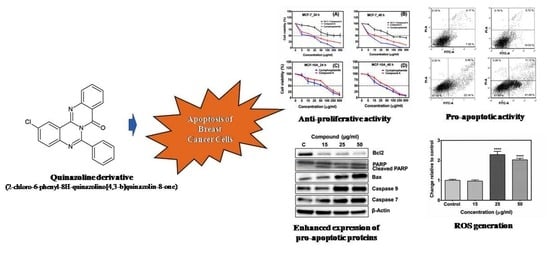
A Natural Quinazoline Derivative from Marine Sponge Hyrtios erectus Induces Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Cells via ROS Production and Intrinsic or Extrinsic Apoptosis Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Compound A Inhibits the Growth of Human Breast Carcinoma Cells (MCF-7) In Vitro
2.2. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Cytotoxicity Test
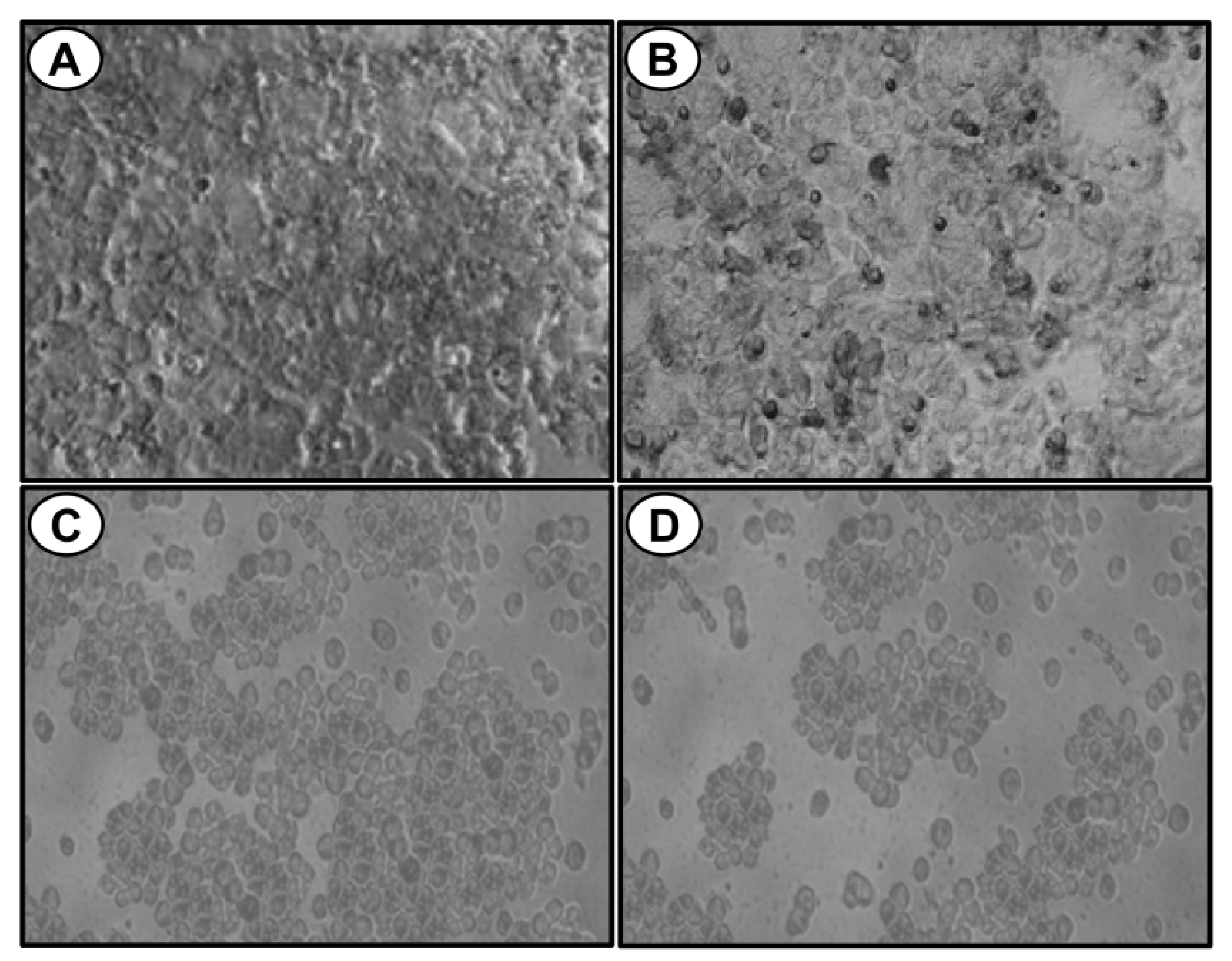
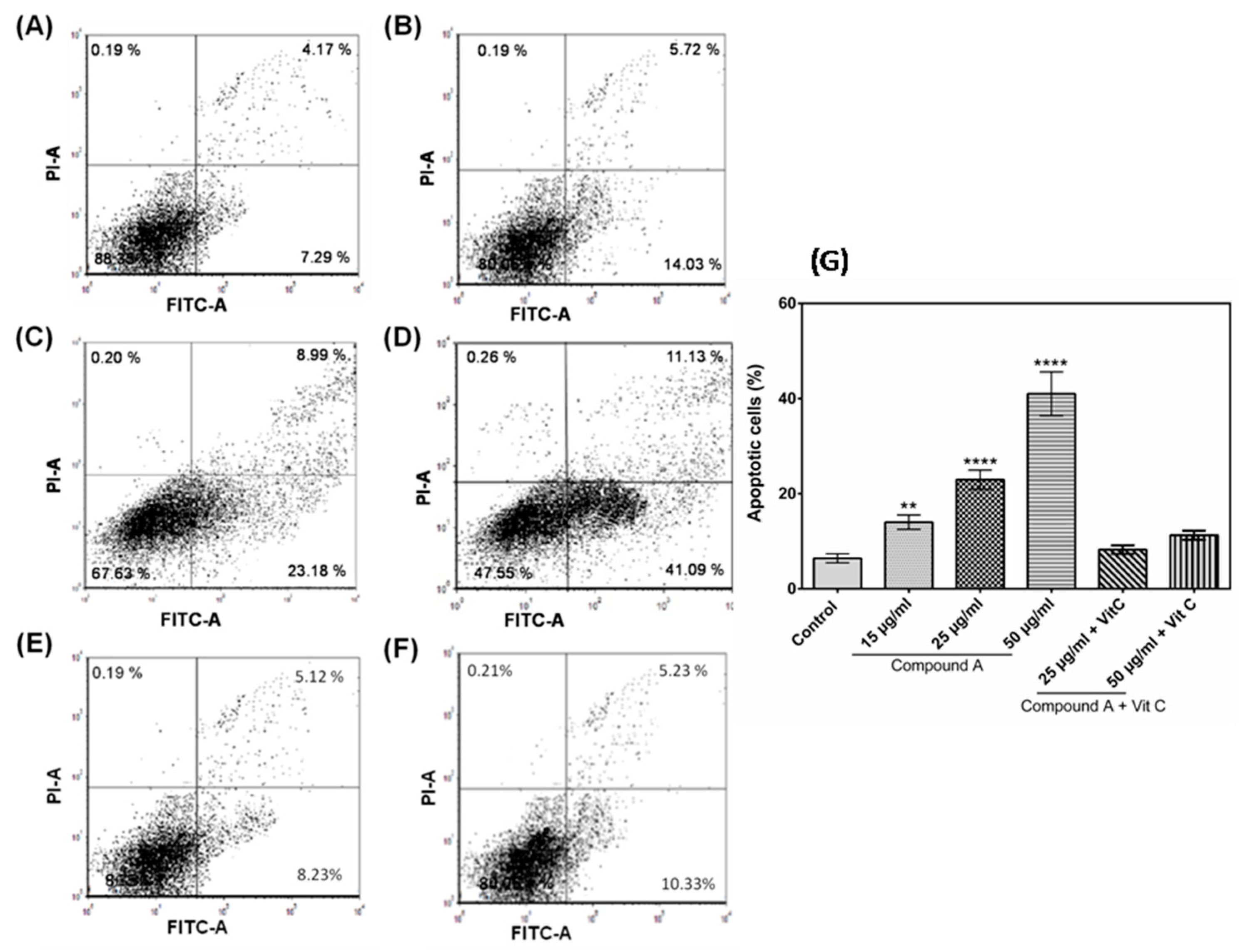
2.3. The Compound A Induces Apoptosis of Cancerous MCF-7 Cells
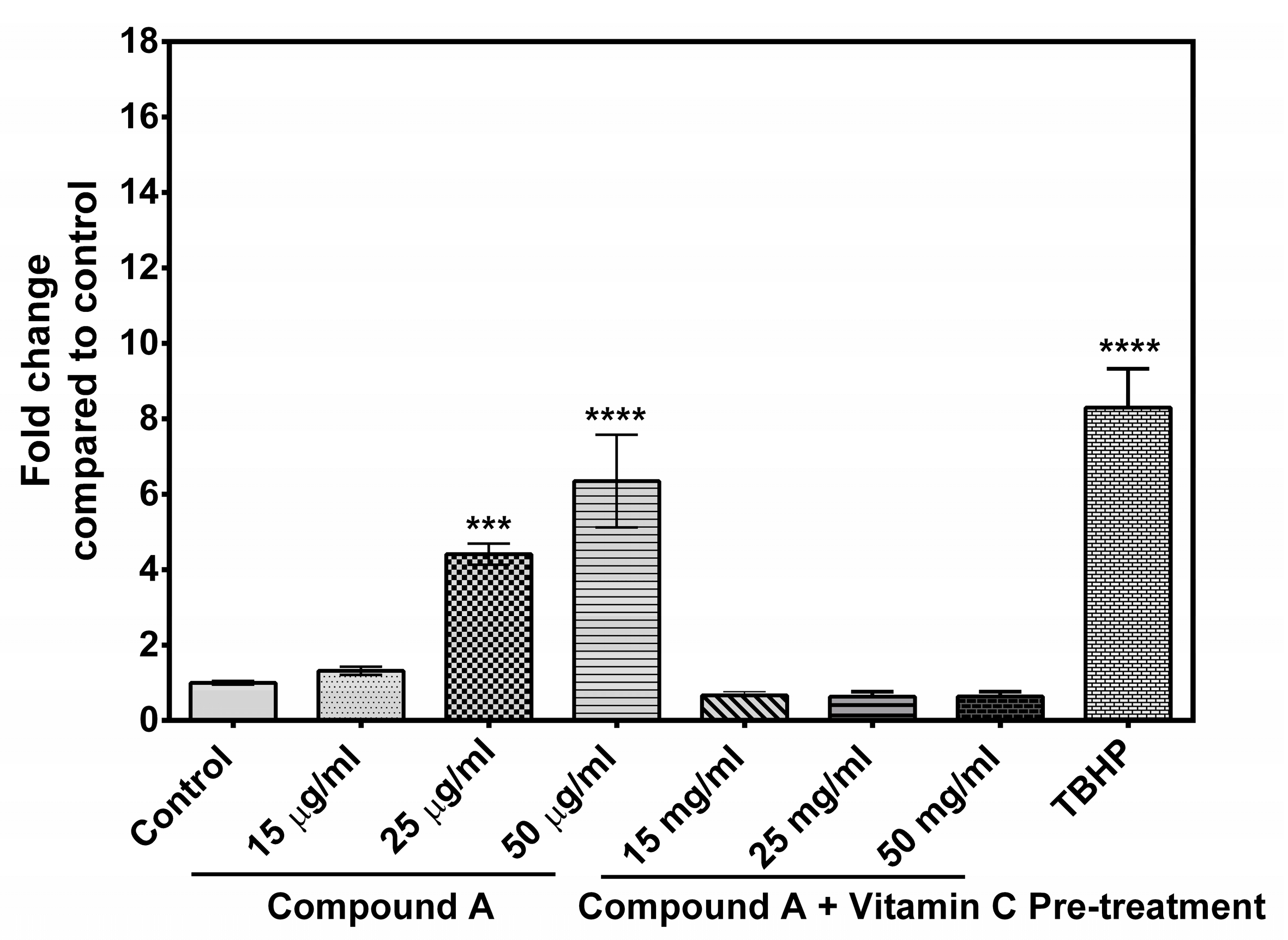
2.4. Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
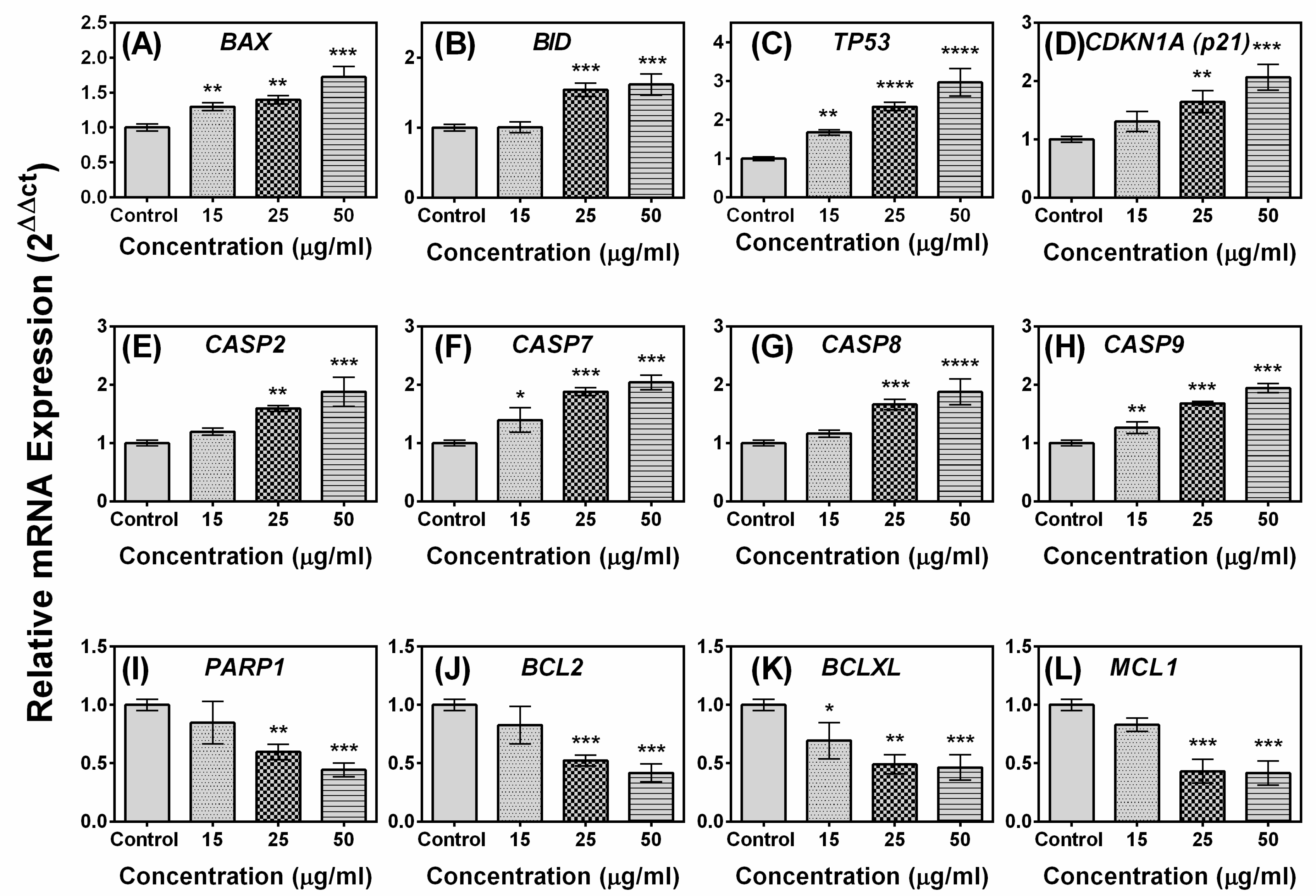
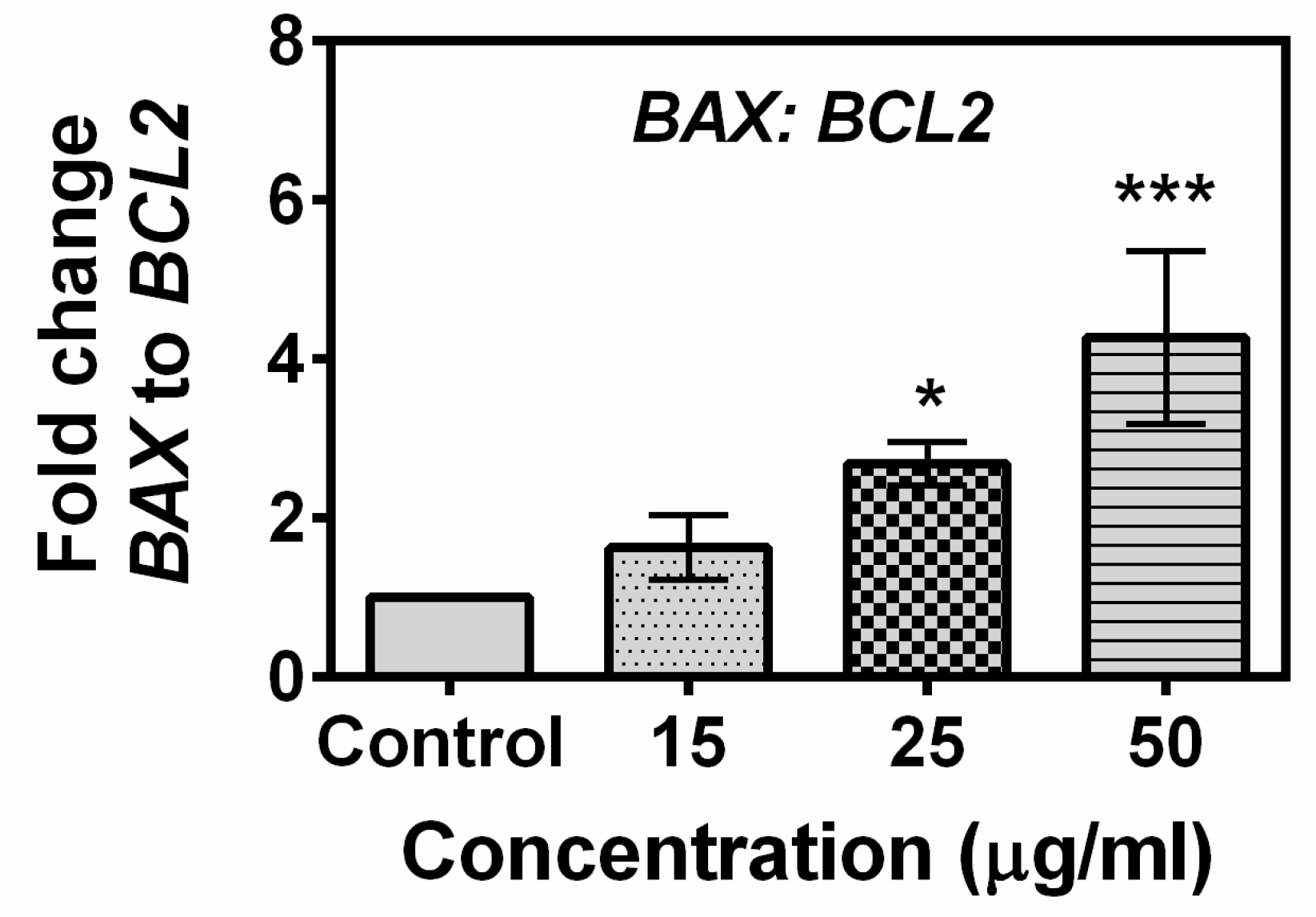
2.5. Effects of Compound A on the Expression of Apoptotic-Related Genes in MCF-7 Cells
2.6. Effects of the Compound A on the Expression of Apoptotic-Related Proteins in MCF-7 Cells
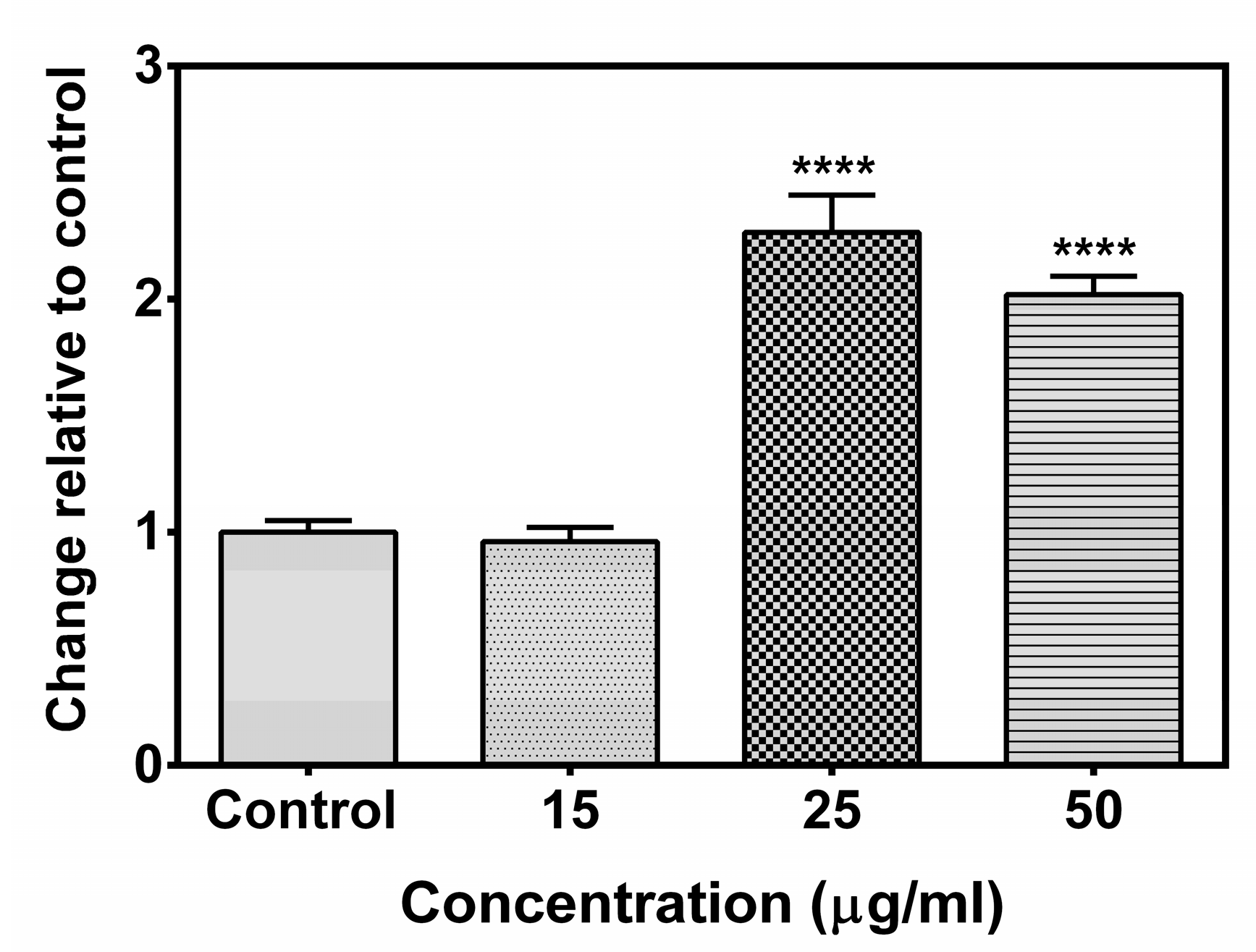
2.7. Effect of the Compound A on Caspase 8 Activity
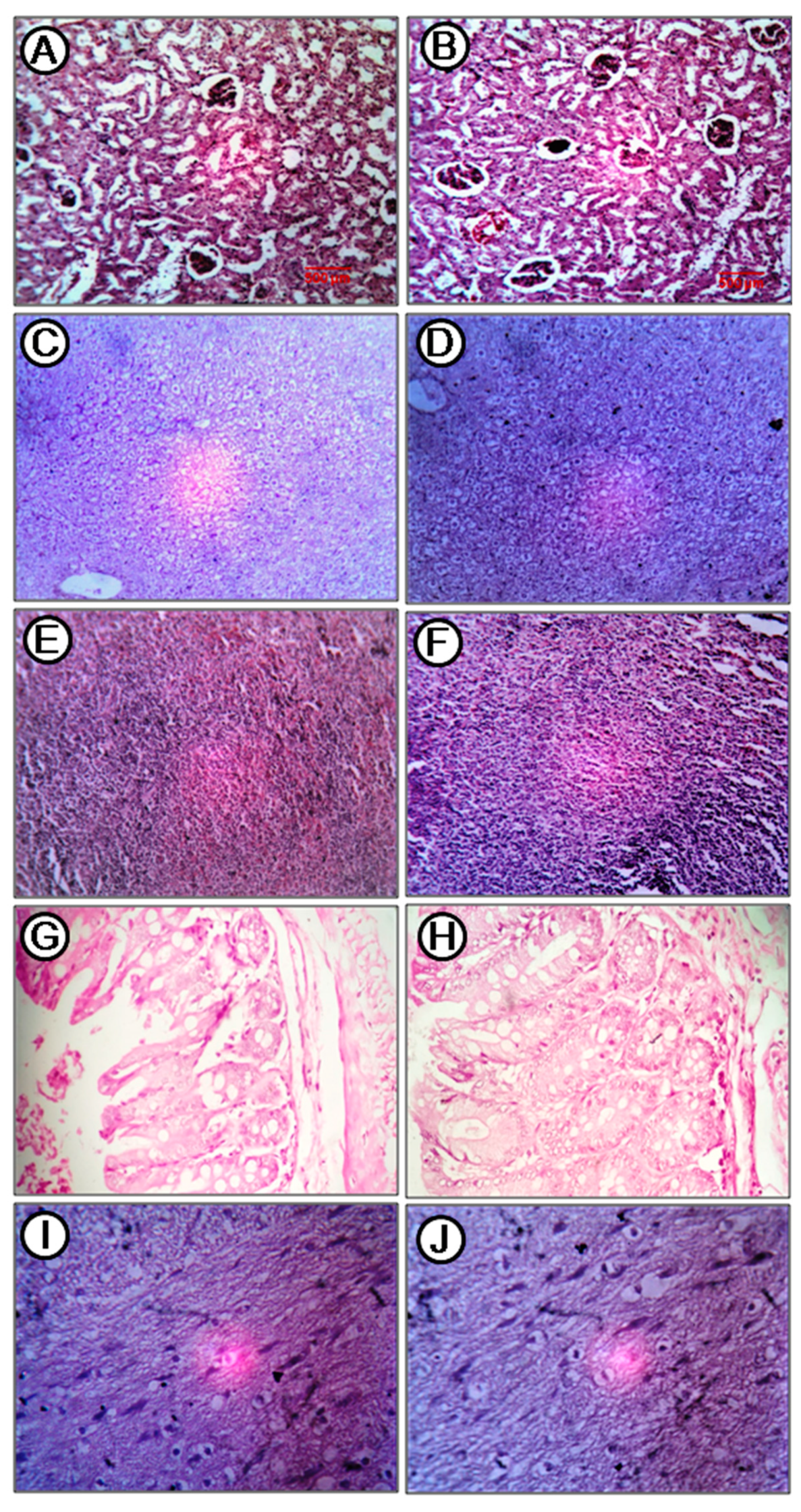
2.8. Acute Toxicity Study
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Sample Collection and Extraction of the Bioactive Compound
4.3. Anticancer Activity of Quinazoline Derivative
4.3.1. Culture of Cell Line
4.3.2. Cell Viability MTT (4,5-Dimethyl Thiazol-2-yl-2,5-Diphenyl Tetrazolium Bromide) Assay
4.3.3. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Assay
4.3.4. Apoptosis Assay
4.3.5. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Assay
4.4. Determination of the Effects of Compound A on the Expression of the Apoptotic Pathway–Related Genes
4.4.1. RNA Isolation
4.4.2. Quantitative RT-PCR
4.5. Determination of the Effects of Compound A on the Expression of Apoptotic Pathway–Related Proteins by Western Blotting
4.6. Caspase 8 Activity Assay
4.7. Acute Toxicity Study of the Compound
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, Q.; Sheng, Y.; Ji, L.; Min, Y.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Z. Acetaminophen-induced cytotoxicity on human normal liver L-02 cells and the protection of antioxidants. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2010, 20, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frizzell, K.M.; Kraus, W.L. PARP inhibitors and the treatment of breast cancer: Beyond BRCA1/2? Breast Cancer Res. 2009, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tew, W.P.; Muss, H.B.; Kimmick, G.G.; Von Gruenigen, V.E.; Lichtman, S.M. Breast and ovarian cancer in the older woman. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 2553–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, W.F.; Katki, H.A.; Rosenberg, P.S. Incidence of breast cancer in the United States: Current and future trends. J. Natl. Cancer. Inst. 2011, 103, 1397–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, J.R.; Jatoi, I. The global breast cancer burden. Future Oncol. 2012, 8, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentschel, U.; Piel, J.; Degnan, S.M.; Taylor, M.W. Genomic insights into the marine sponge microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjasa, O.K.; Vaske, Y.M.; Navarro, G.; Vervoort, H.C.; Tenney, K.; Linington, R.G.; Crews, P. Highlights of marine invertebrate-derived biosynthetic products: Their biomedical potential & possible production by microbial associants. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6658–6674. [Google Scholar]
- Perdicaris, S.; Vlachogianni, T.; Valavanidis, A. Bioactive natural substances from marine sponges: New developments & prospects for future pharmaceuticals. Nat. Prod. Chem. Res. 2013, 1, 115. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, N.L.; Müller, W.E.G. Biotechnological potential of marine sponges. Curr. Sci. 2004, 86, 1506–1512. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Marine natural products and related compounds in clinical and advanced preclinical trials. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1216–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proksch, P.; Edrada, R.A.; Ebel, R. Drugs from the seas - current status & microbiological implications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 59, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trindade, M.; van Zyl, L.J.; Navarro-Fernández, J.; Elrazak, A. Targeted metagenomics as a tool to tap into marine natural product diversity for the discovery and production of drug candidates. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehbub, M.F.; Lei, J.; Franco, C.; Zhang, W. Marine sponge derived natural products between 2001 &2010: Trends& opportunities for discovery of bioactive. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4539–4577. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shady, N.H.; El-Hossary, E.M.; Fouad, M.A.; Gulder, T.A.M.; Kamel, M.S.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Bioactive natural products of marine sponges from the genus Hyrtios. Molecules 2017, 22, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarif, W.M.; Al-Lihaibi, S.S.; Ghandourah, M.A.; Orif, M.I.; Basaif, S.A.; Ayyad, S.E. Cytotoxic scalarane-type sesterterpenes from the Saudi Red Sea sponge Hyrtios erectus. J. Asian. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 18, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzaro, G.; Guiotto, A.; Chilin, A. Quinazoline derivatives as potential anticancer agents: A patent review (2007–2010). Expert. Opin. Ther. Pat. 2012, 22, 223–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeunynck, M.; Baussanne, I. Survey of recent literature related to the biologically active 4(3H)-quinazolinones containing fused heterocycles. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 794–814. [Google Scholar]
- AL-Zubiady, S.; Ibrahim, A.W. Synthesis and characterization of new quinazoline–4(3H)-one Schiff bases. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2013, 5, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Vagdevi, H.M.; Lokesh, M.R.; Gowdarshivannanavar, B.C. Synthesis and antioxidant activity of 3-substituted Schiff bases of quinazoline-2, 4-diones. Int. J. Chem. Tech. Res. 2012, 4, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, S.K.; Ganguly, S.; Veerasamy, R.; Jan, B. Synthesis, antiviral and cytotoxic investigation of 2-phenyl-3-substituted quinazolin-4(3H)-ones. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 15, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.B.; Patel, V.N.; Patel, H.R.; Shaikh, F.M.; Patel, J.C. Synthesis & microbial studies of (4-oxo-thiazolidinyl) sulfonamides bearing quinazolin-4(3H) ones. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2010, 67, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, G.; Pannerselvam, P.; Prakash, C.R. Synthesis and anti-microbial screening of novel schiff bases of 3-amino-2-methyl quinazolin 4-(3H)-one. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2010, 1, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraj, F.L.; Zahedifard, M.; Paydar, M.; Looi, C.Y.; Abdul Majid, N.; Ali, H.M.; Ahmad, N.; Gwaram, N.S.; Abdulla, M.A. Synthesis, characterization, & anticancer activity of new quinazoline derivatives against MCF-7 cells. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchide, N.; Ohyama, K.; Bessho, T.; Toyoda, H. Lactate dehydrogenase leakage as a marker for apoptotic cell degradation induced by influenza virus infection in human fetal membrane cells. Intervirology 2009, 52, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Nagarajan, A.; Uchil, P.D. Analysis of Cell Viability by the Lactate Dehydrogenase Assay. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H.U.; Haj-Yehia, A.