Biochemical and Genomic Characterization of the Cypermethrin-Degrading and Biosurfactant-Producing Bacterial Strains Isolated from Marine Sediments of the Chilean Northern Patagonia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
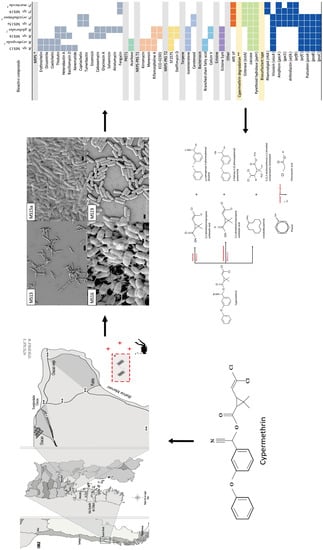
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Marine Bacterial Strains
2.2. Surfactant-Producing Bacteria
2.3. SEM Studies
2.4. Genome Characterization of Selected Strains
2.5. Identification of Secondary Metabolites and Detection of Genes Involved in Cypermethrin Catabolism in MS13, MS15, MS16, and MS19 Marine Bacterial Strains, and Comparison with Reference Strains
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling Site
4.2. Culture Conditions
4.3. Isolation of Bacterial Strains from Cypermethrin-Contaminated Marine Sediments
4.4. 16S rDNA Gene Sequencing
4.5. Determination of Emulsion Index (E24)
4.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.8. Genome Sequencing and Sequence Information
4.9. Identification of Secondary Metabolites, and Detection of Genes Involved in Cypermethrin Catabolism in MS13, MS15a, MS16, and MS19 Bacterial Marine Strains and a Subsequent Comparison with Reference Strains
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bravo, S.; Silva, M.T.; Agustí, C.; Sambra, K.; Horsberg, T.E. The effect of chemotherapeutic drugs used to control sea lice on the hatching viability of egg strings from Caligus rogercresseyi. Aquaculture 2015, 443, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucca, F.; Moya, H.; Pozo, K.; Borghini, F.; Focardi, S.; Barra, R. Occurrence of antiparasitic pesticides in sediments near salmon farms in the Northern Chilean Patagonia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poley, J.D.; Braden, L.M.; Messmer, A.M.; Whyte, S.; Koop, B.F.; Fast, M.D. Cypermethrin exposure induces metabolic and stress-related gene expression in copepodid salmon lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2016, 20, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Jia, L.; Wang, S.; Qu, J.; Li, K.; Xu, L.; Shi, Y.; Yan, Y. Biodegradation of beta-cypermethrin by two Serratia spp. with different cell surface hydrophobicity. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 3423–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). The WHO Recommended Classification of Pesticides by Hazardand Guidelines to Classification 2009; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009; Volume 61. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, S.; Zuberi, A.; Alagawany, M.; Farag, M.; Dadar, M.; Karthik, K.; Tiwari, R.; Dhama, K.; Iqbal, H.M. Cypermethrin induced toxicities in fish and adverse health outcomes: Its prevention and control measure adaptation. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, S.; Das, M.T.; Thakur, I.S. Biodegradation of cypermethrin by Bacillus sp. in soil microcosm and in-vitro toxicity evaluation on human cell line. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 77, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navia, R.; Seeger, M. (Eds.) Biorremediación de Suelos Contaminados con Compuestos Orgánicos Persistentes (COPs); Ediciones Universidad de La Frontera: Temuco, Chile, 2006; 225p, ISBN 956-236-170-5. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes, S.; Méndez, V.; Aguila, P.; Seeger, M. Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons: Catabolic genes, microbial communities, and applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 4781–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, J.M.; Acevedo, F.; González, M.; Seeger, M. Mineralization of PCBs by the genetically modified strain Cupriavidus necator JMS34 and its application for bioremediation of PCBs in soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.; Sultan, S.; Kertesz, M. Determination of Cypermethrin Degradation Potential of Soil Bacteria Along with Plant Growth-Promoting Characteristics. Curr. Microbiol. 2014, 70, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boricha, H.; Fulekar, M. Pseudomonas plecoglossicida as a novel organism for the bioremediation of cypermethrin. Biol. Med. 2009, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Luo, J.; Hu, M.; Lai, K.; Geng, P.; Huang, H. Enhancement of cypermethrin degradation by a coculture of Bacillus cereus ZH-3 and Streptomyces aureus HP-S-01. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, K. Isolation and Characterization of Cypermethrin Degrading Bacteria Screened from Contaminated Soil. In Biodegradation of Hazardous and Special Products; Chamy, R., Ed.; IntechOpen: Valparaíso, Chile, 2013; ISBN 978-953-51-1155-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gür, Ö.; Ozdal, M.; Algur, O.F. Biodegradation of the synthetic pyrethroid insecticide α-cypermethrin by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia OG2. Turk. J. Boil. 2014, 38, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chi, Y.; Wu, S.; Jia, D.; Yao, K. Simultaneous Degradation of Cypermethrin and Its Metabolite, 3-Phenoxybenzoic Acid, by the Cooperation of Bacillus licheniformis B-1 and Sphingomonas sp. SC-1. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 8256–8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangola, S.; Sharma, A.; Bhatt, P.; Khati, P.; Chaudhary, P. Presence of esterase and laccase in Bacillus subtilis facilitates biodegradation and detoxification of cypermethrin. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, Y.-S.; You, A.-Y.; Choi, Y.-L. Biological degradation of cypermethrin by marine bacteria, Cellulophaga lytica DAU203. J. Life Sci. 2018, 28, 483–487. [Google Scholar]
- Pacwa-Płociniczak, M.; Płaza, G.A.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z.; Cameotra, S.S. Environmental Applications of Biosurfactants: Recent Advances. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 633–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasowska, A.; Sigler, K. How microorganisms use hydrophobicity and what does this mean for human needs? Front. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tripathi, L.; Irorere, V.; Marchant, R.; Banat, I.M. Marine derived biosurfactants: A vast potential future resource. Biotechnol. Lett. 2018, 40, 1441–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Yin, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Luo, X.; Cheng, J.; Cheng, F.; Dai, J. Cometabolic biotransformation of fenpropathrin by Clostridium species strain ZP3. Biodegradation 2010, 22, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.; Huang, Y.; Zhan, H.; Chen, S. Insight into Microbial Applications for the Biodegradation of Pyrethroid Insecticides. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Huang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. New insights into the microbial degradation and catalytic mechanism of synthetic pyrethroids. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Koh, H.-W.; Kim, H.; Chae, J.-C.; Park, S.-J. Microbial Community Composition in the Marine Sediments of Jeju Island: Next-Generation Sequencing Surveys. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Floris, R.; Rizzo, C.; Giudice, A.L. Biosurfactants from Marine Microorganisms. Bacteriology 2018, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Techaoei, S.; Leelapornpisid, P.; Santiarwarn, D.; Lumyong, S. Preliminary screening of biosurfactant producing microorganisms isolated from hot spring and garages in northern Thailand. KMITL Sci. Tech. J. 2007, 7, S1. [Google Scholar]
- Borah, D.; Yadav, R. Bioremediation of petroleum based contaminants with biosurfactant produced by a newly isolated petroleum oil degrading bacterial strain. Egypt. J. Pet. 2017, 26, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elsayed, Y.; Refaat, J.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Fouad, M.A. The Genus Rhodococcus as a source of novel bioactive substances: A review. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2017, 6, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Romanenko, L.A.; Tanaka, N.; Svetashev, V.I.; Mikhailov, V.V. Pseudomonas glareae sp. nov., a marine sediment-derived bacterium with antagonistic activity. Arch. Microbiol. 2015, 197, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Undabarrena, A.; Salvà-Serra, F.; Jaén-Luchoro, D.; Castro-Nallar, E.; Mendez, K.; Valencia, R.; Ugalde, J.; Moore, E.; Seeger, M.; Cámara, B. Complete genome sequence of the marine Rhodococcus sp. H-CA8f isolated from Comau fjord in Northern Patagonia, Chile. Mar. Genom. 2018, 40, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, M.; Ito, K.; Nakajima, N.; Yamamura, S.; Tomita, M.; Suzuki, H.; Amachi, S. Genomic Analysis of Pseudomonas sp. Strain SCT, an Iodate-Reducing Bacterium Isolated from Marine Sediment, Reveals a Possible Use for Bioremediation. Genes Genomes Genet. 2019, 9, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceniceros, A.; Dijkhuizen, L.; Petrusma, M.; Medema, M.H. Genome-based exploration of the specialized metabolic capacities of the genus Rhodococcus. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Steinke, K.; Villebro, R.; Ziemert, N.; Lee, S.Y.; Medema, M.H.; Weber, T. antiSMASH 5.0: Updates to the secondary metabolite genome mining pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W81–W87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Guo, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, B.; Sun, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Chemistry and Biology of Siderophores from Marine Microbes. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.-Z.; Guo, P.; Hang, B.-J.; Li, L.; He, J.; Li, S.-P. Cloning of a Novel Pyrethroid-Hydrolyzing Carboxylesterase Gene from Sphingobium sp. Strain JZ-1 and Characterization of the Gene Product. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5496–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chun, C.; Paine, R.; Sowers, K.; May, H. Electrical stimulation of microbial PCB degradation in sediment. Water Res. 2013, 47, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Chi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jia, D.; Yao, K. Co-metabolic degradation of β-cypermethrin and 3-phenoxybenzoic acid by coculture of Bacillus liqueniformis B-1 and Aspergillus oryzae M-4. PLoS ONE 2016, 29, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Shraddha; Shekher, R.; Sehgal, S.; Kamthania, M.; Kumar, A. Laccase: Microbial Sources, Production, Purification, and Potential Biotechnological Applications. Enzym. Res. 2011, 2011, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubicki, S.; Bollinger, A.; Katzke, N.; Jaeger, K.-E.; Loeschcke, A.; Thies, S. Marine Biosurfactants: Biosynthesis, Structural Diversity and Biotechnological Applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shabtai, Y.; Gutnick, D.L. Tolerance of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus RAG-1 to the cationic surfactant cetyltrimethylammonium bromide: Role of the bioemulsifier emulsan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maza, F.; Maldonado, J.; Vásquez-Dean, J.; Mandakovic, D.; Gaete, A.; Cambiazo, V.; González, M. Soil Bacterial Communities from the Chilean Andean Highlands: Taxonomic Composition and Culturability. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, F.M.; Camargo, F.A.D.O.; Okeke, B.C.; Frankenberger, W.T. Diversity of biosurfactant producing microorganisms isolated from soils contaminated with diesel oil. Microbiol. Res. 2005, 160, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.Y.; Glass, E.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid Annotations using Subsystems Technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seppey, M.; Manni, M.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing Genome Assembly and Annotation Completeness. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 1962, pp. 227–245. [Google Scholar]




| Property | Rhodococcus sp. MS13 | Rhodococcus sp. MS16 | Pseudomonas sp. MS15a | Pseudomonas sp. MS19 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 6,460,280 | 6,970,856 | 5,249,999 | 4,496,051 |
| N50 (bp) | 557,702 | 745,857 | 371,249 | 290,555 |
| G+C content | 62% | 62% | 65% | 57% |
| DNA scaffolds | 23 | 37 | 27 | 30 |
| Total genes | 5964 | 6424 | 4849 | 4116 |
| RNA genes | 62 | 58 | 72 | 67 |
| tRNA genes | 54 | 52 | 59 | 56 |
| Pseudogenes | 58 | 158 | 65 | 39 |
| Protein-coding genes | 5844 | 6208 | 4712 | 4010 |
| Complete BUSCOs | 97% | 96% | 98% | 100% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aguila-Torres, P.; Maldonado, J.; Gaete, A.; Figueroa, J.; González, A.; Miranda, R.; González-Stegmaier, R.; Martin, C.; González, M. Biochemical and Genomic Characterization of the Cypermethrin-Degrading and Biosurfactant-Producing Bacterial Strains Isolated from Marine Sediments of the Chilean Northern Patagonia. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18050252
Aguila-Torres P, Maldonado J, Gaete A, Figueroa J, González A, Miranda R, González-Stegmaier R, Martin C, González M. Biochemical and Genomic Characterization of the Cypermethrin-Degrading and Biosurfactant-Producing Bacterial Strains Isolated from Marine Sediments of the Chilean Northern Patagonia. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(5):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18050252
Chicago/Turabian StyleAguila-Torres, Patricia, Jonathan Maldonado, Alexis Gaete, Jaime Figueroa, Alex González, Richard Miranda, Roxana González-Stegmaier, Carolina Martin, and Mauricio González. 2020. "Biochemical and Genomic Characterization of the Cypermethrin-Degrading and Biosurfactant-Producing Bacterial Strains Isolated from Marine Sediments of the Chilean Northern Patagonia" Marine Drugs 18, no. 5: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18050252
APA StyleAguila-Torres, P., Maldonado, J., Gaete, A., Figueroa, J., González, A., Miranda, R., González-Stegmaier, R., Martin, C., & González, M. (2020). Biochemical and Genomic Characterization of the Cypermethrin-Degrading and Biosurfactant-Producing Bacterial Strains Isolated from Marine Sediments of the Chilean Northern Patagonia. Marine Drugs, 18(5), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18050252