Nature’s Lab for Derivatization: New and Revised Structures of a Variety of Streptophenazines Produced by a Sponge-Derived Streptomyces Strain
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Metabolite Spectrum of HB202

2.2. Structural Constitution of Streptophenazines
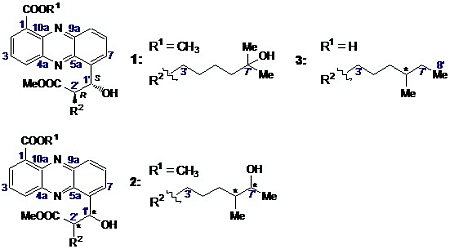
2.2.1. Isolation and Structure of New Streptophenazines

| Position | δC, DEPT | δH, J [Hz] | COSY | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 132.8, C | |||
| 2 | 133.6, CH | 8.29 dd (6.9, 1.4) | 3 | 1-COOCH3, 10a, 4 |
| 3 | 130.9, CH | 7.96 m | 2, 4 | 4a, 1 |
| 4 | 134.8, CH | 8.46 dd (8.8, 1.4) | 3 | 10a, 2 |
| 4a | 144.7, C | |||
| 5a | 142.9, C | |||
| 6 | 143.2, C | |||
| 7 | 130.2, CH | 8.03 m | 8 | 1′, 5a, 9 |
| 8 | 132.5, CH | 7.99 m | 7, 9 | 6 |
| 9 | 130.4, CH | 8.26 dd (8.6, 1.5) | 8 | 7, 5a |
| 9a | 142.8, C | |||
| 10a | 141.9, C | |||
| 1′ | 71.4, CH | 6.16 d (7.7) | 2′ | 2′-COOCH3, 5a, 7 |
| 2′ | 55.0, CH | 3.27 ddd (10.1, 7.7, 4.3) | 1′ | |
| 3′ | 30.5, CH2 | 1.26 m, 1.74 m | ||
| 4′ | 25.2, CH2 | 1.17 m | ||
| 5′ | 29.2, CH2 | 1.17 m | ||
| 6′ | 44.6, CH2 | 1.24 m | 4′ | |
| 7′ | 71.3, C | |||
| 8′ | 29.2, CH3 | 1.03 s | 5′, 6′ | |
| 7′-CH3 | 29.2, CH3 | 1.03 s | 5′, 6′ | |
| 1-COOCH3 | 168.9, C | |||
| 1-COOCH3 | 53.3, CH3 | 4.08 s | 1-COOCH3 | |
| 2′-COOCH3 | 176.8, C | |||
| 2′-COOCH3 | 52.1, CH3 | 3.63 s | 2′-COOCH3 |


2.2.2. Structure Revision of Streptophenazines B–F and H and Structural Comparison
2.3. Bioactivity Assays
| Bacillus subtilis (IC50 [µM]) | Staphylococcus epidermidis (IC50 [µM]) | PDE 4B (IC50 [µM]) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Streptophenazine G 9 | 8.2 µM (± 0.9) | 8.4 µM (± 0.5) | 5.2 (± 1.0) |
| Streptophenazine I 1 | not active | not active | 11. 6 (± 1.1) |
| Streptophenazine J 2 | not active | not active | 12.0 (± 0.9) |
| Streptophenazine K 3 | 21.6 (± 6.8) | 14.5 µM (± 2.0) | 12.2 (± 2.0) |
| Rolipram | not determined | not determined | 0.75 (± 0.05) |
2.4. Biotechnological Upscaling
 pO2 [%], ■ pH,
pO2 [%], ■ pH,  production of streptophenazines I/J [IC].
production of streptophenazines I/J [IC].
 pO2 [%], ■ pH,
pO2 [%], ■ pH,  production of streptophenazines I/J [IC].
production of streptophenazines I/J [IC].

3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Isolation and Identification of Strain Streptomyces sp. HB202
3.3. Cultivation, Extraction and Substance Characterization
 −21° (c 0.0475, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax 215, 251, 347 (sh), 360 (sh), 366; for 1D and 2D NMR data (MeOH-d4, 500 MHz and 125 MHz, respectively) see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z 455.21605 [M + H]+ (calcd for C25H31N2O6: 455.21766).
