Total Synthesis and Anti-Inflammatory Bioactivity of (−)-Majusculoic Acid and Its Derivatives
Abstract
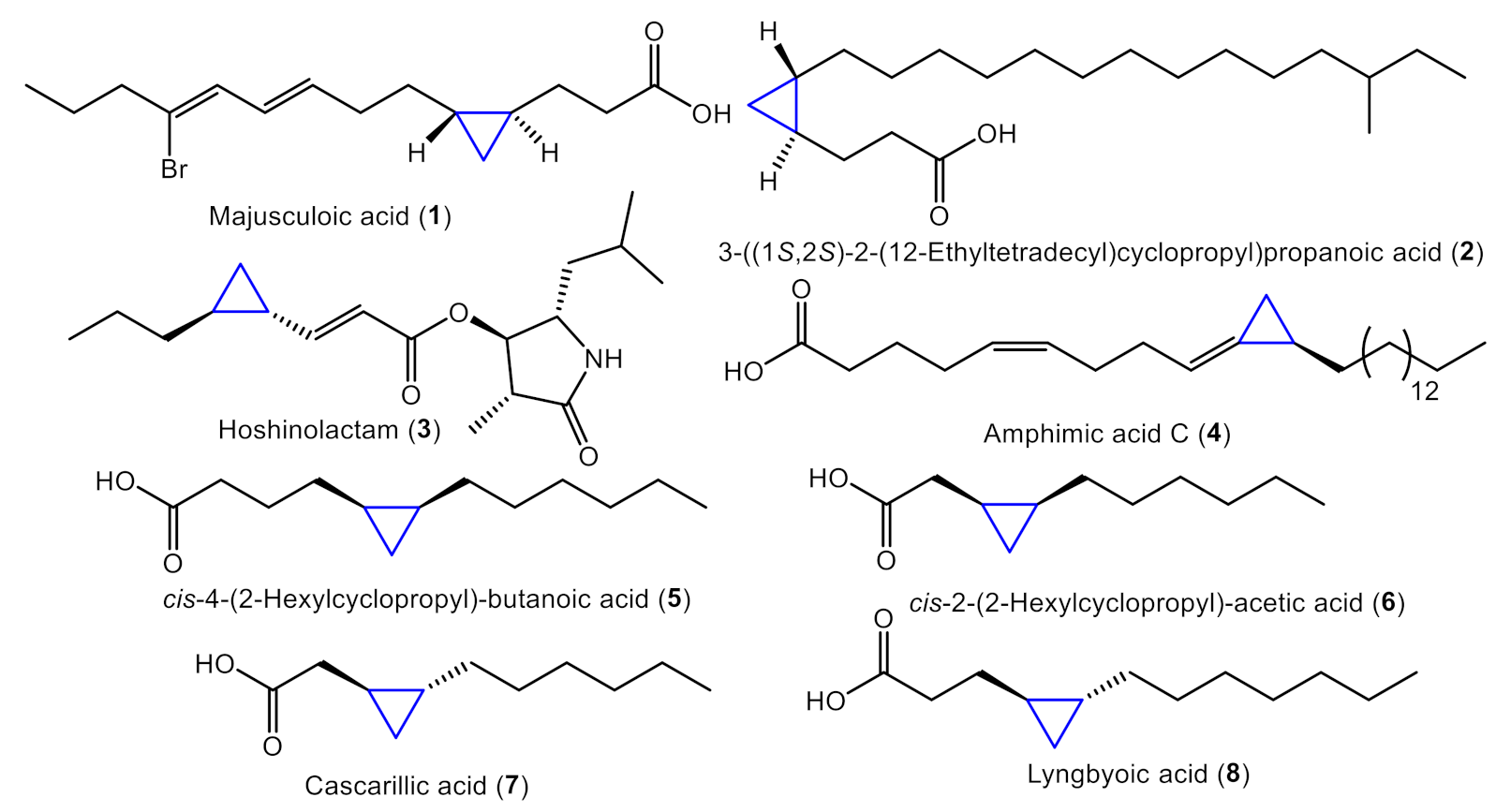
