A Novel Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptide from Takifugu flavidus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
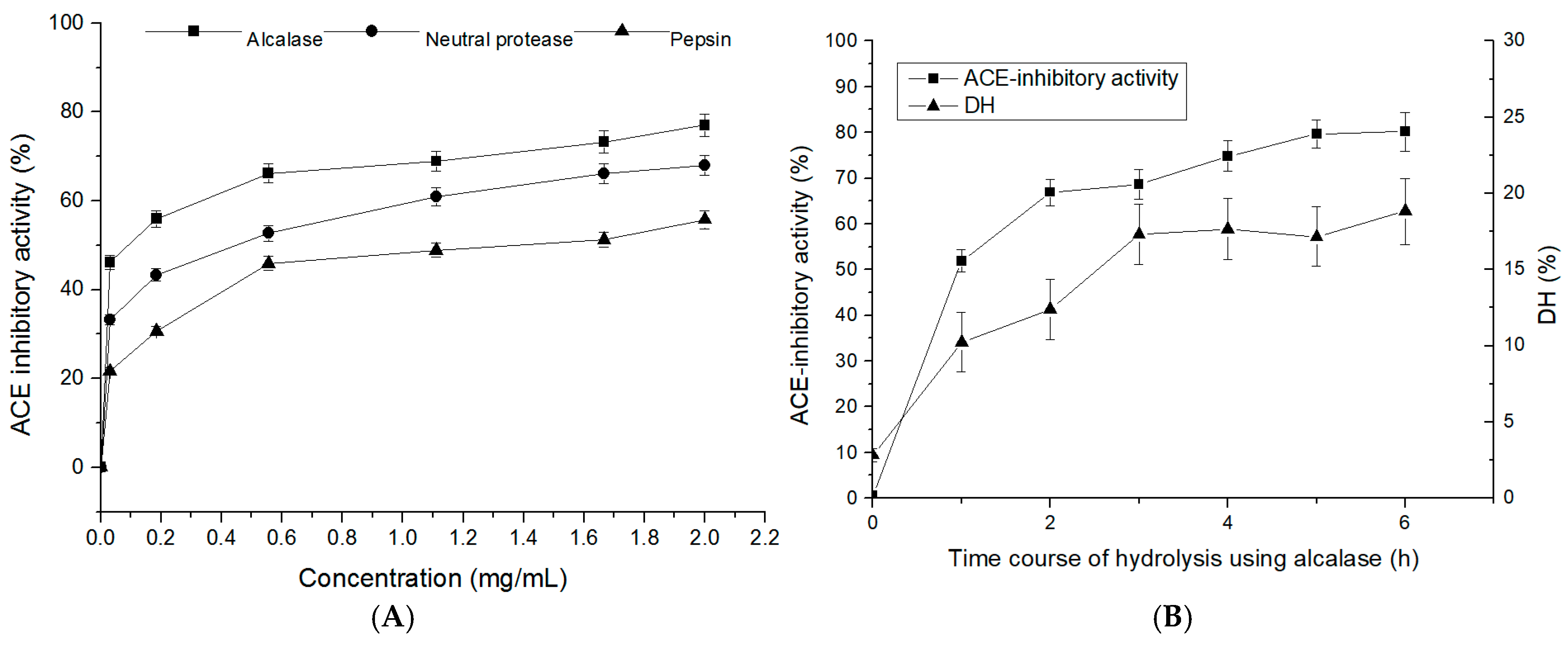
2.1. Degree of Hydrolysis and ACE-Inhibitory Activity of T. flavidus Hydrolysates (TFHs)
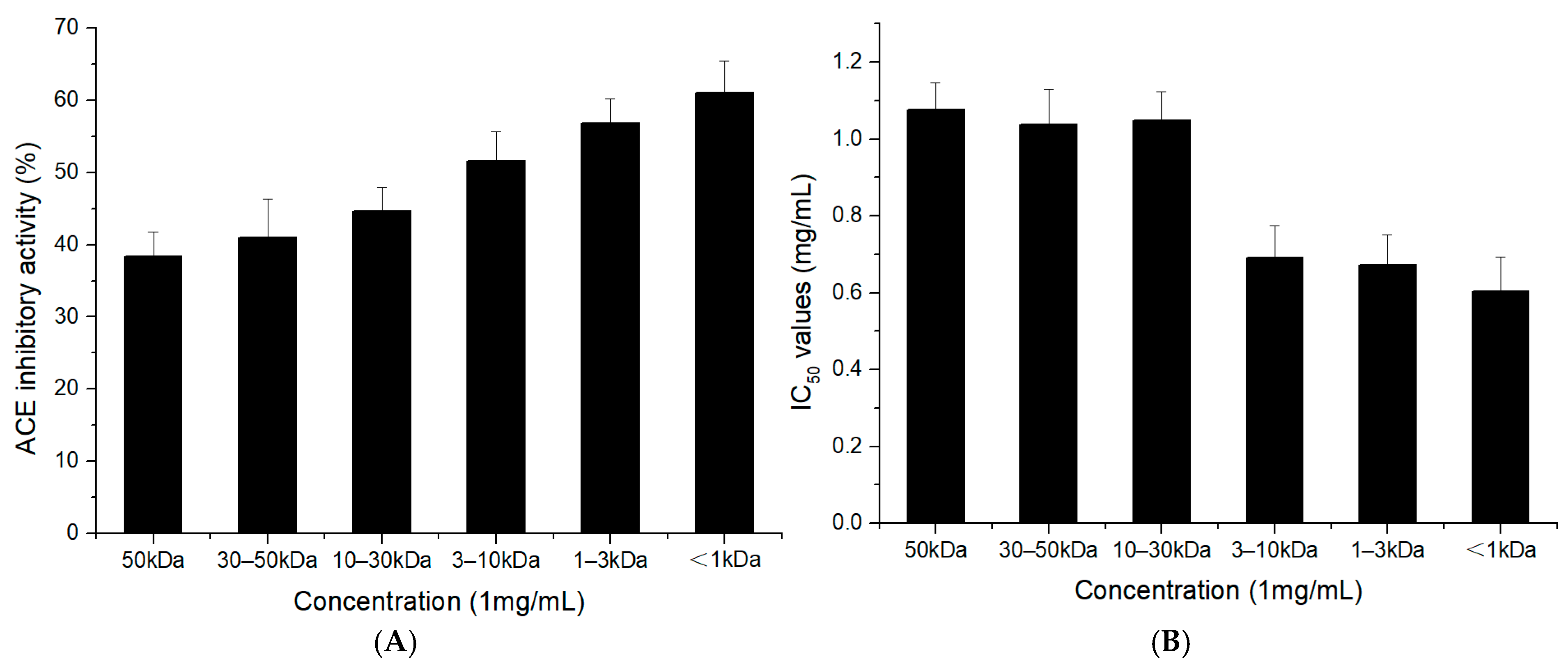
2.2. ACE-Inhibitory Activity of the TFH and Its Ultrafiltrate Fractions
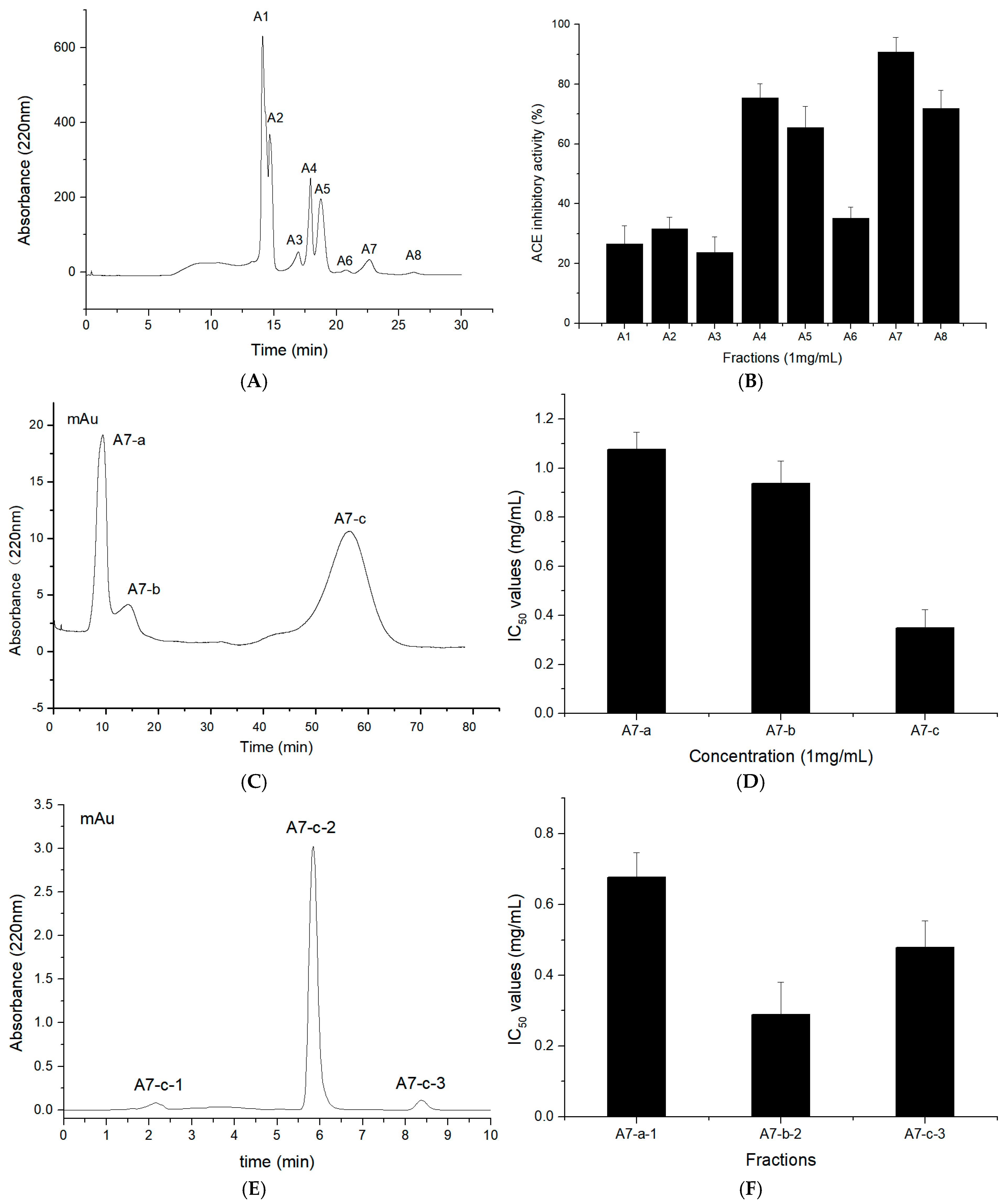
2.3. Purification of T. flavidus Peptides
2.4. Identification of T. flavidus Peptides and Peptide Synthesis
2.5. Molecular Simulation of the Interaction between Peptides and ACE
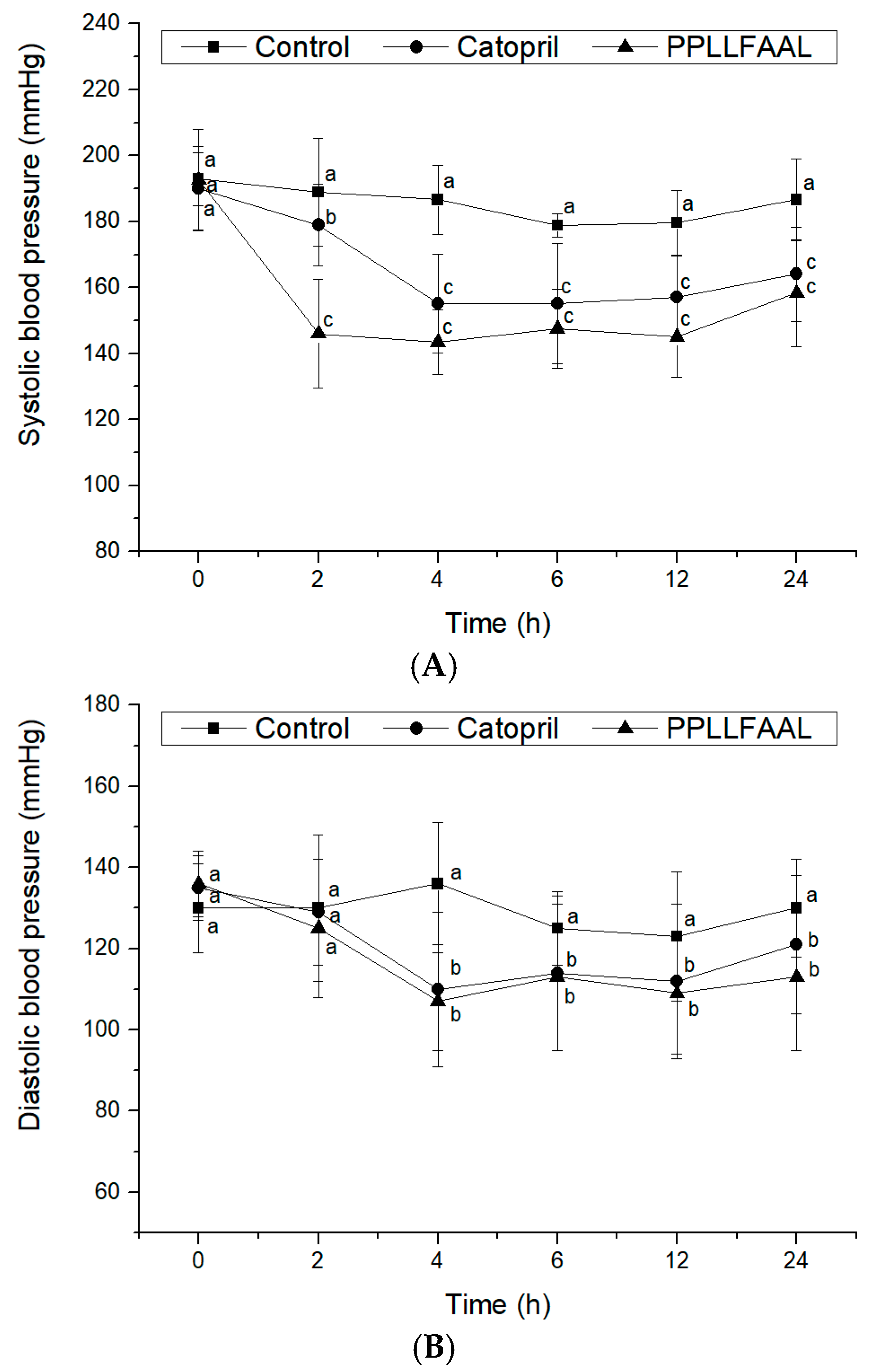
2.6. Antihypertensive Activity of the PPLLFAAL on SHRs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of TFHs
3.3. Ultrafiltration of the ACE-Inhibitory Peptide
3.4. Purification of the ACE-Inhibitory Peptide
3.5. Determination of ACE-Inhibitory Activity
3.6. LC–MS/MS Analysis and Identification of Purified Peptide Sequences
3.7. Chemical Synthesis of Peptides
3.8. Kinetics of ACE Inhibition
3.9. Molecular Simulations
3.10. Antihypertensive Effect In Vivo
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krivohlavý, J. Hypertension, cardiovascular diseases and defense mechanisms. Cas. Lek. Ceskych. 1989, 128, 617–620. [Google Scholar]
- Daskaya-Dikmen, C.; Yucetepe, A.; Karbancioglu-Guler, F.; Daskaya, H.; Ozcelik, B. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides from plants. Nutrients 2017, 9, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studdy, P.R.; Lapworth, R.; Bird, R. Angiotensin-converting enzyme and its clinical significance—A review. J. Clin. Pathol. 1983, 36, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aluko, R.E. Antihypertensive peptides from food proteins. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 235–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abachi, S.; Bazinet, L.; Beaulieu, L. Antihypertensive and angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides from fish as potential cardioprotective compounds. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertrand, M. Provision of cardiovascular protection by ACE inhibitors: A review of recent trials. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2004, 20, 1559–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liao, W.; Udenigwe, C.C. Revisiting the mechanisms of ACE inhibitory peptides from food proteins. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzGerald, R.J.; Meisel, H. Milk protein-derived peptide inhibitors of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme. Br. J. Nutr. 2000, 84, S33–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wijesekara, I.; Kim, S.K. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors from marine resources: Prospects in the pharmaceutical industry. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirdhayati, I.; Hermanianto, J.; Wijaya, C.H.; Sajuthi, D.; Arihara, K. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory and antihypertensive activities of protein hydrolysate from meat of Kacang goat (Capra aegagrus hircus). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 3536–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, S.; Lunow, D.; Kaiser, S.; Henle, T. Identification and quantification of ACE-inhibiting peptides in enzymatic hydrolysates of plant proteins. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruysse, L.; Camp, J.; Smagghe, G. ACE Inhibitory peptides derived from enzymatic hydrolysates of animal muscle protein: A review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8106–8115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Maqueda, D.; Miralles, B.; Recio, I.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. Antihypertensive peptides from food proteins: A review. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghassem, M.; Arihara, K.; Babji, A.S.; Said, M.; Ibrahim, S. Purification and identification of ACE inhibitory peptides from Haruan (Channa striatus) myofibrillar protein hydrolysate using HPLC–ESI-TOF MS/MS. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1770–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Y.; Qiao, R.; Tang, W.; Sun, Z. Production of the angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides and isolation of four novel peptides from jellyfish (Rhopilema esculentum) protein hydrolysate. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 3240–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; He, H.L.; Chen, X.L.; Sun, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhou, B.C. Purification and identification of novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from shark meat hydrolysate. Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Qian, Z.-J.; Kim, S.-K. A novel angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from tuna frame protein hydrolysate and its antihypertensive effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zang, W. Effects of salinity on embryos and larvae of tawny puffer Takifugu flavidus. Aquaculture 2010, 302, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Yang, C.; Song, L. Draft sequencing and analysis of the genome of pufferfish Takifugu flavidus. DNA Res. 2014, 21, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Li, M.; Yi, R.; Bai, K.; Wang, G.; Tan, R.; Sun, S.; Xu, N. Electrodialysis extraction of Pufferfish skin (Takifugu flavidus): A promising source of collagen. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, S.; Xu, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, N. Preparation and identification of ACE inhibitory peptides from the marine macroalga Ulva intestinalis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nekliudov, A.D.; Ivankin, A.; Bertudina, A.V. Characteristics and use of protein hydrolysates (review). Prikl. Biokhimiia Mikrobiol. 2000, 36, 525–534. [Google Scholar]
- Nasri, M. Protein hydrolysates and biopeptides: Production, biological activities, and applications in foods and health benefits. A review. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 81, 109–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisuthiphaet, N.; Kongruang, S.; Chamcheun, C. Production of fish protein hydrolysates by acid and enzymatic hydrolysis. J. Med. Bioeng. 2015, 4, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, P.; Tian, H.; Li, X.; Chen, X. Isolation of novel ACE-inhibitory peptide from naked oat globulin hydrolysates in silico approach: Molecular docking, in vivo antihypertension and effects on renin and intracellular endothelin-1. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheeree, N.; Sangtanoo, P.; Srimongkol, P.; Saisavoey, T.; Reamtong, O.; Choowongkomon, K.; Karnchanatat, A. ACE inhibitory peptides derived from de-fatted lemon basil seeds: Optimization, purification, identification, structure-activity relationship and molecular docking analysis. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 8161–8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhedi, O.; Nasri, R.; Jridi, M.; Mora, L.; Oseguera-Toledo, M.; Aristoy, M.-C.; Ben Amara, I.; Toldrá, F. In silico analysis and antihypertensive effect of ACE-inhibitory peptides from smooth-hound viscera protein hydrolysate: Enzyme-peptide interaction study using molecular docking simulation. Process Biochem. 2017, 58, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.T.; Ross, R.P.; Bolton, D.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. Bioactive peptides from muscle sources: Meat and fish. Nutrients 2011, 3, 765–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sirtori, C.R.; Galli, C.; Anderson, J.W.; Arnoldi, A. Nutritional and nutraceutical approaches to dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis prevention: Focus on dietary proteins. Atherosclerosis 2009, 203, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.-L.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, Q.; Fu, Y.