Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistor for Biological Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Operating Principle of FET-Based Biosensors
3. Applications of ISFET Biosensors
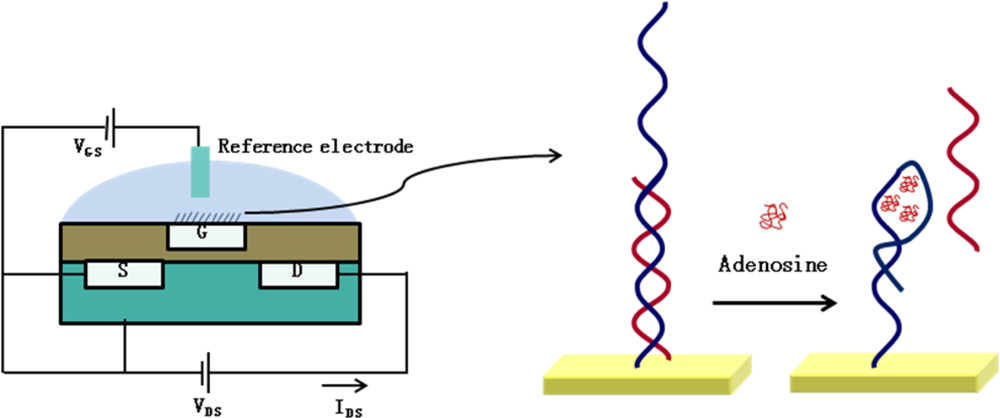
3.1. Applications of DNA-Based ISFET
3.2. Applications ISFET for Electro-Immunological Sensing
3.3. Applications of Enzyme Based-ISFET
3.4. Applications of ISFET for Monitoring Living Cell Responses
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Schöning, M.; Poghossian, A. Recent advances in biologically sensitive field-effect transistors (BioFETs). Analyst 2002, 127, 1137–1151. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, J.; Ito, N.; Kuriyama, T.; Kikuchi, M.; Arai, T.; Negishi, N.; Tomita, Y. A novel blood glucose monitoring method an ISFET biosensor applied to transcutaneous effusion fluid. J. Electrochem. Soc 1989, 136, 1744–1747. [Google Scholar]
- Bergveld, P. Development of an ion-sensitive solid-state device for neurophysiological measurements. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng 1970, 17, 70–71. [Google Scholar]
- Caras, S.; Janata, J. Field effect transistor sensitive to penicillin. Anal. Chem 1980, 52, 1935–1937. [Google Scholar]
- Sedra, A.; Smith, K. Microelectronic Circuits; Oxford University Press: Cary, NC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pijanowska, D.; Torbicz, W. Biosensors for bioanalytical applications. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. - Tech. Sci 2005, 53, 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Schöning, M.; Poghossian, A. Bio FEDs (Field-Effect devices): State-of-the-art and new directions. Electroanalysis 2006, 18, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar]
- Ingebrandt, S.; Han, Y.; Nakamura, A.; Poghossian, A.; Schöning, M.J.; Offenhausser, A. Label-free detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms utilizing the differential transfer function of field-effect transistors. Biosens. Bioelectron 2007, 22, 2834–2840. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtake, T.; Hamai, C.; Uno, T.; Tabata, H.; Kawai, T. Immobilization of Probe DNA on Ta2O5 Thin Film and Detection of Hybridized Helix DNA using IS-FET. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys 2004, 43, L1137–L1139. [Google Scholar]
- Fritz, J.; Cooper, E.; Gaudet, S.; Sorger, P.; Manalis, S. Electronic detection of DNA by its intrinsic molecular charge. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 14142–14146. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Jeong, Y.; Lyu, H.; Park, H.; Kim, H.; Shin, J.; Choi, P.; Lee, J.; Lim, G.; Ishida, M. Fabrication and characteristics of a field effect transistor-type charge sensor for detecting deoxyribonucleic acid sequence. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys 2003, 42, 4111–4115. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.; Kim, D.; Park, H.; Lim, G. Detection of DNA and protein molecules using an FET-type biosensor with gold as a gate metal. Electroanalysis 2004, 16, 1912–1918. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Jeong, Y.; Park, H.; Shin, J.; Choi, P.; Lee, J.; Lim, G. An FET-type charge sensor for highly sensitive detection of DNA sequence. Biosens. Bioelectron 2004, 20, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Park, H.; Jung, H.; Shin, J.; Jeong, Y.; Choi, P.; Lee, J.; Lim, G. Field Effect Transistor-based Bimolecular Sensor Employing a Pt Reference Electrode for the Detection of Deoxyribonucleic Acid Sequence. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys 2004, 43, 3855–3859. [Google Scholar]
- Uslu, F.; Ingebrandt, S.; Mayer, D.; Böcker-Meffert, S.; Odenthal, M.; Offenhäusser, A. Labelfree fully electronic nucleic acid detection system based on a field-effect transistor device. Biosens. Bioelectron 2004, 19, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar]
