biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 2470–2486. [Google Scholar]
- Soh, N. Selective Chemical Labeling of Proteins with Small Fluorescent Molecules Based on Metal-Chelation Methodology. Sensors 2008, 8, 1004–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Shaner, N.C.; Steinbach, P.A.; Tsien, R.Y. A guide to choosing fluorescent proteins. Nat. Meth. 2005, 2, 905–909. [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Patterson, G.H. Development and use of fluorescent protein markers in living cells. Science 2003, 300, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Sagar, A.; Rakowski, R.F. Access Channel Model for the Voltage Dependence of the Forward-running Na+/K + Pump. J. Gen. Physiol. 1994, 103, 869–894. [Google Scholar]
- Catterall, W.A. From ionic currents to molecular mechanisms: The structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron 2000, 26, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Adorante, J.S.; Ehring, G.R.; Donello, J. High-throughput screen for identifying channel blockers that selectively distinguish transient from persistent sodium channels. US Pat. 6,991,910, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.C.; Gill, S.S.; Gill, R.K. High-throughput screening assay for Na+,K+-ATPase using atomic absorption spectroscopy. US Pat. Appl. 20070092970.












| Inhibitor | IC50 (M) | Tissue | Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiotonic glycosides | ||||
| Ouabain | 1.5×10-9 | cardiac tissue | coupled enzyme assay | [51] |
| 9.4×10-6 | CHO-K1 cells | FRET | [181] | |
| digoxin | a2.5×10-8 | rat brain SPM | coupled enzyme assay | [49] |
| b1.3×10-4 | ||||
| a4.6×10-6 | human erythrocytes | spectrophotometric | [67] | |
| b1.0×10-3 | ||||
| Gitoxin | a2.8×10-7 | human erythrocytes | spectrophotometric | [67] |
| b4.1×10-4 | ||||
| metildigoxin | 2.9×10-3 | rat brain SPM | spectrophotometric | [78] |
| Pharmaceuticals | ||||
| propranolol | 3.7×10-3 | rat brain SPM | spectrophotometric | [78] |
| verapamil | 1.9×10-3 | rat brain SPM | spectrophotometric | [78] |
| oleandrin | rat brain SPM | spectrophotometric | [78] | |
| promethazine | 8.4×10-4 | rat brain SPM | spectrophotometric | [78] |
| Metal ions | ||||
| Cu2+ | 5.9×10-6 | rat brain SPM | bioluminiscence | [163] |
| Hg2+ | 1.1×10-6 | rat brain SPM | immobilized enzyme | [104] |
| Cd2+ | 2.0×10-6 | rat brain SPM | coupled enzyme assay | [118] |
| Pb2+ | 7.0×10-6 | red cell membranes | spectrophotometric | [118] |
| Platinum anticancer drugs | ||||
| [PdCl(dien)]+ | 1.2×10-4 | Porcine cerebral cortex | spectrophotometric | [101] |
| [PdCl4]- | 2.3×10-5 | Porcine cerebral cotrex | spectrophotometric | [101] |
| [AuCl4]- | 6.9×10-5 | dog brain microsomes | spectrophotometric | [68] |
| 5.1×10-5 | human kidney homogenate | |||
| cis-platinum | 7.0×10-4 | Ca9-22 cells | spectrophotometric | [106] |
| Pesticides | ||||
| 2,4-dichlorophenoxy-acetic acid | <4.0×10-3 | Erythrocyte | spectrophotometric | [54] |