−21° (c 0.0475, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax 215, 251, 347 (sh), 360 (sh), 366; for 1D and 2D NMR data (MeOH-d4, 500 MHz and 125 MHz, respectively) see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z 455.21605 [M + H]+ (calcd for C25H31N2O6: 455.21766). −18° (c 0.1125, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax 215, 251, 348 (sh), 360 (sh), 366; 1H NMR (CH3OH-d4, 500 MHz) δH 8.45 (1H, m, H-4), 8.28 (1H, dd, J = 7.0, 1.4, H-2), 8.26 (1H, dd, J = 8.6, 1.5, H-9), 8.03 (1H, d, J = 6.9, H-7), 7.99 (1H, m, H-8), 7.95 (1H, m, H-3), 6.17 (1H, d, J = 7.8, H-1′), 4.08 (3H, s, 1-COOCH3), 3.63 (3H, s, 2′-COOCH3), 3.44 (1H, m, H-7′), 3.27 (1H, ddd, J = 10.3, 7.8, 4.4, H-2′), 1.73 (1H, m, H-3′a), 1.29 (m, 1H, H-5′a), 1.25 (1H, m, H-3′b), 1.24 (2H, m, H-4′), 1.23 (1H, m, H-6′), 0.97 (3H, m, H-8′), 0.93 (1H, m, H-5′b), 0.73 (3H, m, 6′-CH3); 13C NMR (CH3OH-d4, 500 MHz): δC 176.8 (C, 2′-COOCH3), 168.9 (C, 1-COOCH3), 144.7 (C, C-6), 143.1 (C, C-5a), 142.9 (C, C-4a), 142.8 (C, C-9a), 141.8 (C, C-10a), 134.8 (CH, C-4), 133.6 (CH, C-2), 132.7 (C, C-1), 132.5 (CH, C-8), 130.8 (CH, C-3), 130.5 (CH, C-9), 130.2 (CH, C-7), 72.0 (CH, C-7′), 71.3 (CH, C-1′), 55.0 (CH, C-2′), 53.3 (CH3, 1-COOCH3), 52.1 (CH3, 2′-COOCH3), 40.8 (CH, C-6′), 33.3 (CH2, C-5′), 30.8 (CH2, C-3′), 26.3 (CH2, C-4′), 20.2 (CH3, C-8′), 14.7 (CH3, 6′-CH3); HRESIMS m/z 455.21637 [M + H]+ (calcd for C25H31N2O6: 455.21766).
−18° (c 0.1125, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax 215, 251, 348 (sh), 360 (sh), 366; 1H NMR (CH3OH-d4, 500 MHz) δH 8.45 (1H, m, H-4), 8.28 (1H, dd, J = 7.0, 1.4, H-2), 8.26 (1H, dd, J = 8.6, 1.5, H-9), 8.03 (1H, d, J = 6.9, H-7), 7.99 (1H, m, H-8), 7.95 (1H, m, H-3), 6.17 (1H, d, J = 7.8, H-1′), 4.08 (3H, s, 1-COOCH3), 3.63 (3H, s, 2′-COOCH3), 3.44 (1H, m, H-7′), 3.27 (1H, ddd, J = 10.3, 7.8, 4.4, H-2′), 1.73 (1H, m, H-3′a), 1.29 (m, 1H, H-5′a), 1.25 (1H, m, H-3′b), 1.24 (2H, m, H-4′), 1.23 (1H, m, H-6′), 0.97 (3H, m, H-8′), 0.93 (1H, m, H-5′b), 0.73 (3H, m, 6′-CH3); 13C NMR (CH3OH-d4, 500 MHz): δC 176.8 (C, 2′-COOCH3), 168.9 (C, 1-COOCH3), 144.7 (C, C-6), 143.1 (C, C-5a), 142.9 (C, C-4a), 142.8 (C, C-9a), 141.8 (C, C-10a), 134.8 (CH, C-4), 133.6 (CH, C-2), 132.7 (C, C-1), 132.5 (CH, C-8), 130.8 (CH, C-3), 130.5 (CH, C-9), 130.2 (CH, C-7), 72.0 (CH, C-7′), 71.3 (CH, C-1′), 55.0 (CH, C-2′), 53.3 (CH3, 1-COOCH3), 52.1 (CH3, 2′-COOCH3), 40.8 (CH, C-6′), 33.3 (CH2, C-5′), 30.8 (CH2, C-3′), 26.3 (CH2, C-4′), 20.2 (CH3, C-8′), 14.7 (CH3, 6′-CH3); HRESIMS m/z 455.21637 [M + H]+ (calcd for C25H31N2O6: 455.21766). −64° (c 0.0900, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax 216, 252, 271 (sh), 361 (sh), 370; 1H NMR (CH3OH-d4, 500 MHz) δH 8.81 (1H, dd, J = 7.0, 1.4, H-2), 8.56 (1H, dd, J = 8.7, 1.4, H-4), 8.26 (1H, dd, J = 7.9, 2.2, H-9), 8.11 (1H, m, H-7), 8.09 (1H, m, H-8), 8.08 (1H, m, H-3), 6.18 (1H, d, J = 7.5, H-1′), 3.62 (3H, s, 2′-COOCH3), 3.25 (1H, ddd, J = 10.4, 7.5, 4.6, H-2′), 1.72 (1H, m, H-3′a), 1.30 (1H, m, H-7′a), 1.24 (2H, m, H-4′), 1.11-1.19 (3H, m, H-3′b, H-5′a, H-6′), 0.93-1.05 (2H, m, H-5′b, H-7′b), 0.75 (3H, m, 6′-CH3), 0.74 (3H, m, H-8′); 13C NMR (CH3OH-d4, 500 MHz): δC 176.6 (C, 2′-COOCH3), 168.5 (C, 1-COOH), 143.7 (C, C-6), 143.6 (C, C-4a), 143.4 (C, C-5a), 141.6 (C, C-9a), 141.3 (C, C-10a), 138.1 (CH, C-2), 136.5 (CH, C-4), 134.4 (CH, C-8), 131.7 (CH, C-3), 130.6 (CH, C-7), 128.7 (CH, C-9), 126.6 (C, C-1), 70.9 (CH, C-1′), 54.9 (CH, C-2′), 52.1 (CH3, 2′-COOCH3), 37.4 (CH2, C-5′), 35.5 (CH, C-6′), 30.7 (CH2, C-3′), 30.4 (CH2, C-7′), 26.0 (CH2, C-4′), 19.5 (CH3, 6′-CH3), 11.8 (CH3, C-8′); HRESIMS m/z 425.20875 [M + H]+ (calcd for C24H29N2O5: 425.20710).