-H.; Jin, W.-G.; Zhu, B.-W. Affinity purification of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from Volutharpa ampullacea perryi protein hydrolysate using Zn-SBA-15 immobilized ACE. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 244, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Liu, J.; Ma, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Yan, E.; Zhu, H. Isolation and purification of antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory peptides from Yak (Bos grunniens) skin. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e13123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, S.; Jamdar, S.N. Purification and identification of Ace-inhibitory peptides from poultry viscera protein hydrolysate. J. Food Biochem. 2017, 41, e12275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhedi, O. Basic and recent advances in marine antihypertensive peptides: Production, structure-activity relationship and bioavailability. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Cao, J.; Guo, H.; Zhao, B. Studies on purification and the molecular mechanism of a novel ACE inhibitory peptide from whey protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubczyk, A.; Baraniak, B. Angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides obtained after in vitro hydrolysis of pea (Pisum sativum var. Bajka) globulins. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 438459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montone, C.M.; Capriotti, A.L.; Cavaliere, C.; La Barbera, G.; Piovesana, S.; Zenezini Chiozzi, R.; Lagana, A. Peptidomic strategy for purification and identification of potential ACE-inhibitory and antioxidant peptides in Tetradesmus obliquus microalgae. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 3573–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, X.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ulaah, S. Isolation, purification and the anti-hypertensive effect of a novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from Ruditapes philippinarum fermented with Bacillus natto. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5230–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, P.; Lan, X.; Liao, D.; Sun, L.; Zhou, L.; Sun, J.; Tong, Z. Isolation and characterization of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from the enzymatic hydrolysate of carapax trionycis (the shell of the Turtle Pelodiscus sinensis). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7015–7022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Su, R.Q.; Zhang, W.T.; Chen, J. Purification and the secondary structure of a novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from the alcalase hydrolysate of seahorse protein. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 3927–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapel, R.; Rahhou, E.; Lecouturier, D.; Guillochon, D.; Dhulster, P. Characterization of an antihypertensive peptide from an Alfalfa white protein hydrolysate produced by a continuous enzymatic membrane reactor. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuchprapha, A.; Paisansak, S.; Sangtanoo, P.; Srimongkol, P.; Saisavoey, T.; Reamtong, O.; Choowongkomon, K.; Karnchanatat, A. Two novel ACE inhibitory peptides isolated from longan seeds: Purification, inhibitory kinetics and mechanisms. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 12711–12720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Alashi, A.; Young, J.; Therkildsen, M.; Aluko, R. Enzyme inhibition kinetics and molecular interactions of patatin peptides with angiotensin I-converting enzyme and renin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pina, A.; Roque, A. Studies on molecular recognition between bioactive peptides and angiotensin-converting enzyme. J. Mol. Recognit. 2009, 22, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalkute, C.B.; Barage, S.H.; Dhanavade, M.J.; Sonawane, K.D. Molecular dynamics simulation and molecular docking studies of Angiotensin converting enzyme with inhibitor lisinopril and amyloid beta peptide. Protein J. 2013, 32, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Zhang, R.; Liu, F.; Zheng, T.; Wu, W. Molecular mechanism of interactions between inhibitory tripeptide GEF and angiotensin-converting enzyme in aqueous solutions by molecular dynamic simulations. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, M.; Wang, C.; Chen, C.; Zhang, R.; Liu, H.; Lu, W.; Jiang, L.; Du, M. Identification of a novel ACE-inhibitory peptide from casein and evaluation of the inhibitory mechanisms. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wu, S.; Zhao, W.; Ding, L.; Shiuan, D.; Chen, F.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Identification and the molecular mechanism of a novel myosin-derived ACE inhibitory peptide. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompella, U.B.; Lee, V.H. Delivery systems for penetration enhancement of peptide and protein drugs: Design considerations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 211–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tian, H.; Shi, P.; Li, G. Isolation of novel ACE-inhibitory and antioxidant peptides from quinoa bran albumin assisted with an in silico approach: Characterization, in vivo Antihypertension, and Molecular docking. Molecules 2019, 24, 4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yu, R.; Dong, S.; Wu, H. Novel natural angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides derived from sea cucumber-modified hydrolysates by adding exogenous proline and a study of their structure(-)activity relationship. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, K.; Zhang, L.-W.; Han, X.; Cheng, D.-Y. Novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from protease hydrolysates of Qula casein: Quantitative structure-activity relationship modeling and molecular docking study. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 32, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Xue, S.; Yu, Z.; Ding, L.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Novel ACE inhibitors derived from soybean proteins using in silico and in vitro studies. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, Q.; Wan, S.; Zhang, J. Molecular dynamics simulation and free energy calculation studies of the binding mechanism of allosteric inhibitors with TrkA kinase. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Bian, X.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, H. Insight into the binding of ACE-inhibitory peptides to angiotensin-converting enzyme: A molecular simulation. Mol. Simul. 2018, 45, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Y.; Chen, S.; Cai, S.; Liu, S.; Pan, N.; Su, J.; Qiao, K.; Xu, M.; Chen, B.; Yang, S.; et al. A Novel Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptide from Takifugu flavidus. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120651
Su Y, Chen S, Cai S, Liu S, Pan N, Su J, Qiao K, Xu M, Chen B, Yang S, et al. A Novel Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptide from Takifugu flavidus. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(12):651. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120651
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Yongchang, Shicheng Chen, Shuilin Cai, Shuji Liu, Nan Pan, Jie Su, Kun Qiao, Min Xu, Bei Chen, Suping Yang, and et al. 2021. "A Novel Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptide from Takifugu flavidus" Marine Drugs 19, no. 12: 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120651
APA StyleSu, Y., Chen, S., Cai, S., Liu, S., Pan, N., Su, J., Qiao, K., Xu, M., Chen, B., Yang, S., & Liu, Z. (2021). A Novel Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptide from Takifugu flavidus. Marine Drugs, 19(12), 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120651






