Alkynyl-Containing Peptides of Marine Origin: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cyclic Peptides Containing Terminal Alkyne
2.1. Cyclic Peptides with Dhoya Unit from Marine Cyanobacteria
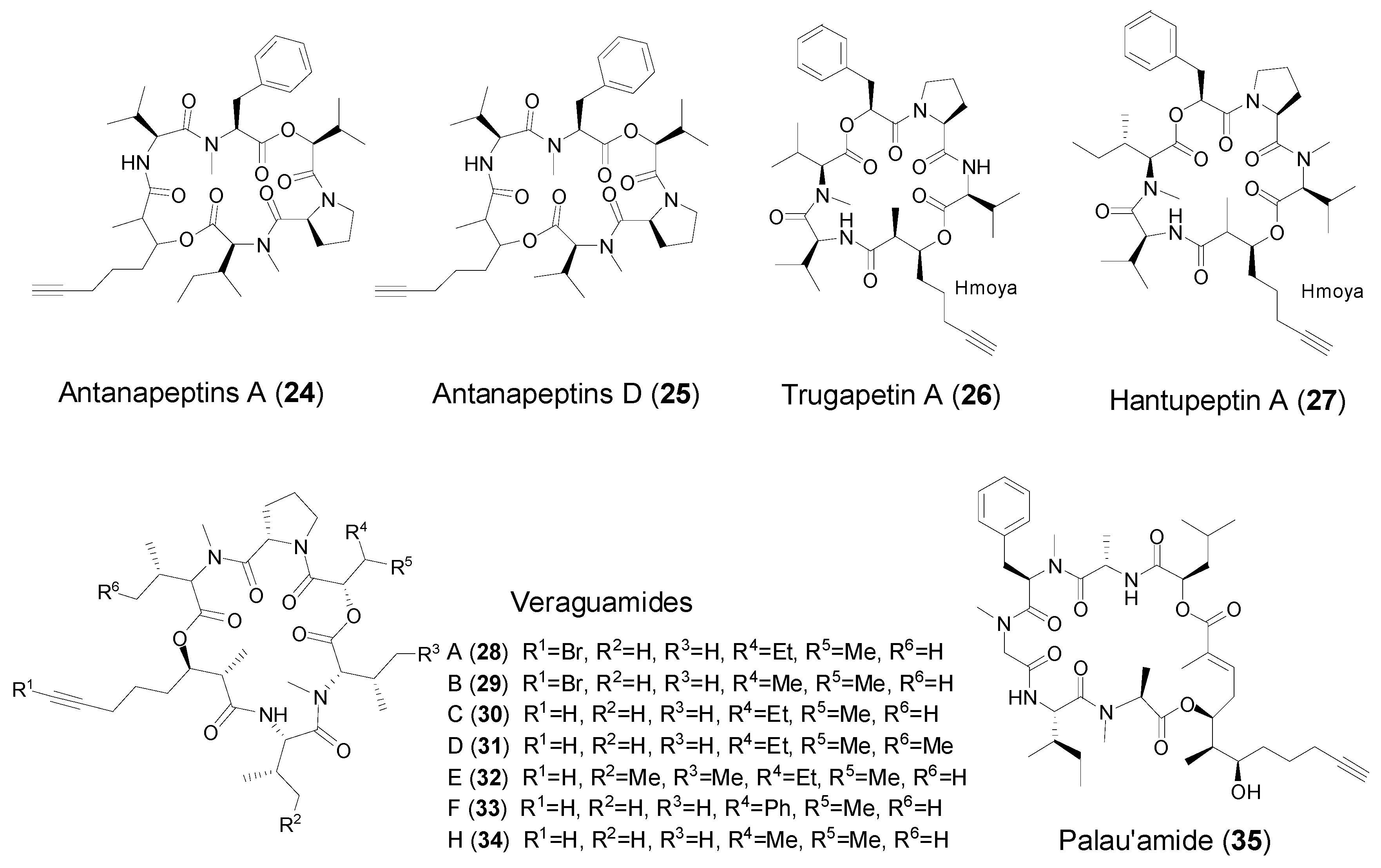
2.2. Cyclic Peptides with Amoya Unit from Marine Cyanobacteria
2.3. Cyclic Peptides with Hmoya/Br-Hmoya/Dddd Units from Marine Cyanobacteria
2.4. Cyclic Peptides from Marine Mollusks
3. Acyclic Lipopeptides Containing Terminal Alkyne from Marine Cyanobacteria
4. Different Methods to Determine the Absolute Configuration of Different Alkynyl Fragments
4.1. Amoya (a)
4.2. Hmoya (b)
4.3. Dhoya (d)
4.4. Moya (h)
4.5. Other Special Fragments
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, M.; Costa-Rodrigues, J.; Fernandes, M.H.; Barros, P.; Vasconcelos, V.; Martins, R. Marine cyanobacteria compounds with anticancer properties: A review on the implication of apoptosis. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2181–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, R.C.; Ng, T.B.; Wong, J.H. Marine peptides: Bioactivities and applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4006–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, C.; Khan, F.F.; Khan, M.I.; Iqbal, J. Marine bioactive peptides: Types, structures, and physiological functions. Food Rev. Int. 2016, 33, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Sheng, J.; Wang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, X.K.; Sun, M. Antitumor peptides from marine organisms. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1840–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipkema, D.; Franssen, M.C.; Osinga, R.; Tramper, J.; Wijffels, R.H. Marine sponges as pharmacy. Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 142–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andavan, G.S.; Lemmens-Gruber, R. Cyclodepsipeptides from marine sponges: Natural agents for drug research. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 810–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, D.S.; Joshi, M.C.; Joshi, P.; Atheaya, H. Marine peptides and related compounds in clinical trial. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2006, 6, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 160–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.J.; Jeong, J.-K.; Choi, Y.M.; Lee, M.S.; Choi, J.H.; Cho, E.J.; Song, H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, J.-H.; Hong, S.S. Dolastatin-10 derivative method of producing the same and anticancer drug composition containing the same. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 6883–6885. [Google Scholar]
