Biosurfactants Produced by Marine Microorganisms with Therapeutic Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Biosurfactants from Marine Microorganisms: New Weapons to Fight Human Pathogens
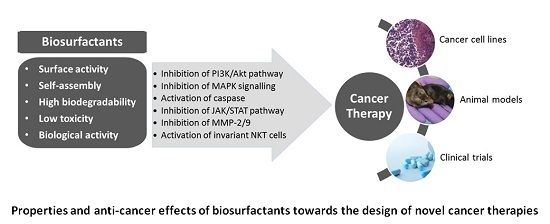
3. Biosurfactants from Marine Microorganisms: Alternative Anti-Cancer Agents
4. New Perspectives for the Discovery of Novel Therapeutics
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhatnagar, I.; Kim, S.K. Immense essence of excellence: Marine microbial bioactive compounds. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2673–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuñez, R.; Garateix, A.; Laguna, A.; Fernández, M.D.; Ortiz, E.; Llanio, M.; Valdés, O.; Rodríguez, A.; Menéndez, R. Caribbean marine biodiversity as a source of new compounds of biomedical interest and other industrial applications. Pharmacologyonline 2006, 3, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, C.C.; Fernandes, P. Production of metabolites as bacterial responses to the marine environment. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 705–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satpute, S.K.; Banat, I.M.; Dhakephalkar, P.K.; Banpurkar, A.G.; Chopade, B.A. Biosurfactants, bioemulsifiers and exopolysaccharides from marine microorganisms. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhar, S.; Sundaramanickam, A.; Balasubramanian, T. Biosurfactant producing microbes and their potential applications: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 1522–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramiah, N. Facets and opportunities. In Marine Microbiology; Ramaiah, N., Ed.; National Institute of Oceanography: Goa, India, 2005; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gudiña, E.J.; Rangarajan, V.; Sen, R.; Rodrigues, L.R. Potential therapeutic applications of biosurfactants. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchant, R.; Banat, I.M. Microbial biosurfactants: Challenges and opportunities for future exploitation. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banat, I.M.; Makkar, R.S.; Cameotra, S.S. Potential commercial applications of microbial surfactants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 53, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, K.R.; Lepo, J.E.; Lewis, M.A. Toxicity comparison of biosurfactants and synthetic surfactants used in oil spill remediation to two estuarine species. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poremba, K.; Gunkel, W.; Lang, S.; Wagner, F. Toxicity testing of synthetic and biogenic surfactants on marine microorganisms. Environ. Toxicol. Water Qual. 1991, 6, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poremba, K.; Gunkel, W.; Lang, S.; Wagner, F. Marine biosurfactants, III. Toxicity testing with marine microorganisms and comparison with synthetic detergents. Z. Naturforsch. C 1991, 46, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fracchia, L.; Cavallo, M.; Martinotti, M.G.; Banat, I.M. Biosurfactants and bioemulsifiers biomedical and related applications: Present status and future potentials. In Biomedical Science, Engineering and Technology; Ghista, D.N., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 325–370. [Google Scholar]
- Ibacache-Quiroga, C.; Ojeda, J.; Espinoza-Vergara, G.; Olivero, P.; Cuellar, M.; Dinamarca, M.A. The hydrocarbon-degrading marine bacterium Cobetia sp. strain MM1IDA2H-1 produces a biosurfactant that interferes with quorum sensing of fish pathogens by signal hijacking. Microb. Biotechnol. 2013, 6, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Sims, J.; Wang, B.; Hamann, M.T. Marine actinomycete Streptomyces sp. ISP2–49E, a new source of rhamnolipid. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 55, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, W.R.; Meyer, H.; Yakimov, M. Novel glycine containing glucolipids from the alkane using bacterium Alcanivorax borkumensis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1393, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banat, I.M. The isolation of a thermophilic biosurfactant producing Bacillus sp. Biotechnol. Lett. 1993, 15, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, S.B.; Smii, L.; Ghram, A.; Maaroufi, A. Screening of potential biosurfactant-producing bacteria isolated from seawater biofilm. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 14153–14158. [Google Scholar]