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction. Apoptosis 2000, 5, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matulionyte, M.; Dapkute, D.; Budenaite, L.; Jarockyte, G.; Rotomskis, R. Photoluminescent Gold Nanoclusters in Cancer Cells: Cellular Uptake, Toxicity, and Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comsa, S.; Cîmpean, A.M.; Raica, M. The Story of MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Line: 40 years of Experience in Research. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 3147–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Han, B.; Yu, Y.; Yao, W.; Bose, S.; Karlan, B.Y.; Giuliano, A.E.; Cui, X. Evaluation of MCF10A as a reliable model for normal human mammary epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, T.; Arya, R.K.; Meena, S.; Joshi, P.; Pal, M.; Meena, B.; Upreti, D.K.; Rana, T.S.; Datta, D. Isolation, Characterization and Anticancer Potential of Cytotoxic Triterpenes from Betulautilis Bark. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttke, T.M.; Sandstrom, P.A. Oxidative stress as a mediator of apoptosis. Immunol. Today 1994, 15, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tor, Y.S.; Yazan, L.S.; Foo, J.B.; Wibowo, A.; Ismail, N.; Cheah, Y.K.; Abdullah, R.; Ismail, M.; Ismail, I.S.; Yeap, S.K. Induction of Apoptosis in MCF-7 Cells via Oxidative Stress Generation, Mitochondria-Dependent and Caspase-Independent Pathway by Ethyl Acetate Extract of Dillenia suffruticosa and Its Chemical Profile. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamzami, N.; Marchetti, P.; Castedo, M.; Decaudin, D.; Macho, A.; Hirsch, T.; Susin, S.A.; Petit, P.X.; Mignotte, B.; Kroemer, G. Sequential reduction of mitochondrial transmembrane potential and generation of reactive oxygen species in early programmed cell death. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldman, T.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. P21 is necessary for the p53-mediated G1 arrest in human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 5187–5190. [Google Scholar]
- Piccolo, M.T.; Crispi, S. The Dual Role Played by p21 May Influence the Apoptotic or Anti-Apoptotic Fate in Cancer. J. Can. Res. 2012, 1, 189–202. [Google Scholar]