- Luesch, H.; Moore, R.E.; Paul, V.J.; Mooberry, S.L.; Corbett, T.H. Isolation of dolastatin 10 from the marine cyanobacterium symploca species vp642 and total stereochemistry and biological evaluation of its analogue symplostatin 1. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 907–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, J.; Fernández, R.; Quiñoá, E.; Riguera, R.; Debitus, C.; Bouchetj, P. Onchidin: A cytotoxic depsipeptide with C2 symmetry from a marine mollusc. Tetmhedron Lett. 1994, 35, 9239–9242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitachitta, N.; Williamson, R.T.; Gerwick, W.H. Yanucamides a and b, two new depsipeptides from an assemblage of the marine cyanobacteria Lyngbya majuscula and Schizothrix species. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mevers, E.; Liu, W.T.; Engene, N.; Mohimani, H.; Byrum, T.; Pevzner, P.A.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Spadafora, C.; Gerwick, W.H. Cytotoxic veraguamides, alkynyl bromide-containing cyclic depsipeptides from the marine cyanobacterium cf. Oscillatoria margaritifera. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, L.M.; Lopez, D.; Vesely, B.A.; Della Togna, G.; Gerwick, W.H.; Kyle, D.E.; Linington, R.G. Almiramides a–c: Discovery and development of a new class of leishmaniasis lead compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4187–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minto, R.E.; Blacklock, B.J. Biosynthesis and function of polyacetylenes and allied natural products. Prog. Lipid Res. 2008, 47, 233–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Park, H.-J.; Ishizuka, S.; Omata, K.; Hirama, M. Chemistry and antimicrobial activity of caryoynencins analogs. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 5015–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarajan, M.; Maruthanayagam, V.; Sundararaman, M. A review of pharmacological and toxicological potentials of marine cyanobacterial metabolites. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2012, 32, 153–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, R.; Hemaiswarya, S.; Ganesan, V.; Carvalho, I.S. Recent developments in therapeutic applications of cyanobacteria. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, A.D. Numbers of Living Species in Australia and the World; Departmwnt of the Environment: Canberra, Australia, 2010.
