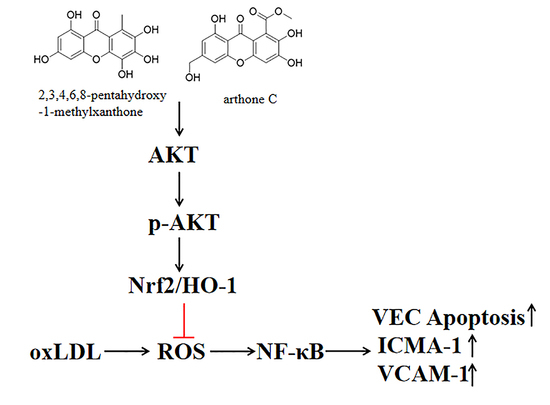
Protective Effect of Flavonoids from a Deep-Sea-Derived Arthrinium sp. against ox-LDL-Induced Oxidative Injury through Activating the AKT/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway in Vascular Endothelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Compounds 1 and 2 Inhibited ox-LDL-Induced HUVEC Apoptosis and Adhesion Factors Expression
2.2. The Compounds 1 and 2 Significantly Inhibited the Accumulation of ROS and the Activation of NF-κB in HUVECs
2.3. The Compounds 1 and 2 Activated AKT/Nrf2/HO-1 Antioxidant Pathway
2.4. Compounds 1 and 2 Protected VECs and Mediated Nrf2 Activation through AKT
2.5. Knockdown of Nrf2 Abolished the Inhibition Effects of Compounds on ox-LDL-Induced Apoptosis and Adhesion Factor Expression
2.6. Knockdown of the Nrf2 Suppressed the Effects of the Compounds 1 and 2 on the Increased ROS Level and the NF-κB Nuclear Translocation Induced by ox-LDL in HUVECs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Immunofluorescence Assay
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. TUNEL Staining
4.6. Hoechst33258 Staining for Apoptosis
4.7. Intracellular ROS Assay
4.8. Transient Transfection and RNA Interference
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, P.; Xiu, C.H.; Wang, L.F. The relationship between carotid atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Chin. J. Atheroscler. 2014, 22, 1175–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Xu, Y. Essential oils from fructose A. zerumbet protect human aortic endothelial cells from apoptosis induced by Ox-LDL in vitro. Evid. Complement. Alternat. Med. 2014, 14, 956824. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, M.M.; Samuel, T.; Mitchell, T. Birc2 (cIap1) regulates endothelial cell integrity and blood vessel homeostasis. Nat. Genet. 2017, 39, 1397–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Kim, C.W.; Simmons, R.D.; Jo, H. Role of flow-sensitive microRNAs in endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis: Mechanosensitive atheromiRs, Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 2206–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, W.; Zhang, L. MicroRNA-26a prevents endothelial cell apoptosis by directly targeting TRPC6 in the setting of atherosclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Incalza, M.A.; D’Oria, R.; Natalicchio, A.; Perrini, S.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F. Oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species in endothelial dysfunction associated with cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2018, 100, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Setorki, M.; Doudi, M.; Baradaran, A.; Nasri, H. Atherosclerosis: Process, indicators, risk factors and new hopes. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2014, 5, 927. [Google Scholar]
- Suciu, C.F.; Prete, M.; Ruscitti, P.; Favoino, E.; Giacomelli, R.; Perosa, F. Oxidized low density lipoproteins: The bridge between atherosclerosis and autoimmunity. Possible implications in accelerated atherosclerosis and for immune intervention in autoimmune rheumatic disorders. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.H.; Li, J.M.; Zhou, Q.L.; Li, G.Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.W. Effects of miR-590 on ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell apoptosis: Roles of p53 and NF-κB. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zou, Z.; Wang, X.; Ji, X.; Yang, J. Pinoresinol Diglucoside Alleviates ox-LDL-Induced Dysfunction in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 3124519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattoor, A.J.; Kanuri, S.H.; Mehta, J.L. Role of Ox-LDL and LOX-1 in Atherogenesis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 1693–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.W.; Ding, P. New Bioactive Metabolites from the Marine-derived Fungi Aspergillus. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 1072–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Wu, Z.; Guo, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, S. A Review of Terpenes from Marine-Derived Fungi: 2015–2019. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Yi, M.; Ding, L.; He, S. A Review of Anti-Inflammatory Compounds from Marine Fungi, 2000–2018. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willems, T.; De Mol, M.L.; De Bruycker, A.; De Maeseneire, S.L.; Soetaert, W.K. Alkaloids from Marine Fungi: Promising Antimicrobials. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, E., Jr.; Kandaswami, C.; Theoharides, T.C. The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells: Implications for inflammation, heart disease, and cancer. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000, 52, 673–751. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, J.; He, F.; Yu, J.H.; Zhai, H.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Jiang, C.S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; et al. New Chromones from a Marine-Derived Fungus, Arthrinium sp., and Their Biological Activity. Molecules 2018, 23, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wairata, J.; Sukandar, E.R.; Fadlan, A.; Purnomo, A.S.; Taher, M.; Ersam, T. Evaluation of the Antioxidant, Antidiabetic, and Antiplasmodial Activities of Xanthones Isolated from Garcinia forbesii and their in silico Studies. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.H.; Nguyen, V.T.; Le, H.T.; Nguyen, H.M.; Tran, T.H.; Do Thi, T.; Nguyen, X.C.; Ha, M.T. Garcinoxanthones SV, new xanthone derivatives from the pericarps of Garcinia mangostana together with their cytotoxic and antioxidant activities. Fitoterapia 2021, 151, 104880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, A.R.; Farag, M.A. Marine and terrestrial endophytic fungi: A mine of bioactive xanthone compounds, recent progress, limitations, and novel applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2021, 15, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.H.; Liu, D.