Four Antioxidant Peptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Red Stingray (Dasyatis akajei) Cartilages: Isolation, Identification, and In Vitro Activity Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation of APs from Water-Soluble Protein Hydrolysate (RSH) of Red Stingray Cartilages
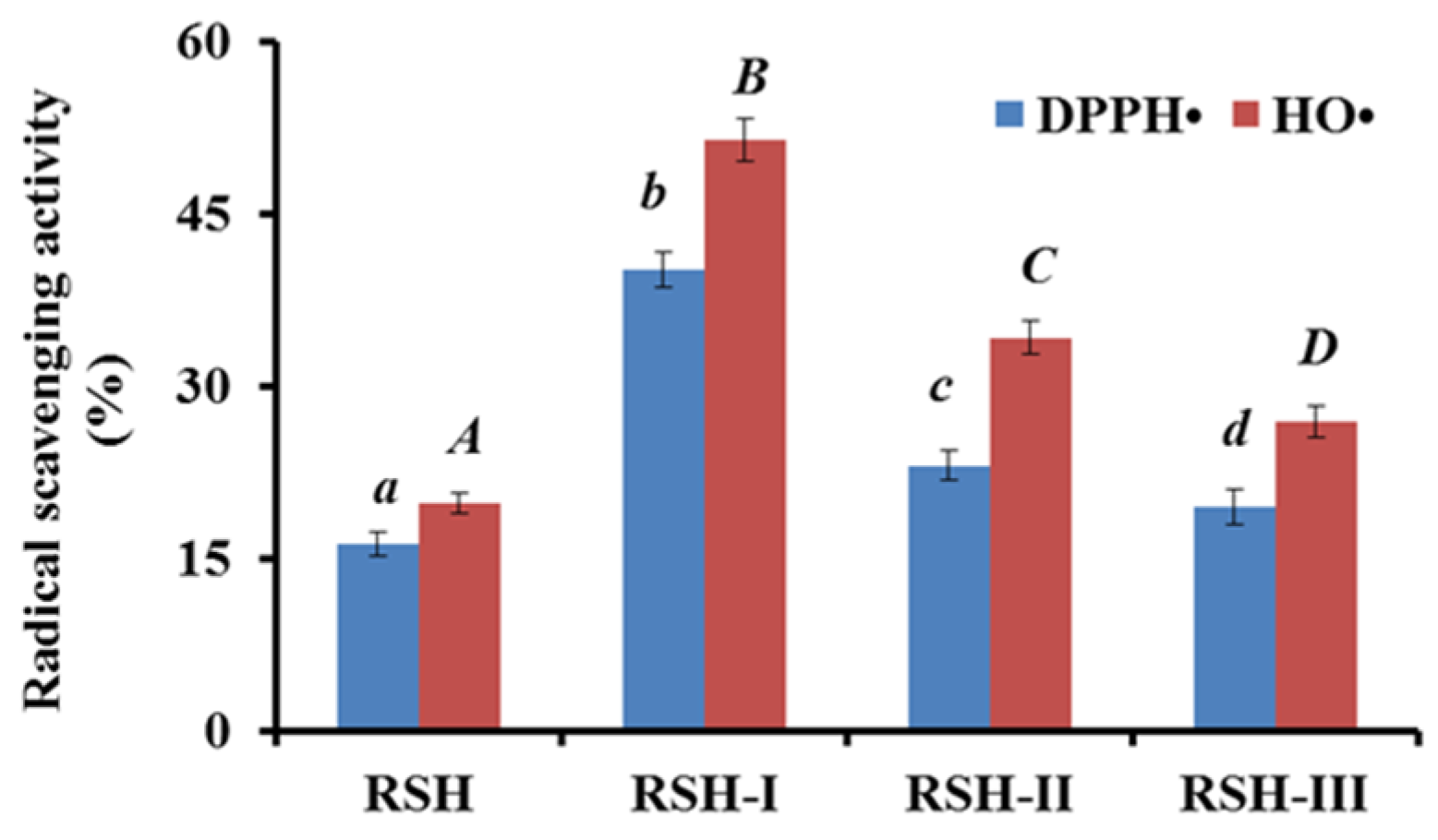
2.1.1. Fractionation of RSH by Ultrafiltration
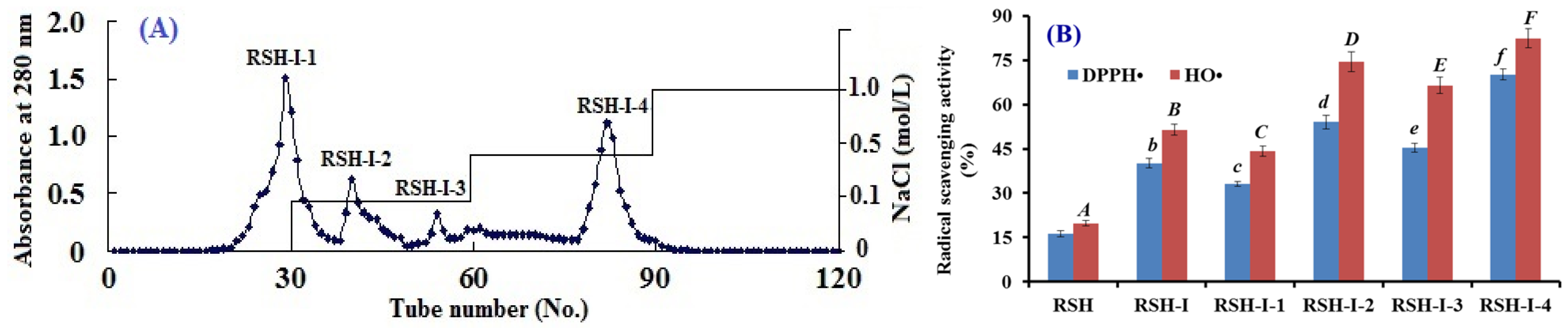
2.1.2. Anion-Exchange Chromatography of RSH-I
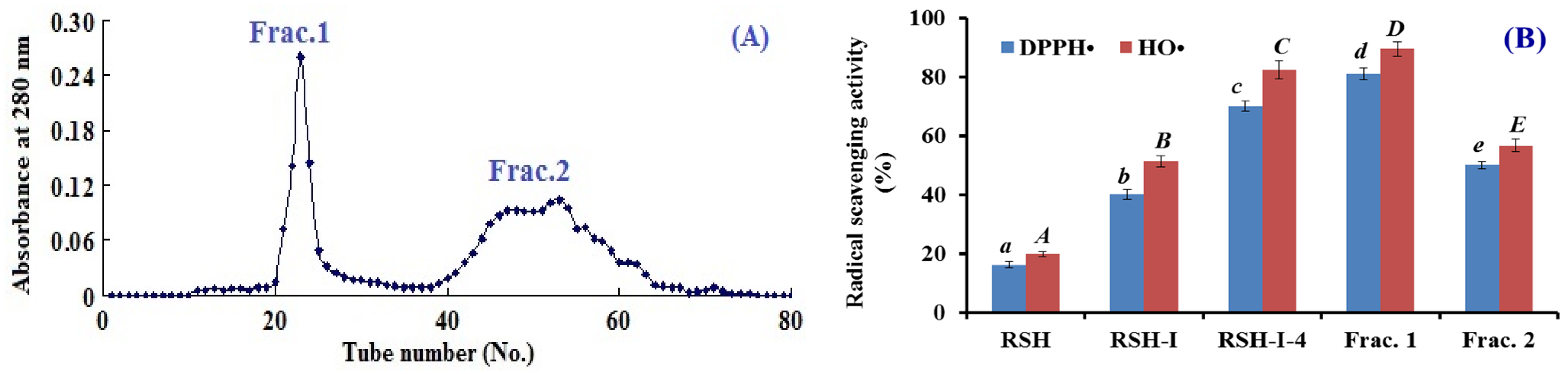
2.1.3. Gel filtration Chromatography of RSH-I-4
2.1.4. Isolation of APs from Frac.1 by RP-HPLC
2.2. Amino Acid Sequence and Mass Spectrometry Analysis of APs (RSHP-A~D)
2.3. Antioxidant Activity
2.3.1. Radical Scavenging Activity
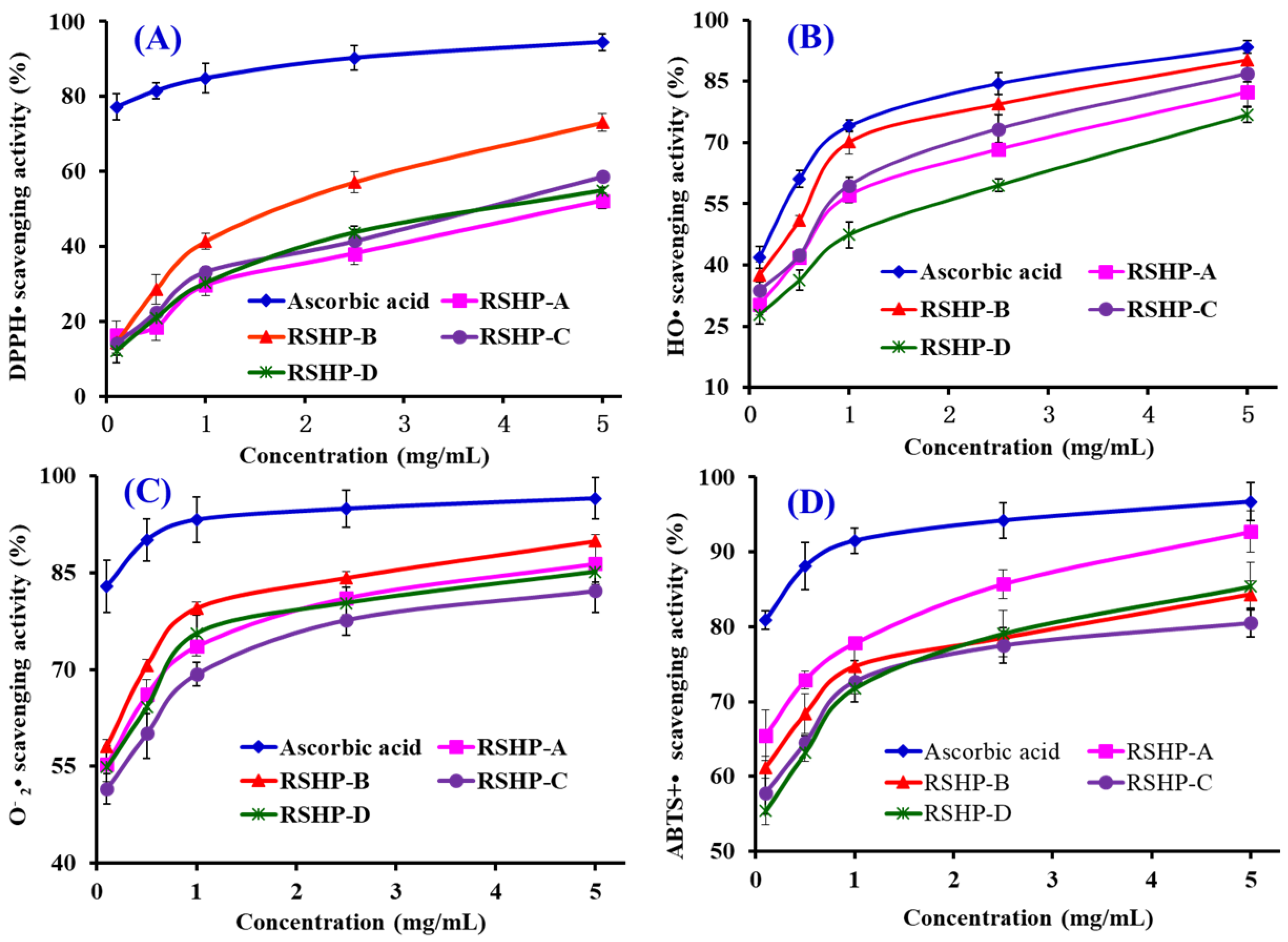
DPPH• Scavenging Activity
HO• Scavenging Activity
• Scavenging Activity
ABTS+• Scavenging Activity
2.3.2. Fe2+-Chelating Ability
2.3.3. Reducing Power
2.3.4. Lipid Peroxidation Inhibition Ability
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Water-Soluble Proteins and Hydrolysate from Red Stingray Cartilages
4.3. Isolation of Peptides from RSH
4.4. Amino Acid Sequence and Molecular Mass Analysis
4.5. Antioxidant Activity
4.5.1. Radical Scavenging Activity
4.5.2. Fe2+-Chelating Assay
4.5.3. Reducing Power Assay
4.5.4. Lipid Peroxidation Inhibition Assay
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sila, A.; Bougatef, A. Antioxidant peptides from marine by-products: Isolation, identification and application in food systems. A review. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, L.; Chi, C.F.; Ma, J.H.; Luo, H.Y.; Xu, Y.F. Purification and characterisation of a novel antioxidant peptide derived from blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, C.B.; Kim, J.G.; Je, J.Y. Purification and antioxidant properties of octapeptide from salmon byproduct protein hydrolysate by gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem. 2014, 147, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Y.M.; Chi, C.F.; Hu, F.Y.; Deng, S.G.; Ma, J.Y. Isolation and characterization of collagen and antioxidant collagen peptides from scales of croceine croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4641–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, J.M.; Vargas, F.C.; Strozzi, I.; Pateiro, M.; Furtado, M.M.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Rocchetti, G.; Barba, F.J.; Dominguez, R.; Lucini, L.; do Amaral Sobral, P.J. Influence of pitanga leaf extracts on lipid and protein oxidation of pork burger during shelf-life. Food Res. Int. 2018, 114, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agregán, R.; Franco, D.; Carballo, J.; Tomasevic, I.; Barba, F.J.; Gómez, B.; Muchenje, V.; Lorenzoa, J.M. Shelf life study of healthy pork liver pâté with added seaweed extracts from Ascophyllum nodosum, Fucus vesiculosus and Bifurcaria bifurcate. Food Res. Int. 2018, 112, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, R.P.P.; Trindade, M.A.; Tonin, F.G.; Pugine, S.M.P.; Lima, C.G.; Lorenzo, J.M.; de Melo, M.P. Evaluation of oxidative stability of lamb burger with Origanum vulgare extract. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafian, L.; Babji, A.S. A review of fish-derived antioxidant and antimicrobial peptides: Their production, assessment, and applications. Peptides 2012, 33, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Pan, X.; Chi, C.F.; Sun, K.L.; Wang, B. Ten new pentapeptides from protein hydrolysate of miiuy croaker (Miichthys miiuy) muscle: Preparation, identification, and antioxidant activity evaluation. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 105, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, J.M.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Gómez, B.; Barba, F.J.; Mora, L.; Pérez-Santaescolástica, C.; Toldrá, F. Bioactive peptides as natural antioxidants in food products-A review. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2018, 79, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ding, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Ma, S.; Liu, J. Intracellular ROS scavenging and antioxidant enzyme regulating capacities of corn gluten meal-derived antioxidant peptides in HepG2 cells. Food Res. Int. 2016, 90, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnedy, P.A.; FitzGerald, R.J. Bioactive peptides from marine processing waste and shellfish: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.R.; Chi, C.F.; Li, L.; Wang, B. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of scalloped hammerhead (Sphyrna lewini) cartilage. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagi, C.M.; Berryman, E.R.; Teo, S.; Lane, N.E. Oral administration of undenatured native chicken type II collagen (UC-II) diminished deterioration of articular cartilage in a rat model of osteoarthritis (OA). Osteoarthr. Cartilage 2017, 25, 2080–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.B.; Chi, C.F.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Wang, B. Physicochemical properties of acid- and pepsin-soluble collagens from the cartilage of Siberian sturgeon. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 31427–31438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.F.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.R.; Luo, H.Y.; Ding, G.F. Characterization of acid-soluble collagens from the cartilages of scalloped hammerhead (Sphyrna lewini), red stingray (Dasyatis akajei), and skate (Raja porosa). Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 22, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Ling, P.; Wang, Z.; Niu, R.; Hu, C.; Zhang, T.; Lin, X. A novel polypeptide from shark cartilage with potent anti-angiogenic activity. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Gao, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, B.; Yu, G.; Li, B. Collagen peptides administration in early enteral nutrition intervention attenuates burn-induced intestinal barrier disruption: Effects on tight junction structure. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 55, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Elango, J.; Zhang, J.; Bao, B.; Guo, R.; Palaniyandi, K.; Robinson, J.S.; Geevaretnam, J.; Regenstein, J.M.; Wu, W. Immunological effects of collagen and collagen peptide from blue shark cartilage on 6T-CEM cells. Process. Biochem. 2017, 57, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Hu, F.Y.; Wang, B. Preparation and identification of antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of skate (Raja porosa) cartilage. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 25, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Hu, F.Y.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Anticancer activity of a hexapeptide from skate (Raja porosa) cartilage protein hydrolysate in HeLa cells. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Bioactive peptides from cartilage protein hydrolysate of spotless smoothhound and their antioxidant activity In vitro. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Shahidi, F. Isolation and characterization of collagen from the cartilages of brownbanded bamboo shark (Chiloscyllium punctatum) and blacktip shark (Carcharhinus limbatus). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Xu, J.; Yu, X. Isolation and bioactivity of an angiogenesis inhibitor extracted from the cartilage of Dasyatis akajei. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 16, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Chi, C.; Gong, Y.; Luo, H.; Ding, G. Influence of average molecular weight on antioxidant and functional properties of cartilage collagen hydrolysates from Sphyrna lewini, Dasyatis akjei and Raja porosa. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.Y.; Yu, X.W.; Qian, X. Purification and bioactivity of a novel angiogenesis inhibitor extracted from the cartilage of Dasyatis akajei. J. Fish. China 2007, 31, 813–817. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Wu, H.; Yu, X. Effects of mucopolysaccharide from Dasyatis akajei cartilage on plasma lipid and cruor time in rabbits. Chin. J. Biochem. Pharm. 2008, 29, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, C.F.; Cao, Z.H.; Wang, B.; Hu, F.Y.; Li, Z.R.; Zhang, B. Antioxidant and functional properties of collagen hydrolysates from spanish mackerel skin as influenced by average molecular weight. Molecules 2014, 19, 11211–11230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeena Farvin, K.H.; Andersen, L.L.; Otte, J.; Nielsen, H.H.; Jessen, F.; Jacobsen, C. Antioxidant activity of cod (Gadus morhua) protein hydrolysates: Fractionation and characterisation of peptide fractions. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.F.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhang, B.; Deng, S.G. Isolation and characterization of three antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of bluefin leatherjacket (Navodon septentrionalis) heads. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Ahn, C.B.; Je, J.Y. Partial purification and identification of three antioxidant peptides with hepatoprotective effects from blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) hydrolysate by peptic hydrolysis. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 20, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiriyaphan, C.; Chitsomboon, B.; Roytrakul, S.; Yongsawadigul, J. Isolation and identification of antioxidative peptides from hydrolysate of threadfin bream surimi processing byproduct. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1654–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiriyaphan, C.; Xiao, H.; Decker, E.A.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Chemical and cellular antioxidative properties of threadfin bream (Nemipterus spp.) surimi byproduct hydrolysates fractionated by ultrafiltration. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.F.; Hu, F.Y.; Wang, B.; Ren, X.J.; Deng, S.G.; Wu, C.W. Purification and characterization of three antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolyzate of croceine croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) muscle. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.J.; Wu, J.P. Angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory and antioxidant activities of egg protein hydrolysates produced with gastrointestinal and nongastrointestinal enzymes. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, S.; Li, J. Purification and characterization of three antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) skin. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 16, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.Y.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.R.; Chi, C.F.; Zhang, Q.H.; He, G.Y. Preparation and evaluation of antioxidant peptide from papain hydrolysate of Sphyrna lewini muscle protein. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 51, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, Z.R.; Chi, C.F.; Zhang, Q.H.; Luo, H.Y. Preparation and evaluation of antioxidant peptides from ethanol-soluble proteins hydrolysate of Sphyrna lewini muscle. Peptides 2012, 36, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.H.; Luo, Q.B.; Pan, X.; Chi, C.F.; Sun, K.L.; Wang, B. Preparation, identification, and activity evaluation of ten antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of swim bladders of miiuy croaker (Miichthys miiuy). J. Funct. Foods 2018, 47, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.R.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Qiu, Y.T.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Preparation and characterization of gelatin and antioxidant peptides from gelatin hydrolysate of Skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) bone stimulated by in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, C.F.; Wang, B.; Hu, F.