Fucoidan Derived from Fucus vesiculosus Inhibits the Development of Human Ovarian Cancer via the Disturbance of Calcium Homeostasis, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Angiogenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Fucoidan Regulates Proliferation and Apoptosis of Ovarian Cancer
2.2. Efficacy of Fucoidan on ROS Generation, Calcium Homeostasis, and Mitochondrial Membrane Potentials in Ovarian Cancer
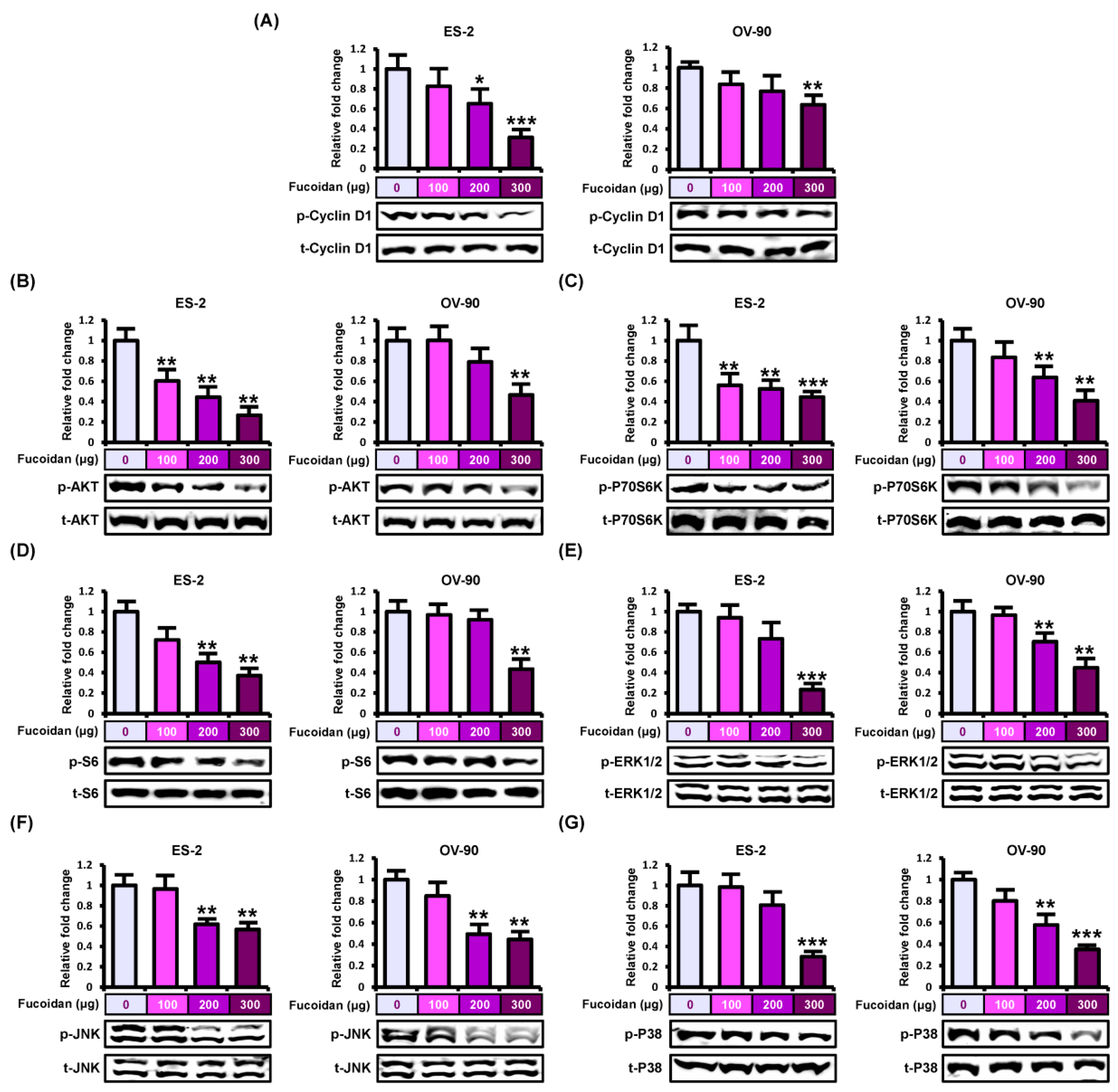
2.3. Fucoidan Regulates Intracellular Signals in Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines
2.4. Disruptiopn of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) by Fucoidan in Human Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines
2.5. In Vivo Toxicity and Xenograft Analysis of Fucoidan Using Zebrafish
2.6. Inhibitory Effects of Fucoidan on Angiogenesis In Vivo and In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Proliferation Analysis
4.4. Observation of Immunofluorescence
4.5. Annexin V and PI Staining
4.6. Cell Cycle Assay
4.7. Determination of Cellular ROS
4.8. Intracellular Level of Free Ca2+
4.9. Measurement of Mitochondrial Ca2+ Concentration
4.10. Observation of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
4.11. TUNEL Assay
4.12. Western Blot Analysis
4.13. In Vivo Toxicity and Xenograft Analysis
4.14. In Vivo Apoptosis Analysis
4.15. Analysis of Angiogenesis in Transgenic Zebrafish
4.16. RNA Isolation
4.17. Quantitative PCR Analysis
4.18. Significances
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Li, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, S. ATP-binding cassette transporter A7 accelerates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer cells by upregulating the transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 5868–5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarhriz, V.; Bandehpour, M.; Dastmalchi, S.; Ouladsahebmadarek, E.; Zarredar, H.; Eyvazi, S. Overview of CD24 as a new molecular marker in ovarian cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 2134–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.; Naishadham, D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2012, 62, 10–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Capriglione, S.; Luvero, D.; Plotti, F.; Terranova, C.; Montera, R.; Scaletta, G.; Schiro, T.; Rossini, G.; Benedetti Panici, P.; Angioli, R. Ovarian cancer recurrence and early detection: May HE4 play a key role in this open challenge? A systematic review of literature. Med. Oncol. 2017, 34, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.A.; Bohlke, K.; Armstrong, D.K.; Bookman, M.A.; Cliby, W.A.; Coleman, R.L.; Dizon, D.S.; Kash, J.J.; Meyer, L.A.; Moore, K.N.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for newly diagnosed, advanced ovarian cancer: Society of Gynecologic Oncology and American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 143, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bast, R.C., Jr.; Hennessy, B.; Mills, G.B. The biology of ovarian cancer: New opportunities for translation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilan, M.I.; Grachev, A.A.; Ustuzhanina, N.E.; Shashkov, A.S.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. Structure of a fucoidan from the brown seaweed Fucus evanescens C.Ag. Carbohydr. Res. 2002, 337, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, F.; Wei, X.; Zhao, R. Fucoidan: Structure and bioactivity. Molecules 2008, 13, 1671–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cumashi, A.; Ushakova, N.A.; Preobrazhenskaya, M.E.; D’Incecco, A.; Piccoli, A.; Totani, L.; Tinari, N.; Morozevich, G.E.; Berman, A.E.; Bilan, M.I.; et al. A comparative study of the anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, antiangiogenic, and antiadhesive activities of nine different fucoidans from brown seaweeds. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruperez, P.; Ahrazem, O.; Leal, J.A. Potential antioxidant capacity of sulfated polysaccharides from the edible marine brown seaweed Fucus vesiculosus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.; Lee, D.J.; Kim, J.K.; You, S. Molecular characterization and immunomodulatory activity of sulfated fucans from Agarum cribrosum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 113, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, P.A.; Hung, Y.L.; Chien, S.Y. Inhibitory activity of Sargassum hemiphyllum sulfated polysaccharide in arachidonic acid-induced animal models of inflammation. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015, 23, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Cao, M.J.; Liu, G.M.; Chen, Q.; Sun, L.; Chen, H. Antibacterial activity and mechanisms of depolymerized fucoidans isolated from Laminaria japonica. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 172, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.K.; Jung, U.; Roh, C. Fucoidan from marine brown algae inhibits lipid accumulation. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Sun, J.; Su, X.; Yu, Q.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, P. A review about the development of fucoidan in antitumor activity: Progress and challenges. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 154, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Huang, T.C.; Lin, L.C.; Shieh, T.M.; Wu, C.H.; Wang, K.L.; Hong, Y.H.; Hsia, S.M. Fucoidan Inhibits the Proliferation of Leiomyoma Cells and Decreases Extracellular Matrix-Associated Protein Expression. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 1970–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, T.M.; Kim, W.J.; Moon, S.K. AKT signaling is involved in fucoidan-induced inhibition of growth and migration of human bladder cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 64, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Q.; Singh, J.; Murata, K.; Itahana, Y.; Parrinello, S.; Liang, S.H.; Gillett, C.E.; Campisi, J.; Desprez, P.Y. A role for Id-1 in the aggressive phenotype and steroid hormone response of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar]
- Vishchuk, O.S.; Sun, H.; Wang, Z.; Ermakova, S.P.; Xiao, J.; Lu, T.; Xue, P.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Xiong, H.; Shao, C.; et al. PDZ-binding kinase/T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase is a target of the fucoidan from brown alga Fucus evanescens in the prevention of EGF-induced neoplastic cell transformation and colon cancer growth. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 18763–18773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, M.D.; Yao, C.J.; Chow, J.M.; Chang, C.L.; Hwang, P.A.; Chuang, S.E.; Whang-Peng, J.; Lai, G.M. Fucoidan Elevates MicroRNA-29b to Regulate DNMT3B-MTSS1 Axis and Inhibit EMT in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6099–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fukahori, S.; Yano, H.; Akiba, J.; Ogasawara, S.; Momosaki, S.; Sanada, S.; Kuratomi, K.; Ishizaki, Y.; Moriya, F.; Yagi, M.; et al. Fucoidan, a major component of brown seaweed, prohibits the growth of human cancer cell lines in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 2008, 1, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Riby, J.E.; Conde, L.; Grizzle, W.E.; Cui, X.; Skibola, C.F. A Fucus vesiculosus extract inhibits estrogen receptor activation and induces cell death in female cancer cell lines. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathew, L.; Burney, M.; Gaikwad, A.; Nyshadham, P.; Nugent, E.K.; Gonzalez, A.; Smith, J.A. Preclinical Evaluation of Safety of Fucoidan Extracts From Undaria pinnatifida and Fucus vesiculosus for Use in Cancer Treatment. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burney, M.; Mathew, L.; Gaikwad, A.; Nugent, E.K.; Gonzalez, A.O.; Smith, J.A. Evaluation Fucoidan Extracts From Undaria pinnatifida and Fucus vesiculosus in Combination With Anticancer Drugs in Human Cancer Orthotopic Mouse Models. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choo, G.S.; Lee, H.N.; Shin, S.A.; Kim, H.J.; Jung, J.Y. Anticancer Effect of Fucoidan on DU-145 Prostate Cancer Cells through Inhibition of PI3K/Akt and MAPK Pathway Expression. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boo, H.J.; Hong, J.Y.; Kim, S.C.; Kang, J.I.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, E.J.; Hyun, J.W.; Koh, Y.S.; Yoo, E.S.; Kwon, J.M.; et al. The anticancer effect of fucoidan in PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2982–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, H.Y.; Kim, G.Y.; Moon, S.K.; Kim, W.J.; Yoo, Y.H.; Choi, Y.H. Fucoidan inhibits the proliferation of human urinary bladder cancer T24 cells by blocking cell cycle progression and inducing apoptosis. Molecules 2014, 19, 5981–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strzalka, W.; Ziemienowicz, A. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA): A key factor in DNA replication and cell cycle regulation. Ann. Bot. 2011, 107, 1127–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atashrazm, F.; Lowenthal, R.M.; Woods, G.M.; Holloway, A.F.; Karpiniec, S.S.; Dickinson, J.L. Fucoidan Suppresses the Growth of Human Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.H.; Lee, D.S.; Jeong, J.W.; Hong, S.H.; Choi, I.W.; Cha, H.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.S.; Park, C.; Kim, G.Y.; et al. Fucoidan Induces ROS-Dependent Apoptosis in 5637 Human Bladder Cancer Cells by Downregulating Telomerase Activity via Inactivation of the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Drug Dev. Res. 2017, 78, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Teng, H.; Liu, Z.; Yang, W.; Hou, L.; Zou, X. Fucoidan derived from Undaria pinnatifida induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells via the ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1961–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopez, J.; Tait, S.W.G. Mitochondrial apoptosis: Killing cancer using the enemy within. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinton, P.; Giorgi, C.; Siviero, R.; Zecchini, E.; Rizzuto, R. Calcium and apoptosis: ER-mitochondria Ca2+ transfer in the control of apoptosis. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6407–6418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azimi, I.; Roberts-Thomson, S.J.; Monteith, G.R. Calcium influx pathways in breast cancer: Opportunities for pharmacological intervention. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 945–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.G.; Pathan, N.; Ethell, I.M.; Krajewski, S.