- Harayama, S.; Kasai, Y.; Hara, A. Microbial communities in oil-contaminated seawater. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2004, 15, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, J.L.; Marsh, T.L.; Wu, K.Y.; Shizuya, H.; DeLong, E.F. Characterization of uncultivated prokaryotes: Isolation and analysis of a 40-kilobase-pair genome fragment from a planktonic marine archaeon. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coates, A.R.M.; Halls, G.; Hu, Y. Novel classes of antibiotics or more of the same? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benincasa, M.; Abalos, A.; Oliveira, I.; Manresa, A. Chemical structure, surface properties and biological activities of biosurfactant produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa LBI from soapstock. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2004, 85, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haba, E.; Pinazo, A.; Jauregui, O.; Espuny, M.J.; Infante, M.R.; Manresa, A. Physicochemical characterization and antimicrobial properties of rhamnolipids produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa 47T2 NCBIM 40044. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2003, 81, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, L.R.; Banat, I.M.; Teixeira, J.A.; Oliveira, R. Biosurfactants: Potential applications in medicine. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, L.R. Inhibition of bacterial adhesion on medical devices. In Bacterial Adhesion: Biology, Chemistry, and Physics, Series: Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Linke, D., Goldman, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; Volume 715, pp. 351–367. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, S.A.; Borchert, E.; O’Gara, F.; Dobson, A.D.W. Metagenomics for the discovery of novel biosurfactants of environmental interest from marine ecosystems. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiran, G.S.; Sabarathnam, B.; Selvin, J. Biofilm disruption potential of a glycolipid biosurfactant from marine Brevibacterium casei. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusane, D.H.; Pawar, V.S.; Nancharaiah, Y.V.; Venugopalan, V.P.; Kumar, A.R.; Zinjarde, S.S. Anti-biofilm potential of a glycolipid surfactant produced by a tropical marine strain of Serratia marcescens. Biofouling 2011, 27, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khopade, A.; Ren, B.; Liu, X.Y.; Mahadik, K.; Zhang, L.; Kokare, C. Production and characterization of biosurfactant from marine Streptomyces species B3. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 367, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivasagan, P.; Sivasankar, P.; Venkatesan, J.; Sivakumar, K.; Kim, S.K. Optimization, production and characterization of glycolipid biosurfactant from the marine actinobacterium, Streptomyces sp. MAB36. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 37, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiran, G.S.; Hema, T.A.; Gandhimathi, R.; Selvin, J.; Thomas, T.A.; Ravji, T.R.; Natarajaseenivasan, K. Optimization and production of a biosurfactant from the sponge-associated marine fungus Aspergillus ustus MSF3. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 73, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Mukherjee, S.; Sen, R. Antimicrobial potential of a lipopeptide biosurfactant derived from a marine Bacillus circulans. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Mukherjee, S.; Sen, R. Antiadhesive action of a marine microbial surfactant. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 71, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivapathasekaran, C.; Mukherjee, S.; Samanta, R.; Sen, R. High-performance liquid chromatography purification of biosurfactant isoforms produced by a marine bacterium. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrance, A.; Balakrishnan, M.; Joseph, T.C.; Sukumaran, D.P.; Valsalan, V.N.; Gopal, D.; Ramalingam, K. Functional and molecular characterization of a lipopeptide surfactant from the marine sponge-associated eubacteria Bacillus licheniformis NIOT-AMKV06 of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 82, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiran, G.S.; Thomas, T.A.; Selvin, J.; Sabarathnam, B.; Lipton, A.P. Optimization and characterization of a new lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by marine Brevibacterium aureum MSA13 in solid state culture. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2389–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhimathi, R.; Kiran, G.S.; Hema, T.A.; Selvin, J.; Raviji, T.R.; Shanmughapriya, S. Production and characterization of lipopeptide biosurfactant by a sponge-associated marine actinomycetes Nocardiopsis alba MSA10. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 32, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvin, J.; Shanmughapriya, S.; Gandhimathi, R.; Kiran, G.S.; Ravji, T.R. Optimization and production of novel antimicrobial agents from sponge associated marine actinomycetes Nocardiopsis dassonvillei MAD08. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 83, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Mukherjee, S.; Sen, R. Substrate dependent production of extracellular biosurfactant by a marine bacterium. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1015–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, S.G.V.A.O.; Déziel, E.; Lépine, F. Characterization of rhamnolipid production by Burkholderia glumae. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 53, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosková, M.; Schreiberová, O.; Jezdík, R.; Chudoba, J.; Masák, J.; Sigler, K.; Rezanka, T. Characterization of rhamnolipids produced by non-pathogenic Acinetobacter and Enterobacter bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 130, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toribio, J.; Escalante, A.E.; Soberón-Chávez, G. Rhamnolipids: Production in bacteria other than Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 112, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittgens, A.; Tiso, T.; Arndt, T.T.; Wenk, P.; Hemmerich, J.; Müller, C. Growth independent rhamnolipid production from glucose using the non-pathogenic Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Microb. Cell Fact. 2011, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, L.F.D.; Silva, P.M.; Junqueira, M.; Mariano, D.C.O.; Nogueira, F.C.S.; Domont, G.B. Characterization of rhamnolipids produced by wild-type and engineered Burkholderia kururiensis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 1909–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolhassani, A. Cancer chemoprevention by natural carotenoids as an efficient strategy. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Plants as a source of anti-cancer agents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 100, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madadi, N.R.; Zong, H.; Ketkar, A.; Zheng, C.; Penthala, N.R.; Janganati, V.; Bommagani, S.; Eoff, R.L.; Guzmanb, M.L.; Crooks, P.A. Synthesis and evaluation of a series of resveratrol analogues as potent anti-cancer agents that target tubulin. MedChemComm 2015, 6, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Verma, N. Nature curing cancer—Review on structural modification studies with natural active compounds having anti-tumor efficiency. Biotechnol. Rep. 2015, 6, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janakiram, N.B.; Mohammed, A.; Rao, C.V. Sea cucumbers metabolites as potent anti-cancer agents. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2909–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawadogo, W.R.; Boly, R.; Cerella, C.; Teiten, M.H.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. A survey of marine natural compounds and their derivatives with anti-cancer activity reported in 2012. Molecules 2015, 20, 7097–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niraula, N.P.; Kim, S.H.; Sohng, J.K.; Kim, E.S. Biotechnological doxorubicin production: Pathway and regulation engineering of strains for enhanced production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, G.; Bharti, R.; Sen, R.; Mandal, M. Microbial amphiphiles: A class of promising new-generation anticancer agents. Drug. Discov. 2015, 20, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janek, T.; Krasowska, A.; Radwanska, A.; Lukaszewicz, M. Lipopeptide biosurfactant pseudofactin II induced apoptosis of melanoma A375 cells by specific interaction with the plasma membrane. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivapathasekaran, C.; Das, P.; Mukherjee, S.; Saravanakumar, J.; Mandal, M.; Sen, R. Marine bacterium derived lipopeptides: Characterization and cytotoxic activity against cancer cell lines. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2010, 16, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tao, X.; Zou, A.; Yang, S.; Zhang, L.; Mu, B. Effect of the microbial lipopeptide on tumor cell lines: Apoptosis induced by disturbing the fatty acid composition of cell membrane. Protein Cell 2010, 1, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, Y. Surfactin suppresses TPA-induced breast cancer cell invasion through the inhibition of MMP-9 expression. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.H.; Wang, A.H.; Jiao, R.Z.; Wang, C.L.; Mao, D.Z.; Yan, L.; Zeng, B. Surfactin induces apoptosis and G(2)/M arrest in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells through cell cycle factor regulation. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 55, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Bae, H.J.; Yi, H.; Yoon, S.H.; Koo, B.S.; Kwon, M.; Cho, J.Y.; Lee, C.E.; Hong, S. Surfactin from Bacillus subtilis displays anti-proliferative effect via apoptosis induction, cell cycle arrest and survival signaling suppression. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Sarkar, S.; Mandal, M.; Sen, R. Green surfactant of marine origin exerting a cytotoxic effect on cancer cell lines. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 53086–53094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, G.; Bharti, R.; Dhanarajan, G.; Das, S.; Dey, K.K.; Kumar, B.N.P.; Sen, R.; Mandal, M. Marine lipopeptide Iturin A inhibits Akt mediated GSK3β and FoxO3α signaling and triggers apoptosis in breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trischman, J.A.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Halobacillin—A cytotoxic cyclic acylpeptide of the iturin class produced by a marine Bacillus. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 5571–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Hua, H.M.; Pei, Y.H.; Yao, X.S. Three new cytotoxic cyclic acylpeptides from marine Bacillus sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 1029–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suyama, T.L.; Gerwick, W.H. Stereospecific total synthesis of somocystinamide A. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 4449–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.M.; Dang, H.T.; Hong, J.; Lee, C.O.; Bae, K.S.; Kim, D.K.; Jung, J.H. A cytotoxic lipopeptide from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; Dang, H.T.; Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Hong, J.; Lee, C.O.; Jung, J.H. A cytotoxic fellutamide analogue from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, 32, 3817–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigemori, H.; Wakuri, S.; Yazawa, K.; Nakamura, T.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, J. Fellutamide-A and fellutamide-B, cytotoxic peptides from a marine fish-possessing fungus Penicillium fellutanum. Tetrahedron 1991, 47, 8529–8534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, T.B. A concise route to the macrocyclic core of the rakicidins. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2011, 47, 12837–12839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, M.I. Rakicidin A effectively induces apoptosis in hypoxia adapted Bcr-Abl positive leukemic cells. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.J.; Zhou, F.; Li, E.M.; Jiang, H.; Du, Z.P.; Lin, R.; Fang, D.S.; Xu, L.Y. FW523-3, a novel lipopeptide compound, induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2011, 4, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Kunimoto, S.; Ikeda, D. Rakicidin A: A hypoxia-selective cytotoxin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, W.R.; Hay, M.P. Targeting hypoxia in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Liu, Y.; Luesch, H. Systematic chemical mutagenesis identifies a potent novel apratoxin A/E hybrid with improved in vivo antitumor activity. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunnery, J.K.; Meyers, E.; Gerwick, W.H. Biologically active secondary metabolites from marine cyanobacteria. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, B.D.; Wengryniuk, S.E.; Coltart, D.M. Asymmetric total synthesis of apratoxin D. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 5192–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornburg, C.C.; Cowley, E.S.; Sikorska, J.; Shaala, L.A.; Ishmael, J.E.; Youssef, D.T.; McPhail, K.L. Apratoxin H and apratoxin A sulfoxide from the Red Sea cyanobacterium Moorea producens. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tidgewell, K.; Engene, N.; Byrum, T.; Media, J.; Doi, T.; Valeriote, F.A.; Gerwick, W.H. Evolved diversification of a modular natural product pathway: Apratoxins F and G, two cytotoxic cyclic depsipeptides from a Palmyra collection of Lyngbya bouillonii. ChemBioChem 2010, 11, 1458–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrasidlo, W.; Mielgo, A.; Torres, V.A.; Barbero, S.; Stoletov, K.; Suyama, T.L.; Klemke, R.L.; Gerwick, W.H.; Carson, D.A.; Stupack, D.G. The marine lipopeptide somocystinamide A triggers apoptosis via caspase 8. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2313–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karanth, N.G.K.; Deo, P.G.; Veenanadig, N.K. Microbial production of biosurfactants and their importance. Curr. Sci. 1999, 77, 116–126. [Google Scholar]
