On the Path to Thermo-Stable Collagen: Culturing the Versatile Sponge Chondrosia reniformis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
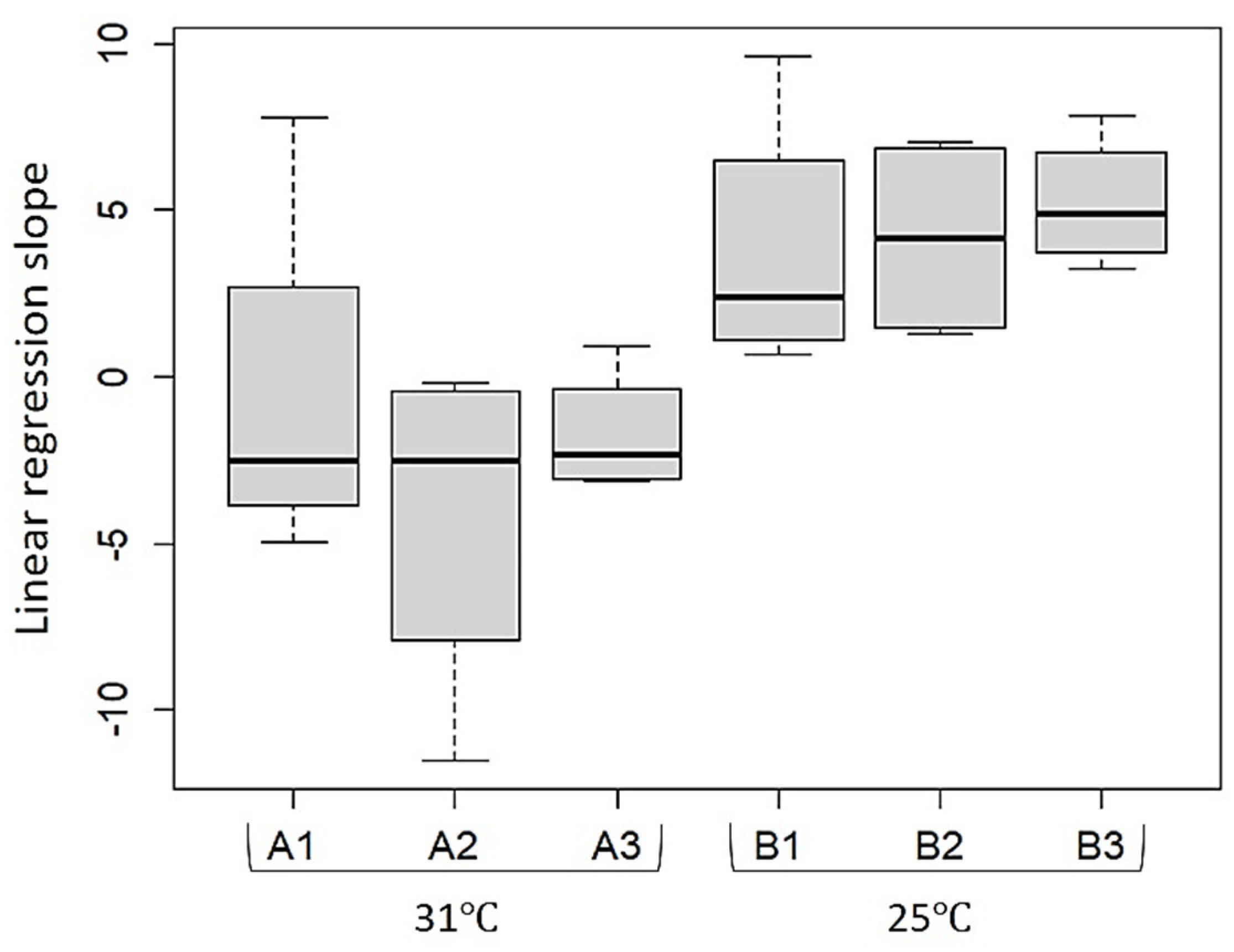
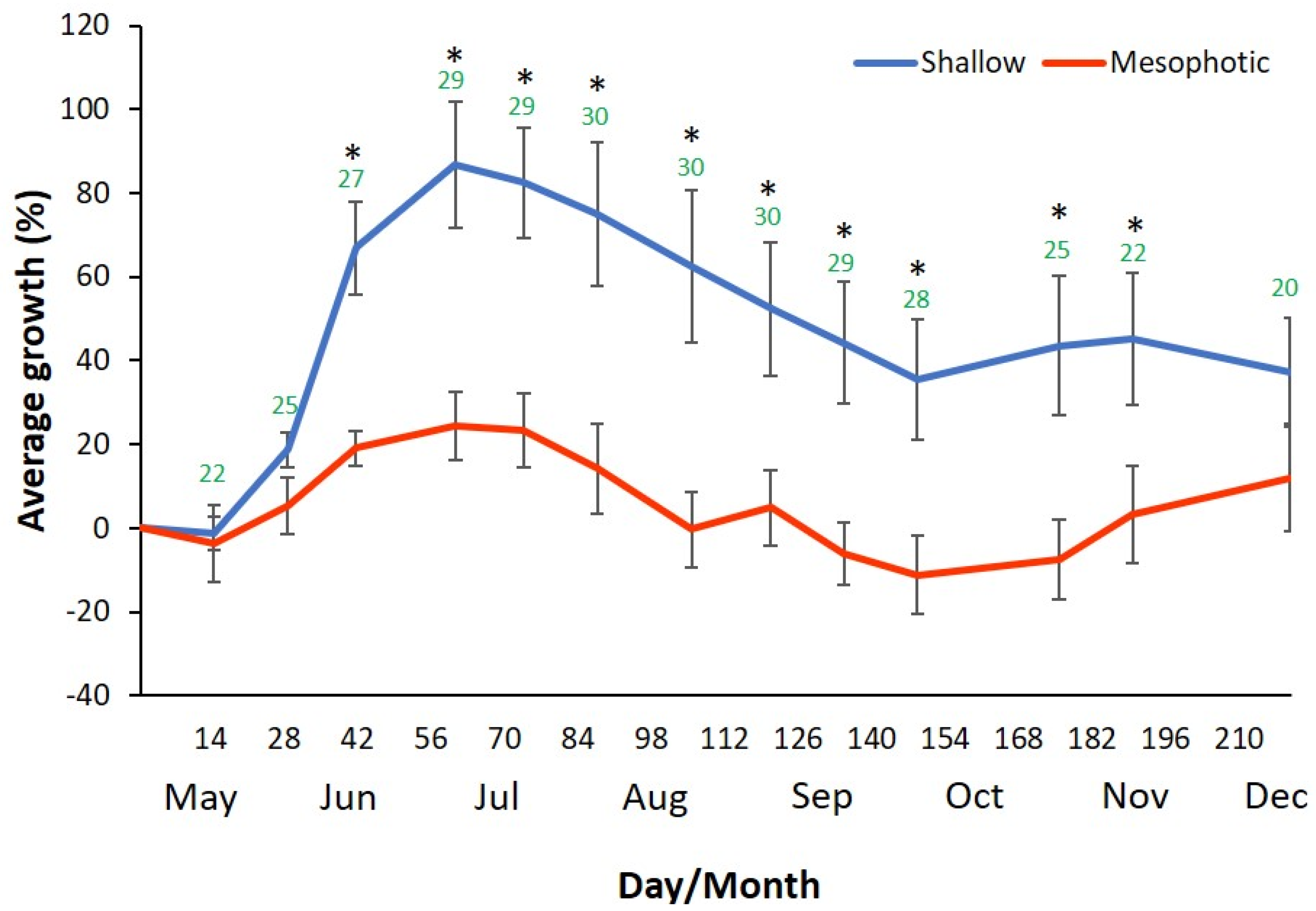
2. Results
2.1. Sea-Based Mariculture System Experiment
2.2. Land-Based Culture System Experiment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Research Sites
4.2. Sponge Collection
4.3. Sea-Based Mariculture System Experiment
4.4. Land-Based Culture Experiment
4.5. Experimental Design
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Measurement Date | p-Value |
|---|---|
| 21 May 2019 | 0.744 |
| 4 June 2019 | 0.137 |
| 24 June 2019 | <0.0001 |
| 12 July 2019 | 0.0008 |
| 25 July 2019 | 0.0001 |
| 8 August 2019 | 0.0128 |
| 26 August 2019 | 0.0086 |
| 12 September 2019 | 0.0235 |
| 26 September 2019 | 0.0042 |
| 10 October 2019 | 0.0128 |
| 7 November 2019 | 0.0086 |
| 21 November 2019 | 0.0235 |
| 21 December 2019 | 0.0975 |
| Measurement Date | Water Temperature (℃) |
|---|---|
| 6 May 2019 | 21 |
| 21 May 2019 | 22 |
| 4 June 2019 | 25 |
| 24 June 2019 | 27 |
| 12 July 2019 | 29 |
| 25 July 2019 | 29 |
| 8 August 2019 | 30 |
| 26 August 2019 | 30 |
| 12 September 2019 | 30 |
| 26 September 2019 | 29 |
| 10 October 2019 | 28 |
| 7 November 2019 | 25 |
| 21 November 2019 | 22 |
| 21 December 2019 | 20 |
References
- Shoulders, M.D.; Raines, R.T. Collagen structure and stability. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 929–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fassini, D.; Wilkie, I.C.; Pozzolini, M.; Ferrario, C.; Sugni, M.; Rocha, M.S.; Giovine, M.; Bonasoro, F.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Diverse and productive source of biopolymer inspiration: Marine collagens. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 1815–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila Rodríguez, M.I.; Rodríguez Barroso, L.G.; Sánchez, M.L. Collagen: A review on its sources and potential cosmetic applications. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Pérez-Mateos, M.; Gómez-Estaca, J.; López-Caballero, E.; Giménez, B.; Montero, P. Fish gelatin: A renewable material for developing active biodegradable films. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Ikeda, T.; Yanagiguchi, K.; Hayashi, Y. Potency of fish collagen as a scaffold for regenerative medicine. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 302932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Tao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xu, T.; Niu, W. Applications of marine collagens in bone tissue engineering. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 16, 042007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.A.; Araujo, T.A.; Avanzi, I.R.; Parisi, J.R.; de Andrade, A.L.M.; Rennó, A.C.M. Collagen from marine sources and skin wound healing in animal experimental studies: A systematic review. Mar. Biotechnol. 