Pharmacokinetic and Tissue Distribution of Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus after Oral Administration to Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chemical Composition of Fucoidan
2.2. Method Validation
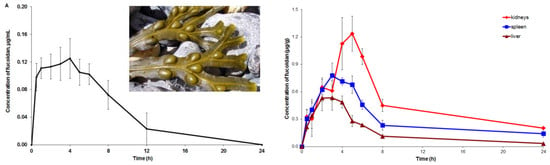
2.3. Pharmacokinetic and Tissue Distribution
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Extraction Procedures
4.3. Analysis of Fucoidan Composition
4.4. Animals
4.5. Analysis of Anti-Xa Activity
- (1)
- fucoidan + antitrombine III (ATIII) → ATIII–fucoidan
- (2)
- ATIII–fucoidan + Xa → ATIII–fucoidan–Xa + Xafree
- (3)
- Xafree + substrate–pNA → peptide + pNA
4.6. Pharmacokinetic and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chapman, V.J.; Chapman, D.J. Seaweed and their Uses; Chapman & Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1980; 334p. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.A.; Brown, L. Seaweeds as potential therapeutic interventions for the metabolic syndrome. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2013, 14, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, S.P.; O’Connor, J.; Fitton, J.H.; Brooks, L.; Rolfe, M.; Connellan, P.; Wohlmuth, H.; Cheras, P.A.; Morris, C. A combined phase I and II open label study on the effects of a seaweed extract nutrient complex on osteoarthritis. Biologics 2010, 4, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, P.J.; Hylands, P.J.; Mensah, A.Y.; Hensel, A.; Deters, A.M. In vitro tests and ethnopharmacological investigations: Wound healing as an example. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 100, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMA. Final Community Herbal Monograph on Fucus vesiculosus L., thallus. European Medicine Agency. 2013. Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Herbal_-_Community_herbal_monograph/2014/08/WC500170924.pdf (accessed on 16 February 2018).
- Ososki, A.L.; Lohr, P.; Reiff, M.; Balick, M.J.; Kronenberg, F.; Fugh-Berman, A.; O’Connor, B. Ethnobotanical literature survey of medicinal plants in the Dominican Republic used for women’s health conditions. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 79, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesinghe, W.A.J.P.; Jeon, Y.J. Biological activities and potential industrial applications of fucose rich sulfated polysaccharides and fucoidans isolated from brown seaweeds: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Cao, R.; Zhang, S.X.; Man, Y.N.; Wu, X.Z. Fucoidan inhibits the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma independent of angiogenesis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumashi, A.; Ushakova, N.A.; Preobrazhenskaya, M.E.; D’incecco, A.; Piccoli, A.; Totani, L.; Tinari, N.; Morozevich, G.E.; Berman, A.E.; Bilan, M.I.; et al. A comparative study of the anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, antiangiogenic, and antiadhesive activities of nine different fucoidans from brown seaweeds. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, S.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Luo, D. Low molecular weight fucoidan ameliorates streptozotocin-induced hyper-responsiveness of aortic smooth muscles in type 1 diabetes rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 191, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Till, S.; Jiang, C.; Knappe, S.; Reutterer, S.; Scheiflinger, F.; Dockal, M. Structure-activity relationship of the pro-and anticoagulant effects of Fucus vesiculosus fucoidan. Thromb. Hhaemos. 2014, 111, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Chung, D.; Shin, I.S.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.; You, S. Effects of molecular weight and hydrolysis conditions on anticancer activity of fucoidans from sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 43, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesekara, I.; Pangestuti, R.; Kim, S.K. Biological activities and potential health benefits of sulfated polysaccharides derived from marine algae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitton, J.H.; Stringer, D.; Karpiniec, S.S. Therapies from fucoidan: An update. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5920–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chollet, L.; Saboural, P.; Chauvierre, C.; Villemin, J.N.; Letourneur, D.; Chaubet, F. Fucoidans in Nanomedicine. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irhimeh, M.R.; Fitton, J.H.; Lowenthal, R.M. Pilot clinical study to evaluate the anticoagulant activity of fucoidan. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2009, 20, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, S.P.; Mulder, A.M.; Baker, D.G.; Robinson, S.R.; Rolfe, M.I.; Brooks, L.; Fitton, J.H. Effects of fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus in reducing symptoms of osteoarthritis: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Biol. Targets Ther. 2016, 10, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irhimeh, M.R.; Fitton, J.H.; Lowenthal, R.M.; Kongtawelert, P. A quantitative method to detect fucoidan in human plasma using a novel antibody. Methods Find Exp. Clin. 2005, 27, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokita, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Mochida, H.; Iha, M.; Nagamine, T. Development of a fucoidan-specific antibody and measurement of fucoidan in serum and urine by sandwich ELISA. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.M.; Nguyen, L.; Barr, M.F.; Morabito, M.; Stringer, D.; Fitton, J.H.; Mowery, K.A. Quantitative determination of fucoidan using polyion-sensitive membrane electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 877, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warttinger, U.; Giese, C.; Harenberg, J.; Krämer, R. Direct quantification of brown algae-derived fucoidans in human plasma by a fluorescent probe assay. arXiv. 2016. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.00108 (accessed on 21.03.2018).