- Aneiros, A.; Garateix, A. Bioactive peptides from marine sources: Pharmacological properties and isolation procedures. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2004, 803, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Jimenez, G.M.; Burgos-Hernandez, A.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M. Bioactive peptides and depsipeptides with anticancer potential: Sources from marine animals. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 963–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luesch, H.; Pangilinan, R.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Moore, R.E.; Paul, V.J. Pitipeptolides a and b, new cyclodepsipeptides from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Gross, H.; McPhail, K.L.; Goeger, D.; Maier, C.S.; Gerwick, W.H. Wewakamide a and guineamide g, cyclic depsipeptides from the marine cyanobacteria Lyngbya semiplena and Lyngbya majuscula. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 21, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, F.; Erickson, K.L. Georgamide, a new cyclic depsipeptide with an alkynoic acid residue from an australian cyanobacterium. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.-T.; Ng, J.; Meluzzi, D.; Bandeira, N.; Gutierrez, M.; Simmons, T.L.; Schultz, A.W.; Linington, R.G.; Moore, B.S.; Gerwick, W.H.; et al. Interpretation of tandem mass spectra obtained from cyclic nonribosomal peptides. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 4200–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaser, R.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Pitipeptolides c-f, antimycobacterial cyclodepsipeptides from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula from guam. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 2068–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunasekera, S.P.; Owle, C.S.; Montaser, R.; Luesch, H.; Paul, V.J. Malyngamide 3 and cocosamides a and b from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula from cocos lagoon, guam. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudreau, P.D.; Byrum, T.; Liu, W.T.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Gerwick, W.H. Viequeamide a, a cytotoxic member of the kulolide superfamily of cyclic depsipeptides from a marine button cyanobacterium. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1560–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reese, M.T.; Gulavita, N.K.; Nakao, Y.; Hamann, M.T.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Coval, S.J.; Scheuer, P.J. Kulolide: A cytotoxic depsipeptide from a cephalaspidean mollusk, philinopsis speciosa1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 11081–11084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, Y.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Szabo, C.M.; Baker, B.J.; Scheuer, P.J. More peptides and other diverse constituents of the marine mollusk philinopsis speciosa. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 3272–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Goeger, D.; Maier, C.S.; Gerwick, W.H. The wewakpeptins, cyclic depsipeptides from a papua new guinea collection of the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya semiplena. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 70, 3133–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horgen, F.D.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Scheuer, P.J. Malevamides a–c, new depsipeptides from the marine cyanobacterium symploca laete-viridis. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.T.; Sitachitta, N.; Gerwick, W.H. The guineamides, novel cyclic depsipeptides from a papua new guinea collection of the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 66, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.G.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Quon, M.K.; Moore, R.E.; Paul, V.J. Ulongapeptin, a cytotoxic cyclic depsipeptide from a palauan marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vining, O.B.; Medina, R.A.; Mitchell, E.A.; Videau, P.; Li, D.; Serrill, J.D.; Kelly, J.X.; Gerwick, W.H.; Proteau, P.J.; Ishmael, J.E.; et al. Depsipeptide companeramides from a panamanian marine cyanobacterium associated with the coibamide producer. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, R.; Rodríguez, J.; Quiñoá, E.; Riguera, R.; Muñoz, L.; Fernández-Suárez, M.; Debitus, C. Onchidin b: A new cyclodepsipeptide from the mollusc Onchidium sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 11635–11643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogle, L.M.; Gerwick, W.H. Isolation of four new cyclic depsipeptides, antanapeptins a–d, and dolastatin 16 from a madagascan collection of Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 65, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunyajetpong, S.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Sitachitta, N.; Kaya, K. Trungapeptins A-C, cyclodepsipeptides from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1539–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, A.; Puddic, J.; Prinsep, M.R.; Lee, P.P.F.; Tan, L.T. Hantupeptin a, a cytotoxic cyclic depsipeptide from a singapore collection of Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador, L.A.; Biggs, J.S.