Presentation of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation
2.1. Case A
2.2. Case B
2.3. Case C
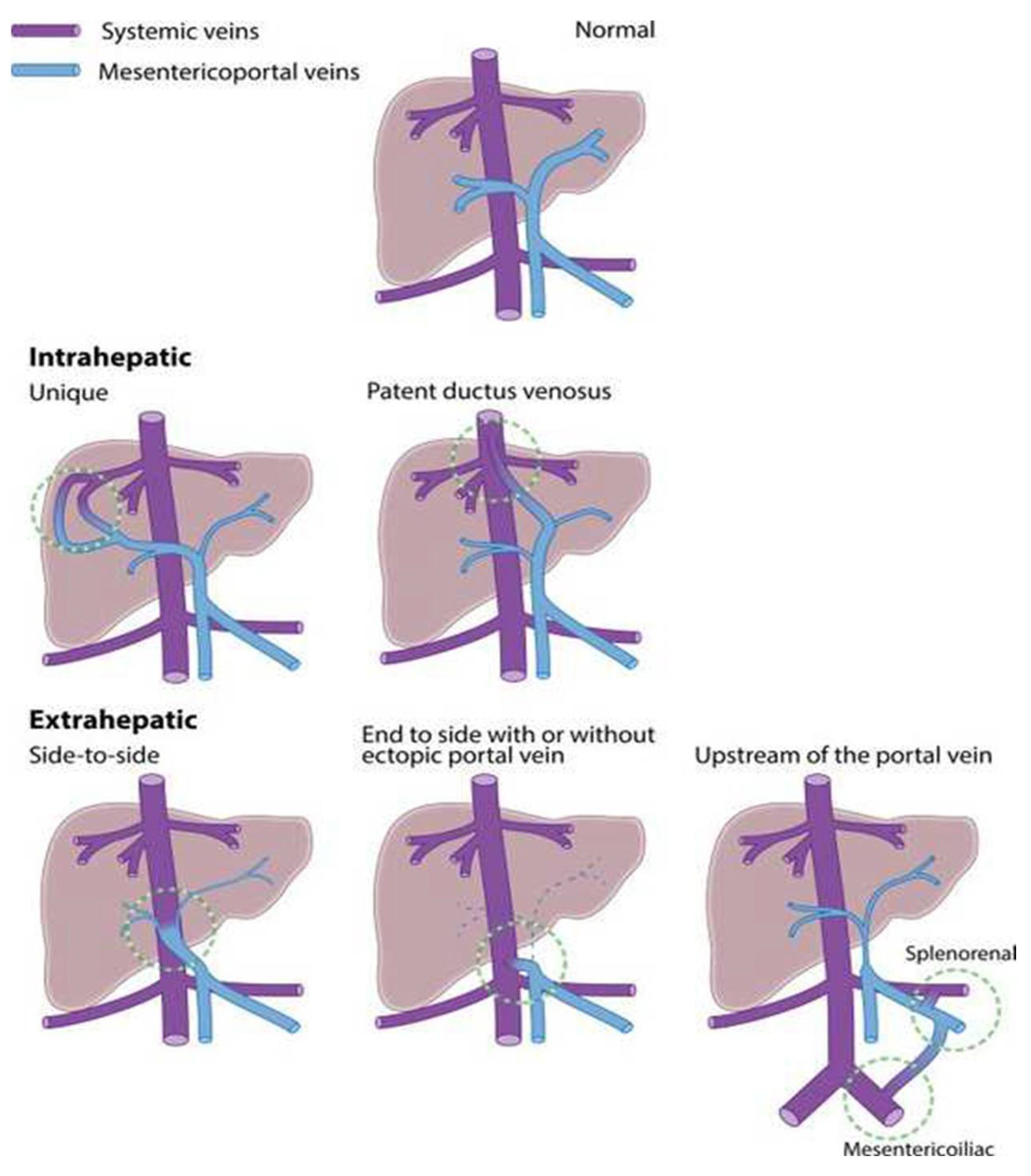
3. Development of CPSS
4. Typical Clinical Presentations of CPSS
4.1. Incidental
4.2. Prenatal US
4.3. Positive Neonatal Screening for Galactosemia
4.4. Neonatal Cholestasis
4.5. Hepatic Manifestations
4.6. Cardiopulmonary Manifestations
4.7. Neurocognitive Manifestations
4.8. Syndromic Associations
5. Other Symptoms and Signs of CPSS
5.1. Endocrine
5.2. Gastrointestinal
5.3. Hematological/Immunological
5.4. Cutaneous Angiomas
5.5. Renal
6. Approach for the Clinician
6.1. Diagnostic Approach
6.2. Management: CPSS Closure and Management of Systemic Manifestations
7. Conclusions
| Key Message Box |
| Suspect CPSS in patients with a constellation of seemingly unrelated symptoms. |
| Liver Doppler US is the first essential step for diagnosis. |
| Identification of a CPSS does not obviate the need for a full cholestasis work-up. |
| Hyperammonemia of unexplained etiology in a neonate or child should prompt screening for CPSS. |
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CPSS | Congenital portosystemic shunt(s) |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| EH | Extrahepatic |
| FNH | Focal nodular hyperplasia |
| HPS | Hepatopulmonary syndrome |
| IH | Intrahepatic |
| mPAP | Mean pulmonary arterial pressure |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| PAH | Pulmonary arterial hypertension |
| PVD | Patent ductus venosus |
| PVRi | Pulmonary vascular resistance index |
| TBG | Thyroïd-binding protein |
| US | Ultrasound |
References
- Bernard, O.; Franchi-Abella, S.; Branchereau, S.; Pariente, D.; Gauthier, F.; Jacquemin, E. Congenital portosystemic shunts in children: Recognition, evaluation, and management. In Seminars in Liver Disease; Thieme Medical Publishers: Stuttgart, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Papamichail, M.; Pizanias, M.; Heaton, N. Congenital portosystemic venous shunt. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2017, 177, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McLin, V.A.; Abella, S.F.; Debray, D.; Guérin, F.; Beghetti, M.; Savale, L.; Wildhaber, B.E.; Gonzales, E. Congenital portosystemic shunts: Current diagnosis and management. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 68, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchi-Abella, S.; Gonzales, E.; Ackermann, O.; Branchereau, S.; Pariente, D.; Guérin, F. Congenital portosystemic shunts: Diagnosis and treatment. Abdom. Radiol. 2018, 43, 2023–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guérin, F.; Franchi-Abella, S.; McLin, V.; Ackermann, O.; Girard, M.; Cervoni, J.P.; Savale, L.; Hernandez-Gea, V.; Valla, D.; Hillaire, D.; et al. Congenital portosystemic shunts: Vascular liver diseases: Position papers from the francophone network for vascular liver diseases, the French Association for the Study of the Liver (AFEF), and ERN-rare liver. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2020, 44, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abernethy, J. IX. Account of two instances of uncommon formation, in the viscera of the human body. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1793, 83, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Uchino, T.; Matsuda, I.; Endo, F. The long-term prognosis of congenital portosystemic venous shunt. J. Pediatr. 1999, 135, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLin, V.A.; Franchi-Abella, S.; Debray, D.; Korff, S.; Casotti, V.; Colledan, M.; d’Antiga, L.; de Ville de Goyet, J.; Lurz, E.; Xavier, S. Intrahepatic and extrahepatic congenital portosystemic shunts differ in in clinical presentation and outcomes in children. Hepatology 2019, 11, 14181. [Google Scholar]
