TTX-Bearing Planocerid Flatworm (Platyhelminthes: Acotylea) in the Ryukyu Islands, Japan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. External Morphology
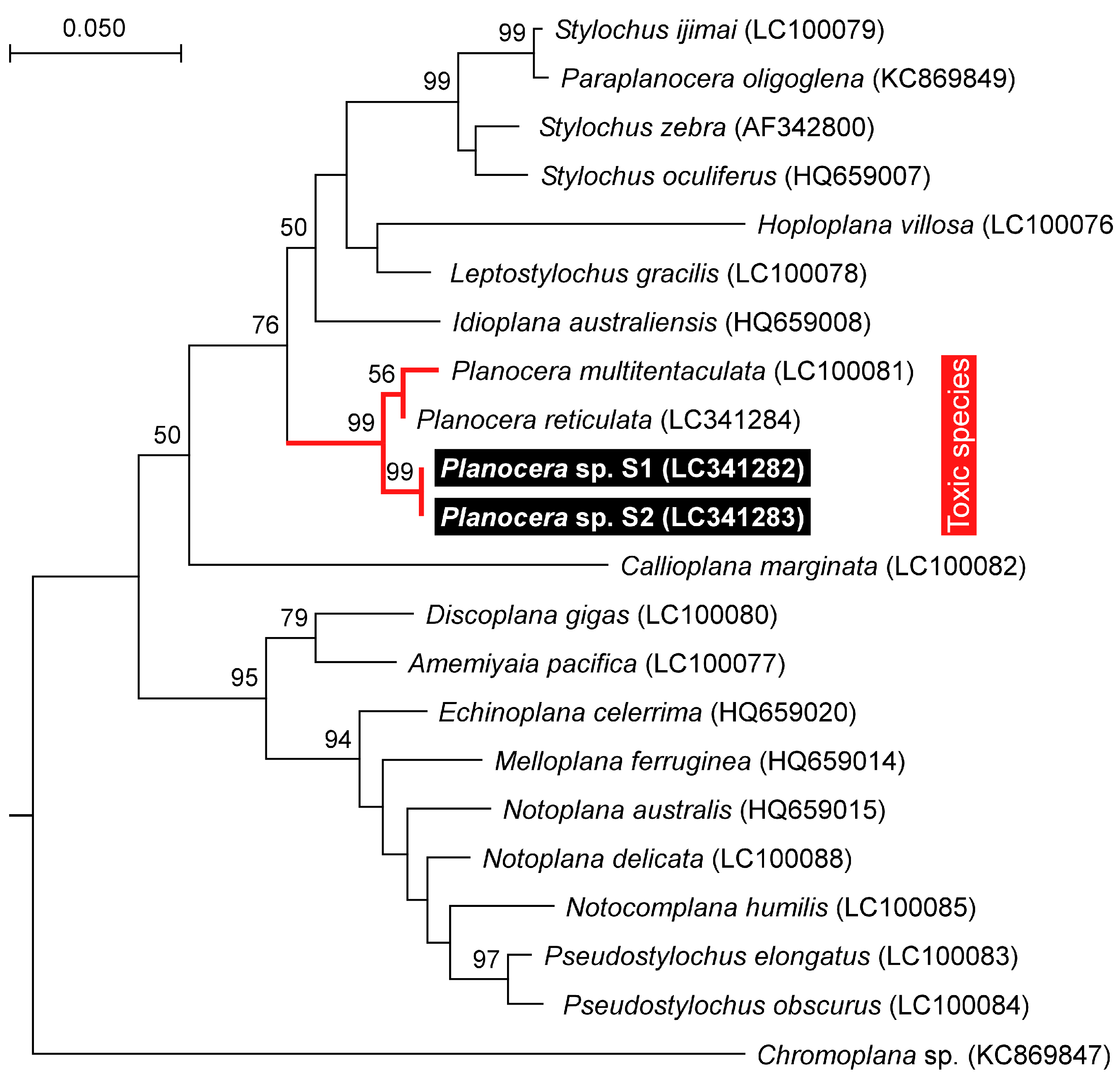
2.2. Molecular Phylogenetic Inference and Taxonomy
2.3. Toxicity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Flatworm Individuals
4.2. DNA Extraction and Polymerase Chain Reaction Amplification
4.3. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.4. LC-MS/MS Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colquhon, D.; Henderson, R.; Ritchie, J.M. The binding of labeled tetrodotoxin to non-myelineated nerve fibres. J. Physiol. 1972, 227, 95–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narahashi, T. Pharmacology of tetrodotoxin. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 2001, 20, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosher, H.S.; Fuhrman, G.J.; Fuhrman, F.A.; Fischer, H.G. Tarichatoxin-tetrodotoxin, a potent neurotoxin. Science 1964, 144, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Mebs, D.; Yasumoto, T. Tetrodotoxin and its analogues in extracts from the toad Atelopus oxyrhynchus (family: Bufonidae). Toxicon 1992, 30, 1489–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Hashimoto, Y. Isolation of tetrodotoxin from a goby Gobius criniger. Toxicon 1973, 11, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheumack, D.D.; Howden, M.E.H.; Spence, I. Maculotoxin: A neurotoxin from the glands of the octopus, Hapalochlaena maculosa identified as tetrodotoxin. Science 1978, 199, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.F.; Tsai, Y.H.; Chai, R.J.; Jeng, S.S. Occurrence of tetrodotoxin and paralytic shellfish poison in Taiwan Crab Zosimus aeneus. Fish. Sci. 1996, 62, 500–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA CONTAM Panel (EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain); Knutsen, H.K.; Alexander, J.; Barregård, L.; Bignami, M.; Brüschweiler, B.; Ceccatelli, S.; Cottrill, B.; Dinovi, M.; Edler, L.; et al. Scientific opinion on the risks for public health related to the presence of tetrodotoxin (TTX) and TTX analogues in marine bivalves and gastropods. EFSA J. 2017, 15, 4752. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, D.F.; Lu, S.C.; Jeng, S.S. Occurrence of tetrodotoxin in the gastropods Rapana rapiformis and R. venosa venosa. Mar. Biol. 1991, 111, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, K.; Jeon, J.K.; Noguchi, T.; Ito, K.; Hashimoto, K. Distribution of tetrodotoxin in the tissues of the flatworm Planocera multitentaculata (Platyhelminthes). Toxicon 1987, 25, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, K.; Higashiyama, M.; Ito, K.; Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O.; Shida, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Tetrodotoxin in two species of ribbon worm (Nemertini), Lineus fuscoviridis and Tubulanus punctatus. Toxicon 1988, 26, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Jeon, J.K.; Arakawa, O.; Sugita, H.; Deguchi, Y.; Shida, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Occurrence of tetrodotoxin and anhydrotetrodotoxin in Vibrio sp. isolated from the intestines of a xanthid crab, Atergatis floridus. J. Biochem. 