Development of Antioxidant Protein Extracts from Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) Side Streams Assisted by Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
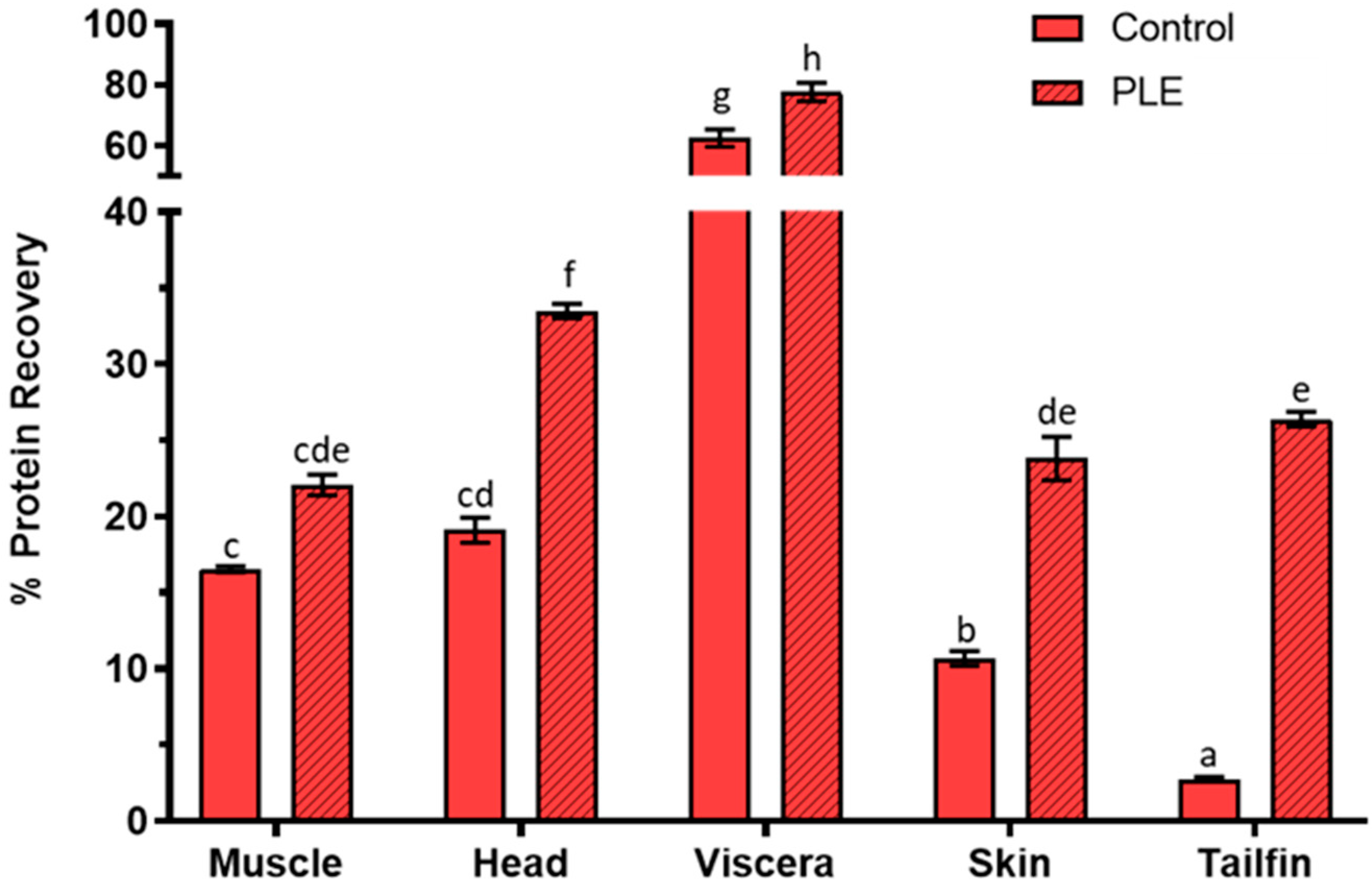
2.1. Protein Recovery Percentage
2.2. Protein Molecular Weight Distribution
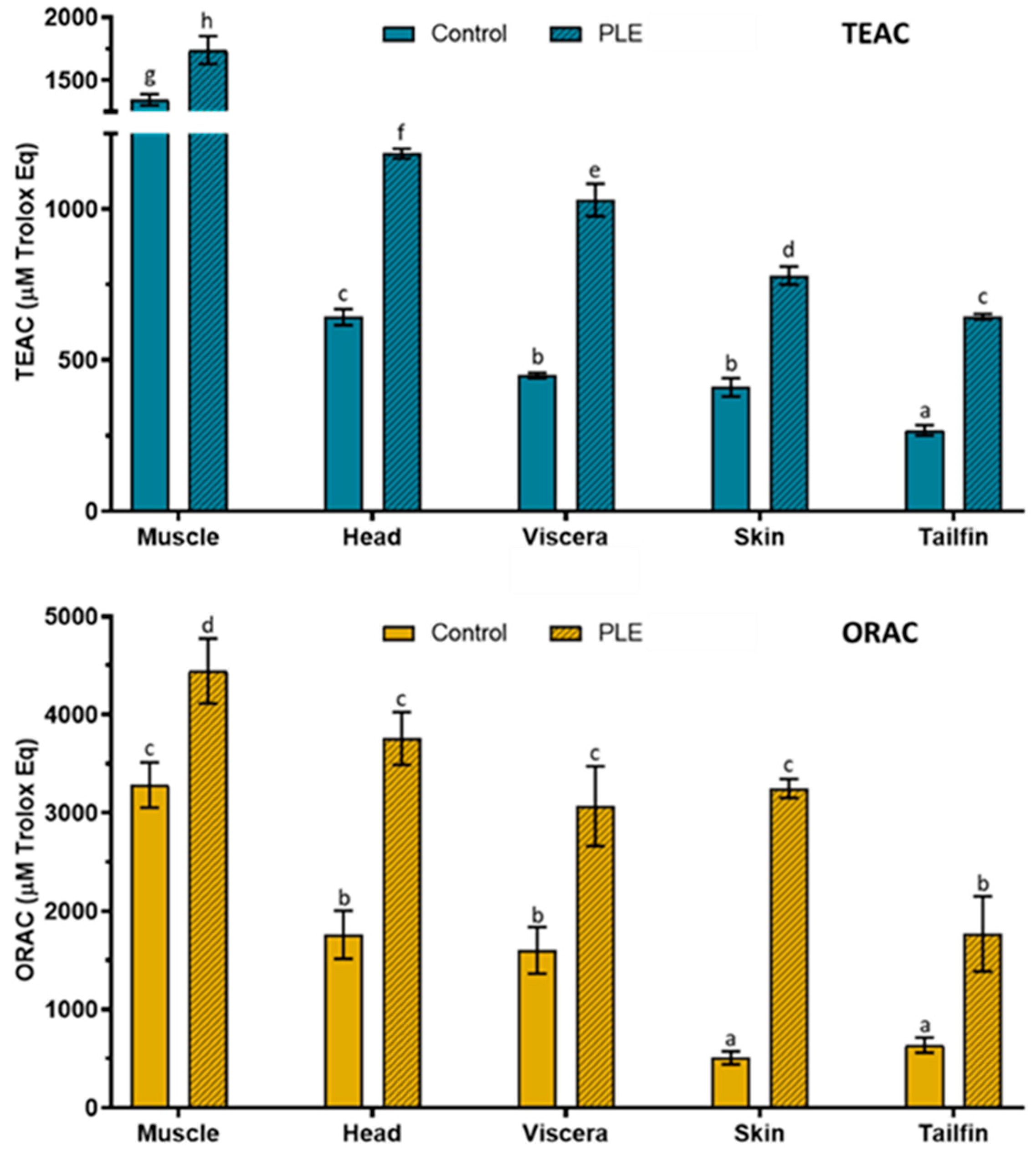
2.3. Total Antioxidant Capacity
2.4. Determination of Heavy Metals and Mycotoxins in Side Streams of Gilthead Sea Bream
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
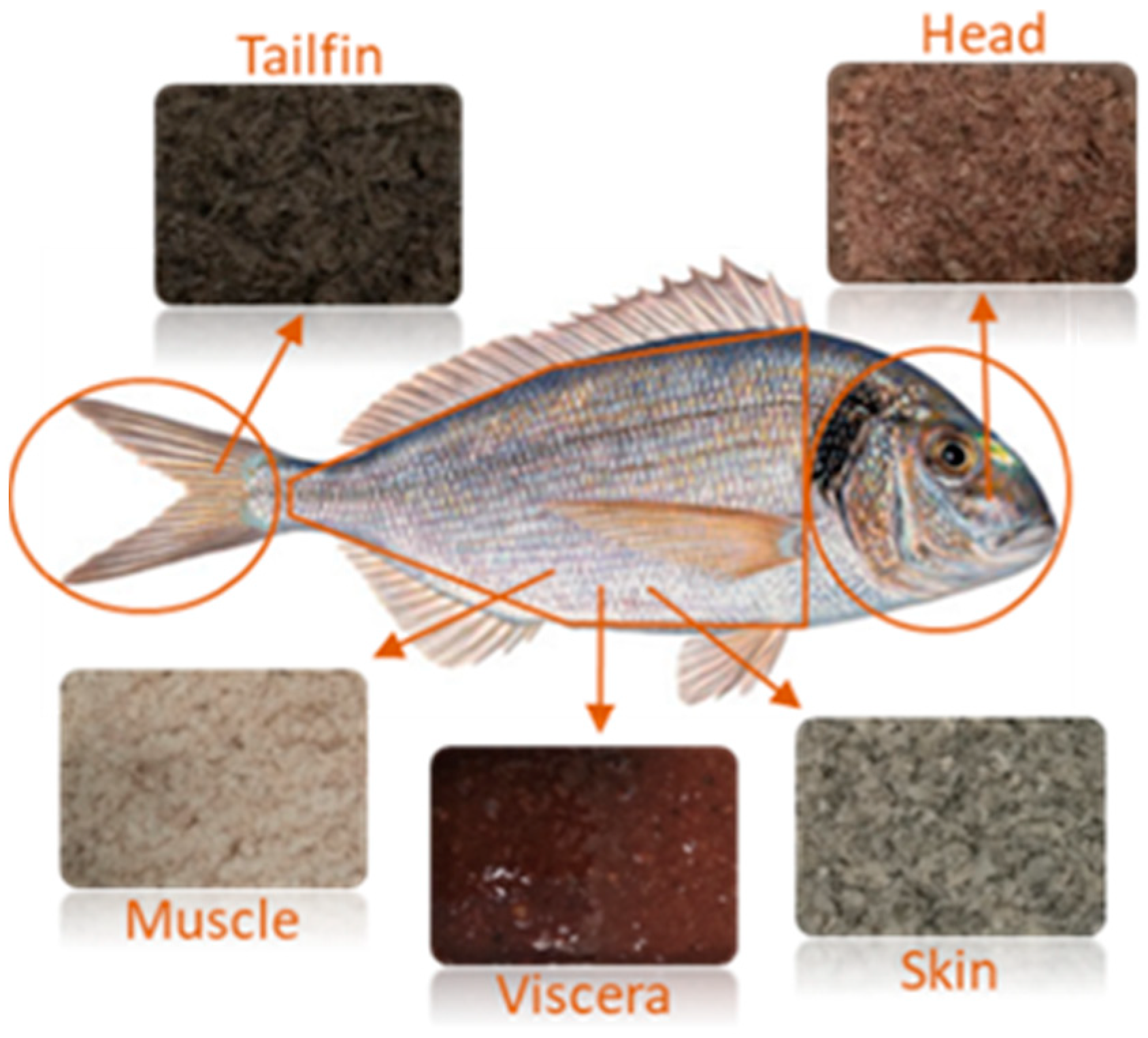
3.2. Raw Material and Sample Preparation
3.3. Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE) Process
3.4. Determination of Protein Recovery
3.5. Molecular Weight Distribution of Protein Fragments
3.6. Evaluation of Total Antioxidant Capacity
3.6.1. Trolox Equivalent Antioxidant Capacity Assay (TEAC)
3.6.2. Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity Assay (ORAC)
3.7. Analysis of Heavy Metals in Gilthead Sea Bream Side Streams
3.8. Analysis of Mycotoxins in Gilthead Sea Bream Side Streams
