Structure-Activity Relationships of Holothuroid’s Triterpene Glycosides and Some In Silico Insights Obtained by Molecular Dynamics Study on the Mechanisms of Their Membranolytic Action
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structure-Activity Relationships (SAR) Observed in the Glycosides from Sea Cucumbers
2.1.1. The Dependence of the Glycosides Hemolytic Activity on Their Carbohydrate Chain Structure
2.1.2. The Dependence of Hemolytic Activity of the Gycosides on the Positions and Quantity of Sulfate Groups
2.1.3. The Dependence of Hemolytic Activity of the Glycosides on Aglycone Structure
2.1.4. The Influence of Hydroxyl Groups in the Aglycones Side Chain to Hemolytic Activity of the Glycosides
2.1.5. Correlation Analysis
- The presence of a developed carbohydrate chain composed of four to six monosaccharide residues or a disaccharide chain with a sulfate group;
- The availability of 18(20)- or 18(16)-lactone and a normal (non-shortened) side chain;
- The presence of 9β-H, 7(8)-ene fragment, or 9(11)-double bond.
2.2. In Silico Analysis of the Interaction of the Glycosides from the Sea Cucumber Eupentacta fraudatrix with the Model Membrane
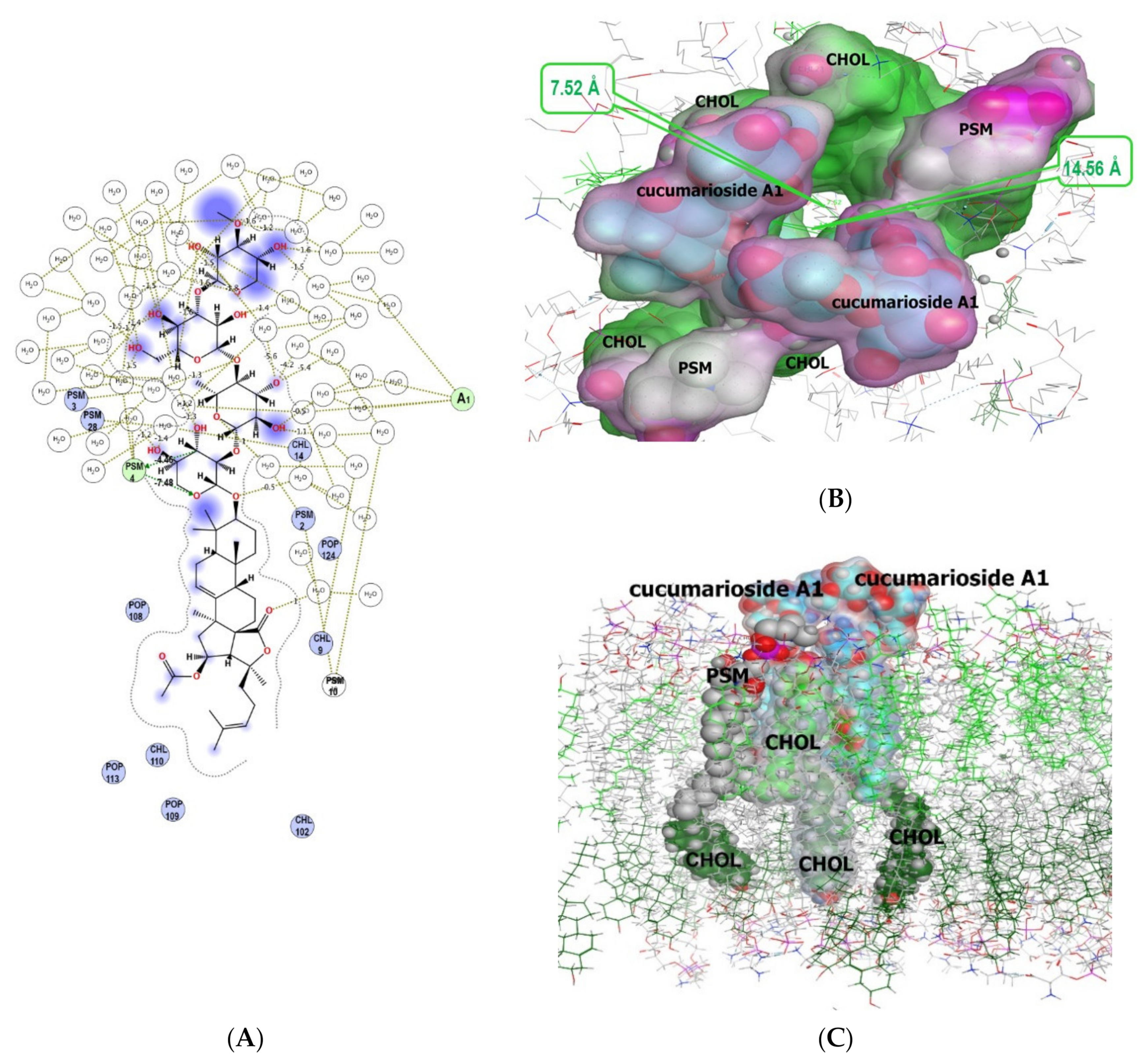
2.2.1. The Modelling of Cucumarioside A1 (40) Membranotropic Action with MD Simulations
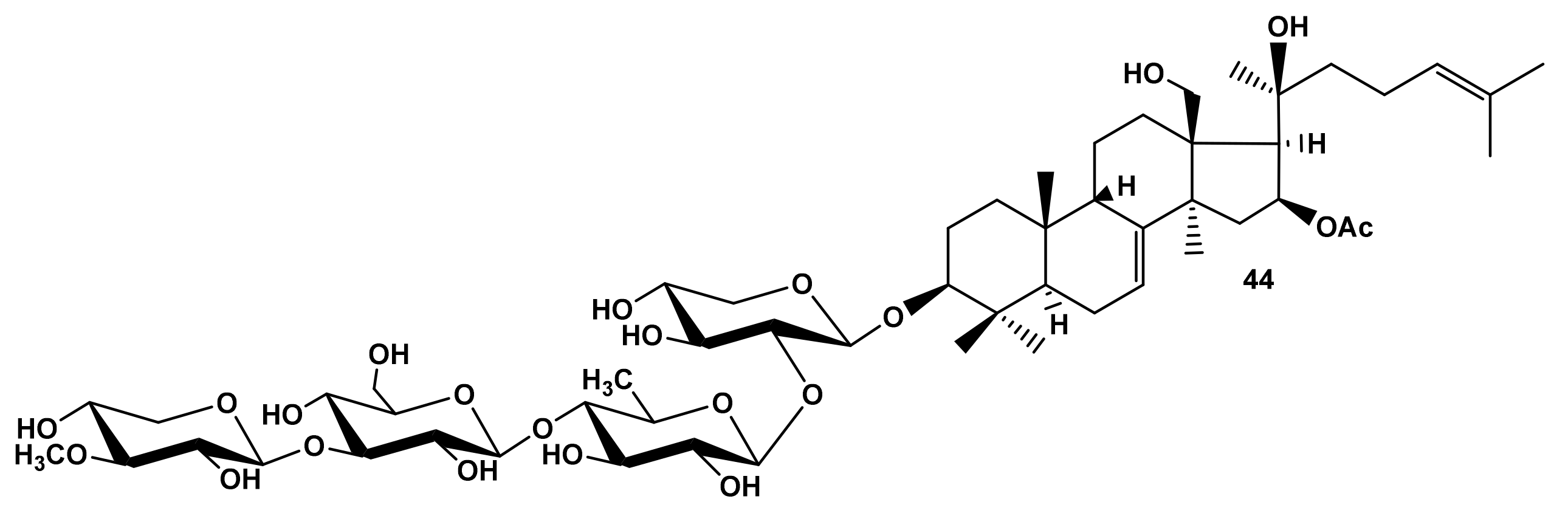
2.2.2. The Modelling of Cucumarioside A8 (44) Membranotropic Action with MD Simulations
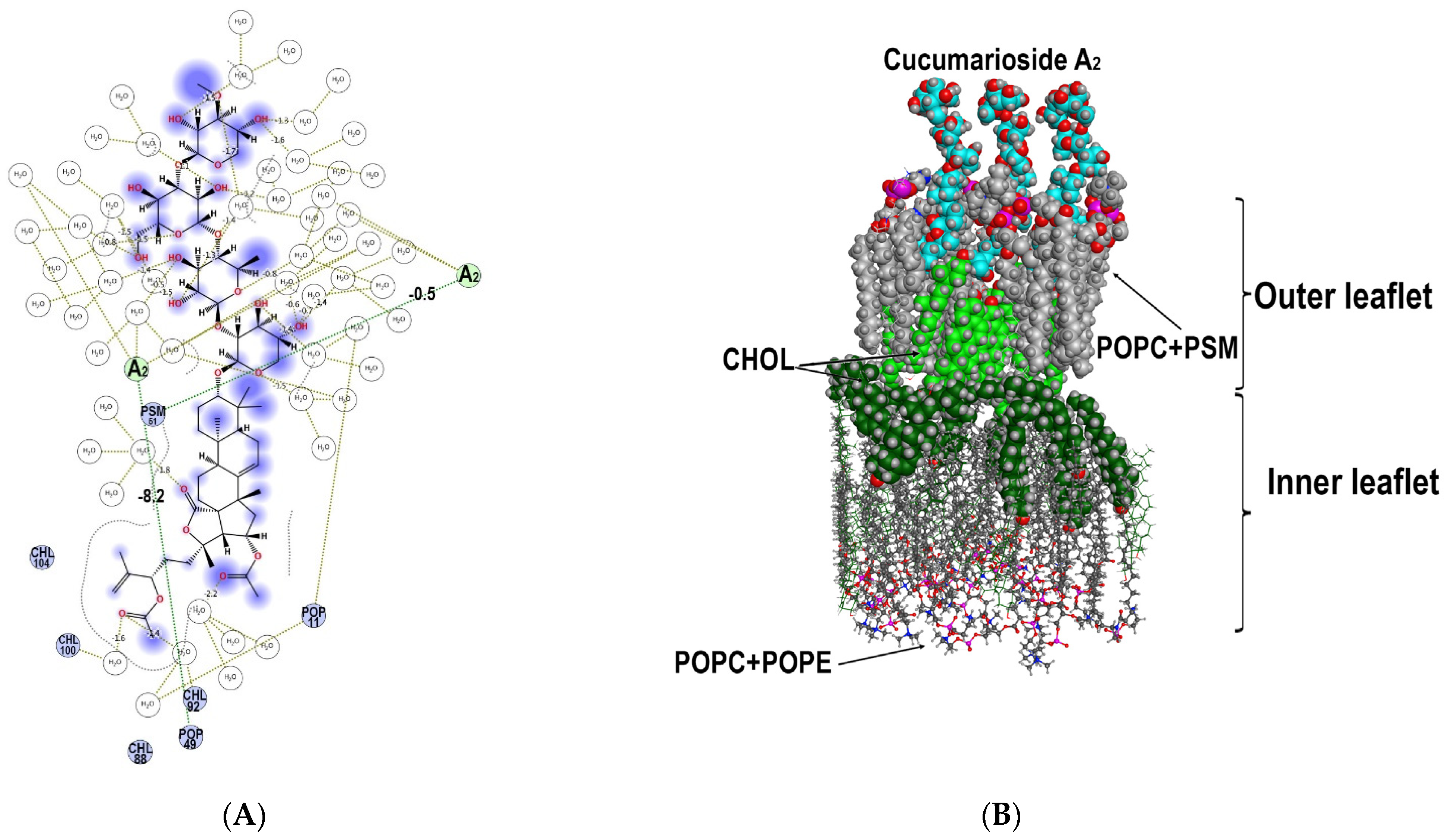
2.2.3. The Modelling of Cucumarioside A2 (59) Membranotropic Action with MD Simulations
2.2.4. The Modelling of Cucumarioside A7 (45) Membranotropic Action with MD Simulations
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Model System for Artificial Plasma Membrane Mimicking the Erythrocyte Membrane
3.2. Full Atom MD Simulations
3.3. Triterpene Glycosides Chosen for MD Simulations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aminin, D.L.; Menchinskaya, E.S.; Pisliagin, E.A.; Silchenko, A.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinin, V.I. Sea cucumber triterpene glycosides as anticancer agents. In Studies in Natural Product Chemistry; Atta-ur-Rahman, Ed.; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 49, pp. 55–105. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinin, V.I.; Prokofieva, N.G.; Likhatskaya, G.N.; Schentsova, E.B.; Agafonova, I.G.; Avilov, S.A.; Drozdova, O.A. Hemolytic activities of triterpene glycosides from the holothurian order Dendrochirotida: Some trends in the evolution of this group of toxins. Toxicon 1996, 34, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Careaga, V.P.; Maier, M.S. Cytotoxic triterpene glycosides from sea cucumbers. In Handbook of Anticancer Drugs from Marine Origin; Kim, S.-K., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 515–528. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinin, V.I.; Aminin, D.L.; Avilov, S.A.; Silchenko, A.S.; Stonik, V.A. Triterpene glycosides from sea cucumbers (Holothuroidea, Echinodermata), biological activities and functions. In Studies in Natural Product Chemistry (Bioactive Natural Products); Atta-ur-Rahman, Ed.; Elsevier Science Publisher: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 35, pp. 135–196. [Google Scholar]
