C-Phycocyanin Suppresses the In Vitro Proliferation and Migration of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells through Reduction of RIPK1/NF-κB Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
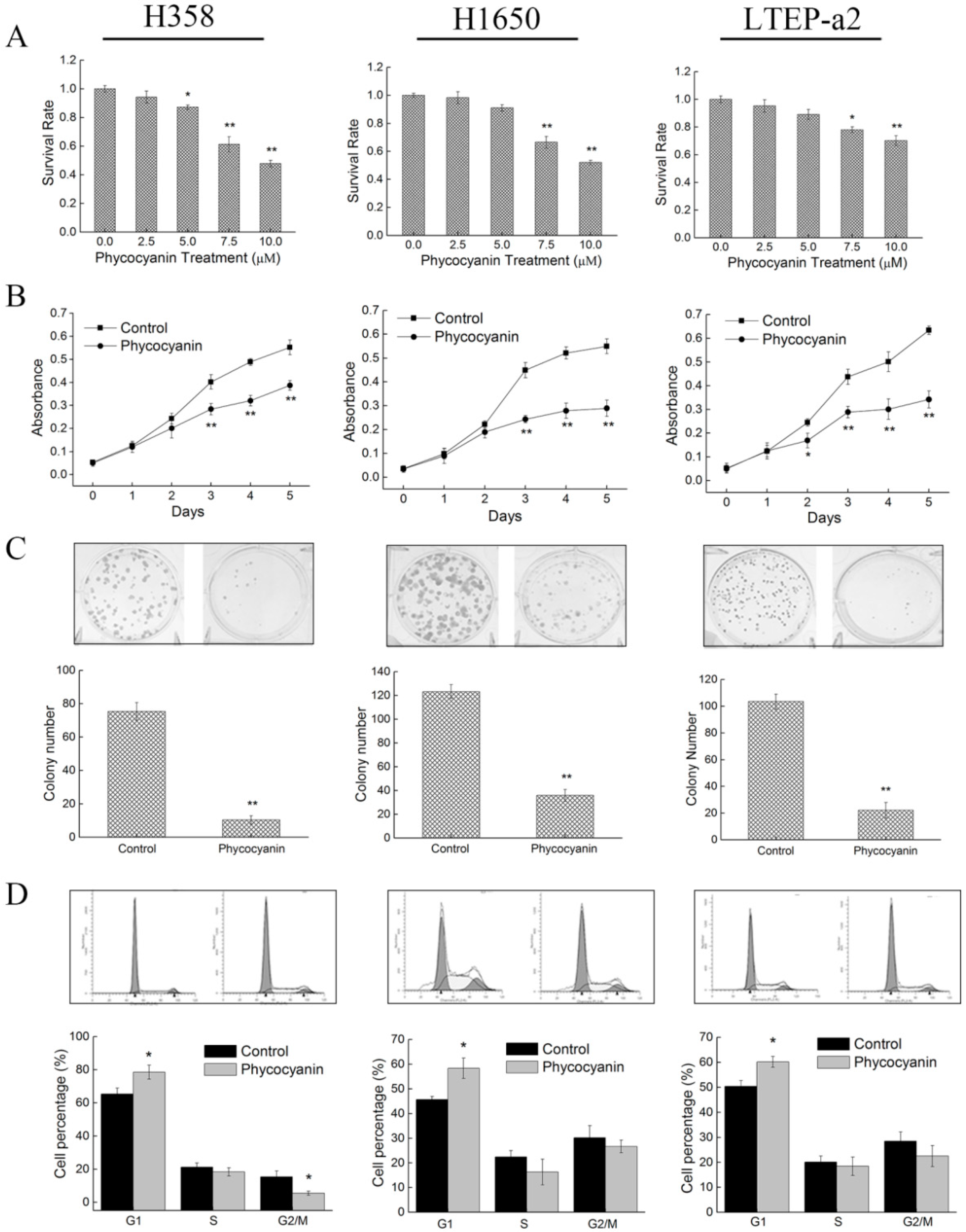
2.1. Phycocyanin Inhibits the in Vitro Proliferation of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells
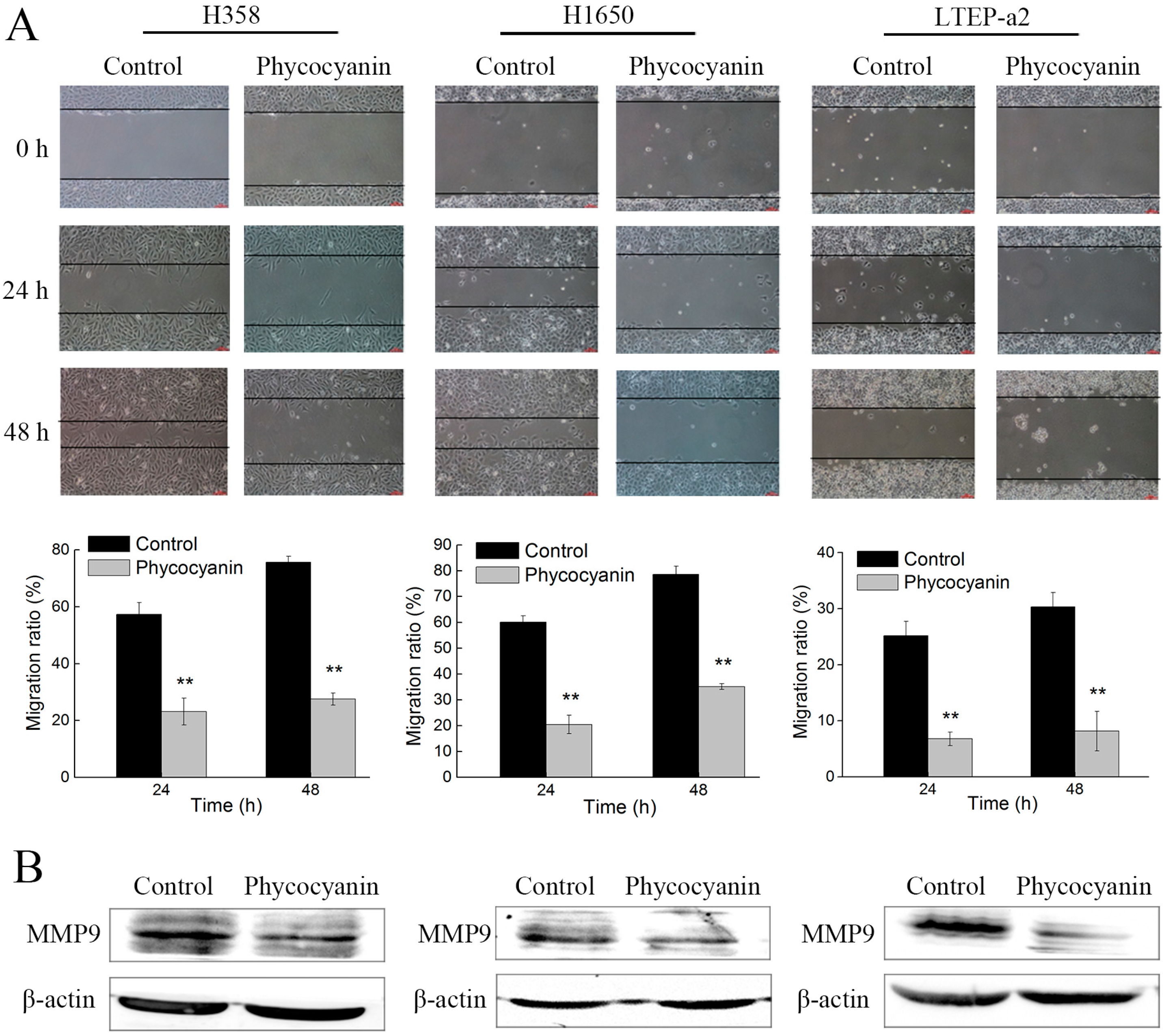
2.2. Phycocyanin Suppresses the In Vitro Migration of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells
2.3. Phycocyanin Induces Apoptosis of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells
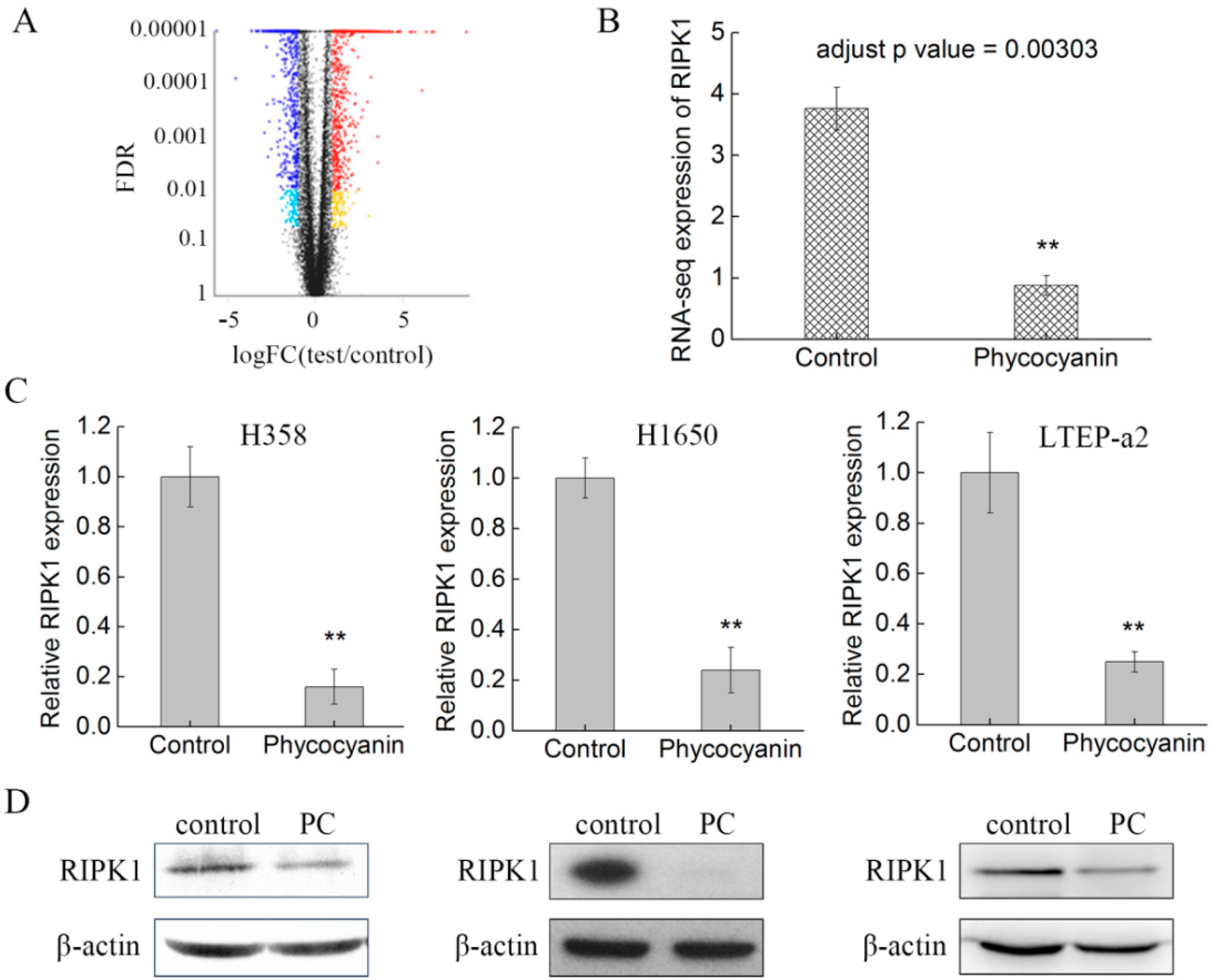
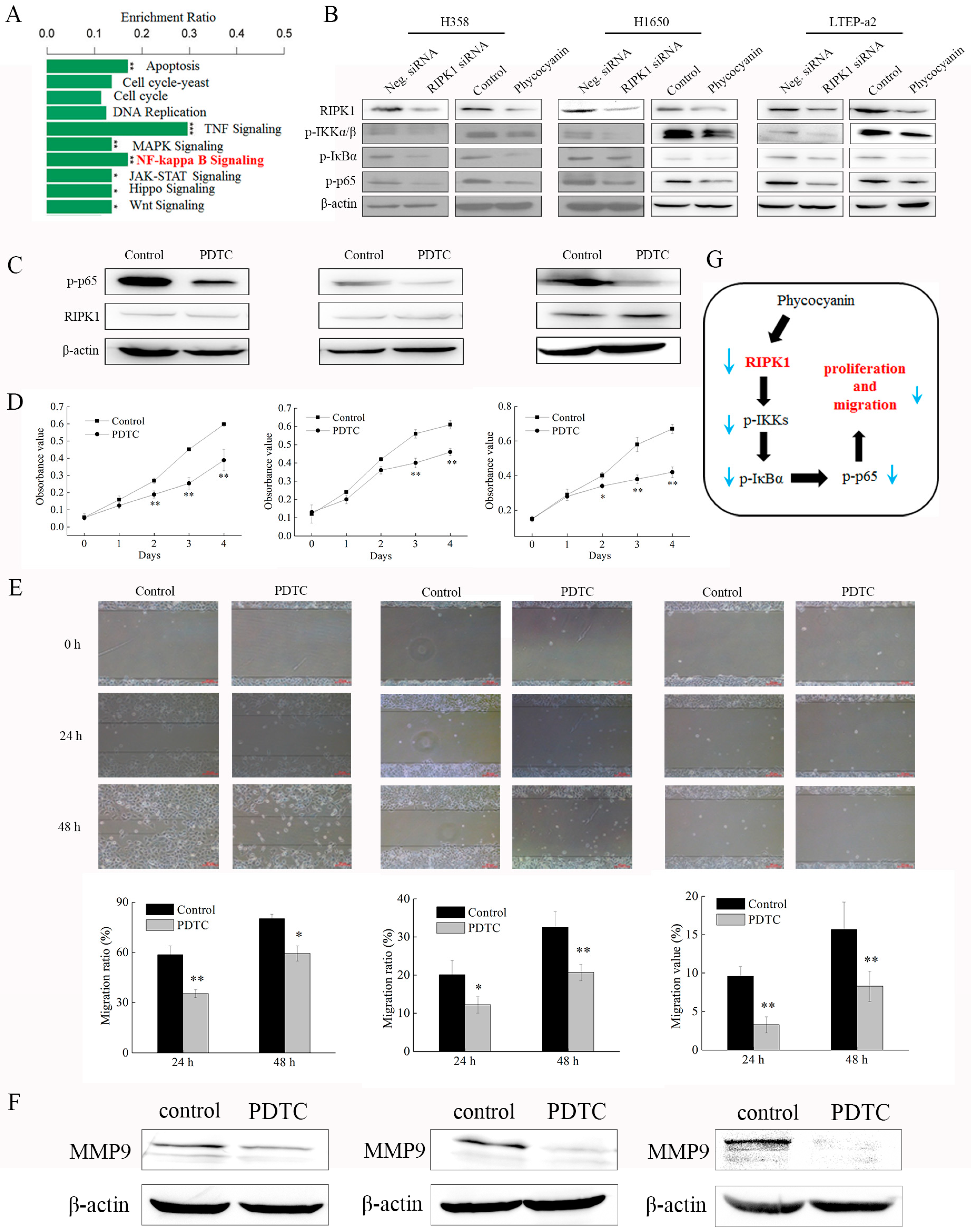
2.4. RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq) Analysis Suggests that RIPK1 is Down-Regulated by Phycocyanin in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells
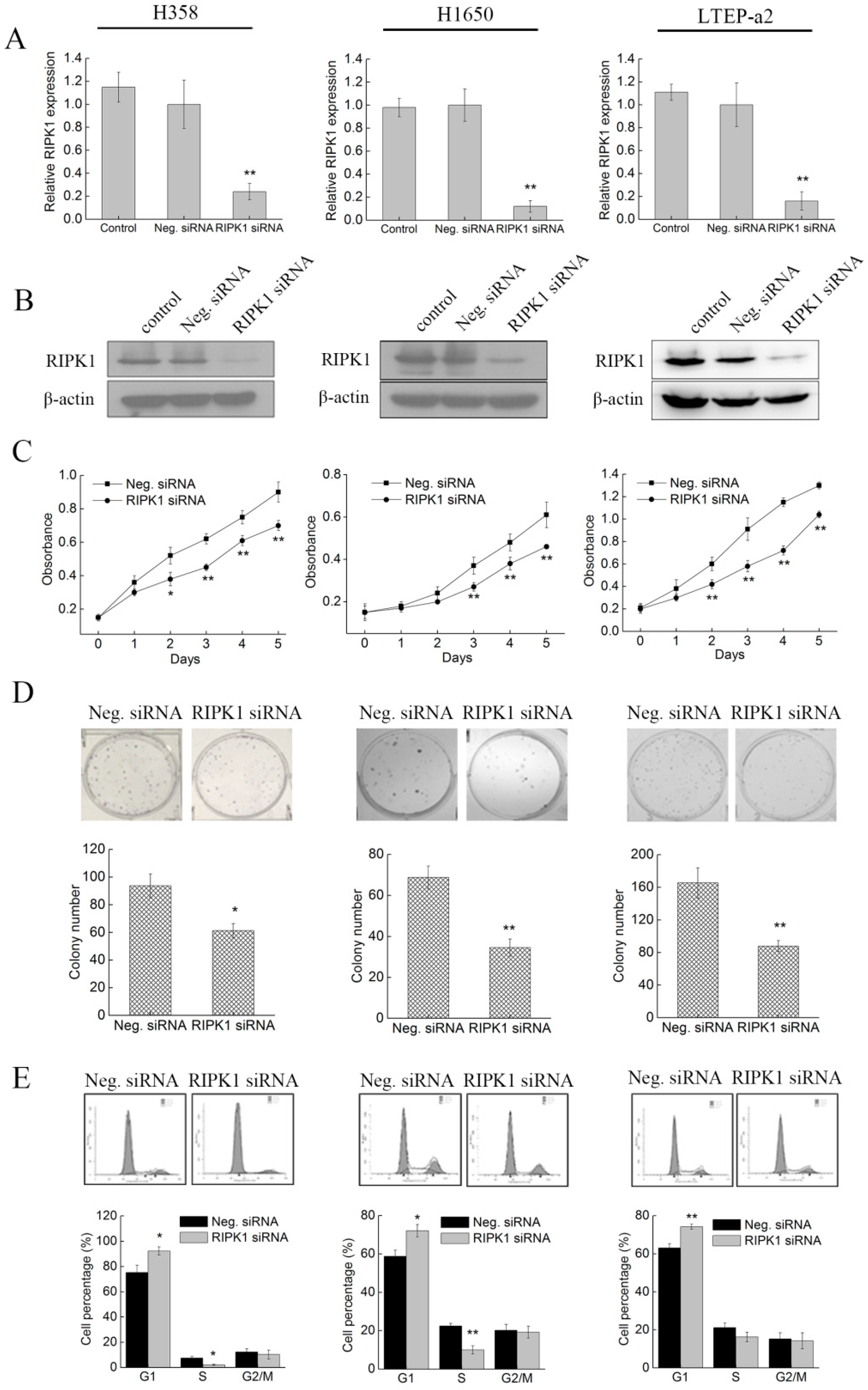
2.5. Knockdown of RIPK1 Expression Inhibits the In Vitro Proliferation of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cell
2.6. Knockdown of RIPK1 Expression Suppresses the In Vitro Migration of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells
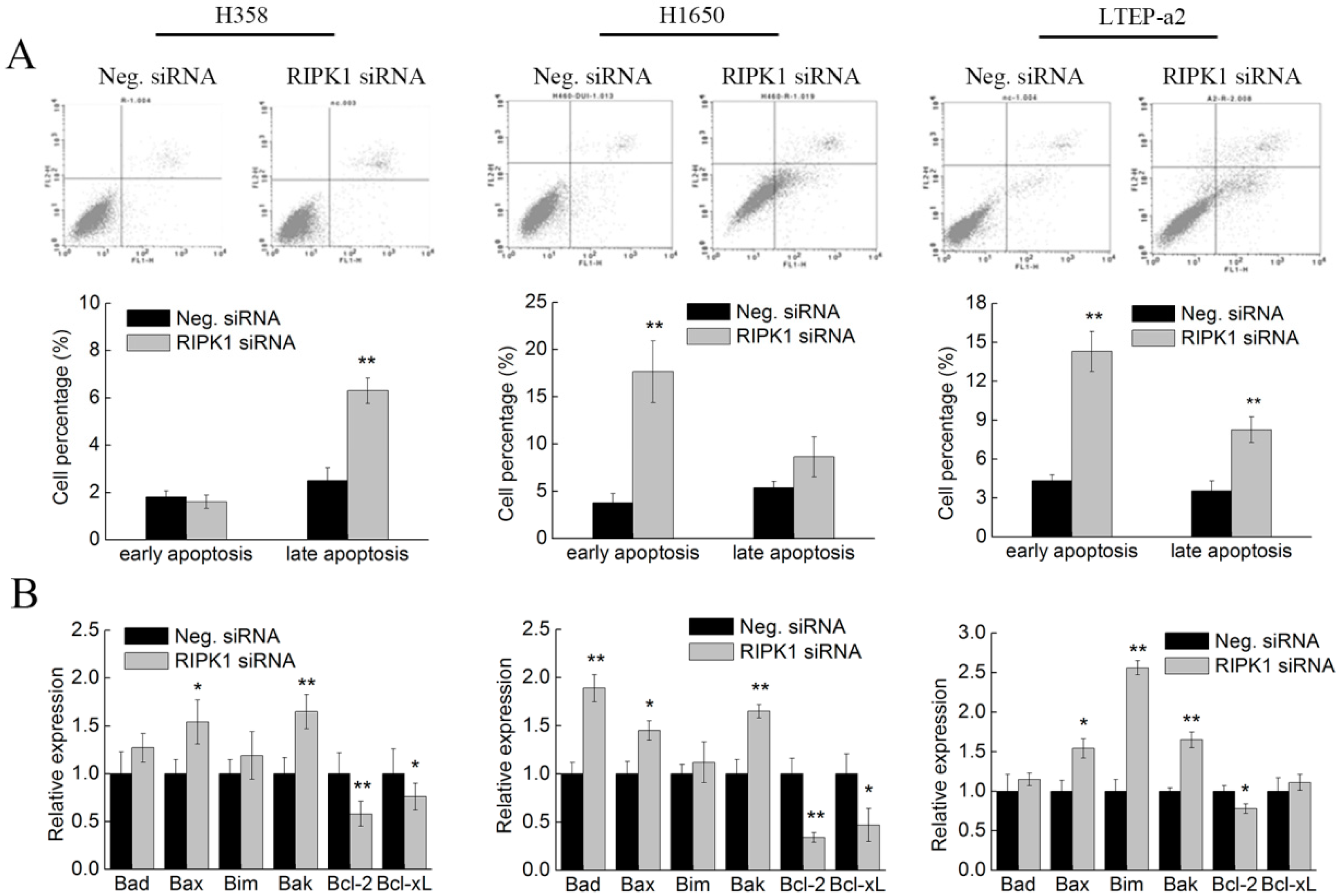
2.7. Knockdown of RIPK1 Expression Induces Apoptosis of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells
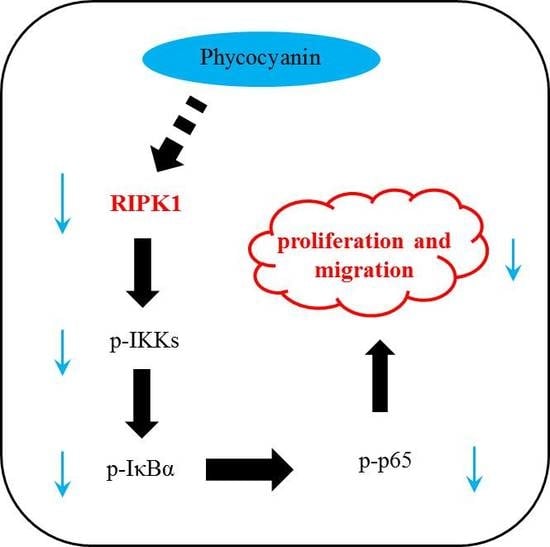
2.8. Phycocyanin Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells Through Down-Regulation of RIPK1/NF-κB Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials, Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
4.2. siRNA Transfection
4.3. Cell Morphology Observation
4.4. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.5. Cell Viability Assay
4.6. Cell Colony Formation Assay
4.7. Cell Cycle Assay
4.8. Wound-Healing Assay
4.9. Cell Apoptosis Assay
4.10. Transcriptome Analysis
4.11. Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.12. Western Blot Analysis