- Bara, L.; Billaud, E.; Gramond, G.; Kher, A.; Samama, M. Comparative pharmacokinetics of a low molecular weight heparin (PK 10 169) and unfractionated heparin after intravenous and subcutaneous administration. Thromb. Res. 1985, 39, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawes, J.; Bara, L.; Billaud, E.; Samama, M. Relationship between biological activity and concentration of a low-molecular-weight heparin (PK 10169) and unfractionated heparin after intravenous and subcutaneous administration. Haemostasis 1986, 16, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Esquivel, A.; Salazar-Sánchez, L. Non-therapeutic anti-Xa levels in medical patients receiving anticoagulant therapy with enoxaparin. Thromb. Res. 2013, 132, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sallami, H.S.; Medlicott, N.J. Investigation of an anti-activated factor X (anti-Xa) assay for the quantification of enoxaparin in human plasma. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Federation of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers & Associations (IFPMA). ICH, Q2A, Harmonized Tripartite Guideline, Text on Validation of Analytical Procedures. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Harmonization, Geneva, Switzerland, 1–5 March 1994. [Google Scholar]
- International Federation of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers & Associations (IFPMA). ICH, Q2B, Harmonized Tripartite Guideline, Validation of Analytical Procedure: Methodology, IFPMA. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Harmonization, Geneva, Switzerland, 1–8 March 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, D.; Zhao, X.; Jin, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q. Microanalysis and preliminary pharmacokinetic studies of a sulfated polysaccharide from Laminaria japonica. Chin. J. Oceanolog. Limnolog. 2016, 34, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamine, T.; Nakazato, K.; Tomioka, S.; Iha, M.; Nakajima, K. Intestinal absorption of fucoidan extracted from the brown seaweed, Cladosiphon okamuranus. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Xu, Z.; Niu, X.; Zhang, H. Effects of fucoidan on chronic renal failure in rats. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Li, N.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H. The protective effect of fucoidan in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3292–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.Y.; Moon, S.Y.; Joo, H.G. Differential effects of fucoidans with low and high molecular weight on the viability and function of spleen cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, S.; Itoh, A.; Isoda, K.; Kondoh, M.; Kawase, M.; Yagi, K. Fucoidan partly prevents CCl 4-induced liver fibrosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 580, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.M.; Tsai, Y.H.; Tsai, T.Y.; Chiu, Y.S.; Wei, L.; Chen, W.C.; Huang, C.C. Fucoidan supplementation improves exercise performance and exhibits anti-fatigue action in mice. Nutrients 2015, 7, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obluchinsksya, E.D.; Makarova, M.N.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shikov, A.N. Effects of ultrasound treatment on the chemical composition and anticoagulant properties of dry fucus extract. Pharm. Chem. J. 2015, 49, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obluchinskaya, E.D. Comparative study of the molecular weight distribution of fucoidan from fucus algae. Obz. Klin. Farmacol. Lek. Ter. 2016, 14, 46–47. [Google Scholar]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.T.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, L.J.; Hurst, R.E.; Simpson, L.; Settine, J.M. Analysis of sulfate in complex carbohydrates. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 123, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitter, T.; Muir, H.M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1962, 4, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Jasso, R.M.; Mussatto, S.I.; Pastrana, L.; Aguilar, C.N.; Teixeira, J.A. Extraction of sulfated polysaccharides by autohydrolysis of brown seaweed Fucus vesiculosus. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry: Estimating the Maximum Safe Starting dose in Initial Clinical Trials for Therapeutics in Adult Healthy Volunteers; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), 2005. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidances/ucm078932.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2018).
