Tunicate Heparan Sulfate Enriched in 2-Sulfated β-Glucuronic Acid: Structure, Anticoagulant Activity, and Inhibitory Effect on the Binding of Human Colon Adenocarcinoma Cells to Immobilized P-Selectin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Extraction and Purification of the P. nigra Heparan Sulfate
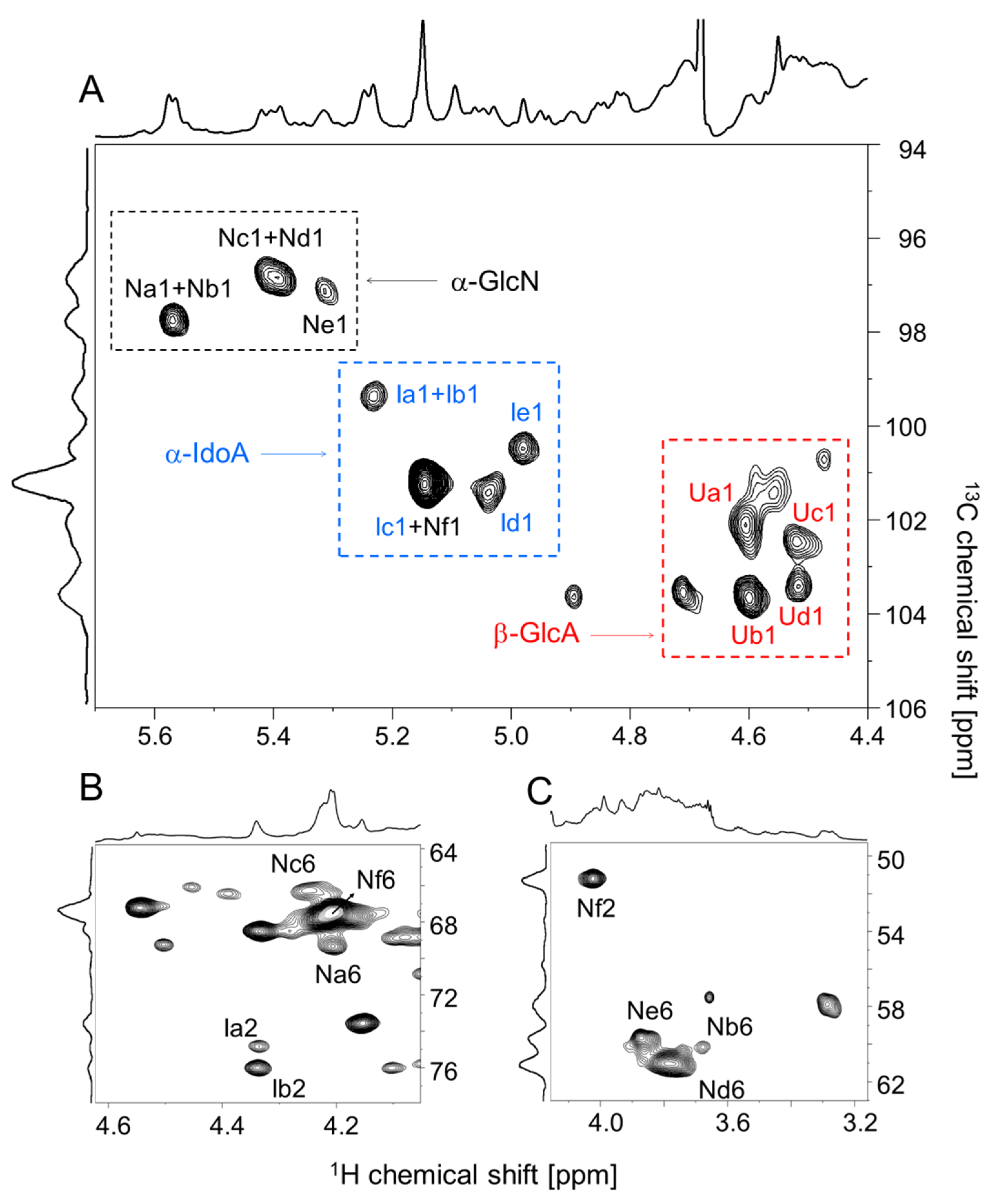
2.2. Structural Characterization of the P. nigra Heparan Sulfate by NMR
2.3. Heparan Sulfate from P. nigra Has Almost No Effect on Coagulation
2.4. Heparan Sulfate from P. nigra Inhibits the Binding of Tumor Cells to Immobilized P-Selectin
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Extraction of Sulfated Glycans from the Ascidian Phallusia Nigra
3.2. Fractionation of Sulfated Glycans from P. nigra
3.2.1. Differential Precipitation with Ethanol
3.2.2. Ion-Exchange Chromatography
3.3. Electrophoresis
3.3.1. Agarose Gel
3.3.2. Polyacrylamide Gel
3.4. Incubation with Heparin Lyases
3.5. NMR
3.6. In Vitro Anticoagulant Activity
3.7. In Vitro Binding of LS 180 Cells to Immobilized P-Selectin
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cássaro, C.M.; Dietrich, C.P. Distribution of sulfated mucopolysaccharides in invertebrates. J. Biol. Chem. 1977, 252, 2254–2261. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, C.P.; Sampaio, L.O.; Montes de Oca, H.; Nader, H.B. Role of sulfated mucopolysaccharides in cell recognition and neoplastic transformation. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 1980, 52, 179–186. [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl, U.; Kusche, M.; Lidholt, K.; Oscarsson, L.G. Biosynthesis of heparin and heparan sulfate. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1989, 556, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabenstein, D.L. Heparin and heparan sulfate: Structure and function. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2002, 19, 312–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Pavão, M.S.; Dos Santos, J.C.; Sugahara, K. A functional dermatan sulfate epitope containing iduronate(2-O-sulfate)alpha1-3GalNAc(6-O-sulfate) disaccharide in the mouse brain: Demonstration using a novel monoclonal antibody raised against dermatan sulfate of ascidian Ascidia nigra. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 23184–23193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavão, M.S.; Mourão, P.A.; Mulloy, B.; Tollefsen, D.M. A unique dermatan sulfate-like glycosaminoglycan from ascidian. Its structure and the effect of its unusual sulfation pattern on anticoagulant activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 31027–31036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavão, M.S.; Aiello, K.R.; Werneck, C.C.; Silva, L.C.; Valente, A.P.; Mulloy, B.; Colwell, N.S.; Tollefsen, D.M.; Mourão, P.A. Highly sulfated dermatan sulfates from Ascidians. Structure versus anticoagulant activity of these glycosaminoglycans. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 27848–27857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.C.; Mesquita, J.M.; Belmiro, C.L.; da Silveira, C.B.; Viskov, C.; Mourier, P.A.; Pavão, M.S. Isolation and characterization of a heparin with low antithrombin activity from the body of Styela plicata (Chordata-Tunicata). Distinct effects on venous and arterial models of thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2007, 121, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalcante, M.C.; Allodi, S.; Valente, A.P.; Straus, A.H.; Takahashi, H.K.; Mourão, P.A.; Pavão, M.S. Occurrence of heparin in the invertebrate styela plicata (Tunicata) is restricted to cell layers facing the outside environment. An ancient role in defense? J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 36189–36196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Lyon, M.; Gallagher, J.T. Distinct substrate specificities of bacterial heparinases against N-unsubstituted glucosamine residues in heparan sulfate. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 15742–15748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar, A.M.; Santos, G.R.; Capillé, N.V.; Piquet, A.A.; Glauser, B.F.; Pereira, M.S.; Vilanova, E.; Mourão, P.A. Structural and haemostatic features of pharmaceutical heparins from different animal sources: Challenges to define thresholds separating distinct drugs. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudo, M.; Sato, K.; Chaidedgumjorn, A.; Toyoda, H.; Toida, T.; Imaari, T. (1)H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic analysis for determination of glucuronic and iduronic acids in dermatan sulfate, heparin, and heparan sulfate. Anal. Biochem. 2001, 297, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.H.; Xu, Y.; Keire, D.A.; Liu, J. Chemoenzymatic synthesis and structural characterization of 2-O-sulfated glucuronic acid-containing heparan sulfate hexasaccharides. Glycobiology 2014, 24, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Pagadala, V.; Jester, H.M.; Lim, A.M.; Pham, T.Q.; Goulas, A.M.P.; Liu, J.; Linhardt, R.J. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of heparan sulfate and heparin oligosaccharides and NMR analysis: Paving the way to a diverse library for glycobiologists. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 7932–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourão, P.A.; Vilanova, E.; Soares, P.A. Unveiling the structure of sulfated fucose-rich polysaccharides via nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2018, 50, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Salmivirta, M.; Lidholt, K.; Lindahl, U. Heparan sulfate: A piece of information. FASEB J. 1996, 10, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeds, E.; Feta, A.; Kusche-Gullberg, M. Target selection of heparan sulfate hexuronic acid 2-O-sulfotransferase. Glycobiology 2010, 20, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.J.; Borsig, L.; Varki, N.M.; Varki, A. P-selectin deficiency attenuates tumor growth and metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9325–9330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geng, J.G.; Chen, M.; Chou, K.C. P-selectin cell adhesion molecule in inflammation, thrombosis, cancer growth and metastasis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 2153–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayadas, T.N.; Johnson, R.C.; Rayburn, H.; Hynes, R.O.; Wagner, D.D. Leukocyte rolling and extravasation are severely compromised in P selectin deficient mice. Cell 1993, 74, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, R.J.; Schön, M.P.; Boehncke, W.H. P-selectin: A common therapeutic target for cardiovascular disorders, inflammation and tumour metastasis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2007, 11, 1103–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, R.J.; Boehme, B.; Podda, M.; Henschler, R.; Jager, E.; Tandi, C.; Boehncke, W.H.; Zollner, T.M.; Kaufmann, R.; Gille, J. Endothelial P-selectin as a target of heparin action in experimental melanoma lung metastasis. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2743–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannori, G.; Crottet, P.; Cecconi, O.; Hanasaki, K.; Aruffo, A.; Nelson, R.M.; Varki, A.; Bevilacqua, M.P. Differential colon cancer cell adhesion to E-, P-, and L-selectin: Role of mucin-type glycoproteins. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 4425–4431. [Google Scholar]
- Presta, M.; Leali, D.; Stabile, H.; Ronca, R.; Camozzi, M.; Coco, L.; Moroni, E.; Liekens, S.; Rusnati, M. Heparin derivatives as angiogenesis inhibitors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2003, 9, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorana, A.A.; Sahni, A.; Altland, O.D.; Francis, C.W. Heparin inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation and organization in dependent on molecular weight. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 2110–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakkar, A.K. An expanding role for antithrombotic therapy in cancer patients. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2003, 29, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavão, M.S. Glycosaminoglycans analogs from marine invertebrates: Structure, biological effects, and potential as new therapeutics. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farndale, R.W.; Buttle, D.J.; Barrett, A.J. Improved quantitation and discrimination of sulphated glycosaminoglycans by use of dimethylmethylene blue. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1986, 883, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linhardt, R.J.; Fitzgerald, G.L.; Cooney, C.L.; Langer, R. Mode of action of heparin lyase on heparin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1982, 702, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linhardt, R.J.; Turnbull, J.E.; Wang, H.M.; Loganathan, D.; Gallagher, J.T. Examination of the substrate specificity of heparin and heparan sulfate lyases. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 2611–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, P.A.G.; Ribeiro, K.A.; Valente, A.P.; Capillé, N.V.; Oliveira, S.M.C.G.; Tovar, A.M.F.; Pereira, M.S.; Vilanova, E.; Mourão, P.A.S. A unique fucosylated chondroitin sulfate type II with strikingly homogeneous and neatly distributed α-fucose branches. Glycobiology 2018, 28, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostettler, N.; Naggi, A.; Torri, G.; Ishai-Michaeli, R.; Casu, B.; Vlodavsky, I.; Borsig, L. P-selectin- and heparanase-dependent antimetastatic activity of non-anticoagulant heparins. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 3562–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Signal a | Structure b | Proportion c | 1H/13C Chemical Shift (ppm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||
| (A) α-GlcN Units | ||||||||
| Na | αGlcN(NS,6S)→[βGlcA(2S)] | 5.53 ± 1.40 | 5.57/97.7 | 3.28/57.9 | 3.70/69.7 | 3.93/72.7 | 4.05/70.8 | 4.20/69.4 |
| Nb | αGlcN(NS)→[βGlcA(2S)] | 15.30 ± 1.27 | 5.56/97.7 | 3.26/57.9 | 3.68/67.8 | 3.97/72.9 | 4.01/70.9 | 3.67/60.1 |