2021, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.H.; Moreira-Silva, J.; Marques, A.L.P.; Domingues, A.; Bayon, Y.; Reis, R.L. Marine origin collagens and its potential applications. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5881–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhagwat, P.K.; Dandge, P.B. Collagen and collagenolytic proteases: A review. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 15, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felician, F.F.; Xia, C.; Qi, W.; Xu, H. Collagen from marine biological sources and medical applications. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1700557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrone, R.; Huc, A.; Junqua, S. Fine structure and physicochemical studies on the collagen of the marine sponge Chondrosia reniformis Nardo. J. Ultrasruct. Res. 1975, 52, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Grosvenor, A.J.; Dyer, J.M. Marine Spongia collagens: Protein characterization and evaluation of hydrogel films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, E.E. Invertebrate Zoology: A Functional Evolutionary Approach, 7th ed.; Thomson-Brooks/Cole: Belmont, CA , USA, 2004; ISBN 0030259827. [Google Scholar]
- John, H.; van Soest, R. Systema Porifera: A Guide to the Classification of Sponges; Kluwer Academi/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mehbub, M.F.; Lei, J.; Franco, C.; Zhang, W. Marine sponge derived natural products between 2001 and 2010: Trends and opportunities for discovery of bioactives. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4539–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rotter, A.; Barbier, M.; Bertoni, F.; Bones, A.M.; Cancela, M.L.; Carlsson, J.; Carvalho, M.F.; Cegłowska, M.; Chirivella-Martorell, J.; Conk Dalay, M.; et al. The essentials of marine biotechnology. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, R.; Ruocco, N.; Viel, T.; Federico, S.; Zupo, V.; Costantini, M. Sponges and their symbionts as a source of valuable compounds in Cosmeceutical Field. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sionkowska, A.; Kaczmarek, B.; Lewandowska, K.; Grabska, S.; Pokrywczyńska, M.; Kloskowski, T.; Drewa, T. 3D composites based on the blends of chitosan and collagen with the addition of hyaluronic acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 89, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, M.; Castilho, M.; Yue, Z.; Glattauer, V.; Hughes, T.C.; Ramshaw, J.A.M.; Wallace, G.G. Shaping collagen for engineering hard tissues: Towards a printomics approach. Acta Biomater. 2021, 131, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handley, S.; Page, M.; Northcote, P. Anti-cancer sponge : The race is on for aquaculture supply. Water Atmos. 2006, 14, 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Conkling, M.; Hesp, K.; Munroe, S.; Sandoval, K.; Martens, D.E.; Sipkema, D.; Wijffels, R.H.; Pomponi, S.A. Breakthrough in marine invertebrate cell culture: Sponge cells divide rapidly in improved nutrient medium. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scarfì, S.; Pozzolini, M.; Oliveri, C.; Mirata, S.; Salis, A.; Damonte, G.; Fenoglio, D.; Altosole, T.; Ilan, M.; Bertolino, M.; et al. Identification, purification and molecular characterization of chondrosin, a New Protein with anti-tumoral activity from the marine sponge Chondrosia reniformis nardo 1847. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechev, J.; Christie, W.W.; Robaina, R.; De Diego, F.M.; Ivanova, A.; Popov, S.; Stefanov, K. Chemical composition of the sponge Chondrosia reniformis from the Canary Islands. Hydrobiologia 2002, 489, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonasoro, F.; Wilkie, I.C.; Bavestrello, G.; Cerrano, C.; Candia Carnevali, M.D. Dynamic structure of the mesohyl in the sponge Chondrosia reniformis (Porifera, Demospongiae). Zoomorphology 2001, 121, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavestrello, G.; Cerrano, C.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Sara, M.; Calabria, F.; Cortesogno, L. Selective incorporation of foreign material in Chondrosia reniformis (Porifera, Demospongiae). Ital. J. Zool. 2009, 63, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavestrello, G.; Benatti, U.; Calcinai, B.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Cerrano, C.; Favre, A.; Giovine, M.; Lanza, S.; Pronzato, R.; Sara, M. Body polarity and mineral selectivity in the demosponge Chondrosia reniformis. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 195, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, S.; Ehrlich, H.; Douglas, T.; Heinemann, C.; Worch, H.; Schatton, W.; Hanke, T. Ultrastructural studies on the collagen of the marine sponge Chondrosia reniformis nardo. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3452–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imhoff, J.M.; Garrone, R. Solubilization and characterization of Chondrosia reniformis sponge collagen. Connect. Tissue Res. 1983, 11, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzolini, M.; Bruzzone, F.; Berilli, V.; Mussino, F.; Cerrano, C.; Benatti, U.; Giovine, M. Molecular characterization of a nonfibrillar collagen from the marine sponge Chondrosia reniformis Nardo 1847 and positive effects of soluble silicates on its expression. Mar. Biotechnol. 2012, 14, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swatschek, D.; Schatton, W.; Kellermann, J.; Müller, W.E.G.; Kreuter, J. Marine sponge collagen: Isolation, characterization and effects on the skin parameters surface-pH, moisture and sebum. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2002, 53, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzolini, M.; Scarfì, S.; Gallus, L.; Castellano, M.; Vicini, S.; Cortese, K.; Gagliani, M.C.; Bertolino, M.; Costa, G.; Giovine, M. Production, characterization and biocompatibility evaluation of collagen membranes derived from marine sponge chondrosia reniformis Nardo, 1847. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nickel, M.; Brümmer, F. In vitro sponge fragment culture of Chondrosia reniformis (Nardo, 1847). J. Biotechnol. 