Generation of Internal-Image Functional Aptamers of Okadaic Acid via Magnetic-Bead SELEX
Abstract
:1. Introduction
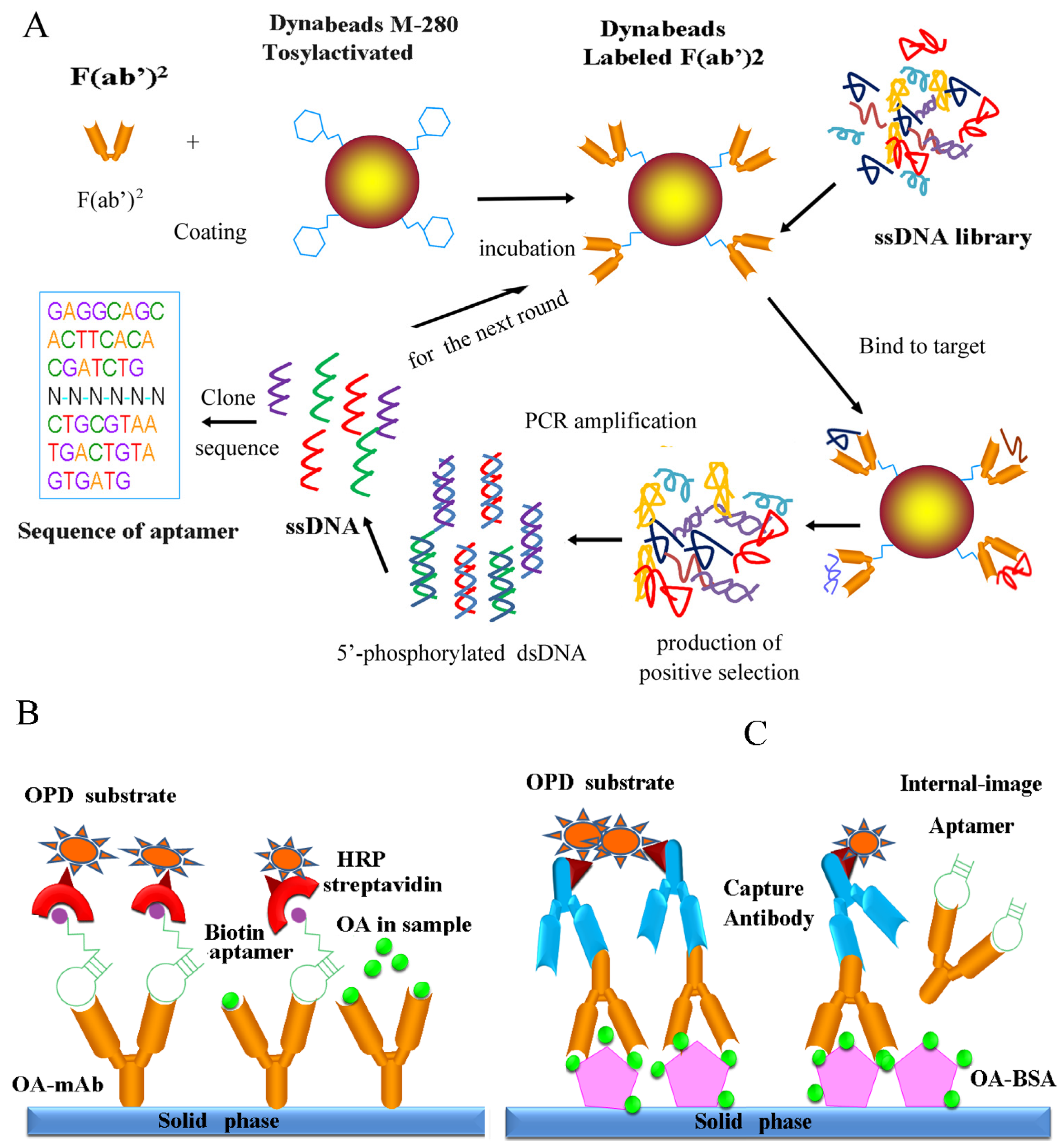
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
| Sequence ID | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| ssDNA library | 5′-GAGGCAGCACTTCACACGATCTG-N40-CTGCGTAATGACTGTAGTGATG-3′ |
| forward primer | 5′-GAGGCAGCACTTCACACGAT-3′ |
| reverse primer | 5′-CATCACTACAGTCATTACGCAG-3′ |
| biotin-primer | Bio-GAGGCAGCACTTCACACGAT-3′ |
| phosphate-primer | Pho-CATCACTACAGTCATTACGCAG-3′ |
2.2. Preparation of the F(ab′)2 Fragment as a Screening Target
2.3. Immobilization of F(ab′)2 Fragments Onto Dynabeads
2.4. In Vitro Selection of Aptamers for OA-mAb-F(ab′)2
2.5. PCR Amplification
2.6. ssDNA Generation
2.7. Cloning, Sequencing and Structure Analysis of the Selected Aptamers
2.8. Affinity Measurements of Selected Aptamers
2.9. Identification and Characterization of Internal-Image Aptamers
2.10. Inter and Intra-Assay Variation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of F(ab′)2 Fragments
3.2. Immobilization of OA-mAb-F(ab′)2 onto Dynabeads

3.3. In Vitro Selection of OA-mAb-F(ab′)2-Targeting Aptamers
| SELEX | ssDNA Library | Target | Elution Times |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rounds | (pmol) | (μM) | (times) |
| 1 | 2000 | 200 | 6 |
| 2 | 1500 | 200 | 9 |
| 3 | 1000 | 150 | 10 |
| 4 | 500 | 150 | 10 |
| 5 | 500 | 100 | 15 |
| 6 | 400 | 100 | 15 |
| 7 | 200 | 50 | 18 |
| 8 | 200 | 50 | 20 |
| 9 | 200 | 25 | 20 |
| 10 | 100 | 25 | 25 |
| 11 | 100 | 20 | 25 |
| 12 | 100 | 10 | 25 |
3.4. The Result of SELEX

3.5. Prediction of the Secondary Structures of Selected Aptamers

3.6. The Results of the Specificity and Ka Tests

3.7. Internal-Image Function of the Selected Aptamers

3.8. Intra and Inter-Assay Variation
| Apatmer | Concentration (ng·mL−1) | Inter-Assay (n = 3) | Intra-Assay (n = 3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OD492 Mean ± SD (X ± SD) | CV% | OD492 Mean ± SD (X ± SD) | CV% | ||
| Ab-24 | 0 | 1.04 ± 0.016 | 1.5 | 1.17 ± 0.047 | 4.0 |
| 10 | 0.63 ± 0.028 | 4.4 | 0.75 ± 0.035 | 4.6 | |
| 50 | 0.17 ± 0.012 | 7.0 | 0.23 ± 0.017 | 7.4 | |
| Ab-31 | 0 | 1.12 ± 0.031 | 2.7 | 1.02 ± 0.032 | 3.1 |
| 10 | 0.62 ± 0.025 | 4.0 | 0.55 ± 0.012 | 2.2 | |
| 50 | 0.09 ± 0.005 | 5.5 | 0.08 ± 0.007 | 8.8 | |
| Ab-39 | 0 | 1.13 ± 0.032 | 2.8 | 1.09 ± 0.023 | 2.1 |
| 10 | 0.71 ± 0.016 | 2.2 | 0.64 ± 0.015 | 2.3 | |
| 50 | 0.13 ± 0.009 | 6.9 | 0.13 ± 0.002 | 1.5 | |
| Ab-40 | 0 | 1.12 ± 0.025 | 2.2 | 1.18 ± 0.045 | 4.4 |
| 10 | 0.69 ± 0.014 | 2.0 | 0.72 ± 0.017 | 2.4 | |
| 50 | 0.18 ± 0.007 | 3.8 | 0.22 ± 0.016 | 7.2 | |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Codd, G.A.; Ward, C.J.; Bell, S.G. Cyanobacterial Toxins: Occurrence, Modes of Action, Health Effects and Exposure Routes; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1997; Volume 19, pp. 399–410. [Google Scholar]