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Veraguamides a–g, cyclic hexadepsipeptides from a dolastatin 16-producing cyanobacterium symploca cf. Hydnoides from guam. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.G.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Quon, M.K.; Moore, R.E.; Paul, V.J. The structure of palau’amide, a potent cytotoxin from a species of the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1545–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettit, G.R. Isolation and Stuctural Elucidation of the Cytostatic Linear and Cyclo-Depsipeptides Dolastatin 16, Dolastatin 17, and Dolastatin 18. U.S. Patent 6,239,104 B1, 29 May 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Luesch, H.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Moore, R.E.; Paul, V.J. Apramides a–g, novel lipopeptides from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1106–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, J.I.; Scheuer, P.J. New lipopeptides from the caribbean cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPhail, K.L.; Correa, J.; Linington, R.G.; González, J.; Ortega-Barría, E.; Capson, T.L.; Gerwick, W.H. Antimalarial linear lipopeptides from a panamanian strain of the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balunas, M.J.; Linington, R.G.; Tidgewell, K.; Fenner, A.M.; Ureña, L.-D.; Togna, G.D.; Kyle, D.E.; Gerwick, W.H. Dragonamide e, a modified linear lipopeptide from Lyngbya majuscula with antileishmanial activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunasekera, S.P.; Ross, C.; Paul, V.J.; Matthew, S.; Luesch, H. Dragonamides c and d, linear lipopeptides from the marine cyanobacterium brown Lyngbya polychroa. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 887–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintana, J.; Bayona, L.M.; Castellanos, L.; Puyana, M.; Camargo, P.; Aristizabal, F.; Edwards, C.; Tabudravu, J.N.; Jaspars, M.; Ramos, F.A. Almiramide d, cytotoxic peptide from the marine cyanobacterium oscillatoria nigroviridis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 6789–6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, T.L.; Engene, N.; Ureña, L.D.; Romero, L.I.; Ortega-Barría, E.; Gerwick, L.; Gerwick, W.H. Viridamides a and b, lipodepsipeptides with antiprotozoal activity from the marine cyanobacterium oscillatoria nigro-wiridis. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, G.J.; Orjala, J.; Schatzman, R.C.; Gerwick, W.H. Carmabins a and b, new lipopeptides from the caribbean cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, D.J.; Marquez, B.L.; Nogle, L.M.; McPhail, K.; Goeger, D.E.; Roberts, M.A.; Gerwick, W.H. Structure and biosynthesis of the jamaicamides, new mixed polyketide-peptide neurotoxins from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. Chem. Biol. 2004, 11, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.C.; Monroe, E.A.; Podell, S.; Hess, W.R.; Klages, S.; Esquenazi, E.; Niessen, S.; Hoover, H.; Rothmann, M.; Lasken, R.S.; et al. Genomic insights into the physiology and ecology of the marine filamentous cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8815–8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W. De novo biosynthesis of terminal alkyne-labeled natural products. Nat. Chem. Boil. 2015, 11, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Rivera, E.; Paul, V.J. Chemical deterrence of a cyanobacterial metabolite against generalized and specialized grazers. J. Chem. Ecol. 2007, 33, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Ye, T. The total synthesis and stereochemical revision of yanucamide a. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 2821–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorde, C.; Hogberg, H.-E.; Hedenström, E. Resolution of 2-methylalkanoic esters: Enantioselective aminolysis by (R)-l-phenylethylamine of ethyl 2-methyloctanoate catalysed by lipase B from Candida antarctica. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1996, 7, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, K.-H. Lipase-catalyzed enantioselective esterification of 2-methylalkanoic acids. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1991, 2, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, P.; Holmquist, M.; Hedenstrom, E.; Hult, K.; Hiigberg, H.-E. 2-Methylalkanoic acids resolved by esterification catalysed by lipase from candida rugosa: Alcohol chain length and enantioselectivity. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 1993, 4, 1869–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Moiety Unit | Compound | Organism | Bioactivities | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dhoya | Yanucamides A (1) and B (2) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscule, Schizothrix sp. | Strong brine shrimp toxicity | [12] |
| Pitipeptolides A (3) Pitipeptolides D–F (4–6) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula | Antitumor cytotoxicity | [22,23] | |
