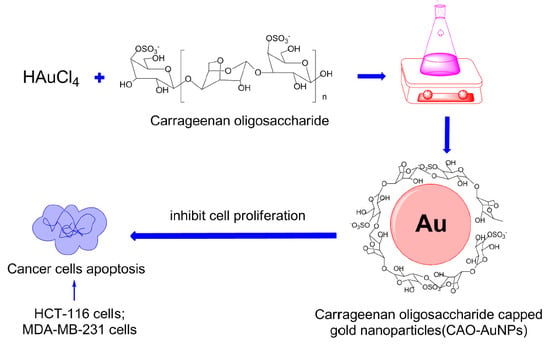
Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Carrageenan Oligosaccharide and Their In Vitro Antitumor Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Carrageenan Oligosaccharide (CAO)
2.2. Optimization of Synthetic Conditions of Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) by Response Surface Methodology (RSM)
2.3. Synthesis of CAO-AuNPs
2.4. Characterization of CAO-AuNPs
2.5. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of Carrageenan Oligosaccharide
3.3. Fourier Transform-Infrared (FT-IR) and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Analysis of Carrageenan Oligosaccharide
3.4. Optimization of Reaction Condition for Synthesis of AuNPs by RSM
3.5. Synthesis of CAO-AuNPs
3.6. Characterization of CAO-AuNPs
3.7. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Study
3.7.1. Cell Viability Assay
3.7.2. Cell Morphology Observation
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhattacharya, R.; Mukherjee, P. Biological properties of “naked” metal nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivasagan, P.; Bharathiraja, S.; Bui, N.Q.; Jang, B.; Oh, Y.-O.; Lim, I.G.; Oh, J. Doxorubicin-loaded fucoidan capped gold nanoparticles for drug delivery and photoacoustic imaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armanetti, P.; Pocoví-Martínez, S.; Flori, A.; Avigo, C.; Cassano, D.; Menichetti, L.; Voliani, V. Dual Photoacoustic/Ultrasound Multi-Parametric Imaging from Passion Fruit-like Nano-Architectures. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 1787–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassano, D.; David, J.; Luin, S.; Voliani, V. Passion fruit-like nano-architectures: A general synthesis route. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faramarzi, M.A.; Sadighi, A. Insights into biogenic and chemical production of inorganic nanomaterials and nanostructures. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2013, 3, 189–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimling, J.; Maier, M.; Okenve, B.; Kotaidis, V.; Ballot, H.; Plech, A. Turkevich method for gold nanoparticle synthesis revisited. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 15700–15707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugie, A.; Hatta, T.; Kanie, K.; Muramatsu, A.; Mori, A. Synthesis of Thiol-capped Gold Nanoparticles with Organometallic Reagents as a New Class of Reducing Agent. Chem. Lett. 2009, 38, 562–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Yadav, S.K. Plant-mediated synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and their applications. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Hong, Y.N.; Weyers, A.; Kim, Y.S.; Linhardt, R.J. Polysaccharides and phytochemicals: A natural reservoir for the green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles. Cheminform 2011, 5, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Li, W.H. Preparation of gold nanoparticles using chitosan oligosaccharide as a reducing and capping reagent and their in vitro cytotoxic effect on Human fibroblasts cells. Mater. Lett. 2015, 138, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Annu, S.I.; Yudha, S.S. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles: A. green approach. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 161, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, L.; Blázquez, M.L.; González, F.; Muñoz, J.A.; Ballester, A. Extracellular biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using sugar beet pulp. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 164, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estela, C.B.; Angel, I.M.A.; Francisco, G.; Jacome, G.E.; Paulina, A.G.; Anatolio, M.; Abraham, B.L.J. Biological Synthesis and Characterization of Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs), using Plant Extracts. J. Nanomater. Mol. Nanotechnol. 2016, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivasagan, P.; Oh, J. Marine polysaccharide-based nanomaterials as a novel source of nanobiotechnological applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanessaleiria, C.; Danielfábio, K.; Dílsonbrazdajr, S.; Ivone, C. Carrageenans: Biological properties, chemical modifications and structural analysis—A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Zhao, X.; Yang, B.; Ren, S.; Guan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lawson, A.M.; Chai, W. Sequence determination of sulfated carrageenan-derived oligosaccharides by high-sensitivity negative-ion electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 8499–8505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joye, I.J.; Mcclements, D.J. Biopolymer-based nanoparticles and microparticles: Fabrication, characterization, and application. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2014, 19, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchezsánchez, M.; Martínillana, A.; Ruizcaro, R.; Bermejo, P.; Abad, M.; Carro, R.; Bedoya, L.M.; Tamayo, A.; Rubio, J.; Fernándezferreiro, A. Chitosan and kappa-carrageenan vaginal acyclovir formulations for prevention of genital herpes. In vitro and ex vivo evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5976–5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Sun, Y.P.; Xin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, Z. In vivo antitumor and immunomodulation activities of different molecular weight lambda-carrageenans from Chondrus ocellatus. Pharmacol. Res. 2004, 50, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, K.B.; Kalla, D.; Uppuluri, K.B.; Anbazhagan, V. Green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles employing levan, a biopolymer from Acetobacter xylinum NCIM 2526, as a reducing agent and capping agent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.C.; Miao, S.; Wen, X.C.; Sun, Y.X. Optimization of polysaccharides (ABP) extraction from the fruiting bodies of Agaricus blazei Murill using response surface methodology (RSM). Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 78, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Sun, X.; Tian, C.; Luo, J.; Zheng, C.; Zhan, J. Polysaccharide extraction from Sphallerocarpus gracilis roots by response surface methodology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 88, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Préchoux, A.; Helbert, W. Preparation and detailed NMR analyses of a series of oligo-α-carrageenans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, B.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Cao, H.; Huang, L.; Wang, J. Structural characterization and antioxidant activities of κ-carrageenan oligosaccharides degraded by different methods. Food Chem. 2015, 178, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, P.; Yu, G.L.; Li, C.X.; Hao, C.; Qi, X.; Zhang, L.J.; Guan, H.S. Preparation and Anti-Influenza A Virus Activity of κ-carrageenan Oligosaccharide and Its Sulphated Derivatives. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makanjuola, S.A.; Enujiugha, V.N.; Omoba, O.S.; Sanni, D.M. Application of RSM and multivariate statistics in predicting antioxidant property of ethanolic extracts of tea-ginger blend. Eur. J. Med. Plants 2015, 6, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Feng, F.; Yuan, F.; Su, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, H.; Song, K.; Nie, B.; Yu, L.; Zhang, F. Simultaneous determination of 13 carbohydrates using high-performance anion-exchange chromatography coupled with pulsed amperometric detection and mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 1843–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, K.S. Controlled synthesis and biomolecular probe application of gold nanoparticles. Micron 2011, 42, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sportelli, M.C.; Volpe, A.; Picca, R.A.; Trapani, A.; Palazzo, C.; Ancona, A.; Lugarà, P.M.; Trapani, G.; Cioffi, N. Spectroscopic Characterization of Copper-Chitosan Nanoantimicrobials Prepared by Laser Ablation Synthesis in Aqueous Solutions†. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivasagan, P.; Oh, J. Production of a Novel Fucoidanase for the Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles by Streptomyces sp. and Its Cytotoxic Effect on HeLa Cells. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6818–6837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Wing, C.; Esparza, R.; Vargas-Hernández, C.; Fernández García, M.E.; José-Yacamán, M. Microwave-assisted synthesis of gold nanoparticles self-assembled into self-supported superstructures. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 2281–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghribi, A.M.; Sila, A.; Gafsi, I.M.; Blecker, C.; Danthine, S.; Attia, H.; Bougatef, A.; Besbes, S. Structural, functional, and ACE inhibitory properties of water-soluble polysaccharides from chickpea flours. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 75, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkakaty, B.; Matsumoto, K.; Endo, T. Synthesis and Radical Polymerization of Adamantyl Methacrylate Monomers Having Hemiacetal Moieties. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 9481–9485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujitha, M.V.; Kannan, S. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Citrus fruits (Citrus limon, Citrus reticulata and Citrus sinensis) aqueous extract and its characterization. Spectrochim. Acta Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 102, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomoaia, G.; Horovitz, O.; Mocanu, A.; Nita, A.; Avram, A.; Racz, C.P.; Soritau, O.; Cenariu, M.; Tomoaia-Cotisel, M. Effects of doxorubicin mediated by gold nanoparticles and resveratrol in two human cervical tumor cell lines. Colloid. Surf. B Biointerface 2015, 135, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Tripp, S.L.; Wei, A. Self-organization of large gold nanoparticle arrays. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 7955–7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orellana, E.A.; Kasinski, A.L. Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Assay in Cell Culture to Investigate Cell Proliferation. Bio-Protocol 2016, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Ballesteros, N.; Prado-López, S.; Rodríguez-González, J.B.; Lastra, M.; Rodríguez-Argüelles, M.C. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using brown algae Cystoseira baccata: Its activity in colon cancer cells. Colloid. Surf. B Biointerface 2017, 153, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, E.J.; Choi, D.G.; Min, S.S. Targeted and effective photodynamic therapy for cancer using functionalized nanomaterials. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.H.; Lee, C.W.; Chiou, A.; Wei, P.K. Size-dependent endocytosis of gold nanoparticles studied by three-dimensional mapping of plasmonic scattering images. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2010, 8, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Song, J.; Li, X.; Li, N.; Dai, J. Immunomodulation and antitumor activity of kappa-carrageenan oligosaccharides. Cancer Lett. 2006, 243, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, K.; Nakamura, M.; Ishimura, K. Near-Infrared Fluorescent Silica-Coated Gold Nanoparticle Clusters for X-Ray Computed Tomography/Optical Dual Modal Imaging of the Lymphatic System. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.T.; Ren, L.; Li, S.; Wang, L.L.; He, X.X.; Zhao, X.; Yu, G.L.; Guan, H.S.; Li, C.X. Study on quality control of sulfated polysaccharide drug, propylene glycol alginate sodium sulfate (PSS). Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 144, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Yu, G.; Guan, H.; Yue, N.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H. Preparation of low-molecular-weight polyguluronate sulfate and its anticoagulant and anti-inflammatory activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 69, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Std Order * | Run Order | Factor1 A:Concentration of Gold Chloride Acid (mmol/L) | Factor2 B:Reaction Time (h) | Factor3 C:Concentration of CAO (mg/5 mL) | Absorbance at 530 nm (R1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | 1 | 0.5 | 3 | 60 | 1.311 |
| 9 | 2 | 0.5 | 3 | 40 | 1.033 |
| 13 | 3 | 0.5 | 4 | 50 | 1.044 |
| 1 | 4 | 0.1 | 3 | 50 | 0.200 |
| 16 | 5 | 0.5 | 4 | 50 | 1.139 |
| 12 | 6 | 0.5 | 5 | 60 | 1.163 |
| 3 | 7 | 0.1 | 5 | 50 | 0.188 |
| 10 | 8 | 0.5 | 5 | 40 | 0.993 |
| 15 | 9 | 0.5 | 4 | 50 | 1.140 |
| 7 | 10 | 0.1 | 4 | 60 | 0.195 |
| 17 | 11 | 0.5 | 4 | 50 | 1.142 |
| 14 | 12 | 0.5 | 4 | 50 | 1.305 |
| 4 | 13 | 1.0 | 5 | 50 | 0.872 |
| 5 | 14 | 0.1 | 4 | 40 | 0.180 |
| 8 | 15 | 1.0 | 4 | 60 | 0.550 |
| 6 | 16 | 1.0 | 4 | 40 | 0.060 |
| 2 | 17 | 1.0 | 3 | 50 | 0.882 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Y.; Yin, J.; Bai, M.; Wang, F. Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Carrageenan Oligosaccharide and Their In Vitro Antitumor Activity. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080277
Chen X, Zhao X, Gao Y, Yin J, Bai M, Wang F. Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Carrageenan Oligosaccharide and Their In Vitro Antitumor Activity. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(8):277. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080277
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiangyan, Xia Zhao, Yanyun Gao, Jiaqi Yin, Mingyue Bai, and Fahe Wang. 2018. "Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Carrageenan Oligosaccharide and Their In Vitro Antitumor Activity" Marine Drugs 16, no. 8: 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080277
APA StyleChen, X., Zhao, X., Gao, Y., Yin, J., Bai, M., & Wang, F. (2018). Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Carrageenan Oligosaccharide and Their In Vitro Antitumor Activity. Marine Drugs, 16(8), 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080277