- Pouthas, F.; Gentil, C.; Cote, D.; Zeck, G.; Straub, B.; Bockelmann, U. Spatially resolved electronic detection of biopolymers. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 31906. [Google Scholar]
- Uno, T.; Ohtake, T.; Tabata, H.; Kawai, T. Direct deoxyribonucleic acid detection using ion-sensitive field-effect transistors based on peptide nucleic acid. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys 2004, 43, L1584–L1587. [Google Scholar]
- Sakata, T.; Kamahori, M.; Miyahara, Y. Immobilization of oligonucleotide probes on Si3N4 surface and its application to genetic field effect transistor. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2004, 24, 827–832. [Google Scholar]
- Sakata, T.; Kamahori, M.; Miyahara, Y. DNA analysis chip based on field-effect transistors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys 2005, 44, 2854–2859. [Google Scholar]
- Sakata, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Nakajima, Y.; Miyahara, Y. Potential behavior of biochemically modified gold electrode for extended-gate field-effect transistor. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys 2005, 44, 2860–2863. [Google Scholar]
- Sakata, T.; Miyahara, Y. Detection of DNA recognition events using multi-well field effect devices. Biosens. Bioelectron 2005, 21, 827–832. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.; Kim, M.; Choi, S. Fabrication and characteristics of MOSFET protein chip for detection of ribosomal protein. Biosens. Bioelectron 2005, 20, 2111–2115. [Google Scholar]
- Janata, J.; Moss, S. Chemically sensitive field effect transistors. Biomed. Eng 1976, 6, 241–245. [Google Scholar]
- Zayats, M.; Kharitonov, A.; Katz, E.; Bückmann, A.; Willner, I. An integrated NAD+-dependent enzyme-functionalized field-effect transistor (ENFET) system: development of a lactate biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron 2000, 15, 671–680. [Google Scholar]
- Schasfoort, R.; Kooyman, R.; Bergveld, P.; Greve, J. A new approach to immunoFET operation. Biosens. Bioelectron 1990, 5, 103–124. [Google Scholar]
- Zayats, M.; Raitman, O.; Chegel, V.; Kharitonov, A.; Willner, I. Probing antigen-antibody binding processes by impedance measurements on ion-sensitive field-effect transistor devices and complementary surface plasmon resonance analyses: development of cholera toxin sensors. Anal. Chem 2002, 74, 4763–4773. [Google Scholar]
- Fromherz, P.; Offenhausser, A.; Vetter, T.; Weis, J. A neuron-silicon junction: a Retzius cell of the leech on an insulated-gate field-effect transistor. Science 1991, 252, 1290–1293. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, B.; Brischwein, M.; Baumann, W.; Ehret, R.; Kraus, M. Monitoring of cellular signalling and metabolism with modular sensor-technique The PhysioControl-Microsystem (PCM®). Biosens. Bioelectron 1998, 13, 501–509. [Google Scholar]
- Goncalves, D.; Prazeres, D.; Chu, V.; Conde, J. Detection of DNA and proteins using amorphous silicon ion-sensitive thin-film field effect transistors. Biosens. Bioelectron 2008, 24, 545–551. [Google Scholar]
- Nebel, C.; Shin, D.; Takeuchi, D.; Yamamoto, T.; Watanabe, H.; Nakamuras, T. Alkene/diamond liquid/solid interface characterization using internal photoemission spectroscopy. Langmuir 2006, 22, 5645–5653. [Google Scholar]
- Estrela, P.; Stewart, A.; Yan, F.; Migliorato, P. Field effect detection of biomolecular interactions. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 4995–5000. [Google Scholar]
- Syvänen, A. Toward genome-wide SNP genotyping. Nat. Genet 2005, 37, S5–S10. [Google Scholar]