−64° (c 0.0900, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax 216, 252, 271 (sh), 361 (sh), 370; 1H NMR (CH3OH-d4, 500 MHz) δH 8.81 (1H, dd, J = 7.0, 1.4, H-2), 8.56 (1H, dd, J = 8.7, 1.4, H-4), 8.26 (1H, dd, J = 7.9, 2.2, H-9), 8.11 (1H, m, H-7), 8.09 (1H, m, H-8), 8.08 (1H, m, H-3), 6.18 (1H, d, J = 7.5, H-1′), 3.62 (3H, s, 2′-COOCH3), 3.25 (1H, ddd, J = 10.4, 7.5, 4.6, H-2′), 1.72 (1H, m, H-3′a), 1.30 (1H, m, H-7′a), 1.24 (2H, m, H-4′), 1.11-1.19 (3H, m, H-3′b, H-5′a, H-6′), 0.93-1.05 (2H, m, H-5′b, H-7′b), 0.75 (3H, m, 6′-CH3), 0.74 (3H, m, H-8′); 13C NMR (CH3OH-d4, 500 MHz): δC 176.6 (C, 2′-COOCH3), 168.5 (C, 1-COOH), 143.7 (C, C-6), 143.6 (C, C-4a), 143.4 (C, C-5a), 141.6 (C, C-9a), 141.3 (C, C-10a), 138.1 (CH, C-2), 136.5 (CH, C-4), 134.4 (CH, C-8), 131.7 (CH, C-3), 130.6 (CH, C-7), 128.7 (CH, C-9), 126.6 (C, C-1), 70.9 (CH, C-1′), 54.9 (CH, C-2′), 52.1 (CH3, 2′-COOCH3), 37.4 (CH2, C-5′), 35.5 (CH, C-6′), 30.7 (CH2, C-3′), 30.4 (CH2, C-7′), 26.0 (CH2, C-4′), 19.5 (CH3, 6′-CH3), 11.8 (CH3, C-8′); HRESIMS m/z 425.20875 [M + H]+ (calcd for C24H29N2O5: 425.20710).3.4. Determination of Biological Activity
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mentel, M.; Ahuja, E.G.; Mavrodi, D.V.; Breinbauer, R.; Thomashow, L.S.; Blankenfeldt, W. Of two make one: The biosynthesis of phenazines. ChemBioChem 2009, 10, 2295–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villavicencio, R.T. The history of blue pus. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 1998, 187, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, J.B.; Nielsen, J. Phenazine natural products: Biosynthesis, synthetic analogues, and biological activity. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 1663–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, J. Dictionary of Natural Products, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2012; Volume 21. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, V.M.; Nadadhur, G.; Daneluzzi, D.; O’Sullivan, J.F.; Gangadharam, P.R.J. Antituberculosis activities of clofazimine and its new analogs B4154 and B4157. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1996, 40, 633–636. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Liu, K.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, T.; Li, X.; Ma, C.; Zheng, M.; Wang, B.; Zhang, G.; et al. Systematic evaluation of structure-activity relationships of the riminophenazine class and discovery of a C2 pyridylamino series for the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Molecules 2012, 17, 4545–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneemann, I.; Wiese, J.; Kunz, A.L.; Imhoff, J.F. Genetic approach for the fast discovery of phenazine producing bacteria. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 772–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneemann, I.; Nagel, K.; Kajahn, I.; Labes, A.; Wiese, J.; Imhoff, J.F. Comprehensive investigation of marine Actinobacteria associated with the sponge Halichondria panicea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3702–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mavrodi, D.V.; Peever, T.L.; Mavrodi, O.V.; Parejko, J.A.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Lemanceau, P.; Mazurier, S.; Heide, L.; Blankenfeldt, W.; Weller, D.M.; et al. Diversity and evolution of the phenazine biosynthesis pathway. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 866–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitova, M.I.; Lang, G.; Wiese, J.; Imhoff, J.F. Subinhibitory concentrations of antibiotics induce phenazine production in a marine Streptomyces sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Jin, X.; Guaciaro, M.; Molino, B.F.; Mocek, U.; Reategui, R.; Rhea, J.; Morley, T. The revised structure, total synthesis, and absolute configuration of streptophenazine A. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 5436–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Jin, X.; Guaciaro, M.; Molino, B.F. Asymmetric synthesis and absolute configuration of streptophenazine G. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 3191–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, M.T.; Gilmore, B.F.; Gorman, S.P. Staphylococcus epidermidis device-related infections: Pathogenesis and clinical management. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 60, 1551–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, K.F. Update on roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, C.P.; Spina, D. Selective PDE inhibitors as novel treatments for respiratory diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2012, 12, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzelmann, A.; Morcillo, E.J.; Lungarella, G.; Adnot, S.; Sanjar, S.; Beume, R.; Schudt, C.; Tenor, H. The preclinical pharmacology of roflumilast-A selective, oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor in development for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 23, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, H.B.; Bethe, B.; Höfs, R.; Zeeck, A. Big effects from small changes: Possible ways to explore nature’s chemical diversity. ChemBioChem 2002, 3, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, J.F.; Labes, A.; Wiese, J. Bio-mining the microbial treasures of the ocean: New natural products. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muffler, K.; Ulber, R. Downstream Processing in Marine Biotechnology. In Marine Biotechnology II; Ulber, R., Gal, Y.L., Eds.; Springer-Berlin: Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 63–103. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, S.; Pramanik, A.; Mitra, A.; Mukherjee, J. Bioprocessing data for the production of marine enzymes. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1323–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackers, R.G.; Moss, D.; Picton, B.E.; Stone, S.M.K.; Morrow, C.C. Sponges of the British Isles (“Sponge V”), a Colour Guide and Working Document; Marine Conservation Society: Edinburgh, Scotand, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, D.; Beese, P.; Ohlendorf, B.; Erhard, A.; Zinecker, H.; Dorador, C.; Imhoff, J.F. Abenquines A–D: Aminoquinone derivatives produced by Streptomyces sp. strain DB634. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2011, 64, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kunz, A.L.; Labes, A.; Wiese, J.; Bruhn, T.; Bringmann, G.; Imhoff, J.F. Nature’s Lab for Derivatization: New and Revised Structures of a Variety of Streptophenazines Produced by a Sponge-Derived Streptomyces Strain. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1699-1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12041699
Kunz AL, Labes A, Wiese J, Bruhn T, Bringmann G, Imhoff JF. Nature’s Lab for Derivatization: New and Revised Structures of a Variety of Streptophenazines Produced by a Sponge-Derived Streptomyces Strain. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(4):1699-1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12041699
Chicago/Turabian StyleKunz, Anna Lena, Antje Labes, Jutta Wiese, Torsten Bruhn, Gerhard Bringmann, and Johannes F. Imhoff. 2014. "Nature’s Lab for Derivatization: New and Revised Structures of a Variety of Streptophenazines Produced by a Sponge-Derived Streptomyces Strain" Marine Drugs 12, no. 4: 1699-1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12041699
APA StyleKunz, A. L., Labes, A., Wiese, J., Bruhn, T., Bringmann, G., & Imhoff, J. F. (2014). Nature’s Lab for Derivatization: New and Revised Structures of a Variety of Streptophenazines Produced by a Sponge-Derived Streptomyces Strain. Marine Drugs, 12(4), 1699-1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12041699