- Fuji, N.; Ueda, Y.; Fujiwara, H.; Toh, T.; Yoshimura, T.; Yamagishi, H. Antitumor effect of alpha-galactosylceramide (KRN7000) on spontaneous hepatic metastases requires endogenous interleukin 12 in the liver. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 3380–3387. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, Y.; Takeda, K.; Yagita, H.; Kakuta, S.; Iwakura, Y.; Van Kaer, L.; Saiki, I.; Okumura, K. Critical contribution of IFN-gamma and NK cells, but not perforin-mediated cytotoxicity, to anti-metastatic effect of alpha-galactosylceramide. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 1720–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakui, M.; Ohta, A.; Sekimoto, M.; Sato, M.; Iwakabe, K.; Yahata, T.; Kitamura, H.; Koda, T.; Kawano, T.; Makuuchi, H.; et al. Potentiation of antitumor effect of NKT cell ligand, alpha-galactosylceramide by combination with IL-12 on lung metastasis of malignant melanoma cells. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2000, 18, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneiders, F.L.; Scheper, R.J.; von Blomberg, B.M.; Woltman, A.M.; Janssen, H.L.; van den Eertwegh, A.J.; Verheul, H.M.; de Gruijl, T.D.; van der Vliet, H.J. Clinical experience with alpha-galactosylceramide (KRN7000) in patients with advanced cancer and chronic hepatitis B/C infection. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 140, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farokhi, F.; Wielgosz-Collin, G.; Robic, A.; Debitus, C.; Malleter, M.; Roussakis, C.; Kornprobst, J.M.; Barnathan, G. Antiproliferative activity against human non-small cell lung cancer of two O-alkyl-diglycosylglycerols from the marine sponges Myrmekioderrna dendyi and Trikentrion laeve. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 49, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felczykowska, A.; Bloch, S.K.; Nejman-Falenczyk, B.; Baranska, S. Metagenomic approach in the investigation of new bioactive compounds in the marine environment. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2012, 59, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, J.; Flemer, B.; Jackson, S.A.; Lejon, D.P.H.; Morrissey, J.P.; O’Gara, F.; Dobson, A.D.W. Marine metagenomics: New tools for the study and exploitation of marine microbial metabolism. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 608–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, J.; O’Leary, N.D.; Kiran, G.S.; Morrissey, J.P.; O’Gara, F.; Selvin, J.; Dobson, A.D.W. Functional metagenomic strategies for the discovery of novel enzymes and biosurfactants with biotechnological applications from marine ecosystems. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 111, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coughlan, L.M.; Cotter, P.D.; Hill, C.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A. Biotechnological applications of functional metagenomics in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biver, S.; Steels, S.; Portetelle, D.; Vandenbol, M. Bacillus subtilis as a tool for screening soil metagenomic libraries for antimicrobial activities. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 23, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, H.A.; Craig, J.W.; Brady, S.F. Antibacterial enzymes from the functional screening of metagenomic libraries hosted in Ralstonia metallidurans. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 354, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, M.D.; Guan, C.; Handelsman, J.; Thomas, M.G. Metagenomic analysis of Streptomyces lividans reveals host-dependent functional expression. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 3622–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, R. Surfactin: Biosynthesis, genetics and potential applications. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 672, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Yu, H.; Shen, Z. A novel high-throughput and quantitative method based on visible color shifts for screening Bacillus subtilis THY-15 for surfactin production. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 42, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegmund, I.; Wagner, F. New method for detecting rhamnolipids excreted by Pseudomonas species during growth on mineral agar. Biotechnol. Tech. 1991, 5, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, A.Y.; Shimada, B.K.; Browne, P.J.; Lindow, S.E. Novel high-throughput detection method to assess bacterial surfactant production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5363–5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Microorganism (Origin) | Biosurfactant Type (Structure) | Activity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brevibacterium casei MSA19 (marine sponge Dendrilla nigra) | Glycolipid (unknown) | Antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, haemolytic Streptococcus, Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus | [27] |