- Purushothaman, S.; Toumazou, C.; Ou, C. Protons and single nucleotide polymorphism detection: A simple use for the ion sensitive field effect transistor. Sens. Actuat. B 2006, 114, 964–968. [Google Scholar]
- Zayats, M.; Huang, Y.; Gill, R.; Ma, C.; Willner, I. Label-free and reagentless aptamer-based sensors for small molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2006, 128, 13666–13667. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasena, S. Aptamers: an emerging class of molecules that rival antibodies in diagnostics. Clin. Chem 1999, 45, 1628–1650. [Google Scholar]
- You, K.; Lee, S.; Im, A.; Lee, S. Aptamers as functional nucleic acids: in vitro selection and biotechnological applications. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng 2003, 8, 64–75. [Google Scholar]
- Luzi, E.; Minunni, M.; Tombelli, S.; Mascini, M. New trends in affinity sensing aptamers for ligand binding. Trends Anal. Chem 2003, 22, 810–818. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Degawa, M.; Yang, J.; Kawarada, H. pH-sensitive diamond field-effect transistors (FETs) with directly aminated channel surface. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 573, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Zhang, G.; Nakamura, Y.; Furukawa, K.; Hiraki, T.; Yang, J.; Funatsu, T.; Ohdomari, I.; Kawarada, H. Label-free DNA sensors using ultrasensitive diamond field-effect transistors in solution. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 74, 041919:1–041919:7. [Google Scholar]
- Yuqing, M.; Jianguo, G.; Jianrong, C. Ion sensitive field effect transducer-based biosensors. Biotechnol. Adv 2003, 21, 527–534. [Google Scholar]
- Luppa, P.; Sokoll, L.; Chan, D. Immunosensors principles and applications to clinical chemistry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2001, 314, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuruta, H.; Yamada, H.; Motoyashiki, Y.; Oka, K.; Okada, C.; Nakamura, M. An automated ELISA system using a pipette tip as a solid phase and a pH-sensitive field effect transistor as a detector. J. Immunol. Methods 1995, 183, 221–229. [Google Scholar]
- Starodub, N.; Dzantiev, B.; Starodub, V.; Zherdev, A. Immunosensor for the determination of the herbicide simazine based on an ion-selective field-effect transistor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 424, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Selvanayagam, Z.; Neuzil, P.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Sridhar, U.; Singh, M.; Ho, L. An ISFET-based immunosensor for the detection of β-Bungarotoxin. Biosens. Bioelectron 2002, 17, 821–826. [Google Scholar]
- Plekhanova, Y.; Reshetilov, A.; Yazynina, E.; Zherdev, A.; Dzantiev, B. A new assay format for electrochemical immunosensors: polyelectrolyte-based separation on membrane carriers combined with detection of peroxidase activity by pH-sensitive field-effect transistor. Biosens. Bioelectron 2003, 19, 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Schasfoort, R.; Bergveld, P.; Kooyman, R.; Greve, J. Possibilities and limitations of direct detection of protein charges by means of an immunological field-effect transistor. Anal. Chim. Acta 1990, 238, 323–329. [Google Scholar]
- Besselink, G.; Schasfoort, R.; Bergveld, P. Modification of ISFETs with a monolayer of latex beads for specific detection of proteins. Biosens. Bioelectron 2003, 18, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, L.; Xia, S.; Bian, C.; Sun, J.; Han, J. A micro-potentiometric hemoglobin immunosensor based on electropolymerized polypyrrole–gold nanoparticles composite. Biosens. Bioelectron 2009, 24, 3419–3424. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.; Kim, S.; Park, K.; Lyu, H.; Lee, C.; Chung, S.; Yun, W.; Kim, M.; Chung, B. An ISFET biosensor for the monitoring of maltose-induced conformational changes in MBP. FEBS Lett 2009, 583, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Poghossian, A.; Yoshinobu, T.; Simonis, A.; Ecken, H.; Lüth, H.; Schöning, M. Penicillin detection by means of field-effect based sensors: EnFET, capacitive EIS sensor or LAPS? Sens. Actuat. B 2001, 78, 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.; Choi, S.; Lee, M.; Sohn, B.; Choi, S. ISFET glucose sensor system with fast recovery characteristics by employing electrolysis. Sens. Actuat. B 2002, 83, 90–97. [Google Scholar]