- Harmon, B.V.; Corder, A.M.; Collins, R.J.; Gobé, G.C.; Allen, J.; Allan, D.J.; Kerr, J.F. Celldeath induced in a murine mastocytoma by 42-47 degrees C heating in vitro:evidence that the form of death changes from apoptosis to necrosis above acritical heat load. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 1990, 58, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmlinger, G.; Yuan, F.; Dellian, M.; Jain, R.K. Interstitial pH & pO2 gradients in solid tumors in vivo: High-resolution measurements reveal a lack of correlation. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 177–182. [Google Scholar]
- Alshatwi, A.A.; Shafi, G.; Hasan, T.N.; Syed, N.A.; Khoja, K.K. Fenugreek induced apoptosis in breast cancer MCF-7 cells mediated independently by fas receptor change. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 5783–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yan, C.; Schor, N.F. Apoptosis in the absence of caspase 3. Oncogene 2001, 20, 6570–6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasula, S.M.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Zangrilli, J.; Robertson, N.; Armstrong, R.C.; Wang, L.; Trapani, J.A.; Tomaselli, K.J.; Litwack, G.; Alnemri, E.S. The Ced-3/interleukin 1ß converting enzyme-like homolog Mch6 and the lamin-cleaving enzyme Mch2a are substrates for the apoptotic mediator CPP32. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 27099–27106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talanian, R.V.; Quinlan, C.; Trautz, S.; Hackett, M.C.; Mankovich, J.A.; Banach, D.; Ghayur, T.; Brady, K.D.; Wong, W.W. Substrate specificities of caspase family proteases. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 9677–9682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oltvai, Z.N.; Milliman, C.L.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell 1993, 74, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardwick, J.M.; Soane, L. Multiple Functions of BCL-2 Family Proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Youle, R.J. The Role of Mitochondria in Apoptosis. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2009, 43, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, K.W.; Reed, J.C. Bcl-2 family proteins and cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6398–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenzel, A.; Grespi, F.; Chmelewskij, W.; Villunger, A. Bcl2 family proteins in carcinogenesis and the treatment of cancer. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, L.J.; Chao, H.C.; Yang, Q.; Liu, X.L.; Sheng, J.F.; Yu, H.Y.; Huang, J.R. Isolation and short term cultivation of swine hepatocytes for bioartificial liver support system. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2005, 4, 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, J.; Chao, D.T.; Korsmeyer, S.J. BAX-induced cell death may not require interleukin 1β-converting enzyme-like proteases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 3, 14559–14563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jürgensmeier, J.M.; Xie, Z.; Deveraux, Q.; Ellerby, L.; Bredesen, D.; Reed, J.C. Bax directly induces release of cytochrome c from isolated mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4997–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaitanya, G.V.; Steven, A.J.; Babu, P.P. PARP-1 cleavage fragments: Signatures of cell-death proteases in neurodegeneration. Cell Commun. Signal 2010, 8, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, S.H.; Desnoyers, S.; Ottaviano, Y.; Davidson, N.E.; Poirier, G.G. Specific proteolytic cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: An early marker of chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 3976–3985. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tewari, M.; Quan, L.T.; O’Rourke, K.; Desnoyers, S.; Zeng, Z.; Beidler, D.R.; Poirier, G.G.; Salvesen, G.S.; Dixit, V.M. Yama/CPP32 beta, a mammalian homolog of CED-3, is a CrmA-inhibitable protease that cleaves the death substrate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Cell 1995, 81, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Nakamura, K.; Sakai, K.; Fromont, J.; Gonoi, T.; Kobayashi, J. Hyrtinadines C and D, New Azepinoindole-Type Alkaloids from a Marine Sponge Hyrtios sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 64, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momose, R.; Tanaka, N.; Fromont, J.; Kobayashi, J. Hyrtimomines A-C, new heteroaromatic alkaloids from a sponge Hyrtios sp. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 2010–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, S.; Ahmad, I. An insight into the therapeutic potential of quinazoline derivatives as anticancer agents. MedChemComm. 2017, 8, 871–885. [Google Scholar]
- Abuelizz, H.A.; Marzouk, M.; Ghabbour, H.; Al-Salahi, R. Synthesis & anticancer activity of new quinazoline derivatives. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Gawad, N.M.A.; Georgey, H.H.; Youssef, R.M.; El-sayed, N.A. Synthesis and antitumor activity of some 2, 3-disubstituted quinazolin-4(3H)-ones and 4, 6- disubstituted- 1, 2, 3, 4-tetrahydroquinazolin-2H-ones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 6058–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-suwaidan, I.A.; Alanazi, A.M.; Abdel-aziz, A.A.; Mohamed, M.A.; El-azab, A.S. Design, synthesis & biological evaluation of 2-mercapto-3-phenethylquinazoline bearing anilide fragments as potential antitumor agents: Molecular docking study. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3935–3941. [Google Scholar]