- Scoging, A.; Bahl, M. Diarrhetic shellfish poisoning in the UK. Lancet 1998, 352, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armi, Z.; Turki, S.; Trabelsi, E.; Ceredi, A.; Riccardi, E.; Milandri, A. Occurrence of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) toxins in clams (Ruditapes decussatus) from Tunis north lagoon. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 184, 5085–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossen, V.; Jourdan-da Silva, N.; Guillois-Becel, Y.; Marchal, J.; Krys, S. Food poisoning outbreaks linked to mussels contaminated with okadaic acid and ester dinophysistoxin-3 in france, June 2009. Euro Surveill. 2011, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Ma, J.; Cao, J.; McCarron, P. Toxins in mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) associated with diarrhetic shellfish poisoning episodes in China. Toxicon 2012, 60, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, S.L.; Tindall, D.R. Determination of okadaic acid content of dinoflagellate cells: A comparison of the HPLC-fluorescent method and two monoclonal antibody ELISA test kits. Toxicon 1996, 34, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacem, I.; Hajjem, B.; Bouaïcha, N. First evidence of okadaic acid in Mytilus galloprovincialis mussels, collected in a mediterranean lagoon, Tunisia. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 82, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Liu, Z.S.; Tan, C.Y.; Guo, Y.P.; Li, L.; Ren, H.L.; Li, Y.S.; Hu, P.; Gong, S.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Contamination of commercially available seafood by key diarrhetic shellfish poisons along the coast of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commission, E. Commission regulation (EU) amending regulation (EC) no 2074/2005 as regards recognized testing methods for detecting marine biotoxins in live bivalve molluscs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2011, 15, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto, T. Occurrence of a new type of shellfish poisoning in the Tohoku district. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1978, 44, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louppis, A.P.; Badeka, A.V.; Katikou, P.; Paleologos, E.K.; Kontominas, M.G. Determination of okadaic acid, dinophysistoxin-1 and related esters in greek mussels using HPLC with fluorometric detection, LC-MS/MS and mouse bioassay. Toxicon 2010, 55, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Quilliam, M.A. LC-MS/MS analysis of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) toxins, okadaic acid and dinophysistoxin analogues, and other lipophilic toxins. Anal. Sci. 2011, 27, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stobo, L.A.; Lacaze, J.-P.C.L.; Scott, A.C.; Gallacher, S.; Smith, E.A.; Quilliam, M.A. Liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry—detection of lipophilic shellfish toxins. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Draisci, R.; Croci, L.; Giannetti, L.; Cozzi, L.; Lucentini, L.; de Medici, D.; Stacchini, A. Comparison of mouse bioassay, HPLC and enzyme immunoassay methods for determining diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins in mussels. Toxicon 1994, 32, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.-Y.; Lin, C.; Li, Y.-S.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, X.-M.; Yu, S.-Y.; Li, Z.-H.; Li, L.; Ren, H.-L.; Liu, Z.-S. A screening lateral flow immunochromatographic assay for on-site detection of okadaic acid in shellfish products. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 422, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.-S.; Lin, C.; Meng, X.-M.; Yan, D.-M.; Li, Z.-H.; Yu, S.-Y.; Liu, Z.-S.; Ren, H.-L. Production of monoclonal antibody and application in indirect competitive ELISA for detecting okadaic acid and dinophytoxin-1 in seafood. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 2619–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vdovenko, M.M.; Hung, C.-T.; Sakharov, I.Y.; Yu, F.-Y. Determination of okadaic acid in shellfish by using a novel chemiluminescent enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method. Talanta 2013, 116, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Liu, Z.-S.; Wang, D.-X.; Ren, H.-L.; Li, Y.-S.; Hu, P.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, Y.-P.; Meng, X.-M.; Lu, S.-Y. Sensitive and reliable micro-plate chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for okadaic acid in shellfish. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 7142–7148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, L.; Polisky, B.; Uhlenbeck, O.; Yarus, M. Diversity of oligonucleotide functions. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1995, 64, 763–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Stormo, G.D. Combining SELEX with quantitative assays to rapidly obtain accurate models of protein-DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuerk, C.; MacDougal, S.; Gold, L. RNA pseudoknots that inhibit human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 6988–6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassanfar, M.; Szostak, J.W. An RNA motif that binds ATP. Nature 1993, 364, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.; Nix, J.; Szostak, J. Functional requirements for specific ligand recognition by a biotin-binding RNA pseudoknot. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 14410–14419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macaya, R.F.; Schultze, P.; Smith, F.W.; Roe, J.A.; Feigon, J. Thrombin-binding DNA aptamer forms a unimolecular quadruplex structure in solution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 3745–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drolet, D.W.; Jenison, R.D.; Smith, D.E.; Pratt, D.; Hicke, B.J. A high throughput platform for systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX). Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 1999, 2, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gong, S.; Ren, H.-L.; Tian, R.-Y.; Lin, C.; Hu, P.; Li, Y.-S.; Liu, Z.-S.; Song, J.; Tang, F.; Zhou, Y.; et al. A novel analytical probe binding to a potential carcinogenic factor of n-glycolylneuraminic acid by selex. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 49, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.K.; Zou, Q.; Sun, J.H.; Wang, H.A.; Sun, X.; Chen, Z.F.; Yan, Y.X. Screening of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) aptamers against a zearalenone monoclonal antibody and development of a ssDNA-based enzyme-linked oligonucleotide assay for determination of zearalenone in corn. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avci-Adali, M.; Paul, A.; Wilhelm, N.; Ziemer, G.; Wendel, H.P. Upgrading SELEX technology by using lambda exonuclease digestion for single-stranded DNA generation. Molecules 2010, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beatty, J.D.; Beatty, B.G.; Vlahos, W.G. Measurement of monoclonal antibody affinity by non-competitive enzyme immunoassay. J. Immunol. Methods 1987, 100, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.S.; Qian, J.; Lou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Soh, H.T. Generation of highly specific aptamers via micromagnetic selection. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5490–5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.-S.; Pan, F.-G.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Lu, S.-Y.; Ren, H.-L.; Li, Z.-H.; Liu, Z.-S.; Zhang, J.-H. Development of a new monoclonal antibody based direct competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of brevetoxins in food samples. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Shen, Q.-F.; Lu, S.-Y.; Ren, H.-L.; Li, Y.-S.; Liu, Z.-S.; Pan, F.-G.; Meng, X.-M.; Zhang, J.-H. Development of a novel antibody probe useful for domoic acid detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3159–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.-S.; Zhi, B.-H.; Lu, S.-Y.; Ren, H.-L.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Li, Z.-H.; Shen, Q.-F.; Meng, X.-M.; Liu, Z.-S.; et al. Detection of nodularin based on a monoclonal antibody in water and aquatic fish samples. Food Control 2011, 22, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, S.; Ren, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, F.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z. Gold nanoparticle probe-based immunoassay as a new tool for tetrodotoxin detection in puffer fish tissues. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 146, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.; Liu, Z.-S.; Wang, D.-X.; Li, L.; Hu, P.; Gong, S.; Li, Y.-S.; Cui, C.; Wu, Z.-C.; Gao, Y.; et al. Generation of Internal-Image Functional Aptamers of Okadaic Acid via Magnetic-Bead SELEX. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 7433-7445. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13127066
Lin C, Liu Z-S, Wang D-X, Li L, Hu P, Gong S, Li Y-S, Cui C, Wu Z-C, Gao Y, et al. Generation of Internal-Image Functional Aptamers of Okadaic Acid via Magnetic-Bead SELEX. Marine Drugs. 2015; 13(12):7433-7445. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13127066
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chao, Zeng-Shan Liu, Dong-Xu Wang, Lin Li, Pan Hu, Sheng Gong, Yan-Song Li, Cheng Cui, Zong-Cheng Wu, Yang Gao, and et al. 2015. "Generation of Internal-Image Functional Aptamers of Okadaic Acid via Magnetic-Bead SELEX" Marine Drugs 13, no. 12: 7433-7445. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13127066
APA StyleLin, C., Liu, Z.-S., Wang, D.-X., Li, L., Hu, P., Gong, S., Li, Y.-S., Cui, C., Wu, Z.-C., Gao, Y., Zhou, Y., Ren, H.-L., & Lu, S.-Y. (2015). Generation of Internal-Image Functional Aptamers of Okadaic Acid via Magnetic-Bead SELEX. Marine Drugs, 13(12), 7433-7445. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13127066