- Härtl, A.; Baur, B.; Stutzmann, M.; Garrido, J.A. Enzyme-modified field effect transistors based on surface-conductive single-crystalline diamond. Langmuir 2008, 24, 9898–9906. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Xu, J.; Zhao, W.; Chen, H. A novel glucose ENFET based on the special reactivity of MnO2 nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron 2004, 19, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Xu, J.; Zhao, W.; Chen, H. Glucose biosensor based on ENFET doped with SiO2 nanoparticles. Sens. Actuat. B 2004, 97, 249–255. [Google Scholar]
- Sant, W.; Pourciel, M.; Launay, J.; Do Conto, T.; Martinez, A.; Temple-Boyer, P. Development of chemical field effect transistors for the detection of urea. Sens. Actuat. B 2003, 95, 309–314. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Chou, J.; Sun, T.; Hsiung, S. Portable urea biosensor based on the extended-gate field effect transistor. Sens. Actuat. B 2003, 91, 180–186. [Google Scholar]
- Soldatkin, A.; Montoriol, J.; Sant, W.; Martelet, C.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. A novel urea sensitive biosensor with extended dynamic range based on recombinant urease and ISFETs. Biosens. Bioelectron 2003, 19, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Aouni, F.; Mlika, R.; Martelet, C.; Ben Ouada, H.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Soldatkin, A. Modelling of the potentiometric response of ENFETs based on enzymatic multilayer membranes. Electroanalysis 2004, 16, 1907–1911. [Google Scholar]
- Rebriiev, A.; Starodub, N. Enzymatic Biosensor Based on the ISFET and Photopolymeric Membrane for the Determinaion of Urea. Electroanalysis 2004, 16, 1891–1895. [Google Scholar]
- Niwa, D.; Omichi, K.; Motohashi, N.; Homma, T.; Osaka, T. Organosilane self-assembled monolayer-modified field effect transistors for on-chip ion and biomolecule sensing. Sens. Actuat. B 2005, 108, 721–726. [Google Scholar]
- Poghossian, A.; Thust, M.; Schroth, P.; Steffen, A.; Lüth, H.; Schöning, M.J. Penicillin detection by means of silicon-based field-effect structures. Sens. Mater 2001, 13, 207–223. [Google Scholar]
- Poghossian, A.; Schöning, M.; Schroth, P.; Simonis, A.; Lüth, H. An ISFET-based penicillin sensor with high sensitivity, low detection limit and long lifetime. Sens. Actuat. B 2001, 76, 519–526. [Google Scholar]
- Sant, W.; Pourciel-Gouzy, M.; Launay, J.; Do Conto, T.; Colin, R.; Martinez, A.; Temple-Boyer, P. Development of a creatinine-sensitive sensor for medical analysis. Sens. Actuat. B 2004, 103, 260–264. [Google Scholar]
- Simonian, A.; Flounders, A.; Wild, J. FET-based biosensors for the direct detection of organophosphate neurotoxins. Electroanalysis 2004, 16, 1896–1906. [Google Scholar]