1986, 99, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simidu, U.; Noguchi, T.; Hwang, D.F.; Shida, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Marine bacteria which produce tetrodotoxin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1987, 53, 1714–1715. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsui, T.; Hamada, S.; Konosu, S. Difference in accumulation of puffer fish toxin and crystalline tetrodotoxin in the puffer fish, Fugu rubripes rubripes. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1981, 47, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Sato, H.; Hamada, S.; Shimizu, C. Comparison of toxicity of the cultured and wild puffer fish Fugu niphobles. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1982, 48, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Maruyama, J.; Kanoh, S.; Jeon, J.-K.; Noguchi, T.; Harada, T.; Murata, O.; Hashimoto, K. Toxicity of the cultured pufferfish Fugu rubripes rubripes along with their resistibility against tetrodotoxin. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1984, 50, 1573–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamori, K.; Kono, M.; Furukawa, K.; Matsui, T. The toxification of juvenile cultured kusafugu Takifugu niphobles by oral administration of crystalline tetrodotoxin. J. Food Hyg. Soc. Jpn. 2004, 45, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, S.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T.; Tachibana, K.; Yagi, M.; Tanigawa, A.; Noguchi, T. Toxification of cultured puffer fish Takifugu rubripes by feeding on tetrodotoxin-containing diet. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 2005, 71, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T. Toxicity of pufferfish Takifugu rubripes cultured in netcages at sea or aquaria on land. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D 2006, 1, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatsuno, R.; Shikina, M.; Shirai, Y.; Wang, J.; Soyano, K.; Nishihara, G.N.; Takatani, T.; Arakawa, O. Change in the transfer profile of orally administered tetrodotoxin to non-toxic cultured pufferfish Takifugu rubripes depending of its development stage. Toxicon 2013, 65, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T. TTX accumulation in pufferfish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D 2006, 1, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O. Tetrodotoxin—Distribution and accumulation in aquatic organisms, and cases of human intoxication. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 220–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoi, S.; Kozaki, A.; Komori, K.; Tsunashima, T.; Noguchi, S.; Kawane, M.; Sugita, H. Toxic Takifugu pardalis eggs found in Takifugu niphobles gut: Implications for TTX accumulation in the pufferfish. Toxicon 2015, 108, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanu, M.B.; Mahmud, Y.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T.; Kajihara, H.; Kawatsu, K.; Hamano, Y.; Asakawa, M.; Miyazawa, K.; Noguchi, T. Immunoenzymatic visualization of tetrodotoxin (TTX) in Cephalothrix species (Nemertea: Anopla: Palaeonemertea: Cephalotrichidae) and Planocera reticulata (Platyhelminthes: Turbellaria: Polycladida: Planoceridae). Toxicon 2004, 44, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritson-Williams, R.