- Kalinin, V.I. System-theoretical (holistic) approach to the modelling of structural-functional relationships of Biomolecules and their evolution: An example of triterpene glycosides from sea cucumbers (Echinodermata, Holothurioidea). J. Theor. Biol. 2000, 206, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-I.; Bae, H.-R.; Kim, C.G.; Stonik, V.A.; Kwak, J.Y. Relationships between chemical structures and functions of triterpene glycosides isolated from sea cucumbers. Front. Chem. 2014, 2, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Claereboudt, E.J.S.; Eeckhaut, I.; Lins, L.; Deleu, M. How different sterols contribute to saponin tolerant plasma membranes in sea cucumbers. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Likhatskaya, G.N.; Yarovaya, T.P.; Rudnev, V.V.; Popov, A.M.; Anisimov, M.M.; Rovin, Y.G. Formation of complex of triterpene glycoside of holothurine A with cholesterol in liposomal membranes. Biofizika 1985, 30, 358–359. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, A.M. A Comparative study of the hemolytic and cytotoxic activities of triterpenoids isolated from ginseng and sea cucumbers. Biol. Bull. 2002, 29, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleu, M.; Crowet, J.M.; Nasir, M.N.; Lins, L. Complementary biophysical tools to investigate lipid specificity in the interaction between bioactive molecules and the plasma membrane: A review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 3171–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lorent, J.H.; Quetin-Leclercq, J.; Mingeot-Leclercq, M.-P. The amphiphilic nature of saponins and their effects on artificial and biological membranes and potential consequences for red blood and cancer cells. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 8803–8822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malyarenko, T.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Kuzmich, A.S.; Stonik, V.A.; Ivanchina, N.V. New triterpene glycosides from the Far Eastern starfish Solaster pacificus and their biological activity. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminin, D.; Pisliagin, E.; Astashev, M.; Es’kov, A.; Kozhemyako, V.; Avilov, S.; Zelepuga, E.; Yurchenko, E.; Kaluzhskiy, L.; Kozlovskaya, E.; et al. Glycosides from edible sea cucumbers stimulate macrophages via purinergic receptors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kersten, G.F.; Crommelin, D.J. Liposomes and ISCOMS as vaccine formulations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1995, 1241, 117–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazeyka, A.N.; Popov, A.M.; Kalinin, V.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Silchenko, A.S.; Kostetsky, E.Y. Complexation between triterpene glycosides of holothurians and cholesterol is the basis of lipid-saponin carriers of subunit protein antigens. Biophysics 2008, 53, 826–835. [Google Scholar]