| Georgamide (7) | Marine cyanobacterium | anti-HIV cytotoxicity | [24] | |
| Mantillamide (10) Dudawalamide A (11) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. | Antitumor cytotoxicity Antimalaria parasites | [25] | |
| Guineamide G (12) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula | Brine shrimp toxicity Antitumor cytotoxicity | [26] | |
| Cocosamides A–B (13–14) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula | Antitumor cytotoxicity | [27] | |
| Viequeamides A–B (15–16) and E–F (17–18) | Marine cyanobacterium Rivularia sp. | Antitumor cytotoxicity | [28] | |
| Kulolide-1 (38) | Marine mollusk Philinopsis speciosa Pease | Antitumor cytotoxicity | [29] | |
| Kulokainalide-1 (39) | Marine cephalaspidean mollusk Philinopsis speciosa | Moderate antitumor cytotoxicity | [30] | |
| Dhoaa | Wewakpeptins A and C (8a–9) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya semiplena | Antitumor cytotoxicity | [31] |
| Amoya | Malevamide C (19) | Marine cyanobacterium Symplocalaete-viridis | No cytotoxicity | [32] |
| Guineamide C (20) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula | Antitumor cytotoxicity | [33] | |
| Ulongapeptin (21) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. | Antitumor cytotoxicity | [34] | |
| Companeramides A–B (22–23) | Marine cyanobacterium Leptolyngbya sp. | Antiplasmodial activity | [35] | |
| Onchidin (36) | Marine pulmonate mollusk Onchidium sp. | Strong antitumor cytotoxicity | [11,36] | |
| Hmoya | Antanapeptin A and D (24–25) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula | Na+ channel modulation Antimicrobial activity | [37] |
| Trungapeptins A (26) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula | Brine shrimp toxicity and ichthyotoxicity | [30,38] | |
| Hantupeptin A (27) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula | Brine shrimp toxicity Antitumor cytotoxicity | [39] | |
| Veraguamides B–F (29–33) | Marine cyanobacterium Symploca cf. hydnoides | Veraguamides A and C, antitumor cytotoxicity | [40] | |
| Veraguamides H (34) | Marine cyanobacterium Oscillatoria margaritifera | No cytotoxicity | [13] | |
| Onchidin B (37) | Marine pulmonate mollusk Onchidium sp. | Strong antitumor cytotoxicity | [11,36] | |
| Kulomo’opunalide-1 (40) and (41) | Marine cephalaspidean mollusk Philinopsis speciosa | Moderate antitumor cytotoxicity | [30] | |
| Dddd | Palau’amide (35) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. | Strong antitumor cytotoxicity | [41] |
| Aoy | Dolastatin 17 (42) | Marine mollusk Dolebella auricularia | Antitumor cytotoxicity | [12,42] |
| Oya | Apramides B and G (44,47) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula | Apramide A exhibited stimulating elastase activity | [43] |
| Moya | Apramides A,D and G (43,45–46) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula | Apramide A exhibited stimulating elastase activity | [43] |
| Dragonamides A–B (48–49) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscule Gomont | Antileishmaniasis | [44,45,46,47] | |
| Dragonamides C–E (50–52) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya polychroa | Antileishmaniasis | [47] | |
| Dragomabin (53) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula | Antiparasite toxicity | [45] | |
| Almiramide B (54) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscule | Antitumor cytotoxicity | [14] | |
| Almiramides D–H (55–59) | Marine cyanobacterium Oscillatoria nigroviridis | Antitumor cytotoxicity | [48] | |
| Mdyna | Viridamides A–B (61–62) | Marine cyanobacterium Oscillatoria nigro-Wiridis | Antitrypanosomal activity Antileishmanial activity | [49] |
| Br-Hmoya | Veraguamides A (28) | Marine cyanobacterium Symploca cf. hydnoides | Veraguamides A and C, antitumor cytotoxicity | [40] |
| Viridamides K–L (63–64) | Marine cyanobacteria, cf. Oscillatoria margaritifera | Antitumor cytotoxicity | [13] | |
| 2,4-dimethyl-9-decynoic acid | Carmabins A (60) | Marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula | Antimalaria against the W2 chloroquine-resistant malaria strain | [50] |
| 9-(chloromethylene)-6-methyltetradec-4-en-13-ynoic acid | Jamaicamide A–B (65–66) | Marine Cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula | not mentioned | [51,52,53] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chai, Q.-Y.; Yang, Z.; Lin, H.-W.; Han, B.-N. Alkynyl-Containing Peptides of Marine Origin: A Review. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14110216
Chai Q-Y, Yang Z, Lin H-W, Han B-N. Alkynyl-Containing Peptides of Marine Origin: A Review. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(11):216. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14110216
Chicago/Turabian StyleChai, Qiu-Ye, Zhen Yang, Hou-Wen Lin, and Bing-Nan Han. 2016. "Alkynyl-Containing Peptides of Marine Origin: A Review" Marine Drugs 14, no. 11: 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14110216
APA StyleChai, Q.-Y., Yang, Z., Lin, H.-W., & Han, B.-N. (2016). Alkynyl-Containing Peptides of Marine Origin: A Review. Marine Drugs, 14(11), 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14110216