- Simonian, A.; Grimsley, J.; Flounders, A.; Schoeniger, J.; Cheng, T.; DeFrank, J.; Wild, J. Enzyme-based biosensor for the direct detection of fluorine-containing organophosphates. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 442, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Dzyadevych, S.; Anh, T.; Soldatkin, A.; Chien, N.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Chovelon, J. Development of enzyme biosensor based on pH-sensitive field-effect transistors for detection of phenolic compounds. Bioelectrochemistry 2002, 55, 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- Soldatkin, A.; Arkhypova, V.; Dzyadevych, S.; El’skaya, A.; Gravoueille, J.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Martelet, C. Analysis of the potato glycoalkaloids by using of enzyme biosensor based on pH-ISFETs. Talanta 2005, 66, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Marrakchi, M.; Dzyadevych, S.; Biloivan, O.; Martelet, C.; Temple, P.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Development of trypsin biosensor based on ion sensitive field-effect transistors for proteins determination. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2006, 26, 369–373. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, P. One-step separation-free amperometric biosensor for the detection of protein. Microchem. J 2000, 64, 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Setford, S.; White, S.; Bolbot, J. Measurement of protein using an electrochemical bi-enzyme sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron 2002, 17, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, R.; Elbaz, J.; Gill, R.; Zayats, M.; Willner, I. Analysis of dopamine and tyrosinase activity on Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistor (ISFET) devices. Chem. Eur. J 2007, 13, 7288–7293. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, R.; Zayats, M.; Willner, I. Dopamine-, L-DOPA-, adrenaline-, and noradrenaline-induced growth of Au nanoparticles: assays for the detection of neurotransmitters and of tyrosinase activity. Anal. Chem 2005, 77, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Mao, C.; Yang, G.; Hou, W.; Zhu, J. Polyaniline/Au composite hollow spheres: synthesis, characterization, and application to the detection of dopamine. Langmuir 2006, 22, 4384–4389. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, R.; Freeman, R.; Xu, J.; Willner, I.; Winograd, S.; Shweky, I.; Banin, U. Probing Biocatalytic Transformations with CdSe ZnS QDs. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2006, 128, 15376–15377. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Gill, R.; Freeman, R.; Willner, I. Probing of enzyme reactions by the biocatalyst-induced association or dissociation of redox labels linked to monolayer-functionalized electrodes. Chem. Commun 2006, 2006, 5027–5029. [Google Scholar]
- Biloivan, O.; Dzyadevych, S.; Boubriak, O.; Soldatkin, A.; El’skaya, A. Development of Enzyme Biosensor Based on ISFETs for Quantitative Analysis of Serine Proteinases. Electroanalysis 2004, 16, 1883–1889. [Google Scholar]
- Durand, P.; Nicaud, J.; Mallevialle, J. Detection of organophosphorous pesticides with an immobilized cholinesterase electrode. J. Anal. Toxicol 1984, 8, 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- Tran-Minh, C. Immobilized enzyme probes for determining inhibitors. Ion-Select. Electr. Rev 1985, 7, 41–75. [Google Scholar]
- Dzyadevich, S.; Shul’ga, A.; Soldatkin, A.; Nyamsi Hendji, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Martelet, C. Conductometric biosensors based on cholinesterases for sensitive detection of pesticides. Electroanalysis 1994, 6, 752–758. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Martelet, C.; Clechet, P.; Nyamsi Hendji, A.; Shul’ga, A.; Dzyadevitch, S.; Netchiporuk, L.; Soldatkin, A. Comparison of Two Transduction Modes for Design of Microbiosensors Applicable to Detection of Pesticides (S&M 0233). Sens. Mater 1996, 8, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Dzyadevych, S.; Soldatkin, A.; Arkhypova, V.; El’skaya, A.; Chovelon, J.; Georgiou, C.; Martelet, C.