Comprehensive Assessment of Nile Tilapia Skin (Oreochromis niloticus) Collagen Hydrogels for Wound Dressings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
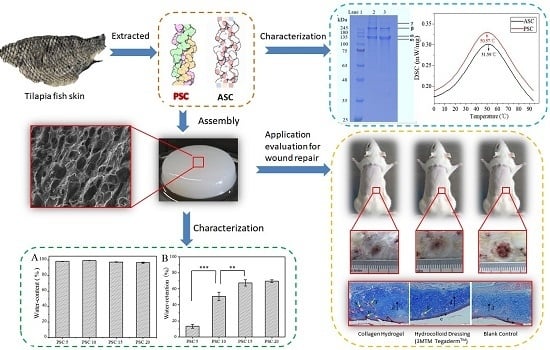
2.1. Extraction and Characterization of ASC and PSC
2.2. Water Content and Water Retention Ratio of Collagen Hydrogels
2.3. Rheological Characterization of Collagen Hydrogels
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) of Collagen Hydrogels
2.5. Cytotoxicity of Collagen Hydrogels
2.6. Healing of Deep Second-Degree Burn of Rat Skin
2.7. Histological Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Extraction and Characterization of ASC and PSC
3.3. Preparation and Characterization of Collagen Hydrogel
3.4. Cytotoxicity Characterization
3.5. Animal Experiments
3.6. Histological Analysis
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, J.; Pan, B.-H.; Wang, K.-A.; Li, H.-H.; Wu, G.-S.; Fang, H.; Zhu, F.; Sheng, J.-J.; Liu, G.-C.; Zhu, B.-H. Micro-Negative Pressure Drainage Dressing: A Substitute for Surgical Treatment of Refractory Wounds after Burns. 2019. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3487708 (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- Virador, G.M.; de Marcos, L.; Virador, V.M. Skin wound healing: Refractory wounds and novel solutions. In Skin Stem Cells; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 221–241. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, G.D. Formation of the scab and the rate of epithelisation of superficial wounds in the skin of the young domestic pig. 1962. J. Wound Care 1995, 193, 366–367. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Lin, Q.; Gong, P.; Ma, L.; Yang, S. A Novel Wound Dressing Based on Ag/Graphene Polymer Hydrogel: Effectively Kill Bacteria and Accelerate Wound Healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3933–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, K.; Banthia, A.K.; Majumdar, D.K. Biomedical evaluation of polyvinyl alcohol—Gelatin esterified hydrogel for wound dressing. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokabi, M.; Sirousazar, M.; Hassan, Z.M. PVA—Clay nanocomposite hydrogels for wound dressing. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, M. Review: Evidence on the effectiveness of honey for healing wounds is limited. Evid. Based Nurs. 2009, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvipriya, K.; Kumar, K.K.; Bhat, A.; Kumar, B.D.; John, A.; Lakshmanan, P. Collagen: Animal sources and biomedical application. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gelse, K.; PoSchl, E.; Aigner, T. Collagens—Structure, function, and biosynthesis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1531–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neel, E.A.A.; Bozec, L.; Knowles, J.C.; Syed, O.; Mudera, V.; Day, R.; Hyun, J.K. Collagen—Emerging collagen based therapies hit the patient. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 429–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeugolis, D.I.; Paul, G.R.; Attenburrow, G. Cross-linking of extruded collagen fibers—A biomimetic three-dimensional scaffold for tissue engineering applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A Off. J. Soc. Biomater. Jpn. Soc. Biomater. Aust. Soc. Biomater. Korean Soc. Biomater. 2009, 89, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenteau-Bareil, R.; Gauvin, R.; Berthod, F. Collagen-based biomaterials for tissue engineering applications. Materials 2010, 3, 1863–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gopinath, D. Dermal wound healing processes with curcumin incorporated collagen films. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Singla, A.Y. Biomedical applications of collagen. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 221, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeugolis, D.I.; Attenburrow, R.G.P. Extruded Collagen-Polyethylene Glycol Fibers for Tissue Engineering Applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 85B, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.; Hudson, A.; Shiwarski, D.; Tashman, J.; Hinton, T.; Yerneni, S.; Bliley, J.; Campbell, P.; Feinberg, A. 3D bioprinting of collagen to rebuild components of the human heart. Science 2019, 365, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Zhang, L.; Li, K.; Fan, H.; Fan, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhang, X. Collagen hydrogel as an immunomodulatory scaffold in cartilage tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2014, 102, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.; Koh, R.H.; Shim, W.; Kim, H.D.; Yim, H.-G.; Hwang, N.S. Riboflavin-induced photo-crosslinking of collagen hydrogel and its application in meniscus tissue engineering. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2016, 6, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piez, K.A. Hierarchical structure and assembly of type I collagen. In The Protein Folding Problem; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2019; pp. 47–63. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, L.C.; Peng, B.Y.; Chen, M.S.; Thalib, B.; Ruslin, M.; Tung, T.D.X.; Chou, H.H.; Ou, K.L. The potential of the stem cells composite hydrogel wound dressings for promoting wound healing and skin regeneration: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2019, 107, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desimone, M.F.; Hélary, C.; Mosser, G.; Giraudguille, M.M.; Livage, J.; Coradin, T. Fibroblast encapsulation in hybrid silica–collagen hydrogels. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 666–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdick, J.A.; Prestwich, G.D. Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, H41–H56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, B.; Kundu, S.C. Silk sericin/polyacrylamide in situ forming hydrogels for dermal reconstruction. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7456–7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnavi, S.; di Blasio, L.; Tonda-Turo, C.; Mancardi, A.; Primo, L.; Ciardelli, G.; Gambarotta, G.; Geuna, S.; Perroteau, I. Gelatin-based hydrogel for vascular endothelial growth factor release in peripheral nerve tissue engineering. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 11, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Avila Rodriguez, M.I.; Rodriguez Barroso, L.G.; Sánchez, M.L. Collagen: A review on its sources and potential cosmetic applications. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongjareonrak, A.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Nagai, T.; Tanaka, M. Isolation and characterisation of acid and pepsin-solubilised collagens from the skin of Brownstripe red snapper (Lutjanus vitta). Food Chem. 2006, 93, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, D.; Vierros, M.; Hamon, G.; Arico, S.; Monagle, C. Marine genetic resources: A review of scientific and commercial interest. Mar. Policy 2009, 33, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Benjakul, S.; Maqsood, S.; Kishimura, H. Isolation and characterisation of collagen extracted from the skin of striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus). Food Chem. 2011, 124, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, M.; Qiao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, J.; Qin, S.; Wu, W. Extraction and characterization of type I collagen from skin of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and its potential application in biomedical scaffold material for tissue engineering. Process Biochem. 2018, 74, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.K.; Zhang, C.-H.; Lin, H.; Yang, P.; Hong, P.-Z.; Jiang, Z. Isolation and characterisation of acid-solubilised collagen from the skin of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Food Chem. 2009, 116, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potaros, T.; Raksakulthai, N.; Runglerdkreangkrai, J.; Worawattanamateekul, W. Characteristics of collagen from nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) skin isolated by two different methods. Nat. Sci. 2009, 43, 584–593. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Jeevithan, E.; Bao, B.; Wang, S.; Gao, K.; Zhang, C.; Wu, W. Structural characterization, in-vivo acute systemic toxicity assessment and in-vitro intestinal absorption properties of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) skin acid and pepsin solublilized type I collagen. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Igawa, K.; Sugimoto, K.; Yoshizawa, Y.; Yanagiguchi, K.; Ikeda, T.; Yamada, S.; Hayashi, Y. Biological Safety of Fish (Tilapia) Collagen. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Rashidy, A.A.; Gad, A.; Abu-Hussein, E.H.G.; Habib, S.I.; Badr, N.A.; Hashem, A.A. Chemical and biological evaluation of Egyptian Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticas) fish scale collagen. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, N.; Xue, Y.; Ding, T.; Liu, X.; Mo, X.; Sun, J. Development of Biomimetic Tilapia Collagen Nanofibers for Skin Regeneration through Inducing Keratinocytes Differentiation and Collagen Synthesis of Dermal Fibroblasts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 3253–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrobak, K.M.; Potter, D.R.; Tien, J. Formation of perfused, functional microvascular tubes in vitro. Microvasc. Res. 2006, 71, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Hou, H. Novel hard capsule prepared by tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) scale gelatin and konjac glucomannan: Characterization, and in vitro dissolution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 206, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.-K.; Liu, D.; Sun, L.-L.; Li, B.-F.; Hou, H. Physicochemical and biocompatibility properties of type I collagen from the skin of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) for biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cross, V.L.; Zheng, Y.; Choi, N.W.; Verbridge, S.S.; Sutermaster, B.A.; Bonassar, L.J.; Fischbach, C.; Stroock, A.D. Dense type I collagen matrices that support cellular remodeling and microfabrication for studies of tumor angiogenesis and vasculogenesis in vitro. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8596–8607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, M.S.S.; Nazeer, R.A. Characterization of Acid and Pepsin Soluble Collagen from the Skin of Horse Mackerels (Magalaspis cordyla) and Croaker (Otolithes ruber). Int. J. Food Prop. 2013, 16, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muyonga, J.; Cole, C.; Duodu, K. Characterisation of acid soluble collagen from skins of young and adult Nile perch (Lates niloticus). Food Chem. 2004, 85, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H. Effect of heat treatment on the enzymatic stability of grass carp skin collagen and its ability to form fibrils in vitro. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Lin, W.; He, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Ma, H. Hydrolysis kinetics and antioxidant activity of collagen under simulated gastrointestinal digestion. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 11, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Melacini, G.; Taulane, J.P.; Goodman, M. Acetyl-Terminated and Template-Assembled Collagen-Based Polypeptides Composed of Gly-Pro-Hyp Sequences. 2. Synthesis and Conformational Analysis by Circular Dichroism, Ultraviolet Absorbance, and Optical Rotation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 10351–10358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruylants, G.; Wouters, J.; Michaux, C. Differential scanning calorimetry in life science: Thermodynamics, stability, molecular recognition and application in drug design. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 2011–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kozlowska, J.; Sionkowska, A.; Skopinska-Wisniewska, J.; Piechowicz, K. Northern pike (Esox lucius) collagen: Extraction, characterization and potential application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, L.; Wu, Z.; Wangb, Y.; Ding, L.; Wang, Y. Role of pH-induced structural change in protein aggregation in foam fractionation of bovine serum albumin. Biotechnol. Rep. 2016, 9, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Veis, A. The self-assembly of collagen molecules. Biopolymers 1973, 12, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreger, S.; Bell, B.; Bailey, J.; Stites, E.; Kuske, J.; Waisner, B.; Voytik-Harbin, S. Polymerization and matrix physical properties as important design considerations for soluble collagen formulations. Biopolym. Orig. Res. Biomol. 2010, 93, 690–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozza, N.; Bonani, W.; Motta, A.; Migliaresi, C. Evaluation of alternative sources of collagen fractions from Loligo vulgaris squid mantle. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 87, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, A.; Yannas, I.; Bonfield, W. Antigenicity and immunogenicity of collagen. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. Off. J. Soc. Biomater. Jpn. Soc. Biomater. Aust. Soc. Biomater. Korean Soc. Biomater. 2004, 71, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Jin, S.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, F.; Yang, Z.; Yu, F.; Ding, G. Physicochemical properties and biocompatibility evaluation of collagen from the skin of giant croaker (Nibea japonica). Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, M.; Jiang, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Xu, H.; An, X.; Li, Y. Preparation of self-assembled collagen fibrillar gel from tilapia skin and its formation in presence of acidic polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 2020, 115831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrana, N.; Builles, N.; Kocak, H.; Gulay, P.; Justin, V.; Malbouyres, M.; Ruggiero, F.; Damour, O.; Hasirci, V. EDC/NHS cross-linked collagen foams as scaffolds for artificial corneal stroma. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2007, 18, 1527–1545. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Phaechamud, T.; Issarayungyuen, P.; Pichayakorn, W. Gentamicin Sulfate-Loaded Porous Natural Rubber Films for Wound Dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 85, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Hirota, N.; Okuda, M.; Takeguchi, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Hanagata, N.; Ikoma, T. Microstructures and rheological properties of tilapia fish-scale collagen hydrogels with aligned fibrils fabricated under magnetic fields. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velegol, D.; Lanni, F. Cell traction forces on soft biomaterials. I. Microrheology of type I collagen gels. Biophys. J. 2001, 81, 1786–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.S.; Park, B.S.; Sung, J.H.; Yang, J.M.; Park, S.B.; Kwak, S.J.; Park, J.S. Wound healing effect of adipose-derived stem cells: A critical role of secretory factors on human dermal fibroblasts. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2007, 48, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.; Benditt, E.P. Wound Healing and Collagen Formation. IV. Distortion of Ribosomal Patterns of Fibroblasts in Scurvy. J. Cell Biol. 1964, 22, 365–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montesano, R.; Orci, L. Transforming growth factor beta stimulates collagen-matrix contraction by fibroblasts: Implications for wound healing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 4894–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helary, C.; Zarka, M.; Giraud-Guille, M.M. Fibroblasts within concentrated collagen hydrogels favour chronic skin wound healing. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2012, 6, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, P.; Zhou, C.; Li, S.; Hong, P. Marine collagen peptides from the skin of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): Characterization and wound healing evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandevord, P.J.; Matthew, H.W.T.; Desilva, S.P.; Lois, M.; Bin, W.; Wooley, P.H. Evaluation of the biocompatibility of a chitosan scaffold in mice. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2010, 59, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Hou, H.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of acid- and pepsin-soluble collagen extracted from the skin of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Pei, X.; Liu, H.; Zhou, D. Extraction and characterization of acid-soluble and pepsin-soluble collagen from skin of loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, R.M.T.; Neto, R.G.C.; Paschoal, C.W.A.; Rohling, J.H.; Bezerra, C.W.B. Collagen films from swim bladders: Preparation method and properties. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 62, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Du, Z.; Qin, S. Preparation and characterization of novel poly (vinyl alcohol)/collagen double-network hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Q.; Wu, M.; Shen, Y. Enhanced swelling ratio and water retention capacity for novel super-absorbent hydrogel. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 583, 123972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Bulcke, A.I.; Bogdanov, B.; De Rooze, N.; Schacht, E.H.; Cornelissen, M.; Berghmans, H. Structural and rheological properties of methacrylamide modified gelatin hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2000, 1, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiocco, L.; Li, S.; Stevens, M.M.; Bernardo, E.; Jones, J.R. Biocompatibility and bioactivity of porous polymer-derived Ca-Mg silicate ceramics. Acta Biomater. 2017, 50, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, B.; Dong, X.; Duan, L.; Tian, H.; He, C.; Chen, X. Injectable polysaccharide hybrid hydrogels as scaffolds for burn wound healing. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 94248–94256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, C.C.; Whaley, D.; Babu, R.; Zhang, J.; Krishna, P.; Beckman, E.; Pasculle, A.W.; Wells, A. The effect of multifunctional polymer-based gels on wound healing in full thickness bacteria-contaminated mouse skin wound models. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 3977–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Region | Peak Wavenumber (cm−1) | Assignment | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASC | PSC | ||
| Amide A | 3336.25 | 3343.96 | NH stretch coupled with hydrogen bond |
| Amide B | 2942.84 | 2927.41 | CH2 symmetrical stretch |
| Amide I | 1660.41 | 1658.48 | C=O stretch/hydrogen bond coupled with COO− |
| Amide II | 1552.42 | 1554.34 | NH bend coupled with CN stretch |
| Amide III | 1241.93 | 1241.93 | NH bend coupled with CN stretch |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, B.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, N.; Qin, S. Comprehensive Assessment of Nile Tilapia Skin (Oreochromis niloticus) Collagen Hydrogels for Wound Dressings. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18040178
Ge B, Wang H, Li J, Liu H, Yin Y, Zhang N, Qin S. Comprehensive Assessment of Nile Tilapia Skin (Oreochromis niloticus) Collagen Hydrogels for Wound Dressings. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(4):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18040178
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Baosheng, Haonan Wang, Jie Li, Hengheng Liu, Yonghao Yin, Naili Zhang, and Song Qin. 2020. "Comprehensive Assessment of Nile Tilapia Skin (Oreochromis niloticus) Collagen Hydrogels for Wound Dressings" Marine Drugs 18, no. 4: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18040178
APA StyleGe, B., Wang, H., Li, J., Liu, H., Yin, Y., Zhang, N., & Qin, S. (2020). Comprehensive Assessment of Nile Tilapia Skin (Oreochromis niloticus) Collagen Hydrogels for Wound Dressings. Marine Drugs, 18(4), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18040178