- Mabkhot, Y.N.; Al-Majid, A.M.; Barakat, A.; Al-Showiman, S.S.; Al-Har, M.S.; Radi, S.; Naseer, M.M.; Hadda, T.B. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 2-aminobenzamide derivativesas antimicrobial agents: Opening/closing pharmacophore site. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5115–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, R.S.M.; Ismail, N.S.M.; Abuserii, S.; Abou El Ella, D.A. Recent advances in 4-aminoquinazoline based scaffold derivatives targeting EGFR kinases as anticancer agents. Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 2, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, S.; Metwally, K.; El-Shanawani, A.A.; Abdel-Aziz, L.M.; Pratsinis, H.; Kletsas, D. Synthesis and anticancer activity of novel quinazolinone-based rhodanines. Chem. Cent. J. 2017, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Dong, H.; Li, L.; Fu, D.; Li, Y.; Zi, X.; Liu, H.M.; et al. A novel chalcone derivative S17 induces apoptosis through ROSdependent DR5 up-regulation in gastric cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthiyan, R.; Nambikkairaj, B.; Mahanta, N.; Immanuel, T.; Mandal, R.S.; Kumaran, K.; De, A.K. Antiproliferative and proapoptotic activities of marine sponge Hyrtioserectus extract on Breast Carcinoma Cell Line (MCF-7). Pharmacogn. Mag. 2017, 13, S41–S47. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, S.K.; Ghoshal, G.; Gartia, M.R.; Wu, Z.; De, A.K.; Ye, M.; Bromfield, C.R.; Williams, E.M.; Singh, K.; Tangella, K.V.; et al. Trimodal Therapy: Combining Hyperthermia with Repurposed Bexarotene and Ultrasound for Treating Liver Cancer. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 10695–10718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedifard, M.; Faraj, F.L.; Paydar, M.; YengLooi, C.; Hajrezaei, M.; Hasanpourghadi, M.; Kamalideghan, B.; AbdulMajid, N.; MohdAli, H.; AmeenAbdulla, M. Synthesis, characterization and apoptotic activity of quinazolinone Schiff base derivatives towards MCF-7 cells via intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis pathways. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Compound | Cell Line | Cell Type | IC50 (µg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | |||
| Compound A | MCF-7 | Breast carcinoma cells | 22.67 ± 1.53 | 13.04 ± 1.03 |