- Stonik, V.A.; Aminin, D.L.; Boguslavski, V.M.; Avilov, S.A.; Agafonova, I.G.; Silchenko, A.S.; Ponomarenko, L.P.; Prokofieva, N.G.; Chaikina, E.L. Immunostimulatory means Cumaside and pharmaceutical composition on its base. Patent of the Russian Federation No. 2271820, 20 March 2005. Appl. No. 2004120434/17, 2 July 2004.. [Google Scholar]
- Aminin, D.L.; Chaykina, E.L.; Agafonova, I.G.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinin, V.I.; Stonik, V.A. Antitumor activity of the immunomodulatory lead Cumaside. Intern. Immunopharm. 2010, 10, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstraeten, S.L.; Deleu, M.; Janikowska-Sagan, M.; Claereboudt, E.J.S.; Lins, L.; Tyteca, D.; Mingeot-Leclercq1, M.P. The activity of the saponin ginsenoside Rh2 is enhanced by the interaction with membrane sphingomyelin but depressed by cholesterol. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollinedo, F.; Gajate, C. Lipid rafts as major platforms for signaling regulation in cancer. Adv Biol Regul. 2015, 57, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guariento, S.; Bruno, O.; Fossa, P.; Cichero, E. New insights into PDE4B inhibitor selectivity: CoMFA analyses and molecular docking studies. Mol. Divers. 2016, 20, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusnati, M.; Sala, D.; Orro, A.; Bugatti, A.; Trombetti, G.; Cichero, E.; Urbinati, C.; Di Somma, M.; Millo, E.; Galietta, L.J.V.; et al. Speeding Up the Identification of Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator-Targeted Drugs: An Approach Based on Bioinformatics Strategies and Surface Plasmon Resonance. Molecules 2018, 23, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sezgin, E.; Levental, I.; Mayor, S.; Eggeling, C. The mystery of membrane organization: Composition, regulation and roles of lipid rafts. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Andryjaschenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Martyyas, E.A.; Kalinin, V.I.; Jayasandhya, P.; Rajan, G.C.; Padmakumar, K.P. Structures and biological activities of typicosideds A1, A2, B1, C1 and C2, triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumbers Actinocucumis typica. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 301–310. [Google Scholar]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Andryjaschenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Kalinin, V.I.; Yurchenko, E.V.; Dolmatov, I.Y. Colochirosides B1, B2, B3 and C, novel sulfated triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Colochirus robustus (Cucumariidae, Dendrochirotida). Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinin, V.I.; Andrijaschenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Chingizova, E.A.; Ermakova, S.P.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Dautova, T.N. Nine new triterpene glycosides, magnumosides A1–A4, B1, B2, C1, C2 and C4, from the Vietnamese sea cucumber Neothyonidium (=Massinum) magnum: Structures and activities against tumor cells independently and in synergy with radioactive irradiation. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinin, V.I.; Andrijaschenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Chingizova, E.A.; Ermakova, S.P.