Electrodialysis Extraction of Pufferfish Skin (Takifugu flavidus): A Promising Source of Collagen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Quality Measurements
2.2. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) Analyses of T. flavidus Collagen
2.3. Amino Acid Composition of T. flavidus Collagen
2.4. Spectrophotometric Characterization
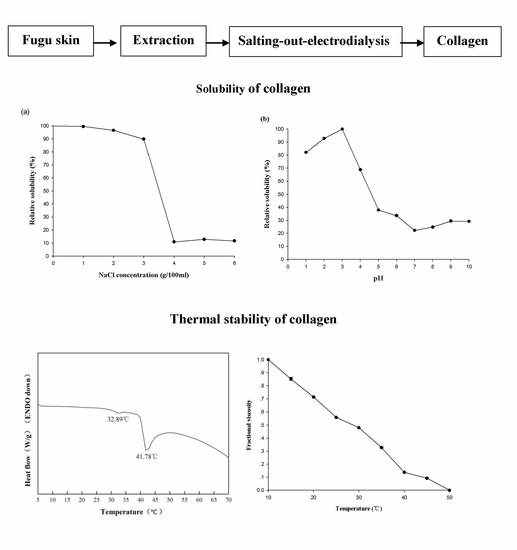
2.5. Thermal Properties
2.6. Relative Solubility
2.7. Cell Proliferation
2.8. Extraction of T. flavidus Collagen
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Isolation and Purification of T. flavidus Collagen
3.3. Quality Measurements
3.3.1. Heavy Metal
3.3.2. Tetrodotoxin
3.4. SDS-PAGE
3.5. Amino Acid Composition
3.6. Spectrophotometric Characterization
3.7. Relative Solubility
3.8. DSC
3.9. Viscosity
3.10. Cell Proliferation
3.11. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.D.; Li, L.; Yi, R.Z.; Gao, R.; He, J.L. Release kinetics of Tilapia scale collagen I peptides during tryptic hydrolysis. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.D.; Liu, Y.; Yi, R.Z.; Li, L.; Gao, R.; Xu, N.H.; Zheng, M.H. Characterization of collagen enzymatic hydrolysates derived from lizardfish (Synodus fuscus) scales. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2017, 26, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, B.; Lin, Y.S.; Brodsky, B. Collagen interactions: Drug design and delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 97, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Gentile, P.; Chiono, V.; Ciardelli, G. Collagen for bone tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 3191–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Guillen, M.C.; Gimenez, B.; Lopez-Caballero, M.E.; Montero, M.P. Functional and bioactive properties of collagen and gelatin from alternative sources: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1813–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Xiao, M.T.; Zhao, P.; Chen, J.D. Progress on collagen aggregates and their aggregation behavior. Curr. Biotechnol. 2017, 7, 587–593. [Google Scholar]
- Jridi, M.; Bardaa, S.; Moalla, D.; Rebaii, T.; Souissi, N.; Sahnoun, Z.; Nasri, M. Microstructure, rheological and wound healing properties of collagen-based gel from cuttlefish skin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 77, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, R.A.J.; Ayling, R.D.; McAuliffe, L. Vaccines for Mycoplasma Diseases in Animals and Man. J. Comp. Pathol. 2009, 140, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, J.; Anil, S.; Kim, S.-K.; Shim, M.S. Marine fish proteins and peptides for cosmeceuticals: A review. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.L.; Zhang, H.T.; Ren, Y.Q.; Zhou, Q. Comparison of growth parameters of tiger puffer Takifugu rubripes from two culture systems in china. Aquaculture 2016, 453, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matmaroh, K.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T.; Encarnacion, A.B.; Kishimura, H. Characteristics of acid soluble collagen and pepsin soluble collagen from scale of spotted golden goatfish (Parupeneus heptacanthus). Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Portier, R.J.; Moody, M.W.; Bell, J.; Schexnayder, M.A.; Losso, J.N. Biochemical properties of bone and scale collagens isolated from the subtropical fish black drum (Pogonia cromis) and sheepshead seabream (Archosargus probatocephalus). Food Chem. 2004, 88, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.S.; Liang, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, P. Extraction and characterisation of pepsin-solubilised collagen from fins, scales, skins, bones and swim bladders of bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis). Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, T.; Suzuki, N. Isolation of collagen from fish waste material—Skin, bone and fins. Food Chem. 2000, 68, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.T.; Li, G.Y.; Shi, B.; Miao, Y.Q.; Wu, X.H. Isolation and partial characterization of pepsin-soluble collagen from the skin of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Food Chem. 2007, 103, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strathmann, H. Electrodialysis, a mature technology with a multitude of new applications. Desalination 2010, 264, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwal, S.; Roblet, C.; Amiot, J.; Doyen, A.; Beaulieu, L.; Legault, J.; Bazinet, L. Recovery of valuable peptides from marine protein hydrolysate by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membrane: Impact of ionic strength. Food Res. Int. 2014, 65, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobihah, N.N.; Zaharin, A.A.; Nizam, M.K.; Juen, L.L.; Kyoung-Woong, K. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in maricultured fish, Lates calcarifer (Barramudi), Lutjanus campechanus (red snapper) and Lutjanus griseus (grey snapper). Chemosphere 2018, 197, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Chen, H.; Xie, Q.L.; Hong, B.H.; Chen, J.D.; Fang, H.; Bai, K.K.; He, J.L.; Yi, R.Z.; Wu, H. Rapid isolation of high purity pepsin-soluble type I collagen from scales of red drum fish (Sciaenops ocellatus). Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsanit, S.; Ke, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.J. Trace elements in two marine fish cultured in fish cages in Fujian province China. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, I. Toxicological Studies of Puffers in Japan; Teikokutosho: Tokyo, Japan, 1945; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, T.; Araki, Y.; Suzuki, N. Collagen of the skin of ocellate puffer fish (Takifugu rubripes). Food Chem. 2002, 78, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Nagai, T.; Tanaka, M. Characterisation of acid-soluble collagen from skin and bone of bigeye snapper (Priacanthus tayenus). Food Chem. 2005, 89, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Ariffin, F.; Huda, N. An alternative source of type I collagen based on by-product with higher thermal stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.M.; Zong, C.H.; Jin, S.J.; Zheng, J.W.; Chen, N.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, F.F.; Yang, Z.S.; Tang, Y.P.; et al. Optimization of extraction conditions and characterization of pepsin-solubilized collagen from skin of giant croaker (Nibea japonica). Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontaine-Vive, F.; Merzel, F.; Johnson, M.R.; Kearley, G.J. Collagen and component polypeptides: Low frequency and amide vibrations. Chem. Phys. 2009, 355, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staicu, T.; Circu, V.; Ionita, G.; Ghica, C.; Popa, V.T.; Micutz, M. Analysis of bimodal thermally-induced denaturation of type I collagen extracted from calfskin. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 38391–38406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, I.; Osatomi, K.; Yoshida, A.; Osako, K.; Yamaguchi, A.; Hara, K. Biochemical properties of acid-soluble collagens extracted from the skins of underutilised fishes. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, H.; Yokoyama, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Mizuta, S.; Yoshinaka, R.; Akahane, Y. Isolation of collagen from tiger pufferfish parts and its solubility in dilute acetic acid. Fish. Sci. 2013, 79, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, R.J.; Bello, J. Ultraviolet absorbance changes accompanying the denaturation of soluble collagen and atelocollagen. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1968, 31, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Tone, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Zikihara, K.; Tokutomi, S.; Ida, T.; Ihara, H.; Hara, M. Studies on fish scale collagen of Pacific saury (Cololabis saira). Mat. Sci. Eng. C Mater. 2013, 33, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Krimm, S.; Randall, H.M. Normal vibrations of crystalline polyglycine-I. Biopolymers 1972, 11, 1817–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veeruraj, A.; Arumugam, M.; Ajithkumar, T.; Balasubramanian, T. Isolation and characterization of collagen from the outer skin of squid (Doryteuthis singhalensis). Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, A.; Zscherp, C. What vibrations tell us about proteins. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2002, 35, 369–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krimm, S.; Bandekar, J. Vibrational spectroscopy and conformation of peptides, polypeptides, and proteins. Adv. Protein Chem. 1986, 38, 181–364. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, S.; Ohno, Y. Fish type I collagen: Tissue-specific existence of two molecular forms (α1)2 and α1α2α3, in Alaska pollack. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Comp. Biochem. 1987, 88, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.Y.; Li, B.F.; Zhao, X.; Ren, G.Y.; Zhuang, Y.L.; Hou, H.; Zhang, X.K.; Chen, L.; Fan, Y. Characterization of acid-soluble collagen from the skin of walleye pollock (Theragra chalcogramma). Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komsa-Penkova, R.; Koynova, R.; Kostov, G.; Tenchov, B. Discrete reduction of type I collagen thermal stability upon oxidation. Biophys. Chem. 2000, 83, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Y.; Shi, Y.H.