Integrating Molecular Networking and 1H NMR Spectroscopy for Isolation of Bioactive Metabolites from the Persian Gulf Sponge Axinella sinoxea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bioactivity Profiling
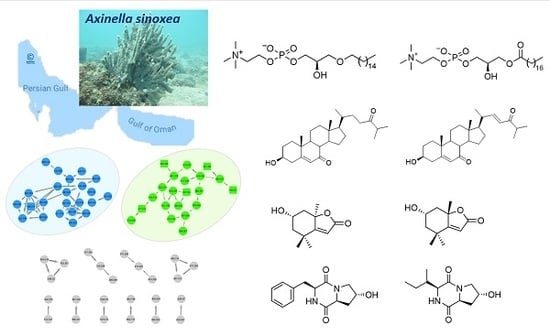
2.2. Molecular Networking-Based Dereplication and 1H NMR Profiling
2.3. Purification and Structure Elucidation
2.4. Bioactivity of Compounds 1–8
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.2. Sponge Material
4.3. Extraction and Isolation
4.4. UPLC-QToF-MS/MS Analysis
4.5. Molecular Networking
4.6. Bioactivity Assays
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Erpenbeck, D.; Gholami, A.; Hesni, M.A.; Ranjbar, M.S.; Galitz, A.; Eickhoff, B.; Namuth, L.; Schumacher, T.; Esmaeili, H.R.; Wörheide, G. Molecular biodiversity of Iranian shallow water sponges. Syst. Biodiver. 2020, 18, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, C.R. Physical environment of the Gulf relevant to marine pollution: An overview. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1993, 27, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braulik, G.T.; Ranjbar, S.; Owfi, F.; Aminrad, T.; Dakhteh, S.M.H.; Kamrani, E.; Mohsenizadeh, F. Marine mammal records from Iran. J. Cetacean Res. Manag. 2010, 11, 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, O. Die Spongien des adriatischen Meeres, 1st ed.; Wilhelm Engelmann: Leipzig, Germany, 1862; pp. 62–83. [Google Scholar]
- Mander, L.; Liu, H.W. Comprehensive Natural Products II: Chemistry and Biology, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 345–350. [Google Scholar]
- Anuradha, V.; Byju, K.; Emilda, R.; Anu, G.; Nair, S.; Chandramohanakumar, N.; Peter, K.P.; Kumar, T.G.; Vasundhara, G. In silico biological activity of steroids from the marine sponge Axinella carteri. Med. Chem. Chem. Res. 2013, 22, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raboisson, P.; Rognan, D.; Aldous, D.; Wermuth, C.G. The Practice of Medicinal Chemistry, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; p. 902. [Google Scholar]
- Vergne, C.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Perez, T.; Martin, M.T.; Adeline, M.T.; Dau, E.T.H.; Al-Mourabit, A. Verpacamides A−D, a sequence of C11N5 diketopiperazines relating cyclo(pro-pro) to cyclo(pro-arg), from the marine sponge Axinella vaceleti: Possible biogenetic precursors of pyrrole-2-aminoimidazole alkaloids. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 2421–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettit, G.R.; Gao, F.; Cerny, R.L.; Doubek, D.L.; Tackett, L.P.; Schmidt, J.M.; Chapuis, J.C. Antineoplastic agents. 278. Isolation and structure of Axinastatins 2 and 3 from a western Caroline Island marine sponge. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 1165–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milanowski, D.J.; Rashid, M.A.; Gustafson, K.R.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Nawrocki, J.P.; Pannell, L.K.; Boyd, M.R. Cyclonellin, a new cyclic octapeptide from the marine sponge Axinella carteri. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimi, A.; Saharkhiz, S.M.; Motallebi, A.; Seydi, E.; Mohseni, A.R.; Nazemi, M.; Pourahmad, J. Standardized extract of the Persian Gulf sponge, Axinella sinoxea selectively induces apoptosis through mitochondria in human chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. J. Anal. Oncol. 2015, 4, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamebozorgi, F.H.; Yousefzadi, M.; Firuzi, O.; Nazemi, M.; Jassbi, A.R. In vitro anti-proliferative activities of the sterols and fatty acids isolated from the Persian Gulf sponge; Axinella sinoxea. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 27, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazemi, M.; Ghaffari, H.; Moradi, Y.; Amiran, M.R.; Dargeri, S.A. Cytotoxic activity of extracts of demosponges Haliclona caerulea, Axinella sinoxea and Ircinia mutans from Persian Gulf. J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 58, 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.; Dewapriya, P.; Li, F.; Blümel, M.; Tasdemir, D. Pyrenosetins A–C, new decalinoylspirotetramic acid derivatives isolated by bioactivity-based molecular networking from the seaweed-derived fungus Pyrenochaetopsis sp. FVE-001. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noda, N.; Tsunefuka, S.; Tanaka, R.; Miyahara, K. Isolation of two 1-O-alkyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholines from the earthworm, Pheretima asiatica. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1992, 40, 1349–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noda, N.; Tanaka, R.; Nishi, M.; Inoue, S.; Miyahara, K. Isolation and characterization of seven lyso platelet-activating factors and two lyso phosphatidylcholines from the crude drug" Suitetsu"(the leech, Hirudo nipponica). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1993, 41, 1366–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, L.; Zhu, W.; Qin, Y.; Chen, Y. Metabolite marker for diagnosing and distinguishing coronary atherosclerosis and stable angina pectoris. CN Patent CN105445408A, 12 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lyons, M.A.; Brown, A.J. 7-ketocholesterol. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1999, 31, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardis, F.; Minale, L.; Iorizzi, M.; Debitus, C.; Lévi, C. Marine sterols. Side-chain-oxygenated sterols, possibly of abiotic origin, from the new Caledonian sponge Stelodoryx chlorophylla. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigemori, H.; Tenma, M.; Shimazaki, K.; Kobayashi, J.I. Three new metabolites from the marine yeast Aureobasidium pullulans. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 696–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.X.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.M.; Lu, C.H.; Shen, Y.M. Four pairs of proline-containing cyclic dipeptides from Nocardiopsis sp. HT88, an endophytic bacterium of Mallotus nudiflorus L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.E.; Kim, Y.A.; Jung, H.A.; Lee, H.J.; Ahn, J.W.; Lee, B.J.; Seo, Y.W. Three norisoprenoids from the brown alga Sargassum thunbergii. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2004, 48, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Z.H.; Han, Z.Z.; Hu, X.Q.; Liu, Q.X.; Zhang, W.D.; Liu, R.H.; Li, H.L. Chemical constituents of Euonymus alatus. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2013, 49, 340–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, Z.J.; Hobson, C.; Needley, R.; Song, L.; Perryman, M.S.; Paul Kerby, P.; Fox, D.J. NMR-based assignment of isoleucine vs. allo-isoleucine stereochemistry. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 9372–9378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitova, M.; Tutino, M.L.; Infusini, G.; Gennaro Marino, G.; Rosa, S.D. Exocellular peptides from Antarctic psychrophile Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis. Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovenden, S.P.; Nielson, J.L.; Liptrot, C.H.; Willis, R.H.; Tapiolas, D.M.; Wright, A.D.; Motti, C.A. A new diketopiperazine, cyclo-(4-S-hydroxy-R-proline-R-isoleucine), from an Australian specimen of the sponge Stelletta sp. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2469–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazemi, N.; Pishehvarzad, F.; Motallebi, A.; Ahmadzadeh, O. Investigation of antibacterial activities of sponge Axinella sinoxea’s extracts from Larak Island, Persian Gulf. J. Aqu. Eco. 2012, 1, 54–65. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdian, D.; Iranshahy, M.; Shakeri, A.; Hoseini, A.; Yavari, H.; Nazemi, M.; Iranshahi, M. Cytotoxicity evaluation of extracts and fractions of five marine sponges from the Persian Gulf and HPLC fingerprint analysis of cytotoxic extracts. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2015, 5, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Janussen, D.; Tasdemir, D. New discorhabdin B dimers with anticancer activity from the Antarctic deep-Sea sponge Latrunculia biformis. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Janussen, D.; Peifer, C.; Victoria, I.P.; Tasdemir, D. Targeted isolation of tsitsikammamines from the Antarctic deep-sea sponge Latrunculia biformis by molecular networking and anticancer activity. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aiello, A.; Ciminiello, P.; Fattorusso, E.; Magno, S. Steroids from sponges: Recent reports. Steroids 1999, 64, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembitsky, V.M.; Rezanka, T.; Srebnik, M. Lipid compounds of freshwater sponges: Family Spongillidae, class Demospongiae. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2003, 123, 117–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, W. Comparative biochemical studies on the lipids of marine invertebrates, with special reference to the sterols. J. Mar. Res. 1949, 8, 137–171. [Google Scholar]
