Algicidal Activity of Bacillamide Alkaloids and Their Analogues against Marine and Freshwater Harmful Algae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
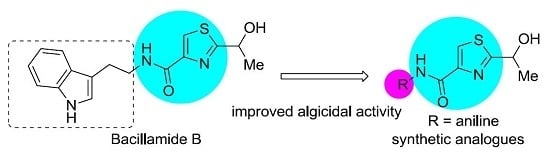
2.1. Synthesis of Bacillamide Alkaloids
2.2. Algicidal Activity
3. Discussion
3.1. Synthesis
3.2. Algicidal Activity
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Procedure for Synthesis of Analogues of Bacillamide A
4.2. General Procedure for Synthesis of Analogues of Bacillamide B
4.3. Algicide Bioassay
4.3.1. Bioassay Method for Red Tide Algae
4.3.2. Bioassay Method for Freshwater Harmful Algae
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masó, M.; Garcés, E. Harmful microalgae blooms (HAB): Problematic and conditions that induce them. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 53, 620–630. [Google Scholar]
- Glibert, P.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Gentien, P.; Graneli, E.; Sellner, K.G. The global, complex phenomena of harmful algal blooms. Oceanography 2005, 18, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauw, A.N.; Los, F.J.; Huisman, J.; Peperzak, L. Nuisance foam events and Phaeocystis globosa blooms in Dutch coastal waters analyzed with fuzzy logic. J. Mar. Syst. 2010, 83, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Zou, H.; Chen, H.; Yuan, X.Z. Removal of harmful cyanobacterial blooms in Taihu Lake using local soils: III. Factors affecting the removal efficiency and an in situ field experiment using chitosan-modified local soils. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 141, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, R.H.; Henry, M.S.; Higham, C.J.; Blum, P.; Sengco, M.R.; Anderson, D.M. Removal of harmful algal cells (Karenia brevis) and toxins from seawater culture by clay flocculation. Harmful Algae 2004, 3, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengco, M.R.; Hagstrom, J.A.; Graneli, E.; Anderson, D.M. Removal of Prymnesium parvum (Haptophyceae) and its toxins using clay minerals. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.H.; Sun, X.X.; Lee, Y.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Han, K.N.; Choi, J.K.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, E.K. Mitigation of harmful algal blooms by sophorolipid. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 13, 651–659. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.J.; Kim, H.R.; Kim, K.I.; Kim, K.Y.; Park, K.H.; Kim, S.T.; Yook, Y.D.; Song, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Seong, K.A.; et al. NaOCl produced by electrolysis of natural seawater as a potential method to control marine red-tide dinoflagellates. Phycologia 2002, 41, 643–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.X.; Choi, J.K.; Kim, E.K. A preliminary study on the mechanism of harmful algal bloom mitigation by use of sophorolipid treatment. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 304, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, J.; Blahoslav, M. Critical review of actually available chemical compounds for prevention and management of cyanobacterial blooms. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar]
- Hare, C.E.; Demir, E.; Coyne, K.J.; Cary, S.C.; Kirchman, D.L.; Hutchins, D.A. A bacterium that inhibits the growth of Pfiesteria piscicida and other dinoflagellates. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Lee, D.S.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, W.; Lee, M.S. Isolation and characterization of a marine algicidal bacterium against the harmful Raphidophyceae Chattonella marina. J. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.; Flynn, K.J. Promotion of harmful algal blooms by zooplankton predatory activity. Biol. Lett. 2006, 2, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrader, K.K.; Rimando, A.M.; Duke, S.O. Natural compounds for the management of undersirable freshwater phytoplankton blooms. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Rahman, A.-U., Ed.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 26, pp. 351–389. [Google Scholar]