| Anti-biofilm activity against mixed and individual cultures of E. coli, P. aeruginosa and Vibrio spp. | |||
| Serratia marcescens (hard marine coral Symphyllia sp.) | Glycolipid (glucose + palmitic acid) | Antimicrobial, anti-adhesive and anti-biofilm activity against Candida albicans and P. aeruginosa | [28] |
| Streptomyces sp. B3 (marine sediment samples) | Glycolipid (unknown) | Antimicrobial activity against C. albicans, E. coli, P. aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus | [29] |
| Streptomyces sp. MAB36 (marine sediment samples) | Glycolipid (unknown) | Antimicrobial activity against Aspergillus niger, Bacillus cereus, C. albicans, Enterococcus faecalis, Shigella boydii, Shigella dysenteriae and S. aureus | [30] |
| Aspergillus ustus MSF3 (marine sponge Fasciospongia cavernosa) | Glycolipoprotein (unknown) | Antimicrobial activity against C. albicans, E. faecalis, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, Micrococcus luteus, P. mirabilis, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis and haemolytic Streptococcus | [31] |
| Bacillus circulans (seawater sample) | Lipopeptide (unknown) | Antimicrobial activity against Acinetobacter calcoaceticus, Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter cloacae, E. coli, Micrococcus luteus, P. mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, Serratia marcescens and multi-drug resistant E. coli a, K. pneumoniae b and S. aureus c | [32,33] |
| Anti-adhesive and anti-biofilm activities against C. freundii, E. coli, P. vulgaris, Salmonella typhimurium and S. marcescens | |||
| Bacillus circulans DMS-2 (marine samples) | Lipopeptide (Mixture of three different Fengycins: β-hydroxy fatty acid of 15, 16 or 17 carbons + cyclic decapeptide) | Antimicrobial activity against C. freundii, E. coli, P. vulgaris and S. marcescens | [34] |
| Bacillus licheniformis NIOT-AMKV06 (marine sponge Acanthella sp.) | Lipopeptide (unknown) | Antimicrobial activity against E. faecalis, K. pneumoniae, M. luteus, P. mirabilis, Salmonella typhi, Shigella flexineri, S. aureus and Vibrio cholera | [35] |
| Brevibacterium aureum MSA13 (marine sponge Dendrilla nigra) | Lipopeptide (Brevifactin: Octadecanoic acid methyl ester + pro-leu-gly-gly) | Antimicrobial activity against C. albicans, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, M. luteus, P. mirabilis, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, S. epidermidis and haemolytic Streptococcus | [36] |
| Nocardiopsis alba MSA10 (marine sponge Fasciospongia cavernosa) | Lipopeptide (unknown) | Antimicrobial activity against C. albicans, E. faecalis, K. pneumoniae, M. luteus, P. mirabilis, S. aureus and S. epidermidis | [37] |
| Nocardiopsis dassonvillei MAD08 (marine sponge Dendrilla nigra) | Unknown | Antimicrobial activity against S. aureus, M. luteus and multi-drug resistant E. coli d, K. pneumoniae d, P. mirabilis d, P. aeruginosa d, S. typhi d, S. epidermidis d, non-haemolytic Streptococcus d and V. cholera d | [38] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gudiña, E.J.; Teixeira, J.A.; Rodrigues, L.R. Biosurfactants Produced by Marine Microorganisms with Therapeutic Applications. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14020038
Gudiña EJ, Teixeira JA, Rodrigues LR. Biosurfactants Produced by Marine Microorganisms with Therapeutic Applications. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(2):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14020038
Chicago/Turabian StyleGudiña, Eduardo J., José A. Teixeira, and Lígia R. Rodrigues. 2016. "Biosurfactants Produced by Marine Microorganisms with Therapeutic Applications" Marine Drugs 14, no. 2: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14020038
APA StyleGudiña, E. J., Teixeira, J. A., & Rodrigues, L. R. (2016). Biosurfactants Produced by Marine Microorganisms with Therapeutic Applications. Marine Drugs, 14(2), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14020038