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Early-warning electrochemical biosensor system for environmental monitoring based on enzyme inhibition. Sens. Actuat. B 2005, 105, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Puig-Lleix, C.; Jimenez, C.; Fabregas, E.; Bartrol, J. Potentiometric pH sensors based on urethane acrylate photocurable polymer membranes. Sens. Actuat. B 1998, 49, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Munoz, J.; Jimenez, C.; Bratov, A.; Bartroli, J.; Alegret, S.; Dominguez, C. Photosensitive polyurethanes applied to the development of CHEMFET and ENFET devices for biomedical sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron 1997, 12, 577–585. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzels, G.; Koole, L. Photoimmobilisation of poly (N-vinylpyrrolidinone) as a means to improve haemocompatibility of polyurethane biomaterials. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar]
- Nakako, M.; Hanazato, Y.; Maeda, M.; Shiono, S. Neutral lipid enzyme electrode based on ion-sensitive field effect transistors. Anal. Chim Acta 1986, 185, 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Do, J. Urea biosensor based on PANi (urease)-Nafion®/Au composite electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron 2004, 20, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayalakshmi, A.; Tarunashree, Y.; Baruwati, B.; Manorama, S.; Narayana, B.; Johnson, R.; Rao, N. Enzyme field effect transistor (ENFET) for estimation of triglycerides using magnetic nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron 2008, 23, 1708–1714. [Google Scholar]
- Migita, S.; Ozasa, K.; Tanaka, T.; Haruyama, T. Enzyme-based field-effect transistor for adenosine triphosphate (ATP) sensing. Analyt. Sci 2007, 23, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Dzyadevych, S.; Soldatkin, A.; El’skaya, A.; Martelet, C.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Enzyme biosensors based on ion-selective field-effect transistors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 568, 248–258. [Google Scholar]
- Volotovsky, V.; Soldatkin, A.; Shul’ga, A.; Rossokhaty, V.; Strikha, V.; El’skaya, A. Glucose-sensitive ion-sensitive field-effect transistor-based biosensor with additional positively charged membrane. Dynamic range extension and reduction of buffer concentration influence on the sensor response. Anal. Chim. Acta 1996, 322, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Ishige, Y.; Shimoda, M.; Kamahori, M. Extended-gate FET-based enzyme sensor with ferrocenyl-alkanethiol modified gold sensing electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron 2009, 24, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Risveden, K.; Ponten, J.; Calander, N.; Willander, M.; Danielsson, B. The region ion sensitive field effect transistor, a novel bioelectronic nanosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron 2007, 22, 3105–3112. [Google Scholar]
- Martinoia, S.; Rosso, N.; Grattarola, M.; Lorenzelli, L.; Margesin, B.; Zen, M. Development of ISFET array-based microsystems for bioelectrochemical measurements of cell populations. Biosens. Bioelectron 2001, 16, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, M.; Baumann, W.; Brischwein, M.; Gahle, H.; Freund, I.; Ehret, R.; Drechsler, S.; Palzer, H.; Kleintges, M.; Sieben, U. Simultaneous measurement of cellular respiration and acidification with a single CMOS ISFET. Biosens. Bioelectron 2001, 16, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Milgrewa, M.; Riehle, M.; Cumming, D. A large transistor-based sensor array chip for direct extracellular imaging. Sens. Actuat. B 2005, 111, 347–353. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, C.; Ingebrandt, S.; Krause, M.; Offenhäusser, A.; Knoll, W. Validation of the use of field effect transistors for extracellular signal recording in pharmacological bioassays. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2001, 45, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Xu, G.; Qin, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, R. Cell-based biosensors and its application in biomedicine. Sens. Actuat. B 2005, 108, 576–584. [Google Scholar]