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Dautova, T.N. Magnumosides B3, B4 and C3, mono- and disulfated triterpene tetraosides from the Vietnamese sea cucumber Neothyonidium (=Massinum) magnum. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 12, 1577–1582. [Google Scholar]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Andryjaschenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Yurchenko, E.A.; Kalinin, V.I. Structures and cytotoxic properties of cucumariosides H2, H3 and H4 from the sea cucumber Eupentacta fraudatrix. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Andryjashenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Martyyas, E.A.; Kalinin, V.I. Triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Eupentacta fraudatrix. Structure and biological actions of cucumariosides A1, A3, A4, A5, A6, A12 and A15, seven new minor non-sulfated tetraosides and unprecedented 25-keto,25-norholostane aglycone. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Andryjaschenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Martyyas, E.A.; Kalinin, V.I. Triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Eupentacta fraudatrix. Structure and cytotoxic action of cucumariosides A2, A7, A9, A10, A11, A13 and A14, seven new minor non-sulated tetraosides and an aglycone with an uncommon 18-hydroxy group. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinin, V.I.; Andrijaschenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Popov, R.S.; Chingizova, E.A.; Ermakova, S.P.; Malyarenko, O.S. Structures and bioactivities of six new triterpene glycosides, psolusosides E, F, G, H, H1 and I and the corrected structure of psolusoside B from the sea cucumber Psolus fabricii. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinin, V.I.; Andrijaschenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Popov, R.S.; Chingizova, E.A. Structures and bioactivities of psolusosides B1, B2, J, K, L, M, N, O, P, and Q from the sea cucumber Psolus fabricii. The first finding of tetrasulfated marine low molecular weight metabolites. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Andrijaschenko, P.V.; Popov, R.S.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Chingizova, E.A.; Ermakova, S.P.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Dautov, S.S.; et al. Structures and bioactivities of quadrangularisosides A, A1, B, B1, B2, C, C1, D, D1–D4, and E from the sea cucumber Colochirus quadrangularis: The first discovery of the glycosides, sulfated by C-4 of the terminal 3-O-methylglucose residue. Synergetic effect on colony formation of tumor HT-29 cells of these glycosides with radioactive irradiation. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, V.I.; Volkova, O.V.; Likhatskaya, G.N.; Prokofieva, N.G.; Agafonova, I.G.; Anisimov, M.M.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Stonik, V.A. Hemolytic activity of triterpene glycosides from Cucumariidae family holothurians and evolution of this group of toxins. J. Nat. Toxins 1992, 1, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-K.; Himaya, S.W.A. Triterpene glycosides from sea cucumbers and their biological activities. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 63, 297–319. [Google Scholar]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Adnryjaschenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Martyyas, E.A.; Kalinin, V.I. Triterpene glycosides from sea cucumber Eupentacta fraudatrix. Structure and biological activity of cucumariosides B1 and B2, two new minor non-sulfated unprecedented triosides. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Andryjaschenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Yurchenko, E.A.; Kalinin, V.I. Structure of cucumariosides H5, H6, H7 and H8. Glycosides from the sea cucumber Eupentacta fraudatrix and unprecedented aglycone with 16,22-epoxy-group. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Andryjascchenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Yurchenko, E.A.; Dolmatov, I.Y.; Kalinin, V.I.; Stonik, V.A. Structure and biological action of cladolosides B1, B2, C, C1, C2 and D, six new triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Cladolabesschmeltzii. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Andryjaschenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Yurchenko, E.A.; Dolmatov, I.Y.; Kalinin, V.I. Structures and biological activities of cladolosides C3, E1, E2, F1, F2, G, H1 and H2, eight triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Cladolabes schmeltzii with one known and four new carbohydrate chains. Carb. Res. 2015, 414, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Andryjaschenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Chingizova, E.A.; Dolmatov, I.Y.; Kalinin, V.I. Cladolosides I1, I2, J1, K1, K2 and L1, monosulfated triterpene glycosides with new carbohydrate chains from the sea cucumber Cladolabes schmeltzii. Carb. Res. 2017, 445, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Andryjaschenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Yurchenko, E.A.; Ermakova, S.P.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Dolmatov, I.Y.; Kalinin, V.I. Cladolosides C4, D1, D2, M, M1, M2, N and Q, new triterpene glycosides with diverse carbohydrate chains from sea cucumber Cladolabes schmeltzii. An uncommon 20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27-okta-nor-lanostane aglycone. The synergism of inhibitory action of non-toxic dose of the glycosides and radioactive irradiation on colony formation of HT-29 cancer cells. Carb. Res. 2018, 468, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Andryjaschenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Yurchenko, E.A.; Ermakova, S.P.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Dolmatov, I.Y.; Kalinin, V.I. Cladolosides O, P, P1–P3 and R, triterpene glycosides with two novel types of carbohydrate chains from the sea cucumber Cladolabes schmeltzii. Inhibition of cancer cells colony formation and its synergy with radioactive irradiation. Carb. Res. 2018, 468, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Adnryjaschenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Kalinin, V.I.; Martyyas, E.A.; Minin, K.V. Fallaxosides C1, C2, D1 and D2, unusual oligosulfated triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Cucumaria fallax (Cucumariidae, Dendrochirotida, Holothuroidea) and a taxonomic status of this animal. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 939–945. [Google Scholar]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Andryjaschenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Martyyas, E.A.; Kalinin, V.I. Triterpene glycosides from sea cucumber Eupentacta fraudatrix. Structure and biological action of cucumariosides I1, I3, I4, three new minor didulfated pentaosides. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Kalinin, V.I.; Andrijaschenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Popov, R.S.; Chingizova, E.A.; Kasakin, M.F. Psolusosides C3 and D2–D5, five novel triterpene hexaosides from the sea cucumber Psolus fabricii (Psolidae, Dendrochirotida): Chemical structures and bioactivities. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molecular Operating Environment (MOE), 2019.01; Chemical Computing Group ULC, 1010 Sherbooke St. West, Suite #910, Montreal, QC, Canada, H3A 2R7, 2021.
- Wildman, S.A.; Crippen, G.M. Prediction of Physiochemical Parameters by Atomic Contributions. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1999, 39, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, L.H.; Kier, L.B. The Molecular Connectivity Chi Indices and Kappa Shape Indices in Structure-Property Modeling. Rev. Comput. Chem. 1991, 2, 367–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroz, V.V.; Golubev, A.M.; Afanasyev, A.V.; Kuzovlev, A.N.; Sergunova, V.A.; Gudkova, O.E.; Chernysh, A.M. The structure and function of a red blood cell in health and critical conditions. Gen. Reanimatol. 2012, 8, 52–60. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Wang, R. Hemolytic mechanism of dioscin proposed by molecular dynamics simulations. J. Mol. Model 2010, 16, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.L.; Souza, C.M.; Pichler, H.; Dewhurst, G.; Schaad, O.; Kajiwara, K.; Wakabayashi, H.; Ivanova, T.; Castillon, G.A.; Piccolis, M.; et al. Functional Interactions between Sphingolipids and Sterols in Biological Membranes Regulating Cell Physiology. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2009, 20, 2083–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabinovich, A.L.; Kornilov, V.V.; Balabaev, N.K.; Leermakers, F.A.M.; Filippov, A.V. Properties of unsaturated phospholipid bilayers: Effect of cholesterol. Biol. Membr. 2007, 24, 490–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Cheng, X.; Swails, J.M.; Yeom, M.S.; Eastman, P.K.; Lemkul, J.A.; Wei, S.; Buckner, J.; Jeong, J.C.; Qi, Y.; et al. CHARMM-GUI input generator for NAMD, GROMACS, AMBER, OpenMM, and CHARMM/OpenMM simulations using the CHARMM36 additive force field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Patel, J.; Ståhle, S.-J.; Park, N.R.; Kern, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, X.; Cheng, M.A.; Valvano, O.; Holst, Y.; et al. Im CHARMM-GUI Membrane Builder for Complex Biological Membrane Simulations with Glycolipids and Lipoglycans. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019, 15, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



