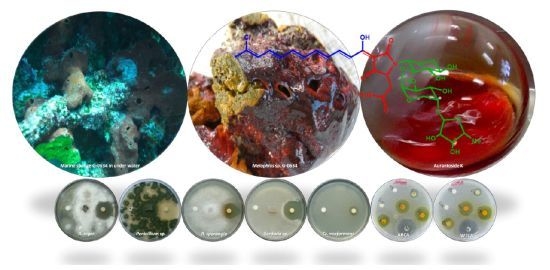
Aurantoside K, a New Antifungal Tetramic Acid Glycoside from a Fijian Marine Sponge of the Genus Melophlus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion


| Position | δH (J in Hz) | δCa | COSY | HMBC b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | c | ||
| 2 | - | c | ||
| 3 | - | 170.3 | ||
| 4 | 4.16 br | 63.8 | 5a, 5b | |
| 5a | 2.54, m | 36.3 | 4 | 3, 6 |
| 5b | 2.59, m | 4 | 3, 6 | |
| 6 | - | 170.3 | ||
| 7 | - | c | ||
| 8 | 6.97 br, d (18.3) | 143.6 | 9 | |
| 9 | 6.61, dd (10.4, 16.9) | 130.6 | 8, 10 | |
| 10 | 6.38, dd (11.3, 13.2) | 127.5 | 9, 11 | |
| 11 | 7.97, dd (13.6, 13.8) | 138.4 | 10, 12 | |
| 12 | 7.12, dd (12.4, 13.1) | 120.2 | 11, 13 | |
| 13 | 7.55, dd (15.1, 11.1) | 144.2 | 12, 14 | |
| 14 | 6.71, d (11.8) | 130.9 | 12, 13, 15 | |
| 15 | 6.58–6.48, m | 133.4 | 14 | |
| 16 | 6.44, d (10.2) | 125.6 | 18 | 18 |
| 17 | - | 133.0 | ||
| 18 | 2.22, s | 26.0 | 16 | 16, 17 |
| 1' | 5.21, m | 79.0 | ||
| 2' | 4.37 br | 79.5 | ||
| 3' | 4.36 br | 83.8 | ||
| 4' | 3.53, m | 63.66 | ||
| 5a' | 3.27, d (8.8) | 77.3 | 2' | |
| 5b' | 3.39, dd (12.3, 6.6) | 2' | ||
| 1" | 4.79, s | 102.3 | ||
| 2" | 3.59, m | 68.4 | 4" | |
| 3" | 3.50, m | 68.9 | 4" | |
| 4" | 3.18, d (11.6) | 63.67 | 2", 3" | 1", 3" |
| 5" | 4.24, d (11.6) | 74.1 | ||
| 1"' | 4.93, m | 102.5 | ||
| 2"' | 3.08, t (10.9) | 67.57 | 3"' | |
| 3"' | 3.71, dd (11.2, 5.5) | 67.60 | 2"', 4"' | 4"' |
| 4"' | 3.38, m | 68.5 | 3"' | |
| 5"' | 1.22 d | c |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedure
3.2. Biological Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Agar Diffusion Assay
3.5. Proliferation Assay
3.6. MTS Dye Conversion Assay
3.7. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration for Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Supplementary Information
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
Supplementary Files
References
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M.; Snader, K.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the period 1981–2002. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1022–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 461–477. [Google Scholar]
- Berrue, F.; Kerr, R.G. Diterpenes from gorgonian corals. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 681–710. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcote, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 165–237. [Google Scholar]
- Marris, E. Marine natural products: Drugs from the deep. Nature 2006, 443, 904–905. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, T.L.; Andrianasolo, E.; McPhail, K.; Flatt, P.; Gerwick, W.H. Marine natural products as anticancer drugs. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 333–342. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, T.L.; Coates, R.C.; Clark, B.R.; Engene, N.; Gonzalez, D.; Esquenazi, E.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Gerwick, W.H. Biosynthetic origin of natural products isolated from marine microorganism-invertebrate assemblages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4587–4594. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, S.; Higuchi, K.; Ye, Y.; Satari, R.; Kobayashi, M. Melophlins A and B, novel tetramic acids reversing the phenotype of ras-transformed cells, from the marine sponge Melophlus sarassinorum. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 1833–1836. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Wang, B.-G.; Wiryowidagdo, S.; Wray, V.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Steube, K.G.; Guan, H.-S.; Proksch, P.; Ebel, R. Melophlins C–O, thirteen novel tetramic acids from the marine sponge Melophlus sarassinorum. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Hasegawa, M.; Harada, K.-I.; Kobayashi, H.; Nagai, H.; Namikoshi, M. Melophlins P, Q, R, and S: Four new tetramic acid derivatives, from two palauan marine sponges of the genus Melophlus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 852–854. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-H.; Seo, Y.; Cho, K.W.; Rho, J.-R.; Shin, J.; Paul, V. New triterpenoid saponins from the sponge Melophlus isis. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 915–919. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, H.-F.; Edrada, R.A.; Ebel, R.; Nimtz, M.; Wray, V.; Proksch, P. Norlanostane triterpenoidal saponins from the marine sponge Melophlus sarassinorum. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, P.; Aalbersberg, W.; Feussner, K.-D.; Wagoner, R.M.V. Papuamides E and F, cytotoxic depsipeptides from the marine sponge Melophlus sp. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 8529–8531. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, S.; Fusetani, N.; Kato, Y.J. Aurantosides A and B: Cytotoxic tetramic acid glycosides from the marine sponge Theonella sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 9690–9692. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, D.; Schmitz, F.J.; Qui, F.; Kelly-Borges, M. Aurantoside C, a new tetramic acid glycoside from the sponge Homophymia conferta. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 170–172. [Google Scholar]
- Sata, N.U.; Matsunaga, S.; Fusetani, N.; van Soest, R.W.M. Aurantosides D, E, and F: New antifungal tetramic acid glycosides from the marine sponge Siliquariaspongia japonica. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 969–971. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnayake, A.S.; Davis, R.A.; Harper, M.K.; Veltri, C.A.; Andjelic, C.D.; Barrows, L.R.; Ireland, C.M. Aurantosides G, H, and I: Three new tetramic acid Glycosides from a Papua New Guinea Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 104–107. [Google Scholar]
- Angawi, R.F.; Bavestrello, G.; Calcinai, B.; Dien, H.A.; Donnarumma, G.; Tufano, M.A.; Paoletti, I.; Grimaldi, E.; Chianese, G.; Fattorusso, E.; et al. Aurantoside J: A new tetramic acid glycoside from Theonella swinhoei. Insights into the antifungal potential of aurantosides. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2809–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G. Marinlit vpc 15.5; University of Canterbury: Christchurch, New Zealand, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, E.W.; Harper, M.K.; Faulkner, D.J. Mozamides A and B, cyclic peptides from a theonellid sponge from mozambique. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 779–782. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, F.Y.F.; Borzilleri, R.; Fairchild, C.R.; Kim, S.H.; Long, B.H.; Raventos-Suarez, C.; Vite, G.D.; Rose, W.C.; Kramer, R.A. A novel epothilone analog with a mode of action similar to paclitaxel but possessing superior antitumor efficacy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar]
- Smilkstein, M.; Sriwilaijaroen, N.; Kelly, J.X.; Wilairat, P.; Riscoe, M. Simple and inexpensive fluorescence-based technique for high-throughput antimalarial drug screening. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1803–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, T.N.; Paguio, M.; Gligorijevic, B.; Seudieu, C.; Kosar, A.D.; Davidson, E.; Roepe, P.D. Novel, rapid, and inexpensive cell-based quantification of antimalarial drug efficacy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1807–1810. [Google Scholar]
- Trager, W.; Jensen, J.B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science 1976, 193, 673–675. [Google Scholar]
- Kubanek, J.; Prusak, A.C.; Snell, T.W.; Giese, R.A.; Hardcastle, K.I.; Fairchild, C.R.; Aalbersberg, W.; Raventos-Suarez, C.; Hay, M.E. Antineoplastic diterpene-benzoate macrolides from the Fijian red alga Callophycus serratus. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 5261–5264. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, R.; Subramani, R.; Feussner, K.-D.; Aalbersberg, W. Aurantoside K, a New Antifungal Tetramic Acid Glycoside from a Fijian Marine Sponge of the Genus Melophlus. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 200-208. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10010200
Kumar R, Subramani R, Feussner K-D, Aalbersberg W. Aurantoside K, a New Antifungal Tetramic Acid Glycoside from a Fijian Marine Sponge of the Genus Melophlus. Marine Drugs. 2012; 10(1):200-208. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10010200
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Rohitesh, Ramesh Subramani, Klaus-D. Feussner, and William Aalbersberg. 2012. "Aurantoside K, a New Antifungal Tetramic Acid Glycoside from a Fijian Marine Sponge of the Genus Melophlus" Marine Drugs 10, no. 1: 200-208. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10010200
APA StyleKumar, R., Subramani, R., Feussner, K.-D., & Aalbersberg, W. (2012). Aurantoside K, a New Antifungal Tetramic Acid Glycoside from a Fijian Marine Sponge of the Genus Melophlus. Marine Drugs, 10(1), 200-208. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10010200