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhang, B.; Deng, S.G.; Wu, C.W. Purification and identification of three novel antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of bluefin leatherjacket (Navodon septentrionalis) skin. Food Res. Int. 2015, 73, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranathunga, S.; Rajapakse, N.; Kim, S.K. Purification and characterization of antioxidative peptide derived from muscle of conger eel (Conger myriaster). Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2006, 222, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, N.; Mendis, E.; Jung, W.K.; Je, J.Y.; Kim, S.K. Purification of a radical scavenging peptide from fermented mussel sauce and its antioxidant properties. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.R.; Zhang, L.; Ding, D.G.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B.; Huo, J.C. Preparation, identification, and activity evaluation of eight antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of hairtail (Trichiurus japonicas) muscle. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhao, M.; Shi, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Cui, C.; Kakuda, Y.; Xue, S.J. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from grass carp muscle hydrolysates by consecutive chromatography and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.F.; Hu, F.Y.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.R.; Luo, H.Y. Influence of amino acid compositions and peptide profiles on antioxidant capacities of two protein hydrolysates from skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) dark muscle. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2580–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.K.; Mishra, P.C. Scavenging of superoxide radical anion and hydroxyl radical by urea, thiourea, selenourea and their derivatives without any catalyst: A theoretical study. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2017, 684, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.K.; Oh, H.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Hwang, J.W.; Ahn, C.B.; Lee, J.S.; Jeon, Y.J.; Moon, S.H.; Sung, S.H.; Jeon, B.T.; Park, P.J. Purification of a novel peptide derived from Mytilus coruscus and in vitro/in vivo evaluation of its bioactive properties. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2013, 34, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Tong, T.; Sun, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Liao, D. Purification and characterization of antioxidative peptides from round scad (Decapterus maruadsi) muscle protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2014, 154, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.Q.; Zeng, L.; Yang, Z.S.; Huang, F.F.; Ding, G.F.; Wang, B. Anti-fatigue effect by peptide fraction from protein hydrolysate of croceine croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) swim bladder through inhibiting the oxidative reactions including DNA damage. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.F.; Wang, B.; Deng, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Deng, S.G.; Ma, J.Y. Isolation and characterization of three antioxidant pentapeptides from protein hydrolysate of monkfish (Lophius litulon) muscle. Food Res. Int. 2014, 55, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapsongphon, N.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Production and purification of antioxidant peptides from a mungbean meal hydrolysate by Virgibacillus sp. SK37 proteinase. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Li, B.; Hou, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X. Identification of iron-chelating peptides from Pacific cod skin gelatin and the possible binding mode. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 35, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Huerta, E.; Maqueda, D.M.; de la Hoz, L.; Nunes da Silva, V.S.; Bertoldo Pacheco, M.T.; Amigo, L.; Recio, I. Short communication: Identification of iron-binding peptides from whey protein hydrolysates using iron (III)- immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography and reversed phase-HPLCtandem mass spectrometry. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodouleas, D.; Fotakis, C.; Papadopoulos, K.; Calokerinos, A.C. Evaluation of total reducing power of edible oils. Talanta 2014, 130, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, B.; Aleman, A.; Montero, P.; Gomez-Guillen, M.C. Antioxidant and functional properties of gelatin hydrolysates obtained from skin of sole and squid. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memarpoor-Yazdi, M.; Asoodeh, A.; Chamani, J. A novel antioxidant and antimicrobial peptide from hen egg white lysozyme hydrolysates. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, M.; Dunn, C.M.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Use of caseinophosphopeptides as natural antioxidants in oil-in-water emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2365–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaei, M.; Mirdamadi, S.; Ehsani, M.R.; Aminlari, M.; Hosseini, E. Purification and identification of antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory peptide from Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein hydrolysate. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaranayaka, A.G.P.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Food-derived peptidic antioxidants: A review of their production, assessment, and potential applications. J. Funct. Foods 2011, 3, 229–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Qi, Y.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Q. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from Chinese cherry (Prunus pseudocerasus Lindl.) seeds. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Mu, T.H. Identification and characterization of antioxidant peptides from sweet potato protein hydrolysates by Alcalase under high hydrostatic pressure. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2017, 43, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zeng, M.; Wang, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, H. Antioxidant and biochemical properties of protein hydrolysates prepared from Silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, G. Preparation and antioxidant property of extract and semipurified fractions of Caulerpa racemosa. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, Z.R.; Yu, D.; Chi, C.F.; Luo, H.Y.; Ma, J.Y. Isolation and characterisation of five novel antioxidant peptides from ethanol-soluble proteins hydrolysate of spotless smoothhound (Mustelus griseus) muscle. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 6, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.Y.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B.; Deng, S.G. Two novel antioxidant nonapeptides from protein hydrolysate of skate (Raja porosa) muscle. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1993–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| RSHP-A | RSHP-B | RSHP-C | RSHP-D | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retention time (min) | 9.434 | 13.435 | 14.137 | 18.610 | |
| Amino acid sequence | VPR | IEPH | LEEEE | IEEEQ | |
| Theoretical mass/ observed mass (Da) | 370.44/ 370.46 | 494.52/ 494.55 | 647.69/ 647.64 | 646.62/ 646.66 | |
| EC50 (mg/mL) | DPPH• | 4.61 | 0.77 | 0.08 | 0.15 |
| HO• | 1.90 | 0.46 | 0.17 | 0.11 | |
| • | 3.69 | 0.70 | 0.15 | 0.19 | |
| ABTS+• | 4.01 | 1.30 | 0.16 | 0.18 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.-M.; Li, L.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Four Antioxidant Peptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Red Stingray (Dasyatis akajei) Cartilages: Isolation, Identification, and In Vitro Activity Evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17050263
Pan X-Y, Wang Y-M, Li L, Chi C-F, Wang B. Four Antioxidant Peptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Red Stingray (Dasyatis akajei) Cartilages: Isolation, Identification, and In Vitro Activity Evaluation. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(5):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17050263
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Xiao-Yang, Yu-Mei Wang, Li Li, Chang-Feng Chi, and Bin Wang. 2019. "Four Antioxidant Peptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Red Stingray (Dasyatis akajei) Cartilages: Isolation, Identification, and In Vitro Activity Evaluation" Marine Drugs 17, no. 5: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17050263
APA StylePan, X. -Y., Wang, Y. -M., Li, L., Chi, C. -F., & Wang, B. (2019). Four Antioxidant Peptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Red Stingray (Dasyatis akajei) Cartilages: Isolation, Identification, and In Vitro Activity Evaluation. Marine Drugs, 17(5), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17050263