- Castellarnau, M.; Zine, N.; Bausells, J.; Madrid, C.; Juarez, A.; Samitier, J.; Errachid, A. Integrated cell positioning and cell-based ISFET biosensors. Sens. Actuat. B 2007, 120, 615–620. [Google Scholar]
- Castellarnau, M.; Zine, N.; Bausells, J.; Madrid, C.; Juarez, A.; Samitier, J.; Errachid, A. ISFET-based biosensor to monitor sugar metabolism in bacteria. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2008, 28, 680–685. [Google Scholar]
- Parce, J.; Owicki, J.; Kercso, K.; Sigal, G.; Wada, H.; Muir, V.; Bousse, L.; Ross, K.; Sikic, B.; McConnell, H. Detection of cell-affecting agents with a silicon biosensor. Science 1989, 246, 243–247. [Google Scholar]
- Baumann, W.; Lehmann, M.; Schwinde, A.; Ehret, R.; Brischwein, M.; Wolf, B. Microelectronic sensor system for microphysiological application on living cells. Sens. Actuat. B 1999, 55, 77–89. [Google Scholar]
- Poghossian, A.; Ingebrandt, S.; Offenhäusser, A.; Schöning, M.J. Field-effect devices for detecting cellular signals. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol 2009, 20, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wegener, J.; Keese, C.; Giaever, I. Electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS) as a noninvasive means to monitor the kinetics of cell spreading to artificial surfaces. Exp. Cell Res 2000, 259, 158–166. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, C.; Lachance, B.; Sunahara, G.; Luong, J. Assessment of cytotoxicity using electric cell-substrate impedance sensing: concentration and time response function approach. Mol. Toxicol 1998, 11, 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, C.; Luong, J. On-line monitoring of cell growth and cytotoxicity using electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS). Biotechnol. Prog 2003, 19, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Solly, K.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Strulovici, B.; Zheng, W. Application of real-time cell electronic sensing (RT-CES) technology to cell-based assays. Assay Drug Dev. Technol 2004, 2, 363–372. [Google Scholar]
- Ceriotti, L.; Ponti, J.; Broggi, F.; Kob, A.; Drechsler, S.; Thedinga, E.; Colpo, P.; Sabbioni, E.; Ehret, R.; Rossi, F. Real-time assessment of cytotoxicity by impedance measurement on a 96-well plate. Sens. Actuat. B 2007, 123, 769–778. [Google Scholar]
- Ceriotti, L.; Kob, A.; Drechsler, S.; Ponti, J.; Thedinga, E.; Colpo, P.; Ehret, R.; Rossi, F. Online monitoring of BALB/3T3 metabolism and adhesion with multiparametric chip-based system. Anal. Biochem 2007, 371, 92–104. [Google Scholar]






© 2009 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, C.-S.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, M. Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistor for Biological Sensing. Sensors 2009, 9, 7111-7131. https://doi.org/10.3390/s90907111
Lee C-S, Kim SK, Kim M. Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistor for Biological Sensing. Sensors. 2009; 9(9):7111-7131. https://doi.org/10.3390/s90907111
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Chang-Soo, Sang Kyu Kim, and Moonil Kim. 2009. "Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistor for Biological Sensing" Sensors 9, no. 9: 7111-7131. https://doi.org/10.3390/s90907111
APA StyleLee, C.-S., Kim, S. K., & Kim, M. (2009). Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistor for Biological Sensing. Sensors, 9(9), 7111-7131. https://doi.org/10.3390/s90907111