| 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxy-acetic acid | <4.0×10-3 | Erythrocyte | spectrophotometric | [54] |
| parathion | a71.0×10-6 | pig kidney | spectrophotometric | [142] |
| b85.0×10-6 | ||||
| Metal ion | IC50 (μM)[103] | Free activation energy (∆G°')(kJ mol-1)[116] | Solubility constant (log Kso)[116] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp. | Calc. | |||
| Fe2+ | 34 | - | 38.9 | -18.7 |
| Co2+ | 168 | 75 | 40.6 | -17.5 |
| Cu2+ | 7.1 | 0.6 | / | -33.9 |
| Zn2+ | 22 | 13 | 29.3 | -24.4 |
| Hg2+ | 0.7 | / | -48.8 | |
| Cd2+ | 1 | / | -27.3 | |
| Pb2+ | 15 | / | -26.7 | |
| Mg2+ | / | 44.3 | / | |
| Na+ | / | 16.7 | / | |
| K+ | / | 14.2 | / | |
| analyte | conc./M | composition of ATPase assaya | target enzyme | relative absorbance (% of control) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Found | Expect.b | ||||
| Na+ | 1×10−2 | K, Mg, EDTA, ATP | Na+/K+-ATPase | 50 ±3 | 47 |
| K+ | 1×10−3 | Na, Mg, EDTA, ATP | Na+/K+-ATPase | 68 ±2 | 65 |
| Mg2+ | 1×10−4 | ATP, EDTA | Mg2+-ATPase | 49 ± 3> | 52 |
| Heavy metalsc | 1×10−5 | Na, K, Mg, ATP | Na+/K+-ATPase | 0±1 | 0 |
| Na, K, Mg, ATP, EDTA | Na+/K+-ATPase | 100 ±1 | 100 | ||
| pyridine | 1×10−3 | Na, K, Mg, ATP, EDTA | Na+/K+-ATPase | 130 ±5 | 130 |
| Mg, ATP, EDTA | Mg2+-ATPase | 120 ±4 | 120 | ||
| urea | 1×10−3 | Na, K, Mg, ATP, EDTA | Mg2+-ATPase | 130 ± 5 | 130 |
| Mg, ATP, EDTA | Mg2+-ATPase | 100 | 100 | ||
| chlorpyrifos | 1×10−5 | Mg, ATP, EDTA | Mg2+-ATPase | 52 ±3 | 50 |
| digoxin | 1×10−6 | Na, K, Mg, ATP, EDTA | Mg2+/K+-ATPasee | 90 ±2 | 90 |
| Mg, ATP, EDTA | Mg2+-ATPase | 100 | 100 | ||
| gitoxin | 1×10−6 | Na, K, Mg, ATP | Na+/K+-ATPase | 35 ±3 | 35 |
| Mg, ATP, EDTA | Mg2+-ATPase | 100 | 100 | ||
| target analyte | sample | labelled content/Ma | found content/Mb |
|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ | mineral water | 1.96× 10−2 | (1 5±0.5)× 10−2 |
| K+ | mineral water | 1.64×10−3 | (2.2±0.4)× l0−3 |
| Mg2+ | mineral water | 2.58×l0−3 | (2.4±0.4)× l0−3 |
| heavy metals | mineral water | - | not found |
| digoxin | LanoxinR injection | 0 32×10−3 | (0.31 ± 0.02) ×10−3 |
© 2008 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasić, V.; Momić, T.; Petković, M.; Krstić, D. Na+,K+-ATPase as the Target Enzyme for Organic and Inorganic Compounds. Sensors 2008, 8, 8321-8360. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8128321
Vasić V, Momić T, Petković M, Krstić D. Na+,K+-ATPase as the Target Enzyme for Organic and Inorganic Compounds. Sensors. 2008; 8(12):8321-8360. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8128321
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasić, Vesna, Tatjana Momić, Marijana Petković, and Danijela Krstić. 2008. "Na+,K+-ATPase as the Target Enzyme for Organic and Inorganic Compounds" Sensors 8, no. 12: 8321-8360. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8128321
APA StyleVasić, V., Momić, T., Petković, M., & Krstić, D. (2008). Na+,K+-ATPase as the Target Enzyme for Organic and Inorganic Compounds. Sensors, 8(12), 8321-8360. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8128321