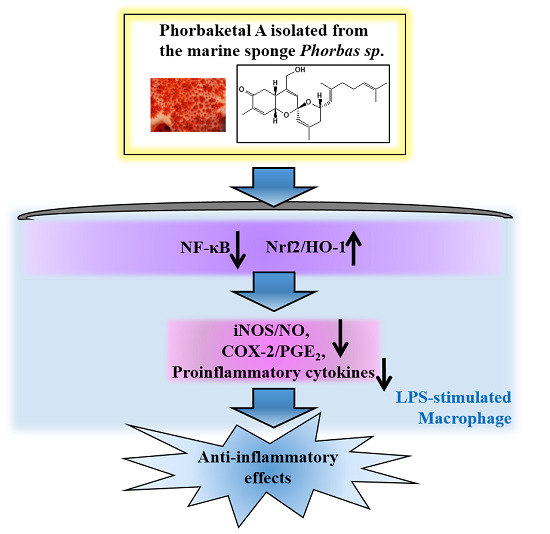
Phorbaketal A, Isolated from the Marine Sponge Phorbas sp., Exerts Its Anti-Inflammatory Effects via NF-κB Inhibition and Heme Oxygenase-1 Activation in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Macrophages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Phorbaketal A Inhibits LPS-Induced NO Production and iNOS Expression in RAW 264.7 Cells




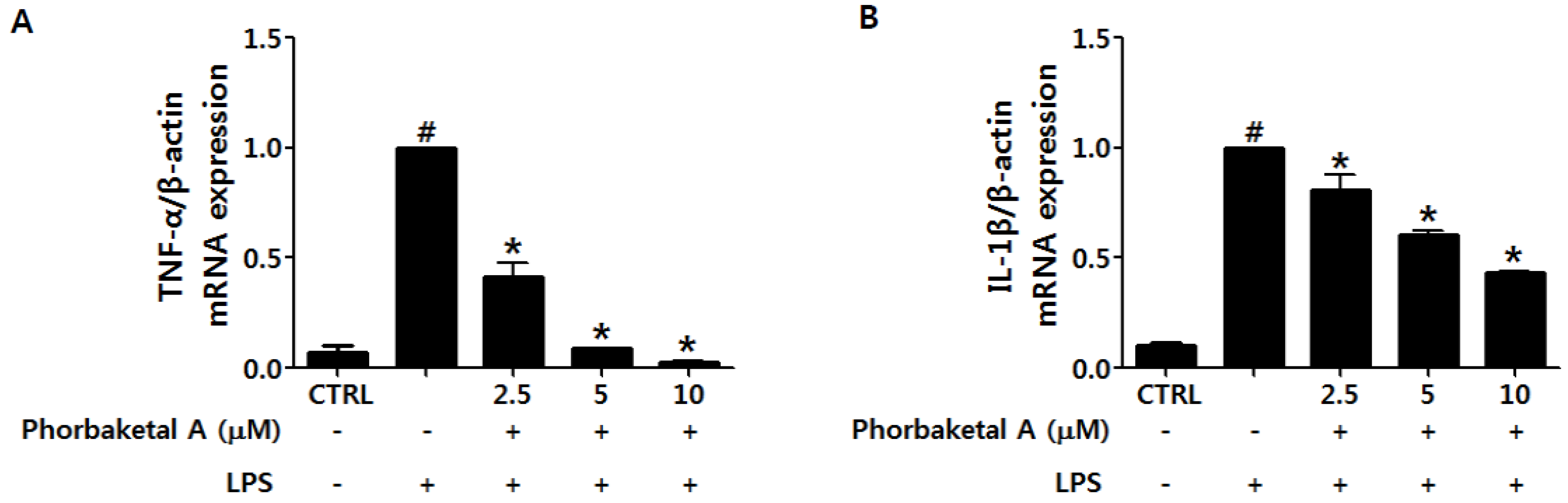
2.2. Phorbaketal A Inhibits the LPS-Induced Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in RAW 264.7 Cells

2.3. Phorbaketal A Inhibits the LPS-Induced Transcriptional Activity of NF-κB in RAW 264.7 Cells

2.4. Phorbaketal A Regulates the HO-1 Pathway in RAW 264.7 Cells

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Preparation of Phorbaketal A
3.2. Materials
3.3. Cell Culture and Sample
3.4. Cell Viability Assay
3.5. Determination of NO Production
3.6. Determination of PGE2 Production
3.7. Real-Time RT-PCR Analysis
3.8. Preparation of Nuclear Fractions
3.9. Western Blot Analysis
3.10. Transfection and Luciferase Assay
3.11. Detection of ROS Production
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shin, J.S.; Noh, Y.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Cho, Y.W.; Baek, N.I.; Choi, M.S.; Jeong, T.S.; Kang, E.; Chung, H.G.; Lee, K.T. Arvelexin from Brassica rapa suppresses NF-κB-regulated pro-inflammatory gene expression by inhibiting activation of IκB kinase. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskin, D.L.; Pendino, K.J. Macrophages and inflammatory mediators in tissue injury. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1995, 35, 655–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaillon, J.M.; Haeffner-Cavaillon, N. Cytokines and inflammation. Rev. Prat. 1993, 43, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Viatour, P.; Merville, M.P.; Bours, V.; Chariot, A. Phosphorylation of NF-kappaB and IkappaB proteins: Implications in cancer and inflammation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005, 30, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, A.; Baltimore, D. Circuitry of nuclear factor kappaB signaling. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 210, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farlik, M.; Reutterer, B.; Schindler, C.; Greten, F.; Vogl, C.; Muller, M.; Decker, T. Nonconventional initiation complex assembly by STAT and NF-kappaB transcription factors regulates nitric oxide synthase expression. Immunity 2010, 33, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paine, A.; Eiz-Vesper, B.; Blasczyk, R.; Immenschuh, S. Signaling to heme oxygenase-1 and its anti-inflammatory therapeutic potential. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1895–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryter, S.W.; Alam, J.; Choi, A.M. Heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide: From basic science to therapeutic applications. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 583–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, R.P.; Ewanick, S.M.; Chung, P.A.; Au-Yeung, K.; del Rio, L.; Mabee, W.; Saddler, J.N. Comparison of methods to assess the enzyme accessibility and hydrolysis of pretreated lignocellulosic substrates. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otterbein, L.E.; Bach, F.H.; Alam, J.; Soares, M.; Lu, H.T.; Wysk, M.; Davis, R.J.; Flavell, R.A.; Choi, A.M.K. Carbon monoxide has anti-inflammatory effects involving the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wiesel, P.; Foster, L.C.; Pellacani, A.; Layne, M.D.; Hsieh, C.M.; Huggins, G.S.; Strauss, P.; Yet, S.F.; Perrella, M.A. Thioredoxin facilitates the induction of heme oxygenase-1 in response to inflammatory mediators. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 24840–24846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, G.Y.; Jin, Y.; Yi, A.K.; Wang, X.M.; Choi, A.M. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein mediates carbon monoxide-induced suppression of cyclooxygenase-2. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 35, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, G.S.; Pae, H.O.; Lee, B.S.; Kim, B.N.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, H.R.; Jeon, S.B.; Jeon, W.K.; Chae, H.J.; Chung, H.T. Hydrogen sulfide inhibits nitric oxide production and nuclear factor-κB via heme oxygenase-1 expression in RAW264.7 macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Nioi, P.; Pickett, C.B. The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 13291–13295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Johnson, J.A. An important role of Nrf2-ARE pathway in the cellular defense mechanism. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 37, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcote, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2004, 21, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erwin, P.M.; Lopez-Legentil, S.; Schuhmann, P.W. The pharmaceutical value of marine biodiversity for anti-cancer drug discovery. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 70, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, F.; Jaspars, M.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Marine natural products as targeted modulators of the transcription factor NF-kappa B. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proksch, P.; McPhee, D.J.; Lin, S.K. Biomedical compounds from marine organisms (retraction of volume 2, p. 123, 2004). Mar. Drugs 2005, 3, 123–146. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Rodriguez, A.D.; Berlinck, R.G.S.; Hamann, M.T. Marine pharmacology in 2005-6: Marine compounds with anthelmintic, antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; affecting the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 283–308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.J.; Desbois, A.P.; Dyrynda, E.A. Conventional and unconventional antimicrobials from fish, marine invertebrates and micro-algae. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1213–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Hu, W.P.; Munro, M.H.; Northcote, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 170–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, T.R.A.; Kavlekar, D.P.; LokaBharathi, P.A. Marine drugs from sponge-microbe association-A review. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1417–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, W.J.; Heo, S.J.; Han, S.C.; Lee, H.J.; Kang, G.J.; Kang, H.K.; Hyun, J.W.; Koh, Y.S.; Yoo, E.S. Anti-inflammatory effect of sargachromanol G isolated from sargassum siliquastrum in RAW 264.7 cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, D.; Manzoor, Z.; Kim, S.C.; Kim, S.; Oh, T.H.; Yoo, E.S.; Kang, H.K.; Hyun, J.W.; Lee, N.H.; Ko, M.H.; et al. Apo-9′-fucoxanthinone, isolated from sargassum muticum, inhibits CpG-induced inflammatory response by attenuating the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3272–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Capon, R.J. Phorbasins D–F: Diterpenyl-taurines from a southern Australian marine sponge, Phorbas sp. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 1959–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rho, J.R.; Hwang, B.S.; Sim, C.J.; Joung, S.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, H.J. Phorbaketals A, B, and C, sesterterpenoids with a spiroketal of hydrobenzopyran moiety isolated from the marine sponge Phorbas sp. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5590–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, M.R.; Lee, C.H.; Hwang, J.H.; Kim, A.R.; Moon, S.A.; Sung, M.K.; Roh, J.R.; Hwang, E.S.; Hong, J.H. Phorbaketal A inhibits adipogenic differentiation through the suppression of PPARγ-mediated gene transcription by TAZ. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 718, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, M.R.; Kim, A.R.; Hwang, J.H.; Sung, M.K.; Lee, Y.K.; Hwang, B.S.; Rho, J.R.; Hwang, E.S.; Hong, J.H. Phorbaketal A stimulates osteoblast differentiation through TAZ mediated Runx2 activation. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samavati, L.; Rastogi, R.; Du, W.J.; Huettemann, M.; Fite, A.; Franchi, L. STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation is critical for interleukin 1 beta and interleukin-6 production in response to lipopolysaccharide and live bacteria. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 1867–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viedt, C.; Dechend, R.; Fei, J.; Hansch, G.M.; Kreuzer, J.; Orth, S.R. MCP-1 induces inflammatory activation of human tubular epithelial cells: Involvement of the transcription factors, nuclear factor-kappaB and activating protein-1. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 1534–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, D.E.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. Stats: Transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.J. The JAK-STAT signaling pathway: Input and output integration. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 2623–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfitzner, E.; Kliem, S.; Baus, D.; Litterst, C.M. The role of STATs in inflammation and inflammatory diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 2839–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinne, R.W.; Brauer, R.; Stuhlmuller, B.; Palombo-Kinne, E.; Burmester, G.R. Macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2000, 2, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Surh, Y.J.; Chun, K.S.; Cha, H.H.; Han, S.S.; Keum, Y.S.; Park, K.K.; Lee, S.S. Molecular mechanisms underlying chemopreventive activities of anti-inflammatory phytochemicals: Down-regulation of COX-2 and iNOS through suppression of NF-kappa B activation. Mutat. Res. 2001, 480–481, 243–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreck, R.; Meier, B.; Mannel, D.N.; Droge, W.; Baeuerle, P.A. Dithiocarbamates as potent inhibitors of nuclear factor kappa B activation in intact-cells. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 175, 1181–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, C.K.; Packer, L. Antioxidant and redox regulation of gene transcription. FASEB J. 1996, 10, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.; Schreck, R.; Baeuerle, P.A. H2O2 and antioxidants have opposite effects on activation of NF-kappa B and AP-1 in intact-cells: AP-1 as secondary antioxidant-responsive factor. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 2005–2015. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Staal, F.J.; Anderson, M.T.; Herzenberg, L.A. Redox regulation of activation of NF-kappa B transcription factor complex: Effects of N-acetylcysteine. Methods Enzymal. 1995, 252, 168–174. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, R.; Beauparlant, P.; Elford, H.; Ponka, P.; Hiscott, J. Selective inhibition of I kappaB alpha phosphorylation and HIV-1 LTR-directed gene expression by novel antioxidant compounds. Virology 1997, 234, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sappey, C.; Legrandpoels, S.; Bestbelpomme, M.; Favier, A.; Rentier, B.; Piette, J. Stimulation of glutathione-peroxidase activity decreases HIV type-1 activation after oxidative stress. Aids Res. Hum. Retroviruses 1994, 10, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.H.; McGrath, K.C.Y.; Tran, V.H.; Li, Y.M.; Duke, C.C.; Roufogalis, B.D.; Heather, A.K. Attenuation of proinflammatory responses by S-[6]-gingerol via inhibition of ROS/NF-kappa B/COX2 activation in HuH7 cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Balla, J.; Otterbein, L.; Smith, R.N.; Brouard, S.; Lin, Y.; Csizmadia, E.; Sevigny, J.; Robson, S.C.; Vercellotti, G.; et al. Carbon monoxide generated by heme oxygenase-1 suppresses the rejection of mouse-to-rat cardiac transplants. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 4185–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, G.; Kong, A.N. Nrf2 plays an important role in coordinated regulation of phase ii drug metabolism enzymes and phase iii drug transporters. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2009, 30, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.S.; Hong, M.Z.; Ren, J.L. Reactive oxygen species: A double-edged sword in oncogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 1702–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aruoma, O.I.; Grootveld, M.; Bahorun, T. Free radicals in biology and medicine: From inflammation to biotechnology. Biofactors 2006, 27, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lum, H.; Roebuck, K.A. Oxidant stress and endothelial cell dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2001, 280, C719–C741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Jung, J.H.; Zhang, S. Sesterterpenoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 1401–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, J.R. Diterpenoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1996, 13, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013, 30, 237–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evidente, A.; Kornienko, A.; Lefranc, F.; Cimmino, A.; Dasari, R.; Evidente, M.; Mathieu, V.; Kiss, R. Sesterterpenoids with anticancer activity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 3502–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyaoka, H.; Yamada, Y. Total synthesis of bioactive marine terpenoids. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2002, 75, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebada, S.S.; Lin, W.; Proksch, P. Bioactive sesterterpenes and triterpenes from marine sponges: Occurrence and pharmacological significance. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 313–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, Y.-J.; Lee, K.-T.; Rho, J.-R.; Choi, J.-H. Phorbaketal A, Isolated from the Marine Sponge Phorbas sp., Exerts Its Anti-Inflammatory Effects via NF-κB Inhibition and Heme Oxygenase-1 Activation in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Macrophages. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 7005-7019. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13117005
Seo Y-J, Lee K-T, Rho J-R, Choi J-H. Phorbaketal A, Isolated from the Marine Sponge Phorbas sp., Exerts Its Anti-Inflammatory Effects via NF-κB Inhibition and Heme Oxygenase-1 Activation in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Macrophages. Marine Drugs. 2015; 13(11):7005-7019. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13117005
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Yun-Ji, Kyung-Tae Lee, Jung-Rae Rho, and Jung-Hye Choi. 2015. "Phorbaketal A, Isolated from the Marine Sponge Phorbas sp., Exerts Its Anti-Inflammatory Effects via NF-κB Inhibition and Heme Oxygenase-1 Activation in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Macrophages" Marine Drugs 13, no. 11: 7005-7019. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13117005
APA StyleSeo, Y. -J., Lee, K. -T., Rho, J. -R., & Choi, J. -H. (2015). Phorbaketal A, Isolated from the Marine Sponge Phorbas sp., Exerts Its Anti-Inflammatory Effects via NF-κB Inhibition and Heme Oxygenase-1 Activation in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Macrophages. Marine Drugs, 13(11), 7005-7019. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13117005