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.L.; Lin, W.H. Antioxidant xanthones and anthraquinones isolated from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 16, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.J.; Hu, G.Y.; Jiang, J.L.; Xiang, H.L.; Deng, H.W.; Li, Y.J. Relationship between protective effect of xanthone on endothelial cells and endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 5171–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Zhang, D.L.; Jia, M.; Hao, W.H.; Li, Y.J. Mangiferin inhibits high-fat diet induced vascular injury via regulation of PTEN/AKT/eNOS pathway. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 137, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhu, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y. Nicotine-mediated autophagy of vascular smooth muscle cell accelerates atherosclerosis via nAChRs/ROS/NF-κB signaling pathway. Atherosclerosis 2019, 284, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loboda, A.; Damulewicz, M.; Pyza, E.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: An evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3221–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Wang, M.; Ye, J.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Mechanism overview and target mining of atherosclerosis: Endothelial cell injury in atherosclerosis is regulated by glycolysis (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirillo, A.; Norata, G.D.; Catapano, A.L. LOX-1, ox-LDL, and atherosclerosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 152786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grassi, D.; Desideri, G.; Ferri, C. Flavonoids: Antioxidants against atherosclerosis. Nutrients 2010, 2, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, D.J.; Jiang, J.L.; Tan, G.S.; Huang, Z.Z.; Deng, H.W.; Li, Y.J. Demethylbellidifolin inhibits adhesion of monocytes to endothelial cells via reduction of tumor necrosis factor alpha and endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitor level. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 1150–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.Q.; Chen, X. A simple reproducible model of free radical-injured isolated heart induced by 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH). J. Pharm. Toxicol. Methods 1998, 39, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cominacini, L.; Garbin, U.; Pasini, A.F.; Davoli, A.; Campagnola, M.; Pastorino, A.M.; Gaviraghi, G.; Lo Cascio, V. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein increases the production of intracellular reactive oxygen species in endothelial cells: Inhibitory effect of lacidipine. J. Hypertens. 1998, 16 Pt 2, 1913–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Buttari, B.; Panieri, E.; Profumo, E.; Saso, L. An Overview of Nrf2 Signaling Pathway and Its Role in Inflammation. Molecules 2020, 25, 5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juurlink, B.H. Dietary Nrf2 activators inhibit atherogenic processes. Atherosclerosis 2012, 225, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Kishimoto, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Sato, A.; Kamiya, T.; Kondo, K.; Iida, K. Terminalia bellirica (Gaertn.) Roxb. Extract and Gallic Acid Attenuate LPS-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via MAPK/NF-κB and AKT/AMPK/Nrf2 Pathways. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 9364364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Han, Z.; Bu, X.; Yu, W.; Wang, J. Retraction notice to “Cytoprotective effects of euxanthone against ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell injury is mediated via Nrf2. Life Sci. 2019, 223, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, M.B.; Rajendran, P.; AbuZahra, H.M.; Veeraraghavan, V.P. Mangiferin Inhibits Apoptosis in Doxorubicin-Induced Vascular Endothelial Cells via the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; He, J.; He, S.; Yin, Y. Resveratrol Attenuates Oxidative Stress-Induced Intestinal Barrier Injury through PI3K/Akt-Mediated Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 7591840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakaso, K.; Yano, H.; Fukuhara, Y.; Takeshima, T.; Wada-Isoe, K.; Nakashima, K. PI3K is a key molecule in the Nrf2-mediated regulation of antioxidative proteins by hemin in human neuroblastoma cells. FEBS Lett. 2003, 546, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, J.-R.; Wang, Y.-H.; Zhong, Y.-N.; Che, T.-T.; Hu, Y.; Bao, J.; Meng, N. Protective Effect of Flavonoids from a Deep-Sea-Derived Arthrinium sp. against ox-LDL-Induced Oxidative Injury through Activating the AKT/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway in Vascular Endothelial Cells. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120712
Hou J-R, Wang Y-H, Zhong Y-N, Che T-T, Hu Y, Bao J, Meng N. Protective Effect of Flavonoids from a Deep-Sea-Derived Arthrinium sp. against ox-LDL-Induced Oxidative Injury through Activating the AKT/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway in Vascular Endothelial Cells. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(12):712. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120712
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Jia-Rong, Yan-Hong Wang, Ying-Nan Zhong, Tong-Tong Che, Yang Hu, Jie Bao, and Ning Meng. 2021. "Protective Effect of Flavonoids from a Deep-Sea-Derived Arthrinium sp. against ox-LDL-Induced Oxidative Injury through Activating the AKT/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway in Vascular Endothelial Cells" Marine Drugs 19, no. 12: 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120712
APA StyleHou, J.-R., Wang, Y.-H., Zhong, Y.-N., Che, T.-T., Hu, Y., Bao, J., & Meng, N. (2021). Protective Effect of Flavonoids from a Deep-Sea-Derived Arthrinium sp. against ox-LDL-Induced Oxidative Injury through Activating the AKT/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway in Vascular Endothelial Cells. Marine Drugs, 19(12), 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19120712