- Mironov, A.N.; Bunyatyan, N.D.; Vasiljev, A.N.; Verstakova, O.L.; Zhuravleva, M.V.; Lepakhin, V.K.; Korobov, N.V.; Merkulov, V.A.; Orekhov, S.N.; Sakaeva, I.V.; et al. Guideline for Preclinical Studies of Drugs; Grif and K: Moscow, Russia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Karlina, M.V.; Shikov, A.N.; Kosman, V.M.; Makarov, V.G.; Casals, E.; Rosenholm, J.M. Pharmacokinetics and tissue disposition of nanosystem-entrapped betulin after endotracheal administration to rats. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 42, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameter | Range |
|---|---|
| Accuracy, % | |
| ULOQ (0.217 μg/mL) | 0.64–3.10 |
| Middle-quality control (0.108 μg/mL) | 1.12–4.20 |
| Low-quality control (0.054 μg/mL) | 5.5–12.0 |
| LLOQ (0.027 μg/mL) | 3.0–7.1 |
| Intraday//Interday precision (RSD), % | |
| ULOQ (0.217 μg/mL) | 0.8–2.5//2.3 |
| Middle-quality control (0.108 μg/mL) | 4.0–4.5//4.6 |
| Low-quality control (0.054 μg/mL) | 6.5–8.1//8.6 |
| LLOQ (0.027 μg/mL) | 0.7–6.2//11.6 |
| LOD, μg/mL | 0.01 |
| Sample | Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC0–t (µg·h/g) * | MRT (h) | T1/2 (h) | ft | |
| Plasma | 0.99 ± 0.27 | 6.79 ± 1.63 | 3.44 ± 1.70 | - |
| Liver | 3.26 ± 1.54 | 9.25 ± 3.78 | 6.44 ± 3.57 | 3.29 |
| Kidneys | 10.74 ± 5.15 | 12.39 ± 4.26 | 7.26 ± 3.09 | 10.85 |
| Spleen | 6.89 ± 2.87 | 14.57 ± 6.51 | 9.32 ± 5.12 | 6.96 |
| Striated muscle | 1.49 ± 0.22 | 5.43 ± 0.82 | 2.36 ± 0.84 | 1.50 |
| Omentum | 1.10 ± 0.22 | 7.78 ± 0.93 | 4.30 ± 0.79 | 1.11 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Shikov, A.N.; Faustova, N.M.; Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Kosman, V.M.; Vuorela, H.; Makarov, V.G. Pharmacokinetic and Tissue Distribution of Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus after Oral Administration to Rats. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16040132
Pozharitskaya ON, Shikov AN, Faustova NM, Obluchinskaya ED, Kosman VM, Vuorela H, Makarov VG. Pharmacokinetic and Tissue Distribution of Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus after Oral Administration to Rats. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(4):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16040132
Chicago/Turabian StylePozharitskaya, Olga N., Alexander N. Shikov, Natalya M. Faustova, Ekaterina D. Obluchinskaya, Vera M. Kosman, Heikki Vuorela, and Valery G. Makarov. 2018. "Pharmacokinetic and Tissue Distribution of Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus after Oral Administration to Rats" Marine Drugs 16, no. 4: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16040132
APA StylePozharitskaya, O. N., Shikov, A. N., Faustova, N. M., Obluchinskaya, E. D., Kosman, V. M., Vuorela, H., & Makarov, V. G. (2018). Pharmacokinetic and Tissue Distribution of Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus after Oral Administration to Rats. Marine Drugs, 16(4), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16040132