- Schrader, K.K.; de Regt, M.Q.; Tidwell, P.D.; Tucker, C.S.; Duke, S.O. Compounds with selective toxicity towards the off-flavor metabolite-producing cyanobacterium Oscillatoria cf. chalybea. Aquaculture 1998, 163, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, K.K.; Dayan, F.E.; Allen, S.N.; de Regt, M.Q.; Tucker, C.S.; Paul, R.N. 9,10-Anthraquinone reduces the photosynthetic efficiency of Oscillatoria perornata and modifies cellular inclusions. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2000, 161, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrader, K.K.; Nanayakkara, N.P.D.; Tucker, C.S.; Rimando, A.M.; Ganzera, M.; Schaneberg, B.T. Novel derivatives of 9,10-anthraquinone are selective algicides against the musty-odor cyanobacterium Oscillatoria perornata. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5319–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanayakkara, N.P.D.; Schrader, K.K. Synthesis of water-woluble 9,10-anthraquinone analogues with potent cyanobactericidal activity toward the musty-odor cyanobacterium Oscillatoria perornata. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, C.S.; Schrader, K.K.; Rimando, A.M. Algicidal activity of stilbene analogues. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 9140–9145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prucaro, R.; Schrader, K.K.; Burandt, C.; DellaGreca, M.; Meepagala, K.M. Algicide constituents from Swinglea glutinosa. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 10632–10635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meepagala, K.M.; Schrader, K.K.; Burandt, C.L.; Wedge, D.E.; Duke, S.O. New class of algicidal comounds and fungicidal activities derived from a chromene amide of Amyris texana. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 9476–9482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blom, J.F.; Brutsch, T.; Barbaras, D.; Bethuel, Y.; Locher, H.H.; Hubschwerlen, C.; Gademann, K. Potent algicides based on the cyanobacterial alkaloid nostocarboline. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becher, P.G.; Beuchat, J.; Gademann, K.; Juttner, F. Nostocarboline: Isolation and synthesis of a new cholinesterase inhibitor from Nostoc 78–12A. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1793–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovejoy, C.; Bowman, J.P.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Algicidal effects of novel marine Pseudoalteromonas isolate (class Proteobacteria, gamma subdivision) on harmful algal bloom species of genera Chattonella, Gymnodinium, and Heterosigma. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2806–2813. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holmstrom, C.; Kjelleberg, S. Marine Pseudoalteromonas species are associated with higher organisms and produce biologically active extracellular agents. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1999, 30, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, G.; Yoshikawa, T.; Yasuda, A.; Sakata, T. Algicidal activity and gliding motility of Saprospira sp. SS98–5. Can. J. Microbiol. 2003, 49, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsutani, A.; Takesue, K.; Kirita, M.; Ishida, Y. Lysis of Skeletonema costatum by Cytophaga sp. isolated from the coastal water of the Ariake Sea. Nippon Suisan Gakk. 1992, 58, 2159–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Liu, J.T.; Yang, L.Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.Q.; Zhao, H.J.; Zhang, N.M. Allelopathic control of cyanobacterial blooms by periphyton biofilms. Environ. Microbl. 2011, 13, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.W.; Zhang, B.Z.; Zhang, J.L.; Huang, L.P.; Lin, J.; Li, X.Y.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.R.; Su, J.L.; et al. A marine algicidal actinomycete and its active substance against the harmful algal bloom species Phaeocystis globosa. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9207–9215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Yan, H.; Wei, H.Y.; Li, X.Q.; Li, Y.H.; Xiao, B.; Li, X.B.; Li, H.; Yin, L.H.; Yue, P.; et al. Isolation, identification and characterization of an algicidal bacterium from Lake Taihu and preliminary studies against Microcystis aeruginosa. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2013, 26, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.H.; Lin, S.Q.; Liu, X.L.; Tan, J.; Pan, J.L.; Yang, H. A freshwater bacterial strain, Shewanella sp. Lzh-2, isolated from Lake Taihu and its two algicidal active substances, hexahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione and 2, 3-indolinedione. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 4737–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.H.; Geng, M.X.; Yang, H. Algicidal activity of Bacillus sp. Lzh-5 and its algicidal compounds against Microcystis aeruginosa. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.L.; Liu, X.L.; Pan, J.L.; Yang, H. Synergistic algicidal effect and mechanism of two diketopiperazines produced by Chryseobacterium sp. strain GLY-1106 on the harmful bloom-forming Microcystis Aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14720. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Volk, R.