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anonymous. The EU Fish Market 2020 Edition Is Now Online|Fisheries. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/fisheries/press/eu-fish-market-2020-edition-now-online_en (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- Directorate-General for Maritime Affairs and Fisheries (European Commission). The EU fish market highlights the EU in the world market supply consumption import-export landings in the EU aquaculture the EU fish market. In Maritime Affairs and Fisheries; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcarcel, J.; Sanz, N.; Vázquez, J.A. Optimization of the enzymatic protein hydrolysis of by-products from seabream (Sparus aurata) and seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax), chemical and functional characterization. Foods 2020, 9, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pateiro, M.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Domínguez, R.; Wang, M.; Barba, F.J.; Bermúdez, R.; Lorenzo, J.M. Nutritional profiling and the value of processing by-products from gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kandyliari, A.; Mallouchos, A.; Papandroulakis, N.; Golla, J.P.; Lam, T.T.; Sakellari, A.; Karavoltsos, S.; Vasiliou, V.; Kapsokefalou, M. Nutrient composition and fatty acid and protein profiles of selected fish by-products. Foods 2020, 9, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kandyliari, A.; Karavoltsos, S.; Sakellari, A.; Anastasiadis, P.; Asderis, M.; Papandroulakis, N.; Kapsofefalou, M. Trace metals in six fish by-products of two farmed fishes, the gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) and the meager (Argyrosomus regius): Interactions with the environment and feed. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. An Int. J. 2020, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. Food and Agriculture Organization. Feed Production. Available online: http://www.fao.org/fishery/affris/species-profiles/gilthead-seabream/feed-production/en/ (accessed on 23 February 2021).
- Nácher-Mestre, J.; Ballester-Lozano, G.F.; Garlito, B.; Portolés, T.; Calduch-Giner, J.; Serrano, R.; Hernández, F.; Berntssen, M.H.G.; Pérez-Sánchez, J. Comprehensive overview of feed-to-fillet transfer of new and traditional contaminants in Atlantic salmon and gilthead sea bream fed plant-based diets. Aquac. Nutr. 2018, 24, 1782–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantzi, I.; Pergantis, S.A.; Black, K.D.; Shimmield, T.M.; Papageorgiou, N.; Tsapakis, M.; Karakassis, I. Metals in tissues of seabass and seabream reared in sites with oxic and anoxic substrata and risk assessment for consumers. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente, B.; Pallarés, N.; Barba, F.J.; Berrada, H. An integrated approach for the valorization of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) side streams: Evaluation of contaminants and development of antioxidant protein extracts by pressurized liquid extraction. Foods 2021, 10, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhoft, A.; Høgåsen, H.R.; Rosenlund, G.; Ivanova, L.; Berntssen, M.H.G.; Alexander, J.; Eriksen, G.S.; Fæste, C.K. Tissue distribution and elimination of deoxynivalenol and ochratoxin A in dietary-exposed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- What is Horizon 2020?|Horizon. 2020. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/programmes/horizon2020/en/what-horizon-2020 (accessed on 21 March 2021).