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Shibasaki, F.; McKeon, F.; Bobo, T.; Franke, T.F.; Reed, J.C. Ca2+-induced apoptosis through calcineurin dephosphorylation of BAD. Science 1999, 284, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diver, J.M.; Sage, S.O.; Rosado, J.A. The inositol trisphosphate receptor antagonist 2-aminoethoxydiphenylborate (2-APB) blocks Ca2+ entry channels in human platelets: Cautions for its use in studying Ca2+ influx. Cell Calcium 2001, 30, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Z.; Zeng, F.; Boulay, G.; Grimm, C.; Harteneck, C.; Beech, D.J. Block of TRPC5 channels by 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate: A differential, extracellular and voltage-dependent effect. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 145, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsien, R.Y. New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons: Design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry 1980, 19, 2396–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Chow, S.C.; Nicotera, P.; Orrenius, S. Intracellular Ca2+ signals activate apoptosis in thymocytes: Studies using the Ca2+-ATPase inhibitor thapsigargin. Exp. Cell Res. 1994, 212, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Tripathy, A.; Pasek, D.A.; Meissner, G. Ruthenium red modifies the cardiac and skeletal muscle Ca2+ release channels (ryanodine receptors) by multiple mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 32680–32691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gordeeva, A.V.; Zvyagilskaya, R.A.; Labas, Y.A. Cross-talk between reactive oxygen species and calcium in living cells. Biochemistry 2003, 68, 1077–1080. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gorlach, A.; Bertram, K.; Hudecova, S.; Krizanova, O. Calcium and ROS: A mutual interplay. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, Y.; Cho, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Yu, S.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, C.Y.; Yoon, J.H. Fucoidan-induced ID-1 suppression inhibits the in vitro and in vivo invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.S.; Kim, G.Y.; Nam, T.J.; Kim, N.D.; Choi, Y.H. Antiproliferative Activity of Fucoidan Was Associated with the Induction of Apoptosis and Autophagy in AGS Human Gastric Cancer Cells. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, T77–T83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosshauer, P.W.; Li, W.; Lin, K.T.; Chan, J.L.; Wang, L.H. Rapamycin by itself and additively in combination with carboplatin inhibits the growth of ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol. Oncol. 2009, 114, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osaki, M.; Oshimura, M.; Ito, H. PI3K-Akt pathway: Its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis 2004, 9, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Teruya, K.; Yoshida, T.; Eto, H.; Shirahata, S. Fucoidan extract enhances the anti-cancer activity of chemotherapeutic agents in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, M.; Ji, X.; Xue, C.; Liang, H.; Ge, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Bian, K.; Zhang, L. Caspase-dependent and caspase-independent induction of apoptosis in breast cancer by fucoidan via the PI3K/AKT/GSK3beta pathway in vivo and in vitro. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.E.; Choi, E.S.; Shin, J.A.; Lee, S.O.; Park, K.S.; Cho, N.P.; Cho, S.D. Fucoidan induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in MC3 human mucoepidermoid carcinoma cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 7, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.Y.; Lin, T.Y.; Hu, C.H.; Shu, D.T.F.; Lu, M.K. Fucoidan upregulates TLR4/CHOP-mediated caspase-3 and PARP activation to enhance cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in human lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2018, 432, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larman, M.; Lucy, J. The endoplasmic reticulum: Structure and function. Mol. Membr. Biol. 1999, 16, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D. Fucoidan induces cancer cell apoptosis by modulating the endoplasmic reticulum stress cascades. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, N.; Yano, H.; Nishida, T.; Kamura, T.; Kojiro, M. Angiogenesis in cancer. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2006, 2, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Hsu, W.L.; Hwang, P.A.; Chou, T.C. Low Molecular Weight Fucoidan Inhibits Tumor Angiogenesis through Downregulation of HIF-1/VEGF Signaling under Hypoxia. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4436–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.H.; Chiu, Y.H.; Chan, Y.L.; Chiu, Y.H.; Wang, H.; Huang, K.C.; Li, T.L.; Hsu, K.H.; Wu, C.J. Prophylactic administration of fucoidan represses cancer metastasis by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in Lewis tumor-bearing mice. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1882–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Primary Antibodies | Dilution | Supplier | Catalog Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phospho-Cyclin D1 (Thr286) | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 3300 |
| Cyclin D1 | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 2922 |
| Phospho-AKT (SER473) | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 4060 |
| AKT | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 9272 |
| Phospho-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204) | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 9101 |
| ERK1/2 | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 4695 |
| Phospho-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 4668 |
| JNK | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 9252 |
| Phospho-P38 (Thr180/Tyr182) | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 4511 |
| P38 | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 9212 |
| Phospho-P70S6K (Thr421/Ser424) | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 9204 |
| P70S6K | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 9202 |
| Phospho-S6 (Ser235/236) | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 2211 |
| S6 | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 2217 |
| IRE1α | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 3294 |
| ATF6α | 1:1000 | Santa Cruz | sc-166659 |
| Phospho-PERK (Thr981) | 1:1000 | Santa Cruz | sc-32577 |
| PERK | 1:1000 | Santa Cruz | sc-13073 |
| Phospho-eIF2α (Ser51) | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 3398 |
| eIF2α | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 5324 |
| GADD153 | 1:1000 | Santa Cruz | sc-7351 |
| GRP78 | 1:1000 | Santa Cruz | sc-13968 |
| VDAC | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 4661 |
| IP3R1 | 1:1000 | Invitrogen | PA1-901 |
| IP3R2 | 1:1000 | Santa Cruz | sc-398434 |
| GRP75 | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 3593 |
| MFN2 | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 11925 |
| VAPB | 1:1000 | Invitrogen | PA5-53023 |
| LC3B | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 3868 |
| BECN1 | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 3495 |
| ATG5 | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 12994 |
| Cleaved caspase-3 | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 9664 |
| Cleaved caspase-9 | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 9501 |
| Cytochrome c | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling | 11940 |