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Liu, J.Z.; Zang, W.L. Effects of salinity on embryos and larvae of tawny puffer Takifugu flavidus. Aquaculture 2010, 302, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoulders, M.D.; Raines, R.T. Collagen Structure and Stability. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 929–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanaboni, G.; Rossi, A.; Onana, A.M.T.; Tenni, R. Stability and networks of hydrogen bonds of the collagen triple helical structure: Influence of pH and chaotropic nature of three anions. Matrix Biol. 2000, 19, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Benjakul, S.; Maqsood, S.; Kishimura, H. Isolation and characterisation of collagen extracted from the skin of striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus). Food Chem. 2011, 124, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.Z.; Horber, H.; Howard, J.; Muller, D.J. Assembly of collagen into microribbons: Effects of pH and electrolytes. J. Struct. Biol. 2004, 148, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vojdani, F. Solubility. In Methods of Testing Protein Functionality, 1st ed.; Hall, G.M., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 11–60. ISBN 9780751400533. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.D.; Li, L.; Yi, R.Z.; Xu, N.H.; Gao, R.; Hong, B.H. Extraction and characterization of acid-soluble collagen from scales and skin of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosker, A.R.; Ozogul, F.; Durmus, M.; Ucar, Y.; Ozogul, Y.; Boga, E.; Ayas, D. Seasonal changes in proximate composition and mineral-heavy metal content of pufferfish (Lagocephalus sceleratus) from northeastern mediterranean sea. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 18, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Yu, R.C.; Luo, X.; Zhou, M.J.; Lin, X.T. Toxin-screening and identification of bacteria isolated from highly toxic marine gastropod Nassarius semiplicatus. Toxicon 2008, 52, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Pei, X.L.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhou, D. Extraction and characterization of acid-soluble and pepsin-soluble collagen from skin of loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Golser, A.V.; Röber, H.G.; Scheibel, S. Engineered collagen: A redox switchable framework for tunable assembly and fabrication of biocompatible surfaces. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 2106–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Heavy Metal | Pufferfish Skin | Collagen Sample | Chinese National Standards a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food Additive Gelatin (GB 6783) | Maximum Concentrations of Contaminants in Foods (GB 2762) | |||
| Pb | 0.562 ± 0.052 | 0.421 ± 0.015 | ≤1.5 | ≤0.5 |
| Cd | 0.042 ± 0.004 | 0.023 ± 0.002 | - | ≤0.1 |
| As | 0.075 ± 0.002 | 0.052 ± 0.001 | ≤1.0 | ≤0.1 |
| Cr | 1.152 ± 0.067 | 0.863 ± 0.072 | ≤2.0 | ≤2.0 |
| Amino acids | T. flavidus |
|---|---|
| Glycine | 268 ± 0.08 |
| Proline | 164 ± 0.05 |
| Hydroxyproline | 82.1 ± 0.04 |
| Arginine | 32.7 ± 0.12 |
| Hydroxylysine | 9.2 ± 0.09 |
| Lysine | 37.7 ± 0.08 |
| Alanine | 119 ± 0.11 |
| Threonine | 39.8 ± 0.03 |
| Valine | 31.0 ± 0.09 |
| Serine | 14.7 ± 0.13 |
| Isoleucine | 13.9 ± 0.07 |
| Leucine | 33.8 ± 0.05 |
| Methionine | 18.5 ± 0.07 |
| Histidine | 13.7 ± 0.06 |
| Phenylalanine | 18.1 ± 0.03 |
| Glutamine acid | 37.1 ± 0.06 |
| Aspartic acid | 60.4 ± 0.05 |
| Cysteine | 0.57 ± 0.09 |
| Tyrosine | 5.43 ± 0.05 |
| Traditional Dialysis | Electrodialysis | |
|---|---|---|
| Essential Instruments | Dialysis bag, beakers and stirring hot plates | DSA-П electrodialysis apparatus |
| Instrument time (h/dialysis) | >96 | 2.0 |
| Dialysis bag (m) | 600 | none |
| Acetic acid (mole) | 18,000 | 45.0 |
| Waste water (L) | 360,000 | 600 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Li, M.; Yi, R.; Bai, K.; Wang, G.; Tan, R.; Sun, S.; Xu, N. Electrodialysis Extraction of Pufferfish Skin (Takifugu flavidus): A Promising Source of Collagen. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17010025
Chen J, Li M, Yi R, Bai K, Wang G, Tan R, Sun S, Xu N. Electrodialysis Extraction of Pufferfish Skin (Takifugu flavidus): A Promising Source of Collagen. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Junde, Min Li, Ruizao Yi, Kaikai Bai, Guangyu Wang, Ran Tan, Shanshan Sun, and Nuohua Xu. 2019. "Electrodialysis Extraction of Pufferfish Skin (Takifugu flavidus): A Promising Source of Collagen" Marine Drugs 17, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17010025
APA StyleChen, J., Li, M., Yi, R., Bai, K., Wang, G., Tan, R., Sun, S., & Xu, N. (2019). Electrodialysis Extraction of Pufferfish Skin (Takifugu flavidus): A Promising Source of Collagen. Marine Drugs, 17(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17010025