- Khan, S.; Rehman, A.; Shah, H.; Aadil, R.M.; Ali, A.; Shehzad, Q.; Ashraf, W.; Yang, F.; Karim, A.; Khaliq, A.; et al. Fish Protein and its derivatives: The novel applications, bioactivities, and their functional significance in food products. Food Rev. Int. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Heimann, K.; Zhang, W. Protein recovery from underutilised marine bioresources for product development with nutraceutical and pharmaceutical bioactivities. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Ge, X.; Lv, Y.; Wang, A. Application of accelerated solvent extraction in the analysis of organic contaminants, bioactive and nutritional compounds in food and feed. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1237, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Rivera, G.; Bueno, M.; Ballesteros-Vivas, D.; Mendiola, J.A.; Ibañez, E. Pressurized liquid extraction. In Liquid-Phase Extraction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 375–398. ISBN 9780128169117. [Google Scholar]
- Andreu, V.; Picó, Y. Pressurized liquid extraction of organic contaminants in environmental and food samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirondart, M.; Rombaut, N.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Bily, A.; Chemat, F. Comparison between pressurized liquid extraction and conventional soxhlet extraction for rosemary antioxidants, yield, composition, and environmental footprint. Foods 2020, 9, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrysson, H.; Hayes, M.; Eimer, F.; Carlsson, N.G.; Toth, G.B.; Undeland, I. Production of protein extracts from Swedish red, green, and brown seaweeds, Porphyra umbilicalis Kützing, Ulva lactuca Linnaeus, and Saccharina latissima (Linnaeus) J. V. Lamouroux using three different methods. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 3565–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Firatligil-Durmus, E.; Evranuz, O. Response surface methodology for protein extraction optimization of red pepper seed (Capsicum frutescens). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadpitchayangkoon, P.; Park, J.W.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Conformational changes and dynamic rheological properties of fish sarcoplasmic proteins treated at various pHs. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, K.M.I.; Park, Y.J.; An, J.H.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Baek, M.K.; Kim, A.; Sohn, J.H.; Choi, J.S. Antioxidant properties of Scomber japonicus hydrolysates prepared by enzymatic hydrolysis. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2018, 27, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prihanto, A.A.; Nurdiani, R.; Bagus, A.D. Production and characteristics of fish protein hydrolysate from parrotfish (Chlorurus sordidus) head. Peer J. 2019, 7, e8297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aspmo, S.I.; Horn, S.J.; Eijsink, V.G.H. Enzymatic hydrolysis of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) viscera. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 1957–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, L.J.; Gómez, N.A.; Zapata, J.E.; López-García, G.; Cilla, A.; Alegría, A. In-vitro antioxidant capacity and cytoprotective/cytotoxic effects upon Caco-2 cells of red tilapia (Oreochromis spp.) viscera hydrolysates. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. Setting Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Food Stuffs (Text with EEA Relevance). 2006. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=celex%3A32006R1881 (accessed on 21 March 2021).
- Renieri, E.A.; Safenkova, I.V.; Alegakis, A.; Slutskaya, E.S.; Kokaraki, V.; Kentouri, M.; Dzantiev, B.B.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Cadmium, lead and mercury in muscle tissue of gilthead seabream and seabass: Risk evaluation for consumers. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolosa, J.; Font, G.; Mañes, J.; Ferrer, E. Natural occurrence of emerging Fusarium mycotoxins in feed and fish from aquaculture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 12462–12470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwitz, W. Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]

| Sea Bream Side Streams | Heavy Metals (µg/g of Wet Weight) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | Hg | Cd | Pb | |
| Muscle | 0.9381 ± 0.0110 | 0.0886 ± 0.0014 | 0.0008 ± 0.0001 | 0.0054 ± 0.0010 |
| Head | 0.8589 ± 0.0370 | 0.0593 ± 0.0001 | 0.0019 ± 0.0001 | 0.0190 ± 0.0002 |
| Viscera | 2.5865 ± 0.0233 | 0.0466 ± 0.0007 | 0.0683 ± 0.0007 | 0.0345 ± 0.0046 |
| Skin | 0.9694 ± 0.0966 | 0.0261 ± 0.0030 | 0.0101 ± 0.0003 | 0.0614 ± 0.0006 |
| Tailfin | 0.4406 ± 0.0055 | 0.0422 ± 0.0009 | 0.0079 ± 0.0004 | 0.0467 ± 0.0007 |
| Legislation * | <13.5 | <0.50 | <0.05 | <0.30 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de la Fuente, B.; Pallarés, N.; Berrada, H.; Barba, F.J. Development of Antioxidant Protein Extracts from Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) Side Streams Assisted by Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE). Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040199
de la Fuente B, Pallarés N, Berrada H, Barba FJ. Development of Antioxidant Protein Extracts from Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) Side Streams Assisted by Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE). Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(4):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040199
Chicago/Turabian Stylede la Fuente, Beatriz, Noelia Pallarés, Houda Berrada, and Francisco J. Barba. 2021. "Development of Antioxidant Protein Extracts from Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) Side Streams Assisted by Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE)" Marine Drugs 19, no. 4: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040199
APA Stylede la Fuente, B., Pallarés, N., Berrada, H., & Barba, F. J. (2021). Development of Antioxidant Protein Extracts from Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) Side Streams Assisted by Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE). Marine Drugs, 19(4), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040199








