Hardware Implementation of Multiple Fan Beam Projection Technique in Optical Fibre Process Tomography
Abstract
:1. Process Tomography Overview
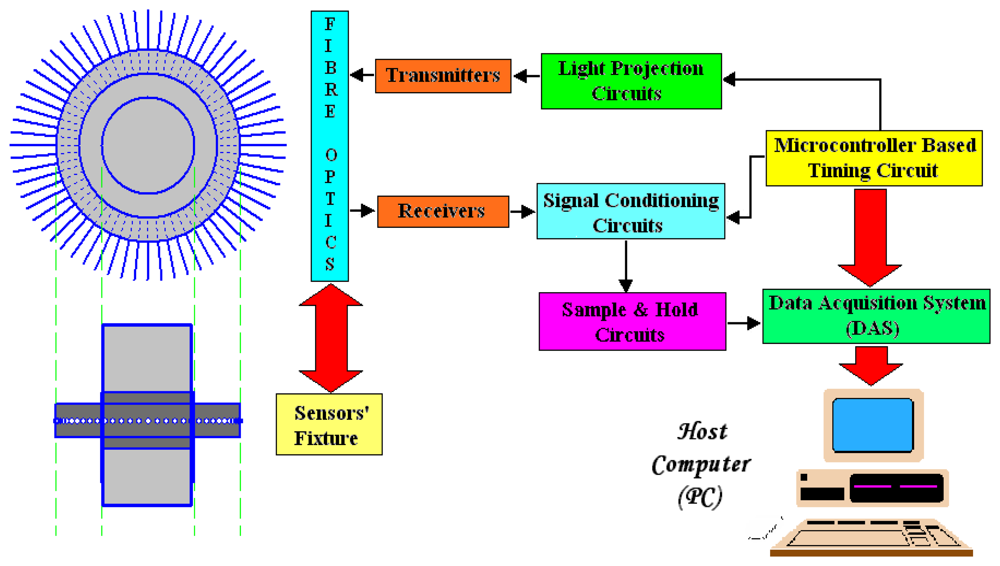
2. Introduction to the Hardware System
3. Selection of Emitters and Receivers
3.1 Preparation of Optical Fibres
- NA = numerical aperture of the fibre optic.
- θA = acceptance angle of the fibre optic.
3.2 Fibre optic coupling
3.3 Optical Fibre Sensor Fixture Design
4. The Signal Processing Circuits
4.1 Infrared Projection Circuit
- Ic = collector current or forward current for the projection circuit.
- Vcc = voltage supply which is 4.5V in this circuit.
- Vf = forward voltage of the SFH484-2 which is 3V as stated in datasheet.
- VCE(sat) = collector-emitter saturation voltage for the ZTX1048A transistor, which is 245mV as stated in datasheet. Rc = resistor with the value of 1Ω.
4.2 Signal Conditioning Circuit
- Vc–v = pre-amp output voltage.
- Ip = photodiode current.
- R1=feedback resistor of 10Ω.
- Vn = voltage at the inverting input.
- Vo = output voltage after the amplifying stage.
- Rf = variable feedback resistor of 500kΩ.
- Rb = resistor of 100kΩ
4.3 Microcontroller signal controlling circuit
4.4 Sample and Hold (S/H) Circuit
5. Data Acquisition Process
6. Results & Discussions
6.1 Measured Signals from Oscilloscope
6.1.1 Photo-sensors
6.1.2 Microcontroller Controlling Signals
6.1.3 Output Voltages
6.1.4 Data Acquisition Rate (DAR)
- DAR = data acquisition rate in frames per second (unit fps).
- Total ConversionTime = the total time needed to convert all the 32 receivers' signals in one frame (either in 2-projection or 4-projection mode).
7. Conclusions
References
- Process Tomography: Principles, techniques and applications; Williams, R.A.; Beck, M.S. (Eds.) 1995; pp. 3–12.
- West, R.M.; Jia, X.; Williams, R.A. Parametric Modelling in Industrial Process Tomography. 1stWorld Congress on Industrial Process Tomography 1999, 444–450. [Google Scholar]
- Ruzairi, A.R. A Tomography Imaging System for Pneumatic Conveyors Using Optical Fibres. Ph.D. Thesis, Sheffield Hallam University, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sallehuddin, I. Measurement of Gas Bubbles in a Vertical Water Column Using Optical Tomography. Ph.D. Thesis, Sheffield Hallam University, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Khoo, B.F. Optical Fibre Sensors for Process Tomography. B.Sc. Thesis, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hisyamuddin, S. Sistem Tomografi Optik Berkejituan Tinggi. B.Sc. Thesis, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, K.S. Time Image Reconstruction for Fan Beam Optical Tomography System. M.Sc. Thesis, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, J.F. Real Time Image Reconstruction for Fan Beam Optical Tomography System. M.Sc. Thesis, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, H.L. Phototransistor. EE210-S00-Lecture 2000, 10, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, K.S.; Ruzairi, A.R. Tomographic Imaging of Pneumatic Conveyor Using Optical Sensor. Proceeding 2ndWorld Engineering Congress in Malaysia 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Van Eijkelenborg, M.A.; Large, M.C.J.; Argyros, A.; Zagari, J.; Manos, S.; Issa, N.A.; Bassett, I.; Fleming, S.; McPhedran, R.C.; de Sterke, C.M.; Nicorovici, N.A.P. Microstructured Polymer Optical Fibre. Optics Express 2001, 9(7), 319–327. [Google Scholar]
- Syms, R.; Cozens, J. Optical Guided Waves and Devices; McGraw-Hill Book Company: United Kingdom, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul Rahim, R.; Chan, K.S.; Pang, J.F.; Leong, L.C. Optical Tomography System Using Switch-Mode Fan Beam Projection: Modelling Techniques. Journal Optical Engineering 2005, 44, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Burr-Brown. Photodiode Monitoring with Op-Amps. Application Bulletin 1995, 1–11.