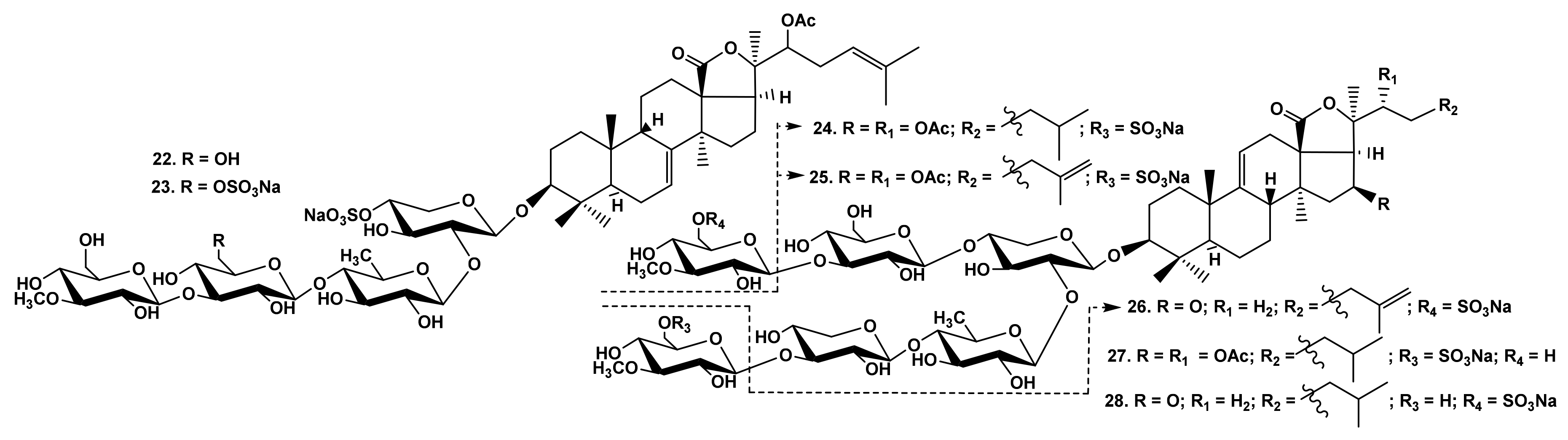
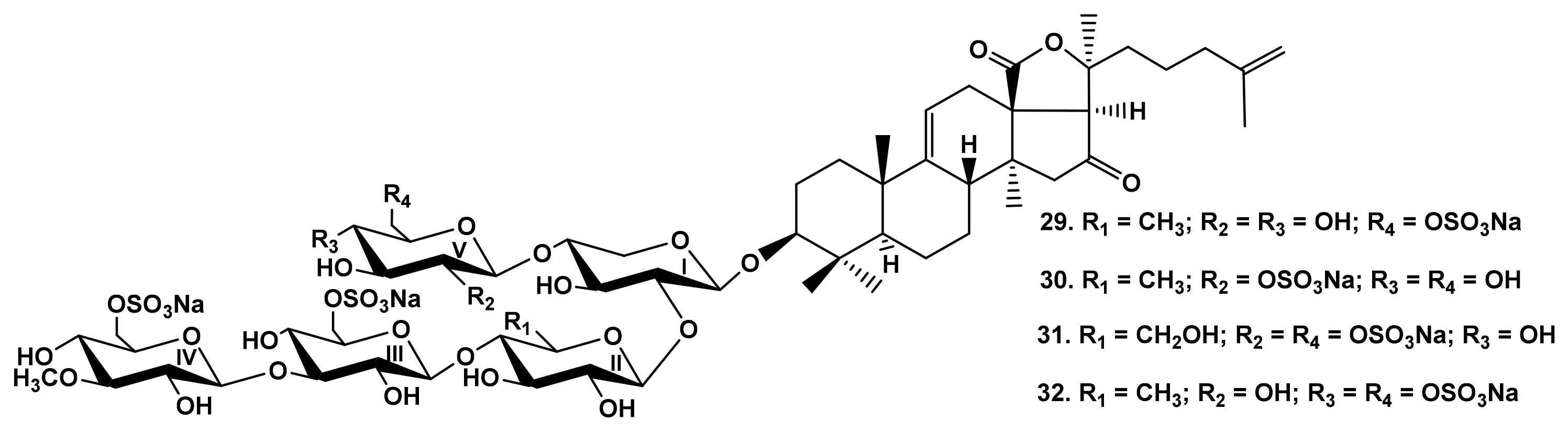

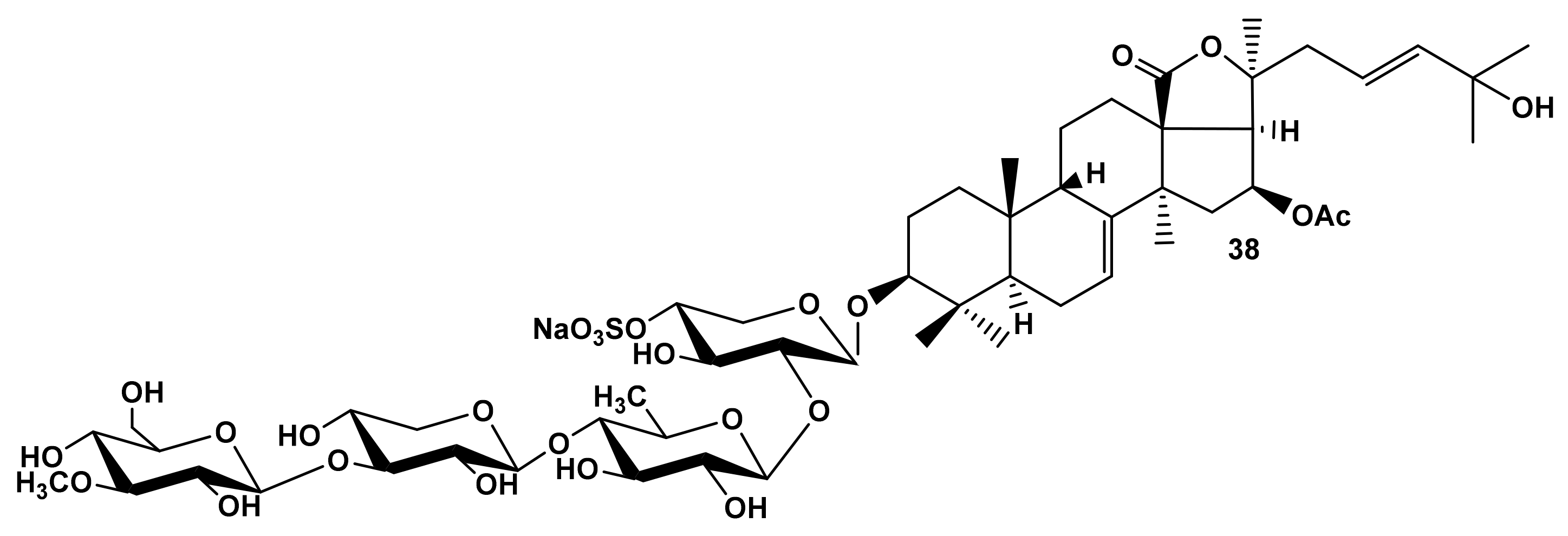

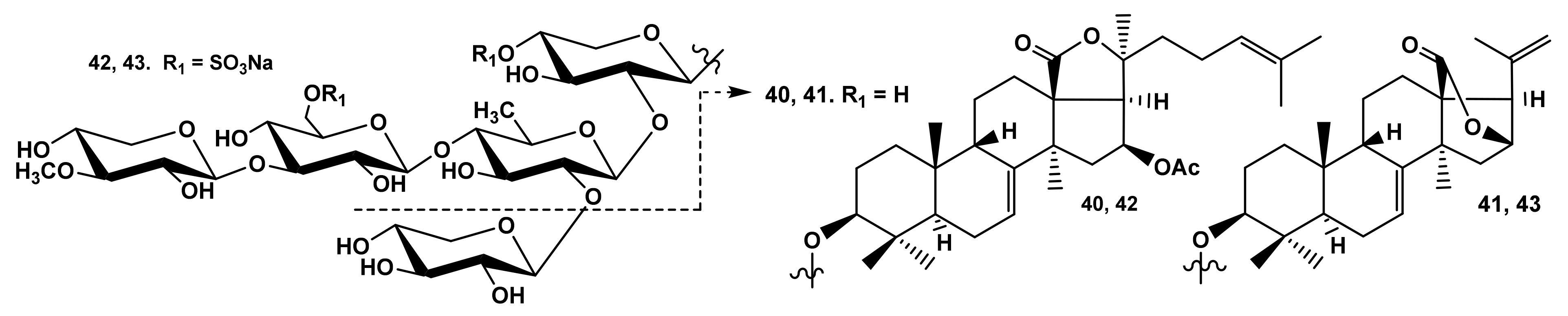




| Glycoside | ED50, µM/mL | Glycoside | ED50, µM/mL | Glycoside | ED50, µM/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cucumarioside B1 (1) | >100 | Psolusoside K (21) | >100 | Cucumarioside A10 (41) | 20.00 |
| Cucumarioside B2 (2) | 18.8 | Typicoside B1 (22) | 0.33 | Cucumarioside I1 (42) | 23.24 |
| Cucumarioside H5 (3) | 3.2 | Typicoside C2 (23) | 0.18 | Cucumarioside I4 (43) | 75.00 |
| Cucumarioside H (4) | 3.8 | Cladoloside I1 (24) | 1.10 | Cucumarioside A8 (44) | 0.70 |
| Magnumoside A2 (5) | 33.33 | Cladoloside I2 (25) | 2.04 | Cucumarioside A7 (45) | >100 |
| Magnumoside A3 (6) | 12.53 | Cladoloside J1 (26) | 1.37 | Cucumarioside A9 (46) | >100 |
| Magnumoside A4 (7) | 20.12 | Cladoloside K1 (27) | 0.18 | Cucumarioside A11 (47) | >100 |
| Magnumoside B1 (8) | 49.57 | Cladoloside L1 (28) | 0.82 | Cucumarioside A14 (48) | >100 |
| Magnumoside B2 (9) | 58.11 | Psolusoside L (29) | 2.42 | Cucumarioside I3 (49) | >100 |
| Magnumoside B3 (10) | 8.49 | Psolusoside M (30) | 67.83 | Colochiroside B1 (50) | 39.5 |
| Magnumoside B4 (11) | 1.42 | Psolusoside Q (31) | >100 | Typicoside C1 (51) | 6.25 |
| Magnumoside C1 (12) | 6.97 | Psolusoside P (32) | 10.92 | Cladoloside D2 (52) | 10.40 |
| Magnumoside C2 (13) | 16.20 | Quadrangularisoside B2 (33) | 0.51 | Cladoloside K2 (53) | 11.41 |
| Magnumoside C3 (14) | 17.80 | QuadrangularisosideD2 (34) | 3.31 | Cladoloside D1 (54) | 0.67 |
| Magnumoside C4 (15) | 6.52 | QuadrangularisosideE (35) | 2.04 | QuadrangularisosideA (55) | 1.57 |
| Psolusoside A (16) | 1.4 | Colochiroside C (36) | 2.5 | QuadrangularisosideA1 (56) | 1.11 |
| Psolusoside E (17) | 0.23 | Psolusoside F (37) | 2.8 | Psolusoside D3 (57) | 1.12 |
| Psolusoside H (18) | 2.5 | Colochiroside B2 (38) | 37.02 | Psolusoside D5 (58) | 12.37 |
| Psolusoside H1 (19) | 2.7 | Cucumarioside A3-2 (39) | 40.6 | Cucumarioside A2 (59) | 4.70 |
| Psolusoside J (20) | >100 | Cucumarioside A1 (40) | 0.07 |
| Type of Bonding | CucumariosideA1 (40) Molecule | Membrane Component | Energy Contribution, kcal/mol | Distance, Å |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen bond | I | PSM4 | −11.94 | 4.05 |
| Hydrophobic | I | PSM4 | −0.5 | 3.31 |
| Hydrophobic | I | POPC108 | −7.21 | 3.93 |
| Hydrophobic | I | PSM2 | −5.52 | 4.13 |
| Hydrophobic | I | POP109 | −4.69 | 3.92 |
| Hydrophobic | I | PSM10 | −3.71 | 4.19 |
| Hydrophobic | I | CHOL9 | −3.69 | 4.13 |
| Hydrophobic | I | CHOL14 | −2.18 | 4.01 |
| Hydrophobic | I | POPC124 | −1.59 | 4.02 |
| Hydrophobic | I | POPC113 | −0.55 | 4.13 |
| Hydrophobic | II | CHOL38 | −11.05 | 4.07 |
| Hydrophobic | II | PSM31 | −10.82 | 4.08 |
| Hydrophobic | II | POPC124 | −8.38 | 4.11 |
| Hydrophobic | II | CHOL46 | −4.77 | 4.06 |
| Hydrophobic | II | CHOL14 | −4.50 | 3.93 |
| Hydrophobic | II | PSM28 | −1.06 | 4.15 |
| Hydrophobic | II | PSM74 | 0.05 | 3.95 |