| TUBA | 1:2000 | Santa Cruz | sc-5286 |
| PCNA | 1:100 | Santa Cruz | sc-56 |
| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′ → 3′) | Size (bp) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | VEGFA (AF022375.1) | Forward | TTGTACAAGATCCGCAGACG | 100 |
| Reverse | TCACATCTGCAAGTACGTTCG | |||
| VEGFB (BC008818.2) | Forward | CAGAGGAAAGTGGTGTCATGG | 90 | |
| Reverse | CATGAGCTCCACAGTCAAGG | |||
| VEGFC (NM_005429.5) | Forward | ATGTGGGGAAGGAGTTTGG | 94 | |
| Reverse | CCCTCACTATTGCAGCAACC | |||
| VEGFD (NM_004469.5) | Forward | TGTAAGTGCTTGCCAACAGC | 96 | |
| Reverse | TTTCTTGGAATGGGAACAGC | |||
| FLT1 (AF063657.2) | Forward | ATGGTCTTTGCCTGAAATGG | 135 | |
| Reverse | TAGAAGCCAGTGTGGTTTGC | |||
| FLT4 (AY233383.1) | Forward | GTACATGCCAACGACACAGG | 131 | |
| Reverse | TCAGGCTTGTTGATGAATGG | |||
| KDR (AF063658.1) | Forward | ACCCACGTTTTCAGAGTTGG | 124 | |
| Reverse | TCCAGAATCCTCTTCCATGC | |||
| GAPDH (BT006893.1) | Forward | GGCTCTCCAGAACATCATCC | 149 | |
| Reverse | TTTCTAGACGGCAGGTCAGG | |||
| Zebrafish | p53 (NM_001271820.1) | Forward | GCTTGTCACAGGGGTCATTT | 94 |
| Reverse | ACAAAGGTCCCAGTGGAGTG | |||
| casp3 (NM_131877.3) | Forward | AAAGGATCCCAGTGGAGGCAGATT | 131 | |
| Reverse | TGGTCATGATCTGCAAGAGCTCCA | |||
| casp8 (NM_131510.2) | Forward | AGAGAAGGGCACAGTTTTGG | 140 | |
| Reverse | CCTGGTTCTCATCTCCTTGG | |||
| casp9 (NM_001007404.2) | Forward | CTGCTGTGTGGTCATCATCC | 134 | |
| Reverse | GACAGTTCTGGCCATTGAGG | |||
| vegfaa (AF016244.1) | Forward | ATTCATACCCAGCAGCTTCG | 137 | |
| Reverse | GCAGACAGATGGAGGAGAGC | |||
| vegfc (AF466147.1) | Forward | GATGTGGGGAAAGAGTTTGG | 112 | |
| Reverse | TGATGTTCCTGCACTGAAGC | |||
| flt1 (BC139515.1) | Forward | CTGGTTATTCGGGATGTTGC | 121 | |
| Reverse | TTTGGGGCTTCACATTTACC | |||
| flt4 (AY833404.1) | Forward | TCACAACTGGATGGATTTGG | 100 | |
| Reverse | GCCGACAGTCTTTTCTTTGC | |||
| kdr (NM_001024653.2) | Forward | CTTGGCAGCCAGAAATATCC | 116 | |
| Reverse | GACGAGCATCTCCTTTACGG | |||
| kdrl (NM_131472.1) | Forward | CCTGATCCACAACTGCTTCC | 142 | |
| Reverse | CACACGACTCAATGCGTACC | |||
| gapdh (BC083506.1) | Forward | TGCTGGTATTGCTCTCAACG | 93 | |
| Reverse | GCCATCAGGTCACATACACG | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Yang, C.; Song, G.; Lim, W. Fucoidan Derived from Fucus vesiculosus Inhibits the Development of Human Ovarian Cancer via the Disturbance of Calcium Homeostasis, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Angiogenesis. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18010045
Bae H, Lee J-Y, Yang C, Song G, Lim W. Fucoidan Derived from Fucus vesiculosus Inhibits the Development of Human Ovarian Cancer via the Disturbance of Calcium Homeostasis, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Angiogenesis. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(1):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18010045
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Hyocheol, Jin-Young Lee, Changwon Yang, Gwonhwa Song, and Whasun Lim. 2020. "Fucoidan Derived from Fucus vesiculosus Inhibits the Development of Human Ovarian Cancer via the Disturbance of Calcium Homeostasis, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Angiogenesis" Marine Drugs 18, no. 1: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18010045
APA StyleBae, H., Lee, J. -Y., Yang, C., Song, G., & Lim, W. (2020). Fucoidan Derived from Fucus vesiculosus Inhibits the Development of Human Ovarian Cancer via the Disturbance of Calcium Homeostasis, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Angiogenesis. Marine Drugs, 18(1), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18010045