- Smyrniotopoulos, V.; Rae, M.; Soldatou, S.; Ding, Y.; Wolff, C.; McCormack, C.; Coleman, C.M.; Ferreira, D.; Tasdemir, D. Sulfated steroid-amino acid conjugates from the Irish marine sponge Polymastia boletiformis. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1632–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Djerassi, C.; Silva, C.J. Biosynthetic studies of marine lipids. 41. Sponge sterols: Origin and biosynthesis. Acc. Chem. Res. 1991, 24, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, R.G.; Baker, B.J. Marine sterols. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1991, 8, 465–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funel, C.; Berrué, F.; Roussakis, C.; Rodriguez, R.F.; Amade, P. New cytotoxic steroids from the Indian Ocean sponge Axinella cf. bidderi. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.H.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, S. Steroids and alkaloids from the south China sea sponge Axinella sp. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 11, 1040–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djerassi, C.; Lam, W.K. Phospholipid studies of marine organisms. Part 25. Sponge phospholipids. Acc. Chem. Res. 1991, 24, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembitsky, V.M.; Gorina, I.A.; Fedorova, I.P.; Solovieva, M.V. Comparative investigation of plasmalogens, alkylacyl and diacyl glycerophospholipids of the marine sponges (type Porifera, class Demospongiae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1989, 92, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, A.; Ayanoglu, E.; Tomer, K.B.; Djerassi, C. High performance liquid chromatography and Fast Atom Bombardment Mass Spectrometry of unusual branched and unsaturated phospholipid molecular species. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1987, 43, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthwick, A.D. 2,5-diketopiperazines: Synthesis, reactions, medicinal chemistry, and bioactive natural products. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3641–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Yan, T.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y. Diketopiperazines from the marine sponge Axinella sp. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2014, 50, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabarczyk, M.; Wińska, K.; Mączka, W.; Potaniec, B.; Anioł, M. Loliolide–the most ubiquitous lactone. Folia Biol. Oecol. 2015, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrot, D.; Blümel, M.; Utermann, C.; Chianese, G.; Krause, S.; Kovalev, A.; Gorb, S.N.; Tasdemir, D. Mapping the surface microbiome and metabolome of brown seaweed Fucus vesiculosus by amplicon sequencing, integrated metabolomics and imaging techniques. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, B.; Hooper, J.N. Taxonomic revision of the order Halichondrida (Porifera: Demospongiae) of northern Australia: Family Axinellidae. Int. J. Soc. 2009, 25, 17–42. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Position | δH, Mult. (J in Hz) | δC, Type |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | 167.7 (C) |
| 3 | 3.72 (dd 12.9, 4.6) 3.42 (m) | 55.1 (CH2) |
| 4 | 4.47 (m) | 68.8 (CH) |
| 5 | 2.29 (m) 2.04 (ddd 13.3, 11.7, 4.3) | 38.6 (CH2) |
| 6 | 4.48 (m) | 58.3 (CH) |
| 7 | - | 172.7 (C) |
| 9 | 4.13 (br s) | 61.2 (CH) |
| 10 | 2.18 (m) | 36.9 (CH) |
| 11 | 1.46 (m) 1.33 (m) | 25.4 (CH2) |
| 12 | 0.94 (t 7.4) | 12.5 (CH3) |
| 13 | 1.08 (d 7.3) | 15.4 (CH3) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohsenian Kouchaksaraee, R.; Moridi Farimani, M.; Li, F.; Nazemi, M.; Tasdemir, D. Integrating Molecular Networking and 1H NMR Spectroscopy for Isolation of Bioactive Metabolites from the Persian Gulf Sponge Axinella sinoxea. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18070366
Mohsenian Kouchaksaraee R, Moridi Farimani M, Li F, Nazemi M, Tasdemir D. Integrating Molecular Networking and 1H NMR Spectroscopy for Isolation of Bioactive Metabolites from the Persian Gulf Sponge Axinella sinoxea. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(7):366. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18070366
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohsenian Kouchaksaraee, Reza, Mahdi Moridi Farimani, Fengjie Li, Melika Nazemi, and Deniz Tasdemir. 2020. "Integrating Molecular Networking and 1H NMR Spectroscopy for Isolation of Bioactive Metabolites from the Persian Gulf Sponge Axinella sinoxea" Marine Drugs 18, no. 7: 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18070366
APA StyleMohsenian Kouchaksaraee, R., Moridi Farimani, M., Li, F., Nazemi, M., & Tasdemir, D. (2020). Integrating Molecular Networking and 1H NMR Spectroscopy for Isolation of Bioactive Metabolites from the Persian Gulf Sponge Axinella sinoxea. Marine Drugs, 18(7), 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18070366