Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol Attenuates Fine Particulate Matter-Induced Subcellular Skin Dysfunction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. DPHC Inhibits PM2.5-Induced ROS Generation
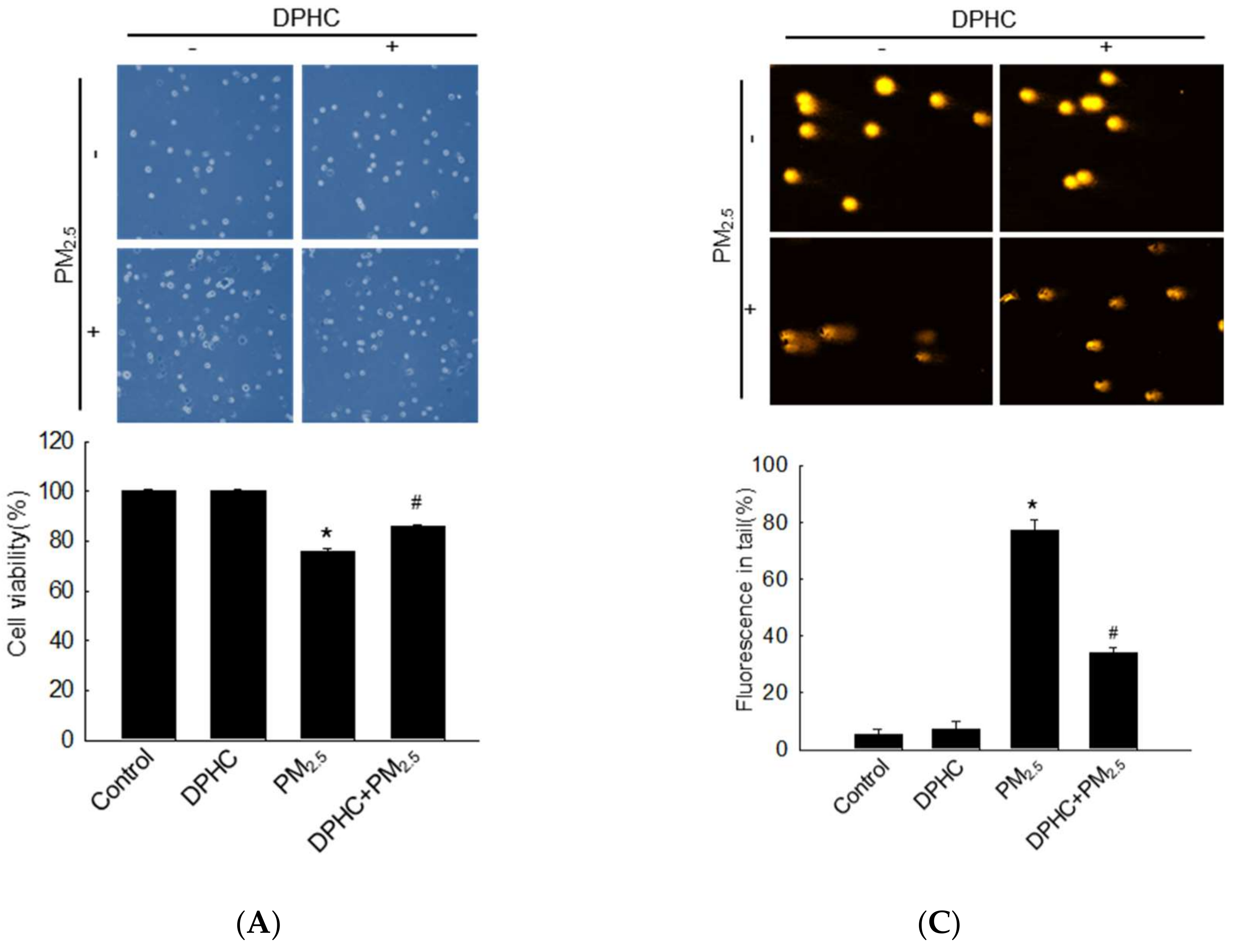
2.2. DPHC Inhibits Cellular Macromolecule Damage via Inhibiting PM2.5-Induced Oxidative Stress
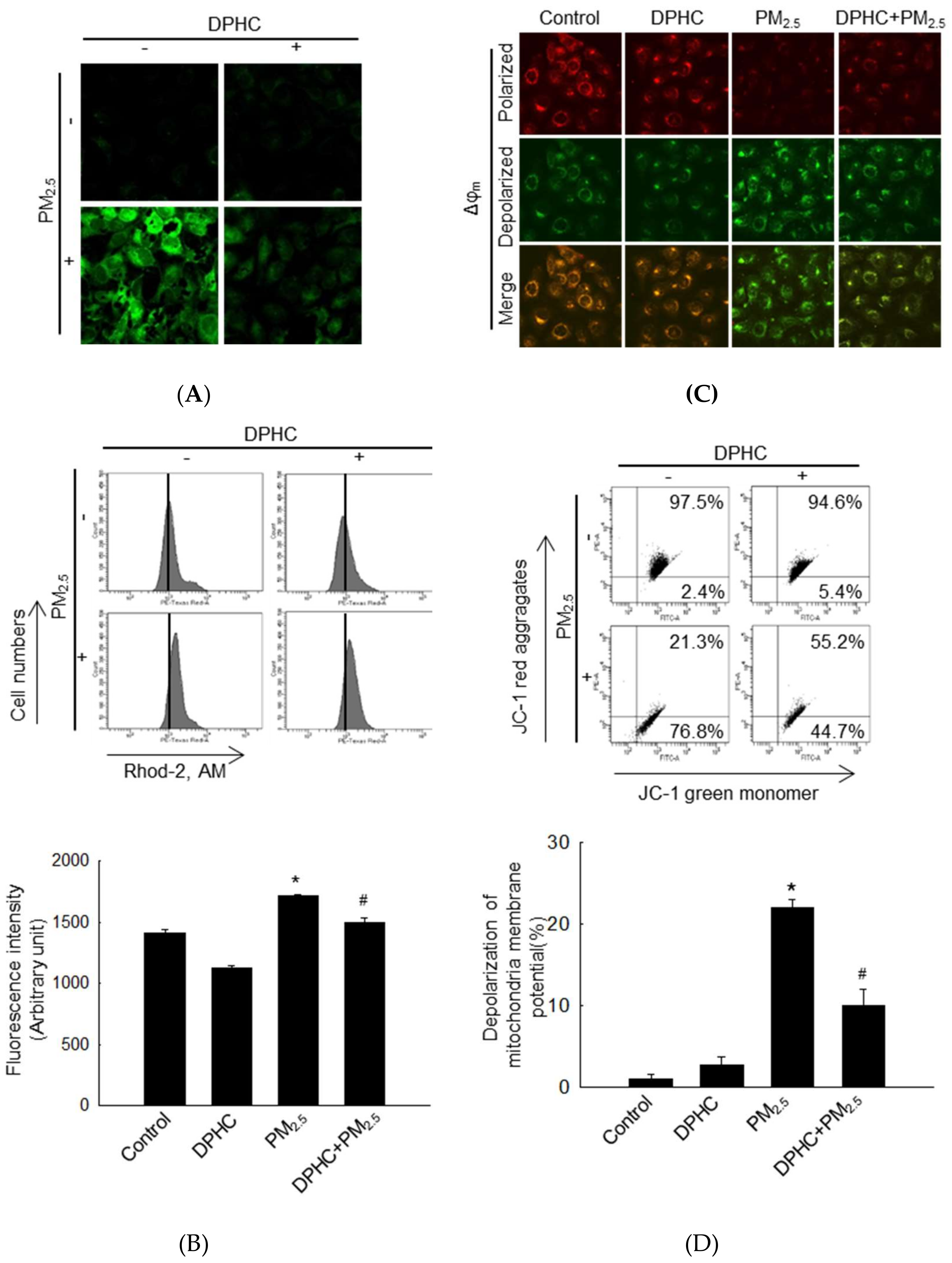
2.3. DPHC Blocks Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Autophagy Induced by PM2.5
2.4. PM2.5-Induced Mitochondrial Damage is Weakened by DPHC
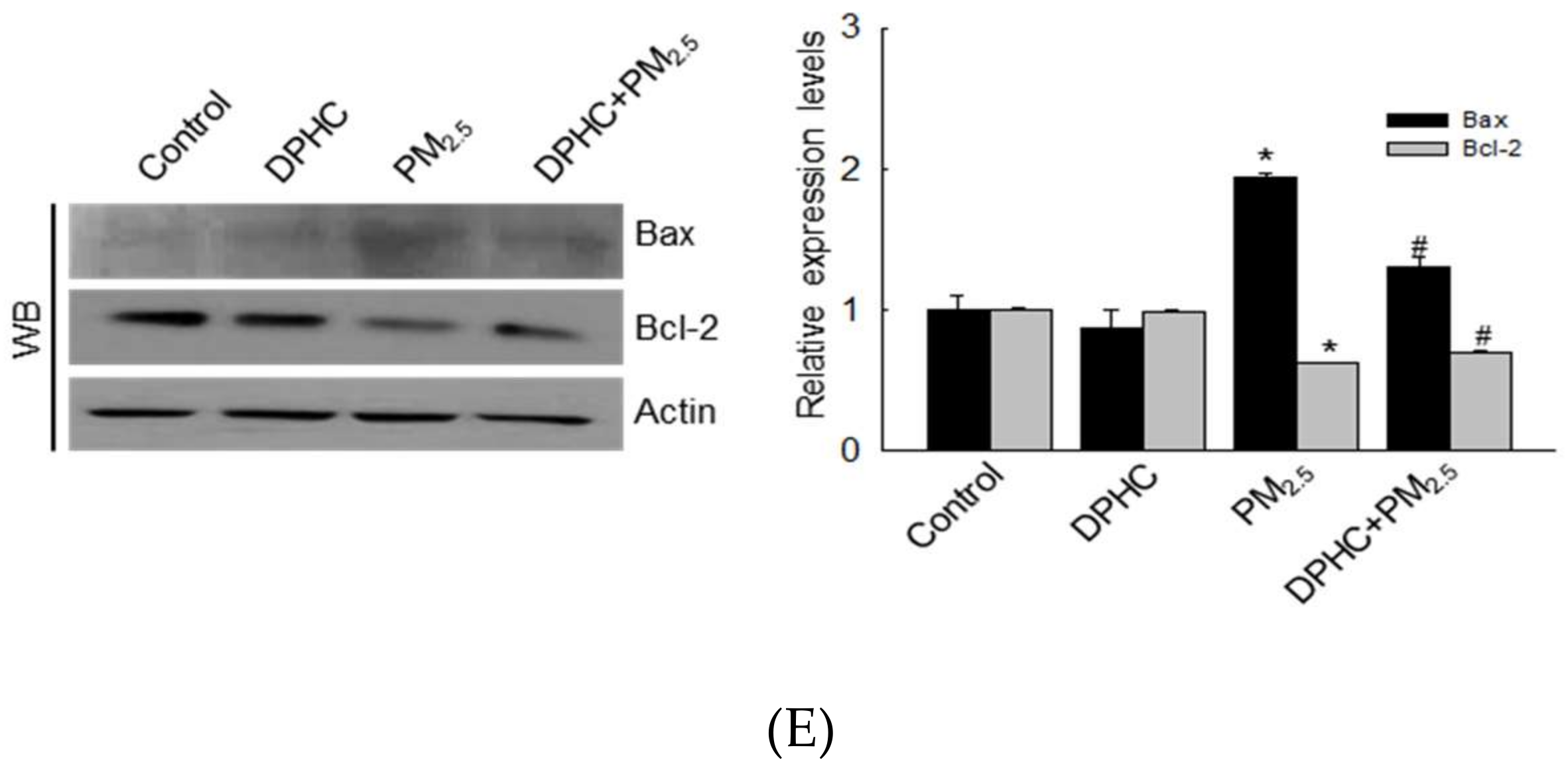
2.5. PM2.5 Accelerates Apoptotic Cell Death
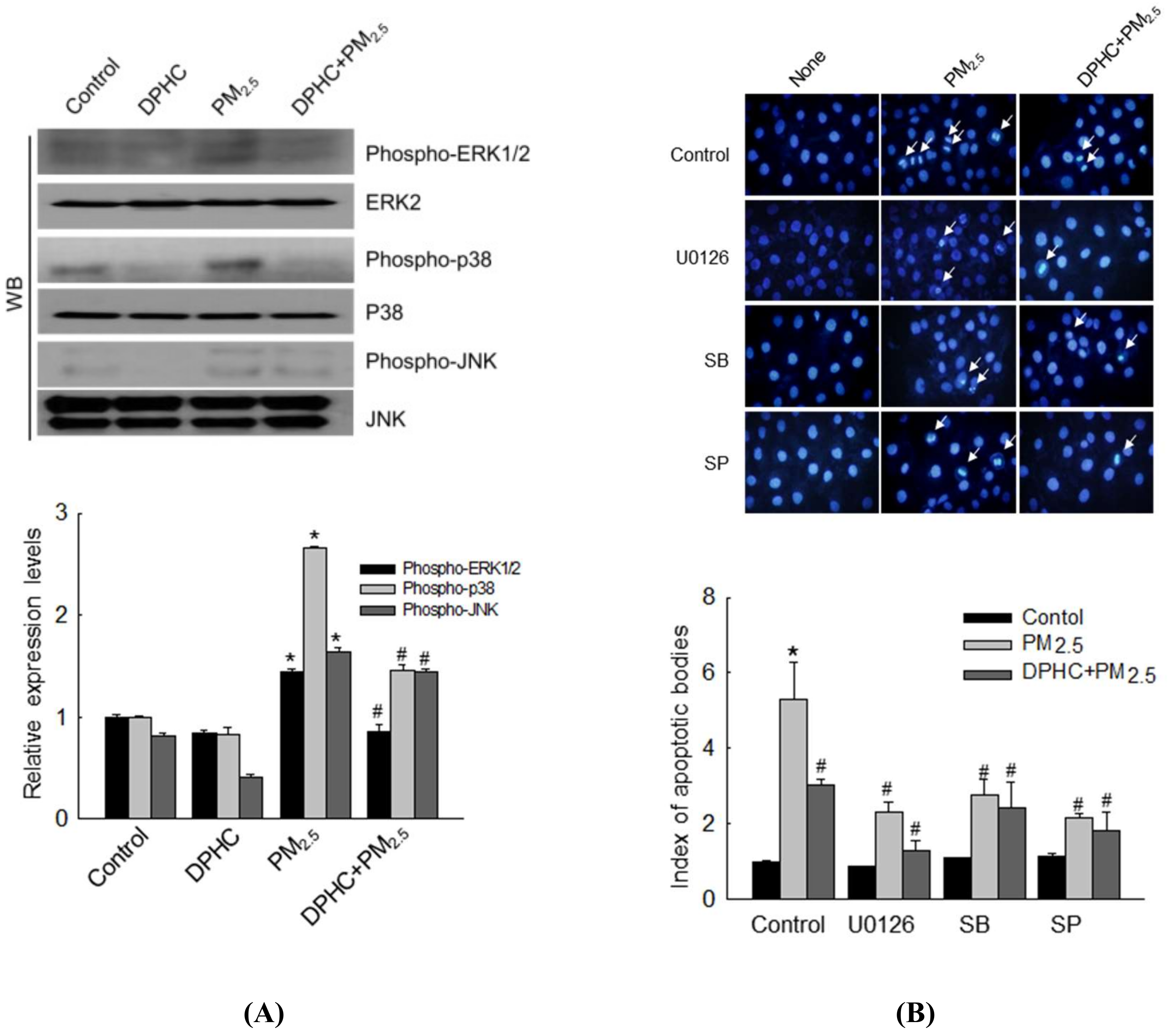
2.6. DPHC Regulates PM2.5-Induced Apoptosis via MAPK Signaling Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. PM2.5 Preparation
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viability
4.4. Animal Experiments
4.5. Determination of ROS
4.6. Trypan Blue Staining
4.7. Lipid Peroxidation Assay
4.8. Comet Assay
4.9. Detection of 8-Oxoguanine
4.10. Western Blotting
4.11. Protein Carbonylation Assay
4.12. 8-Isoprostane Assay
4.13. ER Staining
4.14. Quantification of Ca2+ Level
4.15. Mitochondrial Δψ Membrane Potential (Δψm) Analysis
4.16. Acridine Orange Morphology Assay
4.17. Hoechst 33342 Staining
4.18. Detection of Sub-G1-Phase Cells
4.19. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, P.H.; Tseng, C.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Lee, C.W.; Yen, F.L. Preparation, characterizations and anti-pollutant activity of 7,3′,4′-trihydroxyisoflavone nanoparticles in particulate matter-induced HaCaT keratinocytes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3279–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, P.; Nandar, S.K.; Kathuria, S.; Ramesh, V. Effects of air pollution on the skin: A review. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2017, 83, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.E.; Cho, D.; Park, H.J. Air pollution and skin diseases: Adverse effects of airborne particulate matter on various skin diseases. Life Sci. 2016, 152, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, A. Tobacco smoke causes premature skin aging. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2007, 48, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, R.; Philips, N.; Suárez-Pérez, J.A.; Juarranz, A.; Devmurari, A.; Chalensouk-Khaosaat, J.; González, S. Mechanisms of photoaging and cutaneous photocarcinogenesis, and photoprotective strategies with phytochemicals. Antioxidants 2015, 4, 248–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.H.; Hsu, L.F.; Lee, C.W.; Chiang, Y.C.; Lee, M.H.; How, J.M.; Wu, C.M.; Huang, C.L.; Lee, I.T. Resveratrol inhibits urban particulate matter-induced COX-2/PGE2 release in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes via the inhibition of activation of NADPH oxidase/ROS/NF-κB. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 88, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennolds, J.; Malireddy, S.; Hassan, F.; Tridandapani, S.; Parinandi, N.; Boyaka, P.N.; Cormet-Boyaka, E. Curcumin regulates airway epithelial cell cytokine responses to the pollutant cadmium. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.J.; Kim, J.P.; Jung, W.K.; Lee, N.H.; Kang, H.S.; Jun, E.M.; Park, S.H.; Kang, S.M.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, P.J.; et al. Identification of chemical structure and free radical scavenging activity of diphlorethohydroxycarmalol isolated from a brown alga, ishige okamurae. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 18, 676–681. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, N.J.; Han, S.C.; Kan, G.J.; Koo, D.H.; Koh, Y.S.; Hyun, J.W.; Lee, N.H.; Ko, M.H.; Kang, H.K.; Yoo, E.S. Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol inhibits interleukin-6 production by regulating NF-kB, stat5 and socs1 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated raw 264.7 cells. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2141–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.M.; Hamann, M.T. Marine pharmacology in 2001-2002: Marine compounds with anthelmintic, antibacterial, anticoagulant, antidiabetic, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiplatelet, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; affecting the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 140, 265–286. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Kim, K.C.; Chae, S.; Kim, G.O.; Shin, T.; Kim, H.S.; Hyun, J.W. Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol attenuated cell damage against UVB radiation via enhancing antioxidant effects and absorbing UVB ray in human HaCaT keratinocytes. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 36, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, M.J.; Susara Ruwan Kumara, M.H.; Kim, K.C.; Kang, K.A.; Kang, H.K.; Lee, N.H.; Hyun, J.W. Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol suppresses ultraviolet B-Induced matrix metalloproteinases via inhibition of JNK and ERK signaling in human Keratinocytes. Biomol. Ther. 2015, 23, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, M.J.; Ahn, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Ryu, Y.S.; Hyun, Y.; Shilnikova, K.; Zhen, A.X.; Jeong, J.W.; Choi, Y.H.; Kang, H.K.; et al. Particulate matter 2.5 damages skin cells by inducing oxidative stress, subcellular organelle dysfunction, and apoptosis. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 2077–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, M.; Angebault-Prouteau, C.; Dridi, H.; Notarnicola, C.; Scheuermann, V.; Lacampagne, A.; Matecki, S.; Fauconnier, J. ER stress disturbs SR/ER-mitochondria Ca2+ transfer: Implications in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 2229–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishitoh, H. CHOP is a multifunctional transcription factor in the ER stress response. J. Biochem. 2012, 151, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szegezdi, E.; Logue, S.E.; Gorman, A.M.; Samali, A. Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.S.; Yoo, W.H.; Chae, H.J. ER Stress and Autophagy. Curr. Mol. Med. 2015, 15, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, A.K.; Yadav, N.; Bhat, T.A.; O’Malley, J.; Kumar, S.; Chandra, D. A potential role of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein in mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and its implication in cancer therapy. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, M.J.; Hewage, S.R.; Han, X.; Kang, K.A.; Kang, H.K.; Lee, N.H.; Hyun, J.W. Protective effect of diphlorethohydroxycarmalol against ultraviolet B radiation-induced DNA damage by inducing the nucleotide excision repair system in HaCaT human keratinocytes. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5629–5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Qian, Z.J.; Li, Y.; Kim, M.M.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.K. Antioxidant effects of phlorotannins isolated from Ishige okamurae in free radical mediated oxidative systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7001–7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.J.; Yoon, K.D.; Kim, C.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, C.G.; Kim, J. Inhibitory activity on HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and integrase of a carmalol derivative from a brown Alga, Ishige okamurae. Phytother. Res. 2006, 20, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.J.; Hwang, J.Y.; Choi, J.I.; Han, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Jeon, Y.J. Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol isolated from Ishige okamurae, a brown algae, a potent alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase inhibitor, alleviates postprandial hyperglycemia in diabetic mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 615, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, S.J.; Ko, S.C.; Kang, S.M.; Cha, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kang, D.H.; Jung, W.K.; Affan, A.; Oh, C.; Jeon, Y.J. Inhibitory effect of diphlorethohydroxycarmalol on melanogenesis and its protective effect against UV-B radiation-induced cell damage. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, M.; Moon, C.; Yang, W.; Ko, E.J.; Hyun, J.W.; Joo, H.G.; Jee, Y.; Lee, N.H.; Park, J.W.; Ko, R.K.; et al. Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol, isolated from the brown algae Ishige okamurae, protects against radiation-induced cell damage in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krutmann, J.; Liu, W.; Li, L.; Pan, X.; Crawford, M.; Sore, G.; Seite, S. Pollution and skin: From epidemiological and mechanistic studies to clinical implications. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2014, 76, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Kang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, J.; Yan, S.; Xu, F.; Xu, J. Effects of ambient fine particles PM2.5 on human HaCaT cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Xie, X.Y.; Xu, S.K.; Wang, Y.N.; Jiang, M.; Wen, L.R.; Lai, W.; Guan, L. PM2.5 exposure elicits oxidative stress responses and mitochondrial apoptosis pathway activation in HaCaT keratinocytes. Chin. Med. J. 2017, 130, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Thompson, M.D.; Cohen, R.A.; Tong, X. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and related pathological processes. J. Pharmacol. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 1, 1000107. [Google Scholar]
- Sano, R.; Reed, J.C. ER stress-induced cell death mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Pun, N.T.; Park, P.H. ZFP36L1 and AUF1 induction contribute to the suppression of inflammatory mediators expression by globular adiponectin via autophagy induction in macrophages. Biomol. Ther. 2018, 26, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.Y.; Jee, S.D.; Hwang, J.S.; Yun, E.Y.; Ahn, K.S.; Kim, Y.S. Anti-inflammatory effect of isaria sinclairii glycosaminoglycan in an adjuvant-treated arthritis rat model. Toxicol. Res. 2013, 29, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Chiara, G.; Marcocci, M.E.; Torcia, M.; Lucibello, M.; Rosini, P.; Bonini, P.; Higashimoto, Y.; Damonte, G.; Armirotti, A.; Amodei, S.; et al. Bcl-2 phosphorylation by p38 MAPK: Identification of target sites and biologic consequences. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 21353–21361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.J.; Ryu, S.W.; Song, B.J. JNK- and p38 kinase-mediated phosphorylation of Bax leads to its activation and mitochondrial translocation and to apoptosis of human hepatoma HepG2 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 21256–21265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Kim, M.S.; Park, J.Y.; Woo, J.S.; Kim, Y.K. 15-Deoxy-delta 12,14-prostaglandin J2 induces apoptosis via JNK-mediated mitochondrial pathway in osteoblastic cells. Toxicology 2008, 248, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Lim, J.; Kwon, S.; Jeon, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S. Characterization of particulate matter from diesel passenger cars tested on chassis dynamometers. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 54, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.K.; Smith, T.J.; Garshick, E.; Natkin, J.; Reaser, P.; Lane, K.; Lee, H.K. Exposure of trucking company workers to particulate matter during the winter. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 1677–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Piao, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Shilnikova, K.; Hyun, Y.J.; Oh, S.K.; Jeong, Y.J.; Chae, S.; Hyun, J.W. A benzylideneacetophenone derivative induces apoptosis of radiation-resistant human breast cancer cells via oxidative stress. Biomol. Ther. 2017, 25, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, M.J.; Ahn, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Kim, K.C.; Zheng, J.; Yao, C.W.; Cha, J.W.; Hyun, C.L.; Kang, H.K.; Lee, N.H. Phloroglucinol inhibits ultraviolet B radiation-induced oxidative stress in the mouse skin. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2014, 90, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, L.