- Baiges, A.; Turon, F.; Simón-Talero, M.; Tasayco, S.; Bueno, J.; Zekrini, K.; Plessier, A.; Franchi-Abella, S.; Guerin, F.; Mukund, A.; et al. Congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunts (Abernethy malformation): An international observational study. Hepatology 2020, 71, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, V.; Ladarre, D.; Fortas, F.; Durand, P.; Hervé, P.; Gonzales, E.; Guérin, F.; Savale, L.; McLin, V.A.; Ackermann, O.; et al. Cardiovascular disorders in patients with congenital portosystemic shunts: 23 years of experience in a tertiary referral centre. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 114, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-García, C.; Martín, Y.R.; Del Hoyo, A.A.; Rodríguez, C.M.; Domínguez, M.C. Adams-Oliver syndrome with unusual central nervous system findings and an extrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Pediatr. Rep. 2017, 9, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokollik, C.; Bandsma, R.H.; Gana, J.C.; van den Heuvel, M.; Ling, S.C. Congenital portosystemic shunt: Characterization of a multisystem disease. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 56, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLin, V.; Franchi-Abella, S.; Debray, M.; Korff, S.; Casotti, V.; Colledan, M.; d’Antiga, L.; Goyet, J.D.; Durmaz, O.; Lurz, E.; et al. FRI-436-congenital porto-systemic shunts in children: Preliminary results from the IRCPSS. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting ESPGHAN (European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition), Glasgow, UK, 5–8 June 2019; Volume 70, p. e586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plut, D.; Gorjanc, T. A case of a newborn with an intrahepatic congenital portosystemic venous shunt with concurrent congenital duodenal web. Acta Radiol. Open 2019, 8, 2058460119854173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi-Abella, S.; Branchereau, S. Benign hepatocellular tumors in children: Focal nodular hyperplasia and hepatocellular adenoma. Int. J. Hepatol. 2013, 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pupulim, L.; Vullierme, M.-P.; Paradis, V.; Valla, D.; Terraz, S.; Vilgrain, V. Congenital portosystemic shunts associated with liver tumours. Clin. Radiol. 2013, 68, e362–e369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanada, Y.; Mizuta, K.; Niki, T.; Tashiro, M.; Hirata, Y.; Okada, N.; Yamada, N.; Ihara, Y.; Urahashi, T.; Soejima, Y.; et al. Hepatocellular nodules resulting from congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunts can differentiate into potentially malignant hepatocellular adenomas. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Sci. 2015, 22, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joye, R.; Lador, F.; Aggoun, Y.; Farhat, N.; Wacker, J.; Wildhaber, B.E.; Vallée, J.-P.; Hachulla, A.-L.; McLin, V.A.; Beghetti, M. Outcome of paediatric portopulmonary hypertension in the modern management era: A case report of 6 patients. J. Hepatol. 2020, 74, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bas, S.; Guran, T.; Atay, Z.; Haliloglu, B.; Abali, S.; Turan, S.; Bereket, A. Premature pubarche, hyperinsulinemia and hypothyroxinemia: Novel manifestations of congenital portosystemic shunts (Abernethy malformation) in children. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2015, 83, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, F.; Bernard, O.; Brunelle, F.; Hadchouel, P.; Odievre, M.; Alagille, D. Portal obstruction in children. II. Results of surgical portosystemic shunts. J. Pediatrics 1983, 103, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Romero, R.; Koutouby, R.; Mittal, N.K.; Thompson, J.F.; Schleien, C.L.; Tzakis, A.G. Portosystemic shunting in children during the era of endoscopic therapy: Improved postoperative growth parameters. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2000, 30, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, M.; Yokoya, S.; Hachiya, Y.; Hachiya, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Hoshino, K.; Saji, T. Two hyperandrogenic adolescent girls with congenital portosystemic shunt. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2001, 160, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karashima, S.; Hattori, S.; Nakazato, H.; Awata, H.; Seguchi, S.; Ikeda, S.; Sera, Y.; Endo, F. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis in congenital portosystemic shunt without liver cirrhosis. Clin. Nephrol. 2000, 53, 206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, D.