| Type of Bonding | Cucumarioside A8 (44) Molecule | Membrane Component | Energy Contribution, kcal/mol | Distance, Å |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen bond | II | I | −3.49 | 3.36 |
| Hydrophobic | II | I | −8.75 | 3.95 |
| Hydrophobic | II | PSM20 | −12.41 | 4.03 |
| Hydrophobic | I | PSM2 | −8.60 | 4.07 |
| Hydrophobic | II | POPC13 | −7.93 | 3.97 |
| Hydrophobic | II | CHL7 | −7.20 | 4.02 |
| Hydrophobic | II | PSM2 | −4.28 | 4.04 |
| Hydrophobic | I | CHL9 | −4.06 | 4.06 |
| Hydrophobic | I | PSM10 | −3.91 | 4.08 |
| Hydrophobic | II | POPC108 * | −3.72 | 3.94 |
| Hydrophobic | II | CHL14 | −3.23 | 4.11 |
| Hydrogen bond | II | POPC5 | −3.10 | 2.60 |
| Hydrophobic | I | PSM3 | −2.31 | 3.96 |
| Hydrophobic | II | POPC113 * | −2.02 | 4.21 |
| Hydrophobic | I | POPC13 | −1.39 | 3.59 |
| Hydrophobic | II | PSM28 | −1.01 | 4.26 |
| Hydrogen bond | I | PSM2 | −1.00 | 3.01 |
| Type of Bonding | Cucumarioside A2 (59) Molecule | Membrane Component | Energy Contribution, kcal/mol | Distance, Å |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrophobic | I | PSM51 | −4.63 | 4.21 |
| Hydrophobic | I | POPC11 | −3.34 | 3.99 |
| Hydrophobic | I | CHOL92 | −0.63 | 3.89 |
| Hydrophobic | I | POPC49 | −1.23 | 3.99 |
| Hydrogen bond | II | PSM51 | −0.49 | 3.18 |
| Hydrophobic | II | PSM57 | −6.19 | 4.14 |
| Hydrophobic | II | CHOL104 | −6.1 | 3.98 |
| Hydrophobic | II | PSM55 | −3.3 | 4.07 |
| Hydrophobic | II | POPC11 | −2.78 | 4.17 |
| Hydrophobic | II | PSM51 | −2.18 | 4.08 |
| Hydrogen bond | III | POPC49 | −8.2 | 2.49 |
| Hydrophobic | III | POPC11 | −3.08 | 4.20 |
| Hydrophobic | III | POPC49 | −1.43 | 3.91 |
| Hydrophobic | III | CHOL99 | −0.67 | 3.53 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zelepuga, E.A.; Silchenko, A.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinin, V.I. Structure-Activity Relationships of Holothuroid’s Triterpene Glycosides and Some In Silico Insights Obtained by Molecular Dynamics Study on the Mechanisms of Their Membranolytic Action. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19110604
Zelepuga EA, Silchenko AS, Avilov SA, Kalinin VI. Structure-Activity Relationships of Holothuroid’s Triterpene Glycosides and Some In Silico Insights Obtained by Molecular Dynamics Study on the Mechanisms of Their Membranolytic Action. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(11):604. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19110604
Chicago/Turabian StyleZelepuga, Elena A., Alexandra S. Silchenko, Sergey A. Avilov, and Vladimir I. Kalinin. 2021. "Structure-Activity Relationships of Holothuroid’s Triterpene Glycosides and Some In Silico Insights Obtained by Molecular Dynamics Study on the Mechanisms of Their Membranolytic Action" Marine Drugs 19, no. 11: 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19110604
APA StyleZelepuga, E. A., Silchenko, A. S., Avilov, S. A., & Kalinin, V. I. (2021). Structure-Activity Relationships of Holothuroid’s Triterpene Glycosides and Some In Silico Insights Obtained by Molecular Dynamics Study on the Mechanisms of Their Membranolytic Action. Marine Drugs, 19(11), 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19110604