-B. Antialgal activity of several cyanobacterial exometabolites. J. Appl. Phycol. 2006, 18, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.M.; Sheu, F.S.; Sheu, S.Y. Novel L-amino acid oxidase with algicidal activity against toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa synthesized by a bacterium Aquimarina sp. Enzym. Microbl. Technol. 2011, 49, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.X.; Yang, X.R.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Su, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Zheng, T. A marine bacterium producing protein with algicidal activity against Alexandrium tamarense. Harmful Algae 2012, 13, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socha, A.M.; Long, R.A.; Rowley, D.C. Bacillamides from a hypersaline microbial mat bacterium. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1793–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaeko, K.Y.S.; Satoshi, O.; Masayuki, O. Alkaloid from Thermoactinomyces Species. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1976, 24, 92–96. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Peng, C.S.; Li, Z.Y.; Guo, Y.W. Neobacillamide A, a novel thiazole-containing alkaloid from the marine bacterium Bacillus vallismortis C89, associated with South China Sea Sponge Dysidea Avara . Helv. Chim. Acta 2009, 92, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.Y.; Ishida, K.; Ito, Y.; Okada, S.; Murakami, M. Bacillamide, a novel algicide from the marine bacterium, Bacillus sp. SY-1, against the harmful dinoflagellate, Cochlodinium polykrikoides. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 8005–8007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churro, C.; Alverca, E.; Sam-Bento, F.; Paulino, S.; Figueira, V.C.; Bento, A.J.; Prabhakar, S.; Lobo, A.M.; Calado, A.J.; Pereira, P. Effects of bacillamide and newly synthesized derivatives on the growth of cyanobacteria and microalgae cultures. J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yang, H.S.; Xie, L.G.; Xu, X.H. Synthesis of N-[2-(1H-Indol-3-yl)ethyl]-2-acetylthiazole-4-caboxamide and its analogues. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 30, 238–243. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Joyner, S.; Khoury, K.A.S.; Bacilla, A.D. Bacillamide C: The convergent approach. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrader, K.K.; De Regt, M.Q.; Tucker, C.S.; Duke, S.O. A rapid bioassay for selective algaicides. Weed Technol. 1997, 11, 767–774. [Google Scholar]



| Compound | EC50 (mg/L) after 72 h | EC50 (mg/L) after 96 h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. costatum | G. catenatum | M. aeruginosa | S. obliquus | C. pyrenoidosa | |
| Bacillamide A | 0.011 ± 0.002 | 112.0 ± 2.58 | 19.33 ± 1.45 | 43.76 ± 3.67 | 250.10 ± 4.56 |
| Bacillamide B | 15.59 ± 1.12 | 234.56 ± 7.96 | 75.62 ± 5.34 | 219.38 ± 13.56 | 387.77 ± 10.78 |
| Bacillamide C | 34.70 ± 1.13 | 57.13 ± 2.54 | 291.92 ± 10.32 | 29.54 ± 1.54 | 192.83 ± 6.95 |
| Alkaloid (1) | 8.65 ± 0.78 | 0.58 ± 0.06 | 114.60 ± 3.35 | 14.33 ± 1.15 | 381.57 ± 5.16 |
| Neobacillamide A | - | - | 86.90 ± 5.45 | 4.71 ± 0.46 | 57.87 ± 3.12 |
| 10a | - | - | 13.1 ± 1.54 | 26.7 ± 2.37 | 32.1 ± 1.57 |
| 10b | - | - | 32.1 ± 2.12 | 12.2 ± 0.36 | 23.6 ± 2.18 |
| 10c | - | - | 34.0 ± 3.13 | 11.6 ± 0.98 | 33.9 ± 2.65 |
| 10d | - | - | 2.5 ± 0.12 | 4.0 ± 0.43 | 23.0 ± 1.28 |
| 9a | - | - | 7.56 ± 0.21 | 13.12 ± 0.56 | 7.81 ± 0.65 |
| 9b | - | - | 2.13 ± 0.02 | 3.25 ± 0.14 | 28.91 ± 1.23 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Tao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, N.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X. Algicidal Activity of Bacillamide Alkaloids and Their Analogues against Marine and Freshwater Harmful Algae. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15080247
Wang B, Tao Y, Liu Q, Liu N, Jin Z, Xu X. Algicidal Activity of Bacillamide Alkaloids and Their Analogues against Marine and Freshwater Harmful Algae. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(8):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15080247
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Bo, Yuanyuan Tao, Qisheng Liu, Na Liu, Zhong Jin, and Xiaohua Xu. 2017. "Algicidal Activity of Bacillamide Alkaloids and Their Analogues against Marine and Freshwater Harmful Algae" Marine Drugs 15, no. 8: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15080247
APA StyleWang, B., Tao, Y., Liu, Q., Liu, N., Jin, Z., & Xu, X. (2017). Algicidal Activity of Bacillamide Alkaloids and Their Analogues against Marine and Freshwater Harmful Algae. Marine Drugs, 15(8), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15080247