-G. Macroscopic hematuria caused by congenital portosystemic shunt and concomitant nutcracker syndrome. Pediatr. Int. 2015, 57, e84–e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cudalbu, C.; Xin, L.; Lachat, S.; Valenza, N.; Zangas-Gehri, F.; McLin, V. P: 62 Neurometabolism in grey matter of children with chronic liver disease or portosystemic shunting: A 1H-MRS study at 7T. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, S31–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Ko, J.S.; Seo, J.K.; Yang, H.R.; Chang, J.Y.; Kim, G.B.; Cheon, J.-E.; Kim, W.S. Clinical features of congenital portosystemic shunt in children. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2011, 171, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hikspoors, J.P.; Peeters, M.M.; Kruepunga, N.; Mekonen, H.K.; Mommen, G.M.C.; Köhler, S.E.; Lamers, W.H. Human liver segments: Role of cryptic liver lobes and vascular physiology in the development of liver veins and left-right asymmetry. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collardeau-Frachon, S.; Scoazec, J.Y. Vascular development and differentiation during human liver organogenesis. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Biol. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Biol. 2008, 291, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, B.; Lachaux, A.; Gottrand, F.; de Smet, S. Prenatally diagnosed congenital portosystemic shunts. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2017, 31, 1364–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achiron, R.; Kivilevitch, Z. Fetal umbilical–portal–systemic venous shunt: In-utero classification and clinical significance. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 47, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gitzelmann, R.; Forster, I.; Willi, U.V. Hypergalactosaemia in a newborn: Self-limiting intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunt. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1997, 156, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H.; Mawatari, H.; Mizoguchi, N.; Eguchi, T.; Sakura, N. Clinical features and outcome of eight infants with intrahepatic porto-venous shunts detected in neonatal screening for galactosaemia. Acta Pædiatr. 1998, 87, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchi-Abella, S.; Branchereau, S.; Lambert, V.; Fabre, M.; Steimberg, C.; Losay, J.; Riou, J.-Y.; Pariente, D.; Gauthier, F.; Jacquemin, E.; et al. Complications of congenital portosystemic shunts in children: Therapeutic options and outcomes. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Gamarra, E.; Parrón, M.; Pérez, A.; Prieto, C.; Hierro, L.; López-Santamaría, M. Clinical and radiologic manifestations of congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunts: A comprehensive review. RadioGraphics 2011, 31, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, F. Benign nodular hepatocellular lesions caused by abnormal hepatic circulation: Etiological analysis and introduction of a new concept1. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2001, 16, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, Y.; Shimizu, R.; Saeki, T.; Harada, T.; Sugio, Y.; Nomura, S.; Tanaka, H. Patent ductus venosus in children: A case report and review of the literature. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2004, 39, E1–E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, T.; Endo, F.; Ikeda, S.; Shiraki, K.; Sera, Y.; Matsuda, I. Three brothers with progressive hepatic dysfunction and severe hepatic steatosis due to a patent ductus venosus. Gastroenterology 1996, 110, 1964–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolantonio, G.; Pietrobattista, A.; Candusso, M.; Monti, L.; Goyet, J.D.; Torre, G.; Rollo, M. Congenital double intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: Imaging findings and endovascular closure. Ann. Hepatol. 2015, 14, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, G.B.; Porta, F.; Biamino, E.; Mussa, A.; Garelli, E.; Chiappe, F.; Veltri, A.; Silengo, M.C.; Gennari, F. Remittent hyperammonemia in congenital portosystemic shunt. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2009, 169, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, B.; Feinstein, J.; Cohen, R.A.; Feingold, B.; Kreutzer, J.; Patel, H.; Chan, F.P. Congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunt associated with heterotaxy and polysplenia. Pediatr. Radiol. 2010, 40, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Roisin, R.; Krowka, M.J. Hepatopulmonary syndrome—A liver-induced lung vascular disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2378–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Fallon, M.B. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: Update on pathogenesis and clinical features. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonneau, G.; Montani, D.; Celermajer, D.; Denton, C.P.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Krowka, M.; Williams, P.G.; Souza, R. Haemodynamic definitions and updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasaka, H.; Okano, Y.; Aizawa, M.; Miida, T.; Yorifuji, T.; Tajima, G.; Sakura, N.; Takatani, T.; Sanayama, Y.; Sugamoto, K.; et al. Altered metabolisms of mediators controlling vascular function and enhanced oxidative stress in asymptomatic children with congenital portosystemic venous shunt. Metabolism 2010, 59, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem, A.Y.; Emir, S.; Demir, H.A.; Özyörük, D.; Çetin, I.; Turan, A.; Karakus, E. Focal nodulary hyperplasia of the liver due to congenital portosystemic shunt: A rare condition mimicking hepatocellulary carcinoma. J. Pediatric Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 39, e8–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Rocha, A.; Braga, F.T.; da Silva, C.J.; Maia, A.C.; Mourão, G.S.; Gagliardi, R.J. Reversal of parkinsonism and portosystemic encephalopathy following embolization of a congenital intrahepatic venous shunt: Brain MR imaging and 1H spectroscopic findings. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2004, 25, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.; Yan, Z.; Peng, W.; Hong, H. Hepatic myelopathy: Case report and review of the literature. Liver Res. Open J. 2015, 1, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torigoe, M.; Maeshima, K.; Takeshita, Y. Congenital intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunt presenting with paraparesis as the initial symptom. Intern. Med. 2013, 52, 2439–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- d’Antiga, L.; Dacchille, P.; Boniver, C.; Poledri, S.; Schiff, S.; Zancan, L.; Amodio, P. Clues for minimal hepatic encephalopathy in children with noncirrhotic portal hypertension. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 59, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kundra, A.; Jain, A.; Banga, A.; Bajaj, G.; Kar, P. Evaluation of plasma ammonia levels in patients with acute liver failure and chronic liver disease and its correlation with the severity of hepatic encephalopathy and clinical features of raised intracranial tension. Clin. Biochem. 2005, 38, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Chaturvedi, S.; Gupta, R.K.; Malik, R.; Mathias, A.; Jagannathan, N.R.; Jain, S.; Pandey, C.M.; Yachha, S.K.; Rathore, R.K.S. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy in children with chronic liver disease: Prevalence, pathogenesis and magnetic resonance-based diagnosis. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanquinet, S.; Morice, C.; Courvoisier, D.S.; Cousin, V.; Anooshiravani, M.; McLin, V.A.; Merlini, L. Globus pallidus MR signal abnormalities in children with chronic liver disease and/or porto-systemic shunting. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 8, 381–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, S.; Minami, T.; Sonoda, K.; Gondo, K.; Tasaki, K.; Hijii, T.; Fukushige, J.; Ueda, K.; Hirata, T.; Hayashi, T.; et al. Patent ductus venosus associated with a hyperintense globus pallidum on T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and pulmonary hypertension. Eur. J. Pediatrics 1995, 154, 526–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiPaola, F.; Trout, A.T.; Walther, A.E.; Gupta, A.; Sheridan, R.; Campbell, K.M.; Tiao, G.; Bezerra, J.A.; Bove, K.E.; Patel, M.; et al. Congenital portosystemic shunts in children: Associations, complications, and outcomes. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 65, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, T.; Muneuchi, J.; Ihara, K.; Yuge, T.; Kanaya, Y.; Yamaki, S.; Hara, T. Pulmonary hypertension in patients with congenital portosystemic venous shunt: A previously unrecognized association. Pediatrics 2008, 121, e892–e899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lautz, T.; Tantemsapya, N.; Rowell, E.; Superina, R.A. Management and classification of type II congenital portosystemic shunts. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2011, 46, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanc, T.; Guerin, F.; Franchi-Abella, S.; Jacquemin, E.; Pariente, D.; Soubrane, O.; Branchereau, S.; Gauthier, F. Congenital portosystemic shunts in children: A new anatomical classification correlated with surgical strategy. Ann. Surg. 2014, 260, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witters, P.; Maleux, G.; George, C.; Delcroix, M.; Hoffman, I.; Gewillig, M.; Verslype, C.; Monbaliu, D.; Aerts, R.; Pirenne, J.; et al. Congenital veno-venous malformations of the liver: Widely variable clinical presentations. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, e390–e394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazioli, L.; Alberti, D.; Olivetti, L.; Rigamonti, W.; Codazzi, F.; Matricardi, L.; Fugazzola, C.; Chiesa, A. Congenital absence of portal vein with nodular regenerative hyperplasia of the liver. Eur. Radiol. 2000, 10, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charre, L.; Roggen, F.; Lemaire, J.; Mathijs, J.; Goffette, P.; Danse, E.; Lerut, J. Hematochezia and congenital extrahepatic portocaval shunt with absent portal vein: Successful treatment by liver transplantation. Transplantation 2004, 78, 1404–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomari, A.I.; Chaudry, G.; Fox, V.L.; Fishman, S.J.; Buchmiller, T.L. Atypical manifestation of patent ductus venosus in a child: Intervening against a paradoxical presentation. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 20, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- delle Chiaie, L.; Neuberger, P.; von Kalle, T. Congenital intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: Prenatal diagnosis and possible influence on fetal growth. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. Off. J. Int. Soc. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 32, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.H.; Park, S.B.; Song, M.J.; Lee, K.S.; Lee, Y.-H.; Ko, S.Y.; Lee, Y.K. Congenital portosystemic shunts: Prenatal manifestations with postnatal confirmation and follow-up. J. Ultrasound Med. 2013, 32, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, K.-A.; Lee, Y.-K.; Ko, S.-Y.; Shin, S.-M.; Han, B.-H. A clinical study of congenital intrahepatic portosystemic shunt diagnosed in neonatal period. J. Korean Soc. Neonatol. 2011, 18, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timpanaro, T.; Passanisi, S.; Sauna, A.; Trombatore, C.; Pennisi, M.; Petrillo, G.; Smilari, P.; Greco, F. Congenital portosystemic shunt: Our experience. Case Rep. Pediatr. 2015, 2015, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assaad, S.N.; Cunningham, G.R.; Samaan, N.A. Abnormal growth hormone dynamics in chronic liver disease do not depend on severe parenchymal disease. Metabolism 1990, 39, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, R.N.; Bhatia, V.; Dabadghao, P.; Yachha, S.K. Extrahepatic portal vein obstruction in children: Anthropometry, growth hormone, and insulin-like growth factor I. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1997, 25, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, S.; Grønb, M.; Main, K.; Becker, U.; Skakkeb, N.E. Urinary growth hormone (U-GH) excretion and serum insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 1993, 17, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonefeld, K.; Møller, S. Insulin-like growth factor-I and the liver. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, J.; Gomis, R.; Kravetz, D.; Casamitjana, R.; Terés, J.; Rivera, F.; Rodés, J. Role of spontaneous portal-systemic shunting in hyperinsulinism of cirrhosis. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 1984, 247, G206–G212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.S.; Yeung, T.T.; Ho, P.W.M. Down-regulation of insulin receptors in postnecrotic cirrhosis of liver. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1982, 55, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuqua, J.S. Treatment and outcomes of precocious puberty: An update. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 2198–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabah, S.A.; Gowan, I.L.; Pagnin, M.; Osman, N.; Richardson, S.J. Thyroid hormone distributor proteins during development in vertebrates. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ain, K.B.; Refetoff, S.; Sarne, D.H.; Murata, Y. Effect of estrogen on the synthesis and secretion of thyroxine-binding globulin by a human hepatoma cell line, HEP G2. Mol. Endocrinol. 1988, 2, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hernández-Jaras, J.; Espí-Reig, J.; Alis, R.; García-Martínez, A.-M.; Rodríguez-Ortega, D.; Roca-Argente, L.; Moll-Guillen, J.-L. Immune complex membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis associated with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts in alcoholic cirrhosis: Two case reports. Med. Princ. Pr. 2017, 26, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Smet, A.; Kuypers, D.R.; Evenepoel, P.; Maes, B.; Messiaen, T.; Van Damme, B.; Vanrenterghem, Y. “Full house” positive immunohistochemical membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis in a patient with portosystemic shunt. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2001, 16, 2258–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Konstas, A.A.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Avery, L.L.; Wallace, K.L.; Lisovsky, M.; Misdraji, J.; Hahn, P.F. Congenital portosystemic shunts: Imaging findings and clinical presentations in 11 patients. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 80, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soma, J.; Saito, T.; Sato, H.; Ootaka, T.; Abe, K. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis induced by portosystemic shunt surgery for non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. Clin. Nephrol. 1997, 48, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, H.; Feng, C.; Liu, Z.; Gu, W.; Jin, Y.; Yang, B.; Shen, H. Case report: Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, a rare clinical manifestation of Abernethy malformation type II. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Ye, W.; Liu, C.; Wu, W.; Li, Y. Surgical ligation of portosystemic shunt to resolve severe hematuria and hemafecia caused by type II Abernethy malformation. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 29, 1020.e11–1020.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzounos, C.E.; Tivers, M.; Adamantos, S.; English, K.; Rees, A.L.; Lipscomb, V. Haematology and coagulation profiles in cats with congenital portosystemic shunts. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2017, 19, 1290–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanazawa, H.; Nosaka, S.; Miyazaki, O.; Sakamoto, S.; Fukuda, A.; Shigeta, T.; Nakazawa, A.; Kasahara, M. The classification based on intrahepatic portal system for congenital portosystemic shunts. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2015, 50, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, Y.; Ueda, M.; Doi, H.; Kasahara, M.; Haga, H.; Kamei, H.; Ogawa, K.; Ogura, Y.; Yoshitoshi, E.Y.; Tanaka, K. Successful liver transplantation for congenital absence of the portal vein complicated by intrapulmonary shunt and brain abscess. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2005, 40, e1–e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, A.E.; Hessel, G.; Baracat, J. Abernethy malformation: One of the etiologies of hepatopulmonary syndrome. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2002, 34, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Wang, Q.; Wu, J.; Guo, Y.; Huang, M.; Liu, T.; Chen, Q.; Li, F. Congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunt: An underdiagnosed but treatable cause of hepatopulmonary syndrome. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2015, 175, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molleston, J.P.; Kaufman, B.A.; Cohen, A.; Shackelford, P.G.; Keating, J.P.; Lowell, J.A.; Howard, T.K. Brain abscess in hepatopulmonary syndrome. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1999, 29, 225–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Tokuhara, D.; Shimono, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Higashiyama, S.; Kotani, K.; Kawabe, J.; Okano, Y.; Shiomi, S.; Shintaku, H. Role of per-rectal portal scintigraphy in long-term follow-up of congenital portosystemic shunt. Pediatr. Res. 2014, 75, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kira, T.; Ikeda, S.; Sera, Y.; Tomiguchi, S.; Takahashi, M.; Uchino, T.; Endo, F. Evaluation of persistence of ductus venosus with Tc-99m DTPA galactosyl human serum albumin liver scintigraphy and I-123 iodoamphetamine per-rectal portal scintigraphy. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2000, 14, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganelli, M.; Lipsich, J.E.; Sciveres, M.; Alvarez, F. Predisposing factors for spontaneous closure of congenital portosystemic shunts. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 931–935.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, T.; Ogura, Y.; Doi, H.; Yagi, S.; Kanazawa, H.; Imai, H.; Sakamoto, S.; Okamoto, S.; Uemoto, S. Successful treatment of pulmonary hypertension secondary to congenital extrahepatic portocaval shunts (Abernethy type 2) by living donor liver transplantation after surgical shunt ligation. Transpl. Int. 2009, 23, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, H.; Takada, Y.; Fujimoto, Y.; Ogura, Y.; Kozaki, K.; Ueda, M.; Tanaka, K. Successful surgical ligation under intraoperative portal vein pressure monitoring of a large portosystemic shunt presenting as an intrapulmonary shunt: Report of a case. Surg. Today 2004, 34, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbounova, I.; Hsu, E.K. When, where and how: Lack of management consensus for liver transplantation in children with congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Liver Transpl. 2021, 27, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, H.; Sakamoto, S.; Kasahara, M.; Kudo, H.; Okajima, H.; Nio, M.; Umeshita, K.; Ohdan, H.; Egawa, H.; Uemoto, S.; et al. Longterm outcome of liver transplantation for congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Liver Transpl. 2020, 27, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimaldi, C.; Monti, L.; Falappa, P.; d’Ambrosio, G.; Manca, A.; Goyet, J.D. Congenital intrahepatic portohepatic shunt managed by interventional radiologic occlusion: A case report and literature review. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2012, 47, e27–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Patient | Cause for Referral | Age at First Symptoms/Signs (Years) | Age at Diagnosis (Years) | Cardiovascular Symptoms | Liver Nodules | Other Endocrine Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Suspected PAH | 9 | 11 | Dyspnea | Beta-catenin mutated adenomas | Insulin resistance with hyperinsulinism, acanthosis nigricans and hyperandrogenemia without menarche |
| B | Elevated aminotransferase levels | 0 | 7 | No | Multiple adenomas | Neonatal hypoglycemia |
| C | Liver nodules identified on US performed for abdominal pain | 3 | 5 | No | Beta-catenin mutated FNH-like nodules | No |
| Indications for a Liver Doppler Ultrasound [References] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Syndromes Associated with CPSS [1,3,11,12,54] | Visceral Malformations | Cardiac Defects | Liver Malformations | Other |
| Caroli’s | Mesenteric defects | Ventricular septal defects | Biliary atresia: | Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis |
| Goldhenhar | Duodenal atresia | Atrial septal defects | - Syndromic | Unexplained symptoms/signs in Table 3 |