2003, 100, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökalp, M.; Wijgerde, T.; Sarà, A.; De Goeij, J.M.; Osinga, R. Development of an integrated mariculture for the collagen-rich sponge Chondrosia reniformis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gökalp, M.; Kooistra, T.; Rocha, M.S.; Silva, T.H.; Osinga, R.; Murk, A.J.; Wijgerde, T. The effect of depth on the morphology, bacterial clearance, and respiration of the mediterranean sponge chondrosia reniformis (Nardo, 1847). Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H.; Wysokowski, M.; Zółtowska-Aksamitowska, S.; Petrenko, I.; Jesionowski, T. Collagens of poriferan origin. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkinson, C.R.; Vacelet, J. Transplantation of marine sponges to different conditions of light and current. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1979, 37, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoms, C.; Horn, M.; Wagner, M.; Hentschel, U.; Proksch, P. Monitoring microbial diversity and natural product profiles of the sponge Aplysina cavernicola following transplantation. Mar. Biol. 2003, 142, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, E.L.; Clark, G.F. Recipient environment more important than community composition in determining the success of an experimental sponge transplant. Restor. Ecol. 2007, 15, 638–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckworth, A.R.; Peterson, B.J. Effects of seawater temperature and pH on the boring rates of the sponge Cliona celata in scallop shells. Mar. Biol. 2012, 160, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, M.; Sheridan, C.; Osinga, R.; Dionísio, G.; Rocha, R.; Silva, B.; Rosa, R.; Calado, R. Marine microorganism-invertebrate assemblages: Perspectives to solve the “supply problem” in the initial steps of drug discovery. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3929–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Xue, S.; Zhang, W. Bioactive compounds from marine sponges and cell culture of marine sponges. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 18, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Di Camillo, C.; Coppari, M.; Bartolucci, I.; Bo, M.; Betti, F.; Bertolino, M.; Calcinai, B.; Cerrano, C.; De Grandis, G.; Bavestrello, G. Temporal variations in growth and reproduction of Tedania anhelans and Chondrosia reniformis in the North driatic sea. In Ancient Animals, New Challenges: Developments in Hydrobiology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; p. 219. [Google Scholar]
- Ribes, M.; Coma, R.; Gili, J. Natural diet and grazing rate of the temperate sponge Dysidea avara (Demospongiae, Dendroceratida) throughout an annual cycle. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 176, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riisgard, H.U.; Jakobsenl, H.; Larsen, P.S. Suspension feeding in marine sponges Halichondria panicea and Haliclona urceolus: Effects of temperature on filtration rate and energy cost of pumping. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 96, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rützler, K.; Duran, S.; Piantoni, C. Adaptation of reef and mangrove sponges to stress: Evidence for ecological speciation exemplified by Chondrilla caribensis new species (Demospongiae, Chondrosida). Mar. Ecol. 2007, 28, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionkowska, A.; Adamiak, K.; Musiał, K.; Gadomska, M. Collagen based materials in cosmetic applications: A review. Materials 2020, 13, 4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaniv, M.-T. Life Cycle, Abundance and Distribution of the Mediterranean Sponge Chondrosia reniformis. Master’s Thesis, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; Handley, S.J.; Northcote, P.T.; Cairney, D.; Willan, R.C. Successes and pitfalls of the aquaculture of the sponge Mycale hentscheli. Aquaculture 2011, 312, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. General Rights lmerTest Package: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models lmerTest Package: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models. DTU Orbit. 2017, p. 82. Available online: https://backend.orbit.dtu.dk/ws/portalfiles/portal/140635100/lmerTestJStatSoft2017.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2021).
- Orel, B. Data for the Paper—“On the Path to Thermo-Stable Collagen: Culturing the Versatile Sponge Chondrosia reniformis” Orel et al. 2021 figshare. Dataset. Available online: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.17082071.v1 (accessed on 19 October 2021).







| Collection Site | Coordinates | Depth (m) | Number of Specimens | Collection Date | Collected with | Collected for |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesophotic site off Herzliya’s coast | 32.17710° N, 34.63306° E | ~100 | 9 | 11 February 2019 | ROV | Sea-based mariculture system |
| 8 | 13 February 2019 | |||||
| Shallow site off Sdot-Yam coast | 32.40090° N, 34.86192° E | 2–6 | 20 | 8 March 2019 | SCUBA | Land-based mariculture system |
| 2 | 28 February 2020 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orel, B.; Giovine, M.; Ilan, M. On the Path to Thermo-Stable Collagen: Culturing the Versatile Sponge Chondrosia reniformis. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120669
Orel B, Giovine M, Ilan M. On the Path to Thermo-Stable Collagen: Culturing the Versatile Sponge Chondrosia reniformis. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(12):669. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120669
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrel, Boaz, Marco Giovine, and Micha Ilan. 2021. "On the Path to Thermo-Stable Collagen: Culturing the Versatile Sponge Chondrosia reniformis" Marine Drugs 19, no. 12: 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120669
APA StyleOrel, B., Giovine, M., & Ilan, M. (2021). On the Path to Thermo-Stable Collagen: Culturing the Versatile Sponge Chondrosia reniformis. Marine Drugs, 19(12), 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120669