| MCF-10A | Non-tumorigenic epithelial cell | 102.11 ± 1.89 | 51.25 ± 1.42 | |
| Compound A + Vit C | MCF-7 | Breast carcinoma cells | 249.67 ± 1.32 | 82.33 ± 1.39 |
| Cyclophosphamide | MCF-7 | Breast carcinoma cells | 15.11 ± 1.16 | 8.11 ± 0.84 |
| MCF-10A | Non-tumorigenic epithelial cell | 59.23 ± 1.68 | 26.22 ± 1.07 | |
| Groups | Total Protein (g/L) | Albumin (g/L) | Globulin (g/L) | ALT (IU/L) | AST (IU/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control (Vehicle) | 53.0 ± 1.7 | 13.5 ± 0.65 | 53.7 ± 1.8 | 61.7 ± 6.4 | 264 ± 9.3 |
| Treated (250 mg/kg) | 51.6 ± 1.5 | 12.5 ± 0.72 | 54.4 ± 1.3 | 63.2 ± 4.5 | 262 ± 7.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De, A.K.; Muthiyan, R.; Mondal, S.; Mahanta, N.; Bhattacharya, D.; Ponraj, P.; Muniswamy, K.; Kundu, A.; Kundu, M.S.; Sunder, J.; et al. A Natural Quinazoline Derivative from Marine Sponge Hyrtios erectus Induces Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Cells via ROS Production and Intrinsic or Extrinsic Apoptosis Pathways. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120658
De AK, Muthiyan R, Mondal S, Mahanta N, Bhattacharya D, Ponraj P, Muniswamy K, Kundu A, Kundu MS, Sunder J, et al. A Natural Quinazoline Derivative from Marine Sponge Hyrtios erectus Induces Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Cells via ROS Production and Intrinsic or Extrinsic Apoptosis Pathways. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(12):658. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120658
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe, Arun Kumar, Ramachandran Muthiyan, Samiran Mondal, Nilkamal Mahanta, Debasis Bhattacharya, Perumal Ponraj, Kangayan Muniswamy, Anandamoy Kundu, Madhu Sudhan Kundu, Jai Sunder, and et al. 2019. "A Natural Quinazoline Derivative from Marine Sponge Hyrtios erectus Induces Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Cells via ROS Production and Intrinsic or Extrinsic Apoptosis Pathways" Marine Drugs 17, no. 12: 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120658
APA StyleDe, A. K., Muthiyan, R., Mondal, S., Mahanta, N., Bhattacharya, D., Ponraj, P., Muniswamy, K., Kundu, A., Kundu, M. S., Sunder, J., Karunakaran, D., Bera, A. K., Roy, S. D., & Malakar, D. (2019). A Natural Quinazoline Derivative from Marine Sponge Hyrtios erectus Induces Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Cells via ROS Production and Intrinsic or Extrinsic Apoptosis Pathways. Marine Drugs, 17(12), 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120658