In Vitro Effect of the Synthetic cal14.1a Conotoxin, Derived from Conus californicus, on the Human Parasite Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
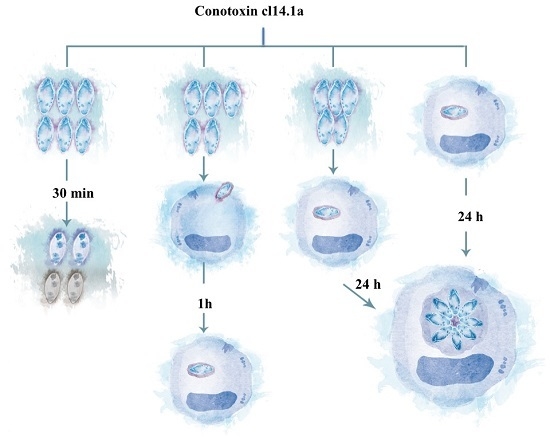
2.1. Decreased Extracellular Viability of Tachyzoites Induced by s-cal14.1a in Vitro
2.2. Invasivity of Tachyzoies of T. gondii after Exposure to s-cal14.1a
2.3. Proliferation of T. gondii Tachyzoites after Exposure to s-cal14.1a
2.4. Presence of s-cal14.1a Toxin in Culture Medium Inhibits Proliferation of Tachyzoites
2.5. Cytotoxic Effects of s-cal14.1a on Tachyzoite Host Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Maintenance and Purification of T. gondii Tachyzoites
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Conotoxin s-cal14.1a
4.5. Exposure of Extracellular Tachyzoites to Conotoxin
4.6. Infection of HEp-2 with RH Strain
4.7. Effects of Conotoxin on Invaded Cell Culture
4.8. Cytotoxic Effect of s-cal14.1a on Tachyzoites Host Cells.
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carruthers, V.; Boothroyd, J.C. Pulling together: An integrated model of Toxoplasma cell invasion. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2007, 10, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.M.; Soldati-Favre, D. Invasion factors are coupled to key signalling events leading to the establishment of infection in apicomplexan parasites. Cell. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, B.A.; Chiappino, M.L. Cytoskeleton of Toxoplasma gondii. J. Protozool. 1987, 34, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patron, S.A.; Mondragon, M.; Gonzalez, S.; Ambrosio, J.R.; Guerrero, B.A.; Mondragon, R. Identification and purification of actin from the subpellicular network of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniz-Hernandez, S.; Carmen, M.G.; Mondragon, M.; Mercier, C.; Cesbron, M.F.; Mondragon-Gonzalez, S.L.; Gonzalez, S.; Mondragon, R. Contribution of the residual body in the spatial organization of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites within the parasitophorous vacuole. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercier, C.; Adjogble, K.D.; Daubener, W.; Delauw, M.F. Dense granules: Are they key organelles to help understand the parasitophorous vacuole of all apicomplexa parasites? Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 829–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenter, A.M.; Heckeroth, A.R.; Weiss, L.M. Toxoplasma gondii: From animals to humans. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1217–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.G.; Liesenfeld, O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffra, N.A.; Seidman, C.J.; Weiss, L.M. Ocular Toxoplasmosis: Controversies in Primary and Secondary Prevention. J. Neuroinfect. Dis. 2013, 4, 235689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Huang, B.; Liu, G.; Wu, B.; Huang, S.; Zheng, H.; Shen, J.; Lun, Z.R.; Wang, Y.; Lu, F. Meta-analysis of prevention and treatment of toxoplasmic encephalitis in HIV-infected patients. Acta Trop. 2013, 127, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villena, I.; Aubert, D.; Leroux, B.; Dupouy, D.; Talmud, M.; Chemla, C.; Trenque, T.; Schmit, G.; Quereux, C.; Guenounou, M.; et al. Pyrimethamine-sulfadoxine treatment of congenital toxoplasmosis: Follow-up of 78 cases between 1980 and 1997. Reims Toxoplasmosis Group. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 30, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Black, M.W.; Boothroyd, J.C. Lytic cycle of Toxoplasma gondii. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000, 64, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akondi, K.B.; Muttenthaler, M.; Dutertre, S.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Discovery, synthesis, and structure-activity relationships of conotoxins. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5815–5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepulveda-Arias, J.C.; Veloza, L.A.; Mantilla-Muriel, L.E. Anti-Toxoplasma activity of natural products: A review. Recent Pat. Antiinfect. Drug Discov. 2014, 9, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantillo-Ciau, Z.; Moo-Puc, R.; Quijano, L.; Freile-Pelegrin, Y. The tropical brown alga Lobophora variegata: A source of antiprotozoal compounds. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1292–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terlau, H.; Olivera, B.M. Conus venoms: A rich source of novel ion channel-targeted peptides. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 41–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliger, C.A.; Richmond, T.A.; Lebaric, Z.N.; Pierce, N.T.; Sweedler, J.V.; Gilly, W.F. Diversity of conotoxin types from Conus californicus reflects a diversity of prey types and a novel evolutionary history. Toxicon 2011, 57, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggs, J.S.; Watkins, M.; Puillandre, N.; Ownby, J.P.; Lopez-Vera, E.; Christensen, S.; Moreno, K.J.; Bernaldez, J.; Licea-Navarro, A.; Corneli, P.S.; et al. Evolution of Conus peptide toxins: Analysis of Conus californicus Reeve, 1844. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 56, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, J.; Gilly, W.F. Piscivorous behavior of a temperate cone snail, Conus californicus. Biol. Bull. 2005, 209, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingham, J.P.; Mitsunaga, E.; Bergeron, Z.L. Drugs from slugs—Past, present and future perspectives of omega-conotoxin research. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 183, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kress, H.G.; Simpson, K.H.; Marchettini, P.; Ver Donck, A.; Varrassi, G. Intrathecal therapy: What has changed with the introduction of ziconotide. Pain Pract. 2009, 9, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durek, T.; Craik, D.J. Therapeutic conotoxins: A US patent literature survey. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2015, 25, 1159–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, I.; Lewis, R.J. Therapeutic potential of cone snail venom peptides (conopeptides). Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 1546–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Maeda, H.; Matsuo, T.; Boldbattar, D.; Umemiya-Shirafuji, R.; Kume, A.; Suzuki, H.; Xuan, X.; Tsuji, N.; Fujisaki, K. Parasiticidal activity of Haemaphysalis longicornis longicin P4 peptide against Toxoplasma gondii. Peptides 2012, 34, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Murakami, S.; Kumura, H.; Igarashi, I.; Shimazaki, K. Parasiticidal activity of bovine lactoperoxidase against Toxoplasma gondii. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 84, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Rahman, M.M.; Battur, B.; Boldbaatar, D.; Liao, M.; Umemiya-Shirafuji, R.; Xuan, X.; Fujisaki, K. Parasiticidal activity of human alpha-defensin-5 against Toxoplasma gondii. Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2010, 46, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonthron-Senecheau, C.; Kaiser, M.; Devambez, I.; Vastel, A.; Mussio, I.; Rusig, A.M. Antiprotozoal activities of organic extracts from French marine seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, L.M.; Kim, K. The development and biology of bradyzoites of Toxoplasma gondii. Front. Biosci. 2000, 5, D391–D405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, D.K.; Honore, S.; Derouin, F.; Sibley, L.D. Determination of genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii strains isolated from patients with toxoplasmosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 1411–1414. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prashanth, J.R.; Brust, A.; Jin, A.H.; Alewood, P.F.; Dutertre, S.; Lewis, R.J. Cone snail venomics: From novel biology to novel therapeutics. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 1659–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondragon, R.; Frixione, E. Ca(2+)-dependence of conoid extrusion in Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1996, 43, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carruthers, V.B.; Sibley, L.D. Mobilization of intracellular calcium stimulates microneme discharge in Toxoplasma gondii. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 31, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoff, E.F.; Carruthers, V.B. Is Toxoplasma egress the first step in invasion? Trends Parasitol. 2002, 18, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oroz-Parra, I.; Navarro, M.; Cervantes-Luevano, K.E.; Álvarez-Delgado, C.; Salvesen, G.; Sanchez-Campos, L.N.; Licea-Navarro, A.F. Apoptosis Activation in Human Lung Cancer Cell Lines by a Novel Synthetic Peptide Derived from Conus californicus Venom. Toxins 2016, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imperial, J.S.; Bansal, P.S.; Alewood, P.F.; Daly, N.L.; Craik, D.J.; Sporning, A.; Terlau, H.; López-Vera, E.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; Olivera, B.M. A novel conotoxin inhibitor of Kv1.6 channel and nAChR subtypes defines a new superfamily of conotoxins. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 8331–8340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, L.; Qin, M.; You, Y.; Pan, W.; Zhou, L.; Sun, D.; Xu, A. Pharmacological characterization of conotoxin lt14a as a potent non-addictive analgesic. Toxicon 2015, 96, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, D.A.; McKnight, C.A.; Liu, J.; Jimenez, V.; Moreno, S.N. Calcium entry in Toxoplasma gondii and its enhancing effect of invasion-linked traits. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 19637–19647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De León-Nava, M.A.; Romero-Núñez, E.; Luna-Nophal, A.; Bernáldez-Sarabia, J.; Sánchez-Campos, L.N.; Licea-Navarro, A.F.; Morales-Montor, J.; Muñiz-Hernández, S. In Vitro Effect of the Synthetic cal14.1a Conotoxin, Derived from Conus californicus, on the Human Parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14040066
De León-Nava MA, Romero-Núñez E, Luna-Nophal A, Bernáldez-Sarabia J, Sánchez-Campos LN, Licea-Navarro AF, Morales-Montor J, Muñiz-Hernández S. In Vitro Effect of the Synthetic cal14.1a Conotoxin, Derived from Conus californicus, on the Human Parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(4):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14040066
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe León-Nava, Marco A., Eunice Romero-Núñez, Angélica Luna-Nophal, Johanna Bernáldez-Sarabia, Liliana N. Sánchez-Campos, Alexei F. Licea-Navarro, Jorge Morales-Montor, and Saé Muñiz-Hernández. 2016. "In Vitro Effect of the Synthetic cal14.1a Conotoxin, Derived from Conus californicus, on the Human Parasite Toxoplasma gondii" Marine Drugs 14, no. 4: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14040066
APA StyleDe León-Nava, M. A., Romero-Núñez, E., Luna-Nophal, A., Bernáldez-Sarabia, J., Sánchez-Campos, L. N., Licea-Navarro, A. F., Morales-Montor, J., & Muñiz-Hernández, S. (2016). In Vitro Effect of the Synthetic cal14.1a Conotoxin, Derived from Conus californicus, on the Human Parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Marine Drugs, 14(4), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14040066