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Paul, V.J. Ecological functions of tetrodotoxin in a deadly polyclad flatworm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3176–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNabb, P.; Selwood, A.I.; Munday, R.; Wood, S.A.; Taylor, D.I.; MacKenzie, L.A.; van Ginkel, R.; Rhodes, L.L.; Cornelisen, C.; Heasman, K.; et al. Detection of tetrodotoxin from the grey side-gilled sea slug—Pleurobranchaea maculata, and associated dog neurotoxicosis on beaches adjacent to the Hauraki Gulf, Auckland, New Zealand. Toxicon 2010, 56, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvitti, L.; Wood, S.A.; Taylor, D.I.; McNabb, P.; Cary, S.C. First identification of tetrodotoxin (TTX) in the flatworm Stylochoplana sp.; a source of TTX for the sea slug Pleurobranchaea maculate. Toxicon 2015, 95, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvitti, L.R.; Wood, S.A.; Winsor, L.; Cary, S.C. Intracellular immunohistochemical detection of tetrodotoxin in Pleurobranchaea maculata (gastropoda) and Stylochoplana sp. (turbellaria). Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kato, K. Polycladida of Japan. J. Sigenkagaku Kenkyusyo 1944, 1, 257–319. [Google Scholar]
- Bolanos, D.M.; Quiroga, S.Y.; Litvaitis, M.K. Five new species of cotylean flatworms (Platyhelminthes: Polycladida) from the wider Caribbean. Zootaxa 2007, 1650, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Rawlinson, K.A.; Gillis, J.A.; Billings, R.E., Jr.; Borneman, E.H. Taxonomy and life history of the Acropora-eating flatworm Amakusaplana acroporae nov. sp. (Polycladida: Prosthiostomidae). Coral Reefs 2011, 30, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlinson, K.A.; Stella, J.S. Discovery of the corallivorous polyclad flatworm, Amakusaplana acroporae, on the Great Barrier Reef, Australia—The first report from the wild. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oya, Y.; Kajihara, H. Description of a new Notocomplana species (Platyhelminthes: Acotylea), new combination and new records of Polycladida from the northeastern Sea of Japan, with a comparison of two different barcoding markers. Zootaxa 2017, 4282, 526–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado, D.; Moro, L.; Norena, C. The polycladida (Platyhelminthes) of the Canary Islands. New genus, species and records. Zootaxa 2017, 4312, 38–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunashima, T.; Hagiya, M.; Yamada, R.; Koito, T.; Tsuyuki, N.; Izawa, S.; Kosoba, K.; Itoi, S.; Sugita, H. A molecular framework for the taxonomy and systematics of Japanese marine turbellarian flatworms (Platyhelminthes, Polycladida). Aquat. Biol. 2017, 26, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faubel, A. The Polycladida, Turbellaria. Proposal and establishment of a new system. Part I. The Acotylea. Mitt. Hambg. Zool. Mus. Inst. 1983, 80, 17–121. [Google Scholar]
- Faubel, A. The Polycladida, Turbellaria. Proposal and establishment of a new system. Part II. The Cotylea. Mitt. Hambg. Zool. Mus. Inst. 1984, 81, 189–259. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, R.; Tsunashima, T.; Takei, M.; Sato, T.; Wajima, Y.; Kawase, M.; Oshikiri, S.; Kajitani, Y.; Kosoba, K.; Ueda, H.; et al. Seasonal changes in the tetrodotoxin content of the flatworm Planocera multitentaculata. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazawa, K.; Noguchi, T. Distribution and origin of tetrodotoxin. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 2001, 20, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xie, L.; Xia, G.; Zhang, J.; Nie, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, R. A new tetrodotoxin-producing actinomycete, Nocardiopsis dassonvillei, isolated from the ovaries of puffer fish Fugu rubripes. Toxicon 2005, 45, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.J.; Yu, R.C.; Luo, X.; Zhou, M.J.; Lin, X.T. Toxin-screening and identification of bacteria isolated from highly toxic marine gastropod Nassarius semiplicatus. Toxicon 2008, 52, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Xu, J.; Liang, S.; Ren, D.; Yan, X.; Bao, B. A novel TTX-producing Aeromonas isolated from the ovary of Takifugu obscurus. Toxicon 2010, 56, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.-J.; Chai, T.-J.; Jeng, S.-S.; Hwang, D.-F. Toxicity of the puffer Takifugu rubripes cultured in northern Taiwan. Fish. Sci. 1998, 65, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T. Taxonomic studies on the puffers (Tetraodontidae, Teleostei) from Japan and adjacent regions—V. Synopsis of the puffer from Japan and adjacent regions. Bull. Biogeogr. Soc. Jpn. 1949, 14, 1–15 and 89–140, pls. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura, K. A review of two morphologically similar puffers, Chelonodon laticeps and C. patoca. Natl. Sci. Mus. Monogr. 2002, 22, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Shibuno, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Horinouchi, M.; Sano, M. Habitat use patterns of fishes across the mangrove-seagrass-coral reef seascape at Ishigaki Island, southern Japan. Ichthyol. Res. 2008, 55, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoi, S.; Ishizuka, K.; Mitsuoka, R.; Takimoto, N.; Yokoyama, N.; Detake, A.; Takayanagi, C.; Yoshikawa, S.; Sugita, H. Seasonal changes in the tetrodotoxin content of the pufferfish Takifugu niphobles. Toxicon 2016, 114, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, T. Assay method for tetrodotoxin. In Food Hygiene Examination Manual; Japan Food Hygiene Association: Tokyo, Japan, 1978; Volume II, pp. 232–240. [Google Scholar]




| Specimen | Body Weight (g) | TTX Concentration (μg/g) | TTX Amount (μg) | Sequence | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28S rRNA | COI | ||||
| Planocera sp. S1 | 1.88 | 249 | 469 | LC341282 | LC341285 |
| Planocera sp. S2 | 2.69 | 1351 | 3635 | LC341283 | LC341286 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ueda, H.; Itoi, S.; Sugita, H. TTX-Bearing Planocerid Flatworm (Platyhelminthes: Acotylea) in the Ryukyu Islands, Japan. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16010037
Ueda H, Itoi S, Sugita H. TTX-Bearing Planocerid Flatworm (Platyhelminthes: Acotylea) in the Ryukyu Islands, Japan. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16010037
Chicago/Turabian StyleUeda, Hiroyuki, Shiro Itoi, and Haruo Sugita. 2018. "TTX-Bearing Planocerid Flatworm (Platyhelminthes: Acotylea) in the Ryukyu Islands, Japan" Marine Drugs 16, no. 1: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16010037
APA StyleUeda, H., Itoi, S., & Sugita, H. (2018). TTX-Bearing Planocerid Flatworm (Platyhelminthes: Acotylea) in the Ryukyu Islands, Japan. Marine Drugs, 16(1), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16010037