- Wong, N. CMOS Integrated Photodiode and Low Voltage Transimpedance; University of Toronto, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Philips Semiconductors. 74HC154 4-16 Line Decoder/Demultiplexer; Data Sheet: Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, J.F.; Abdul Rahim, R.; Chan, K.S. Real Time Image reconstruction System Using Two Data Processing Unit in Optical Tomography. Proceeding 3rd International Symposium on Process Tomography in Lodz, Poland; 2004; pp. 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Texas Instruments. SN54HC04 HEX Inverters; Data Sheet: Texas, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tocci, R.J.; Widmer, N.S. Digital Systems: Principles and Applications, 7th ed; Prentice-Hall: United States, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hallmark, C.L.; Horn, D.T. The Master IC Cookbook, 2nd ed; Tab Books: United States, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Philips Semiconductors. 74HC4016 Quad Bilateral Switches; Data Sheet: Netherlands, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, W. Applying IC Sample-Hold Amplifiers; Analog Devices Inc.: U.S., 1995. [Google Scholar]
- National Semiconductor Corporation. Monolithic Sample-and-Hold Circuits; 1995. [Google Scholar]
- National Semiconductor Corporation. Circuit Applications of Sample-Hold.
- Leonard, B. Picking the Right Sample-And-Hold Amp for Various Data-Acquisition Needs; DATEL Inc.: U.S., 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul Rahim, R.; Chan, K.S. Optical Tomography System for Process Measurement Using LED as a Light Source. Journal Optical Engineering 2004, 43(5), 1251–1257. [Google Scholar]


























| CLK Pulse Number | Tx Group (2-projection mode) | Tx Group (4-projection mode) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Tx0, Tx16 | Tx0, Tx16, Tx8, Tx24 |
| 1 | Tx1, Tx17 | Tx1, Tx17, Tx9, Tx25 |
| 2 | Tx2, Tx18 | Tx2, Tx18, Tx10, Tx26 |
| 3 | Tx3, Tx19 | Tx3, Tx19, Tx11, Tx27 |
| 4 | Tx4, Tx20 | Tx4, Tx20, Tx12, Tx28 |
| 5 | Tx5, Tx21 | Tx5, Tx21, Tx13, Tx29 |
| 6 | Tx6, Tx22 | Tx6, Tx22, Tx14, Tx30 |
| 7 | Tx7, Tx23 | Tx7, Tx23, Tx15, Tx31 |
| 8 | Tx8, Tx24 | N/A |
| 9 | Tx9, Tx25 | N/A |
| 10 | Tx10, Tx26 | N/A |
| 11 | Tx11, Tx27 | N/A |
| 12 | Tx12, Tx28 | N/A |
| 13 | Tx13, Tx29 | N/A |
| 14 | Tx14, Tx30 | N/A |
| 15 | Tx15, Tx31 | N/A |
| Projection Mode | Total Conversion time | DAR |
|---|---|---|
| 2-projection | 3.25 ms | 307.69 fps |
| 4-projection | 1.64 ms | 609.76 fps |
© 2008 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the CreativeCommons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahim, R.A.; Rahiman, M.H.F.; Chen, L.L.; San, C.K.; Fea, P.J. Hardware Implementation of Multiple Fan Beam Projection Technique in Optical Fibre Process Tomography. Sensors 2008, 8, 3406-3428. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8053406
Rahim RA, Rahiman MHF, Chen LL, San CK, Fea PJ. Hardware Implementation of Multiple Fan Beam Projection Technique in Optical Fibre Process Tomography. Sensors. 2008; 8(5):3406-3428. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8053406
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahim, Ruzairi Abdul, Mohd Hafiz Fazalul Rahiman, Leong Lai Chen, Chan Kok San, and Pang Jon Fea. 2008. "Hardware Implementation of Multiple Fan Beam Projection Technique in Optical Fibre Process Tomography" Sensors 8, no. 5: 3406-3428. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8053406
APA StyleRahim, R. A., Rahiman, M. H. F., Chen, L. L., San, C. K., & Fea, P. J. (2008). Hardware Implementation of Multiple Fan Beam Projection Technique in Optical Fibre Process Tomography. Sensors, 8(5), 3406-3428. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8053406