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; Chen, X. Apoptosis of HeLa cells induced by a new targeting photosensitizer-based PDT via a mitochondrial pathway and ER stress. Onco Targets Ther. 2015, 8, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Hyun, Y.J.; Piao, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Ryu, Y.S.; Shilnikova, K.; Zhen, A.X.; Ahn, M.J.; Ahn, Y.S.; Koh, Y.S.; et al. Mackerel-derived fermented fish oil protects skin against UVB-induced cellular damage by inhibiting oxidative stress. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 46, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhen, A.X.; Piao, M.J.; Hyun, Y.J.; Kang, K.A.; Madushan Fernando, P.D.S.; Cho, S.J.; Ahn, M.J.; Hyun, J.W. Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol Attenuates Fine Particulate Matter-Induced Subcellular Skin Dysfunction. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020095
Zhen AX, Piao MJ, Hyun YJ, Kang KA, Madushan Fernando PDS, Cho SJ, Ahn MJ, Hyun JW. Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol Attenuates Fine Particulate Matter-Induced Subcellular Skin Dysfunction. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(2):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020095
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhen, Ao Xuan, Mei Jing Piao, Yu Jae Hyun, Kyoung Ah Kang, Pincha Devage Sameera Madushan Fernando, Suk Ju Cho, Mee Jung Ahn, and Jin Won Hyun. 2019. "Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol Attenuates Fine Particulate Matter-Induced Subcellular Skin Dysfunction" Marine Drugs 17, no. 2: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020095
APA StyleZhen, A. X., Piao, M. J., Hyun, Y. J., Kang, K. A., Madushan Fernando, P. D. S., Cho, S. J., Ahn, M. J., & Hyun, J. W. (2019). Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol Attenuates Fine Particulate Matter-Induced Subcellular Skin Dysfunction. Marine Drugs, 17(2), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020095