| Down’s | Ano-rectal malformations | Hypoplastic left heart | - Non syndromic | |
| Turner | Polyposis syndromes | Left isomerism | Masses: | |
| Leopard | Situs abnormalities | Valvular abnormalities | - Hepatoblastoma | |
| Rendu-Osler | Renal malformations | - Hepatocellular carcinoma | ||
| Grazioli | - Other | |||
| Noonan | Antenatal abnormal imaging: | |||
| Cornelia de Lange | - Left lobe hypoplasia | |||
| Holt-Oram | ||||
| Costello | ||||
| Wolf-Hirschhorn | ||||
| Neurofibromatosis | ||||
| Adams-Oliver | ||||
| Clinical and Biological Symptoms & Signs Encountered in Patients with Congenital Portosystemic Shunts [References] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatic [1,3,4,5,9,12,15,16,17,33,34,35,36,37,38,39] | Gastro- Intestinal [9,55,56,57,58,59,60,61] | Cardio- Pulmonary [1,5,10,18,40,41,42,43,44] | Endocrine/Metabolic [1,3,13,19,20,21,22,29,33,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74] | Renal [23,75,76,77,78,79,80] | Neurocognitive [1,5,9,12,25,26,33,37,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53] | Other [3,5,33,56,81,82,83,84,85,86] |
| Abnormal hepatic vasculature on antenatal ultrasound | Abdominal pain | Hepatopulmonary syndrome | Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia | Proteinuria | Mild cognitive deficits | Brain abscesses (when associated with intrapulmonary shunts) |
| Tumors: | Gastrointestinal bleeding | Pulmonary artery hypertension | Hyperandrogenism | Hematuria | ADHD | Coagulation abnormalities |
| - Nodular regenerative hyperplasia | High-output cardiac failure | Precocious puberty | Post-prandial LOC | Cutaneous and visceral hemangioma | ||
| - Focal nodular hyperplasia | Amenorrhea | Parkinson-like | ||||
| Adenoma | Hypothyroidism | Hepatic myelopathy | ||||
| - Hepatoblastoma | Fetal growth retardation | Portosystemic encephalopathy | ||||
| - Hepatocellular carcinoma | Tall stature/overgrowth | Learning difficulties | ||||
| Hemangioma | Hyperammonemia | Unexplained mental retardation | ||||
| Hypoplastic left liver | Elevated serum bile acids | |||||
| Steatosis | Increased galactose on newborn screen | |||||
| Portal hypertension | ||||||
| Recommended Basic Work-Up when Suspecting a CPSS [3,52] | ||
|---|---|---|
| Thorough clinical examination | Thoraco-abdominal CT-angiography | |
| Other malformations | Anatomy of CPSS | |
| Cutaneous hemangiomas | Hepato-pulmonary shunts | |
| Laboratory | Myocardial contrast echocardiography | |
| Elevated serum aminotransferases | Evidence of right-to-left shunting | |
| Expected | Abnormal coagulation | If elevated right sided pressure: right heart catheterization |
| findings | Elevated fasting bile acids | |
| Elevated fasting ammonia | ||
| Abdominal Doppler ultrasound | Brain MRI | |
| Liver masses | T1 hyperintensity in globus pallidus | |
| Liver biopsy | ||
| Underlying liver disease | ||
| Liver nodules | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bahadori, A.; Kuhlmann, B.; Debray, D.; Franchi-Abella, S.; Wacker, J.; Beghetti, M.; Wildhaber, B.E.; McLin, V.A.; on behalf of the IRCPSS. Presentation of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Children. Children 2022, 9, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9020243
Bahadori A, Kuhlmann B, Debray D, Franchi-Abella S, Wacker J, Beghetti M, Wildhaber BE, McLin VA, on behalf of the IRCPSS. Presentation of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Children. Children. 2022; 9(2):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9020243
Chicago/Turabian StyleBahadori, Atessa, Beatrice Kuhlmann, Dominique Debray, Stephanie Franchi-Abella, Julie Wacker, Maurice Beghetti, Barbara E. Wildhaber, Valérie Anne McLin, and on behalf of the IRCPSS. 2022. "Presentation of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Children" Children 9, no. 2: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9020243
APA StyleBahadori, A., Kuhlmann, B., Debray, D., Franchi-Abella, S., Wacker, J., Beghetti, M., Wildhaber, B. E., McLin, V. A., & on behalf of the IRCPSS. (2022). Presentation of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Children. Children, 9(2), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9020243