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nigam, M.; Suleria, H.A.R.; Farzaei, M.H.; Mishra, A.P. Marine anticancer drugs and their relevant targets: a treasure from the ocean. Daru 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleria, H.A.R.; Gobe, G.; Masci, P.; Osborne, S.A. Marine bioactive compounds and health promoting perspectives; innovation pathways for drug discovery. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.F.; Matthews, J.P.; Young, G.A.; Szer, J.; Gillett, A.; Joshua, D.; et al. A randomized study of high-dose cytarabine in induction in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 1996, 87, 1710–1717. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Glaser, K.B.; Cuevas, C.; Jacobs, R.S.; Kem, W.; Little, R.D.; McIntosh, J.M.; Newman, D.J.; Potts, B.C.; Shuster, D.E. The odyssey of marine pharmaceuticals: A current pipeline perspective. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 31, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, B.L. Seeing new light: recent insights into the occurrence and regulation of chromatic acclimation in cyanobacteria. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 37, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, D.Y.; Sarian, F.D.; van Wijk, A.; Martinez-Garcia, M.; Van Maarel, M. Thermostable phycocyanin from the red microalga Cyanidioschyzon merolae, a new natural blue food colorant. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Cai, T.; Cai, Y. Medical application of Spirulina platensis derived C-Phycocyanin. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 7803846. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, S.; Siddiqui, W.A.; Khandelwal, S. C-Phycocyanin protects against acute tributyltin chloride neurotoxicity by modulating glial cell activity along with its anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory property: A comparative efficacy evaluation with N-acetyl cysteine in adult rat brain. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 238, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manconia, M.; Pendas, J.; Ledon, N.; Moreira, T.; Sinico, C.; Saso, L.; Fadda, A.M. Phycocyanin liposomes for topical anti-inflammatory activity: In-vitro in-vivo studies. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonani, R.R.; Patel, S.; Bhastana, B.; Jakharia, K.; Chaubey, M.G.; Singh, N.K.; Madamwar, D. Purification and antioxidant activity of phycocyanin from Synechococcus sp. R42DM isolated from industrially polluted site. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.J.; Yang, H.; Chen, Y.T.; Li, P.P. Biosynthesis of fluorescent beta subunits of C-phycocyanin from Spirulina subsalsa in Escherichia coli, and their antioxidant properties. Molecules 2018, 23, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Cian, R.E.; Lopez-Posadas, R.; Drago, S.R.; De Medina, F.S.; Martinez-Augustin, O. Immunomodulatory properties of the protein fraction from Phorphyra columbina. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 8146–8154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Baky, H.H.; El-Baroty, G.S. Characterization and bioactivity of phycocyanin isolated from Spirulina maxima grown under salt stress. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, M.; Tentu, S.; Baskar, G.; Prasad, S.R.; Raghavan, S.; Jayaprakash, P.; Jeyakanthan, J.; Rayala, S.K.; Venkatraman, G. Molecular mechanism of anti-cancer activity of phycocyanin in triple-negative breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, H.; Zhu, F.; Ji, H.; Li, B. C-Phycocyanin exerts anti-cancer effects via the MAPK signaling pathway in MDA-MB-231 cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.; Wang, J.; Ji, H.; Lin, C.; Pan, R.; Zhou, L.; Song, Y.; Zhang, E.; Ren, P.; Chen, J.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of phycocyanin inhibitory effects on SKOV-3 cell proliferation. Gene 2016, 585, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, G.; Gao, B.; Gao, Y.; Yang, X.; Cheng, X.; Ou, Y. Phycocyanin inhibits tumorigenic potential of pancreatic cancer cells: Role of apoptosis and autophagy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, M.K.; Sanyal, S.N. Targeting angiogenic pathway for chemoprevention of experimental colon cancer using C-phycocyanin as cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 92, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, C.; Huang, W.; Wang, C.T. Phycocyanin reduces proliferation of melanoma cells through downregulating GRB2/ERK signaling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10921–10929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Mulshine, J.L.; Kwon, R.; Curran, W.J., Jr.; Wu, Y.L.; Paz-Ares, L. Lung cancer: Current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet 2017, 389, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanavaty, P.; Alvarez, M.S.; Alberts, W.M. Lung cancer screening: Advantages, controversies, and applications. Cancer Control 2014, 21, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Yang, D.; He, J.; Krasna, M.J. Epidemiology of lung cancer. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 25, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, J.R.; Yang, P.; Cassivi, S.D.; Schild, S.E.; Adjei, A.A. Non-small-cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo. Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafei, H.; El-Bahesh, E.; Finianos, A.; Nassereddine, S.; Tabbara, I. Immune-based therapies for non-small-cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Huang, T.W.; Tsai, W.C.; Lin, L.F.; Cheng, J.B.; Chang, H.; Lee, S.C. Risk factors of postoperative recurrences in patients with clinical stage I NSCLC. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingula, R.; Dupuis, C.; Pichon, C.; Berthon, J.Y.; Filaire, M.; Pigeon, L.; Filaire, E. Study of the effects of betaine and/or C-phycocyanin on the growth of lung cancer A549 cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Oncol. 2016, 2016, 8162952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gao, M.H.; Chu, X.M.; Teng, L.; Lv, C.Y.; Yang, P.; Yin, Q.F. The synergistic antitumor effects of all-trans retinoic acid and C-phycocyanin on the lung cancer A549 cells in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 749, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gao, M.H.; Lv, C.Y.; Yang, P.; Yin, Q.F. Study of the synergistic effects of all-transretinoic acid and C-phycocyanin on the growth and apoptosis of A549 cells. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 25, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudelet, P.H.; Gagez, A.L.; Berard, J.B.; Juin, C.; Bridiau, N.; Kaas, R.; Thiery, V.; Cadoret, J.P.; Picot, L. Antiproliferative activity of Cyanophora paradoxa pigments in melanoma, breast and lung cancer cells. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4390–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Yan, Y.; Li, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, L.Y.; Wang, C.T. The in vitro anti-tumor activity of phycocyanin against non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Liang, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, F.; Du, D. Knockdown of Diaph1 expression inhibits migration and decreases the expression of MMP2 and MMP9 in human glioma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondylis, V.; Kumari, S.; Vlantis, K.; Pasparakis, M. The interplay of IKK, NF-kappaB and RIPK1 signaling in the regulation of cell death, tissue homeostasis and inflammation. Immunol Rev. 2017, 277, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltzer, N.; Darding, M.; Walczak, H. Holding RIPK1 on the ubiquitin leash in TNFR1 signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Gao, Y.J.; Liang, H.L. Effect of NF- kappa B inhibitor PDTC on VEGF and endostatin expression of mice with Lewis lung cancer. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2015, 8, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwonka, A.; Kalawaj, K.; Slawinska-Brych, A.; Lemieszek, M.K.; Bartnik, M.; Wojtanowski, K.K.; Zdzisinska, B.; Rzeski, W. Anticancer effect of the water extract of a commercial Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis) product on the human lung cancer A549 cell line. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.Y.; He, L.Z.; Song, Z.H.; Chan, L.; He, J.T.; Huang, W.; Zhou, B.W.; Chen, T.F. Phycocyanin-based nanocarrier as a new nanoplatform for efficient overcoming of cancer drug resistance. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2017, 5, 3300–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, I.; Ozen, M.O.; Yesil-Celiktas, O. Supercritical fluid extraction of phycocyanin and investigation of cytotoxicity on human lung cancer cells. J. Supercrit. Fluid 2016, 108, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangam, R.; Suresh, V.; Asenath Princy, W.; Rajkumar, M.; Senthilkumar, N.; Gunasekaran, P.; Rengasamy, R.; Anbazhagan, C.; Kaveri, K.; Kannan, S. C-phycocyanin from Oscillatoria tenuis exhibited an antioxidant and in vitro antiproliferative activity through induction of apoptosis and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest. Food Chem. 2013, 140, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, N.; Kurinjimalar, C.; Thangam, R.; Suresh, V.; Kavitha, G.; Gunasekaran, P.; Rengasamy, R. Further studies and biological activities of macromolecular protein R-Phycoerythrin from Portieria hornemannii. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madamwar, D.; Kaushal, A.; Patel, D.K.; Desai, S.N.; Upadhyay, K.; Devkar, R.V. Cyanobacterial phycoerythrin purified from marine Lyngbya sp induces apoptosis in lung carcinoma cells. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2015, 10, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Ghosh, S. The NF-kappaB family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Ling, Q.; Cai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hoffmann, P.R.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, T.; Huang, Z. Selenium-containing phycocyanin from se-enriched Spirulina platensis reduces inflammation in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by inhibiting NF-kappaB activation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5060–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherng, S.C.; Cheng, S.N.; Tarn, A.; Chou, T.C. Anti-inflammatory activity of c-phycocyanin in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 1431–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, S.; Yan, Y.; Huang, W.W.; Gai, F.; Wang, J.P.; Liu, L.Y.; Wang, C.T. C-phycocyanin reduces inflammation by inhibiting NF-kappa B activity through downregulating PDCD5 in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 42, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yu, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, B.; Jiao, X.; Song, X.; Lv, C.; Qin, S. Phycocyanin attenuates pulmonary fibrosis via the TLR2-MyD88-NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yan, Y.; Chi, M.; Chen, W.; Sun, P.; Qin, S. The protective effect of C-phycocyanin on paraquat-induced acute lung injury in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 32, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Shen, S.; Verma, I.M. NF-kappaB, an active player in human cancers. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishanth, R.P.; Ramakrishna, B.S.; Jyotsna, R.G.; Roy, K.R.; Reddy, G.V.; Reddy, P.K.; Reddanna, P. C-Phycocyanin inhibits MDR1 through reactive oxygen species and cyclooxygenase-2 mediated pathways in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 649, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Yan, Y.; Cao, Q.; Wu, T.T.; Liu, L.Y.; Wang, C.T. Transcriptome analysis of phycocyanin-mediated inhibitory functions on non-small-cell lung cancer A549 cell growth. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, K.W.; Saleh, D.; Degterev, A. Complex pathologic roles of RIPK1 and RIPK3: moving beyond necroptosis. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 202–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.T.; Gautheron, J.; Feoktistova, M.; Roderburg, C.; Loosen, S.H.; Roy, S.; Benz, F.; Schemmer, P.; Buchler, M.W.; Nachbur, U.; et al. RIPK1 suppresses a TRAF2-dependent pathway to liver cancer. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Zhu, S.; Xie, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, L.; Zeng, D.; Wang, P.; Ma, X.; Kroemer, G.; Bartlett, D.L.; et al. JTC801 induces pH-dependent death specifically in cancer cells and slows growth of tumors in mice. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1480–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanggi, K.; Vasilikos, L.; Valls, A.F.; Yerbes, R.; Knop, J.; Spilgies, L.M.; Rieck, K.; Misra, T.; Bertin, J.; Gough, P.J.; et al. RIPK1/RIPK3 promotes vascular permeability to allow tumor cell extravasation independent of its necroptotic function. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van, T.M.; Polykratis, A.; Straub, B.K.; Kondylis, V.; Papadopoulou, N.; Pasparakis, M. Kinase-independent functions of RIPK1 regulate hepatocyte survival and liver carcinogenesis. J. Clin. Invest. 2017, 127, 2662–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, L.; Song, F.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, B.; Fu, Z.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Z. MLKL-PITPalpha signaling-mediated necroptosis contributes to cisplatin-triggered cell death in lung cancer A549 cells. Cancer Lett. 2018, 414, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, S.; Luo, C.L.; Abukiwan, A.; Wang, G.X.; He, J.J.; Huang, L.Y.; Weber, C.E.; Lv, N.; Xiao, X.Y.; Eichmuller, S.B.; et al. miR-137 inhibits proliferation of melanoma cells by targeting PAK2. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, N.; Hao, S.; Luo, C.; Abukiwan, A.; Hao, Y.; Gai, F.; Huang, W.W.; Huang, L.Y.; Xiao, X.Y.; Eichmuller, S.B.; et al. miR-137 inhibits melanoma cell proliferation through downregulation of GLO1. Sci. China Life Sci. 2018, 61, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krylov, D.M.; Wolf, Y.I.; Rogozin, I.B.; Koonin, E.V. Gene loss, protein sequence divergence, gene dispensability, expression level, and interactivity are correlated in eukaryotic evolution. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2229–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, S.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Yan, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C. C-Phycocyanin Suppresses the In Vitro Proliferation and Migration of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells through Reduction of RIPK1/NF-κB Activity. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060362
Hao S, Li S, Wang J, Zhao L, Yan Y, Wu T, Zhang J, Wang C. C-Phycocyanin Suppresses the In Vitro Proliferation and Migration of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells through Reduction of RIPK1/NF-κB Activity. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(6):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060362
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Shuai, Shuang Li, Jing Wang, Lei Zhao, Yan Yan, Tingting Wu, Jiawen Zhang, and Chengtao Wang. 2019. "C-Phycocyanin Suppresses the In Vitro Proliferation and Migration of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells through Reduction of RIPK1/NF-κB Activity" Marine Drugs 17, no. 6: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060362
APA StyleHao, S., Li, S., Wang, J., Zhao, L., Yan, Y., Wu, T., Zhang, J., & Wang, C. (2019). C-Phycocyanin Suppresses the In Vitro Proliferation and Migration of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells through Reduction of RIPK1/NF-κB Activity. Marine Drugs, 17(6), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060362