| Nc | αGlcN(NS,6S)→[αIdoA(2S)] | 13.30 ± 0.13 | 5.42/96.8 | 3.28/57.9 | 3.66/69.8 | 3.89/75.2 | 3.97/69.2 | 4.25/66.2 |
| Nd | αGlcNAc→[βGlcA] | 14.39 ± 0.29 | 5.38/96.8 | 3.88/55.7 | 3.71/69.7 | 3.77/68.2 | 3.85/69.1 | 3.78/61.0 |
| Ne | αGlcN(NS)→[αIdoA(2S)] | 12.48 ± 2.01 | 5.31/97.0 | 3.28/57.9 | 3.73/71.1 | 3.75/77.3 | 3.89/75.2 | 3.87/59.7 |
| Nf | αGlcNAc(6S)→[βGlcA] | 39.00 ± 2.92 | 5.14/101.1 | 4.02/51.2 | 3.70/69.8 | 3.77/68.2 | 3.92/70.7 | 4.20/67.5 |
| (B) α-IdoA Units | ||||||||
| Ia | αIdoA(2S)→[αGlcN(NS)] | 3.16 ± 0.24 | 5.23/99.3 | 4.33/74.8 | 4.23/69.3 | 4.05/75.7 | 4.83/71.1 | - |
| Ib | αIdoA(2S)→[αGlcN(NS,6S)] | 5.93 ± 0.33 | 5.24/99.3 | 4.34/76.0 | 4.23/69.3 | 4.10/76.0 | 4.80/72.7 | - |
| Ic | αIdoA(2S)→[αGlcN(NS)] | 10.46 ± 2.91 | 5.16/101.1 | 4.33/74.8 | 4.16/73.5 | 4.08/77.0 | 4.54/67.1 | - |
| Id | αIdoA→[αGlcNAc(6S)] | 13.42 ± 2.06 | 5.04/101.3 | 3.78/75.8 | 3.37/73.4 | 4.07/75.9 | 4.81/69.5 | - |
| Ie | αIdoA→[αGlcN(NS)] | 11.18 ± 1.95 | 4.98/100.4 | 3.81/76.6 | 3.41/73.5 | 4.01/77.0 | 4.84/68.4 | - |
| ΔIdoA | 44.15 | |||||||
| (C) β-GlcA Units | ||||||||
| Ua | βGlcA(2S)→[αGlcN(NS)] | 17.35 ± 0.09 | 4.60/102.0 | 4.00/77.3 | 3.73/75.1 | 3.84/75.8 | 3.87/74.9 | - |
| Ub | βGlcA(2S)→[αGlcN(NS,6S)] | 16.37 ± 0.86 | 4.60/103.6 | 4.01/78.3 | 3.74/77.4 | 3.82/75.8 | 3.88/75.8 | - |
| Uc | βGlcA→[αGlcNAc] | 11.81 ± 2.92 | 4.52/102.4 | 3.40/72.9 | 3.70/76.4 | 3.86/77.1 | 3.89/75.2 | - |
| Ud | βGlcA→[αGlcNAc(6S)] | 10.33 ± 0.16 | 4.52/103.3 | 3.47/72.8 | 3.70/77.3 | 3.85/74.9 | 3.90/75.3 | - |
| ΔGlcA | 55.85 | |||||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abreu, W.S.; Soares, P.A.G.; Motta, J.M.; Kozlowski, E.O.; Teixeira, F.C.O.B.; Soares, M.A.; Borsig, L.; Mourão, P.A.S.; Pavão, M.S.G. Tunicate Heparan Sulfate Enriched in 2-Sulfated β-Glucuronic Acid: Structure, Anticoagulant Activity, and Inhibitory Effect on the Binding of Human Colon Adenocarcinoma Cells to Immobilized P-Selectin. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060351
Abreu WS, Soares PAG, Motta JM, Kozlowski EO, Teixeira FCOB, Soares MA, Borsig L, Mourão PAS, Pavão MSG. Tunicate Heparan Sulfate Enriched in 2-Sulfated β-Glucuronic Acid: Structure, Anticoagulant Activity, and Inhibitory Effect on the Binding of Human Colon Adenocarcinoma Cells to Immobilized P-Selectin. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(6):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060351
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbreu, Wallace S., Paulo A. G. Soares, Juliana M. Motta, Eliene O. Kozlowski, Felipe C. O. B. Teixeira, Mariana A. Soares, Lubor Borsig, Paulo A. S. Mourão, and Mauro S. G. Pavão. 2019. "Tunicate Heparan Sulfate Enriched in 2-Sulfated β-Glucuronic Acid: Structure, Anticoagulant Activity, and Inhibitory Effect on the Binding of Human Colon Adenocarcinoma Cells to Immobilized P-Selectin" Marine Drugs 17, no. 6: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060351
APA StyleAbreu, W. S., Soares, P. A. G., Motta, J. M., Kozlowski, E. O., Teixeira, F. C. O. B., Soares, M. A., Borsig, L., Mourão, P. A. S., & Pavão, M. S. G. (2019). Tunicate Heparan Sulfate Enriched in 2-Sulfated β-Glucuronic Acid: Structure, Anticoagulant Activity, and Inhibitory Effect on the Binding of Human Colon Adenocarcinoma Cells to Immobilized P-Selectin. Marine Drugs, 17(6), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060351