:1. Introduction
2. Results
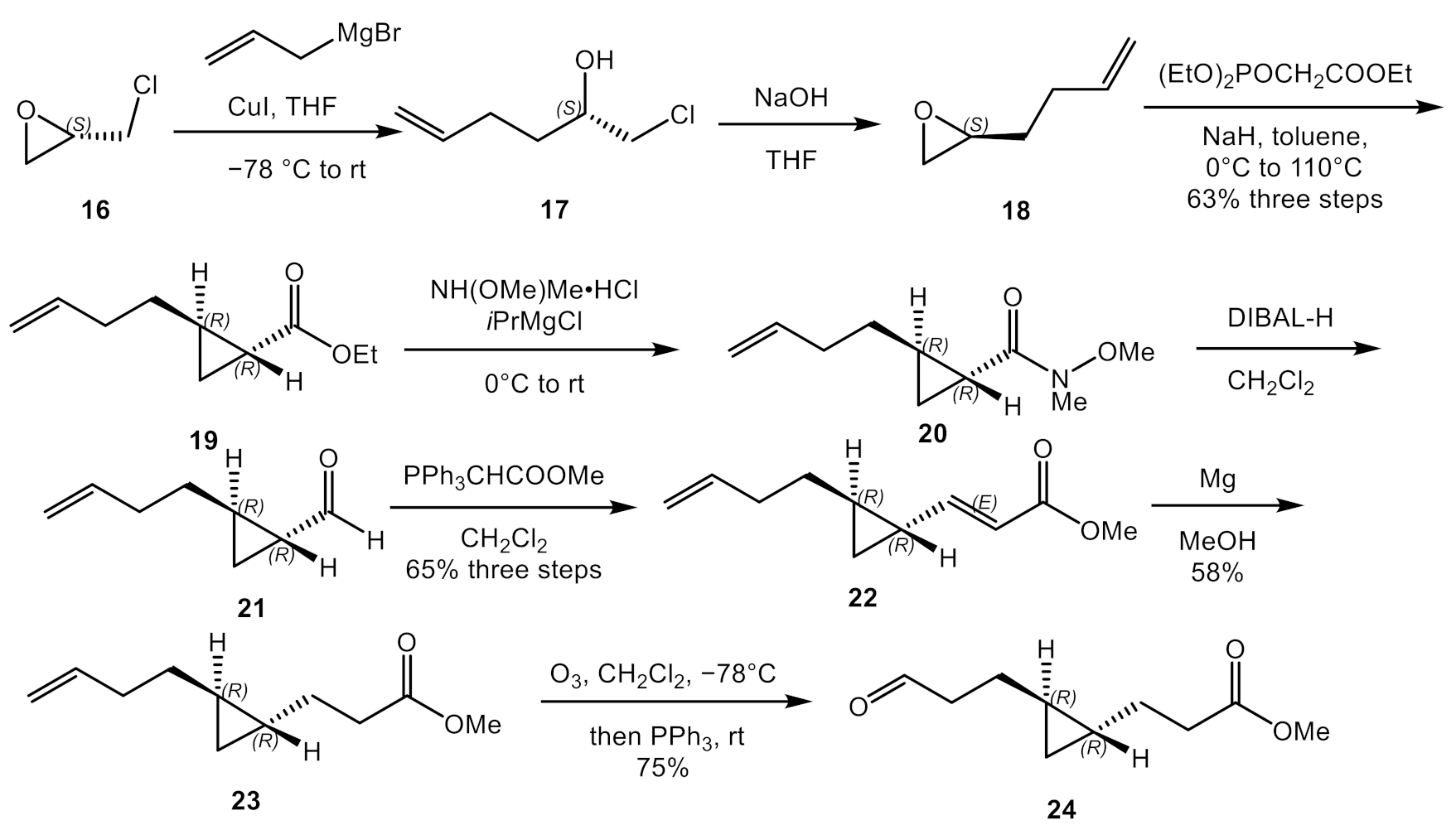
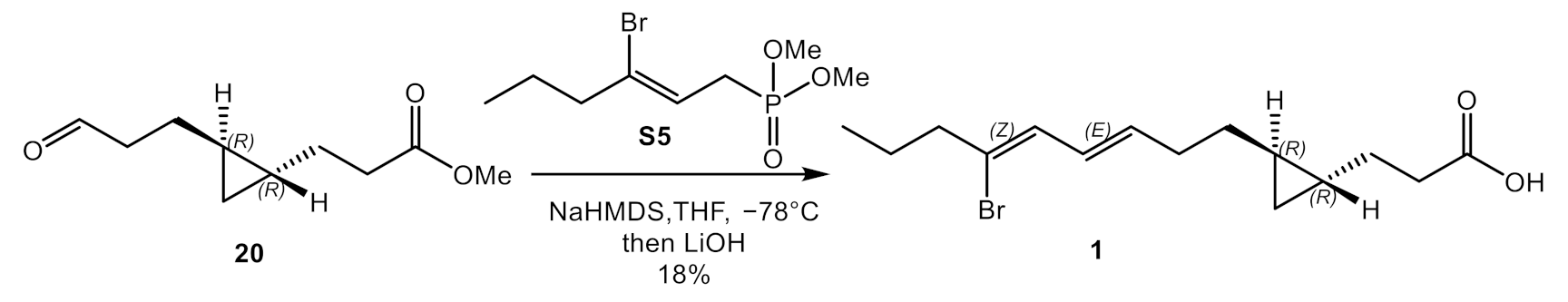
2.1. Total Synthesis of Majusculoic Acid
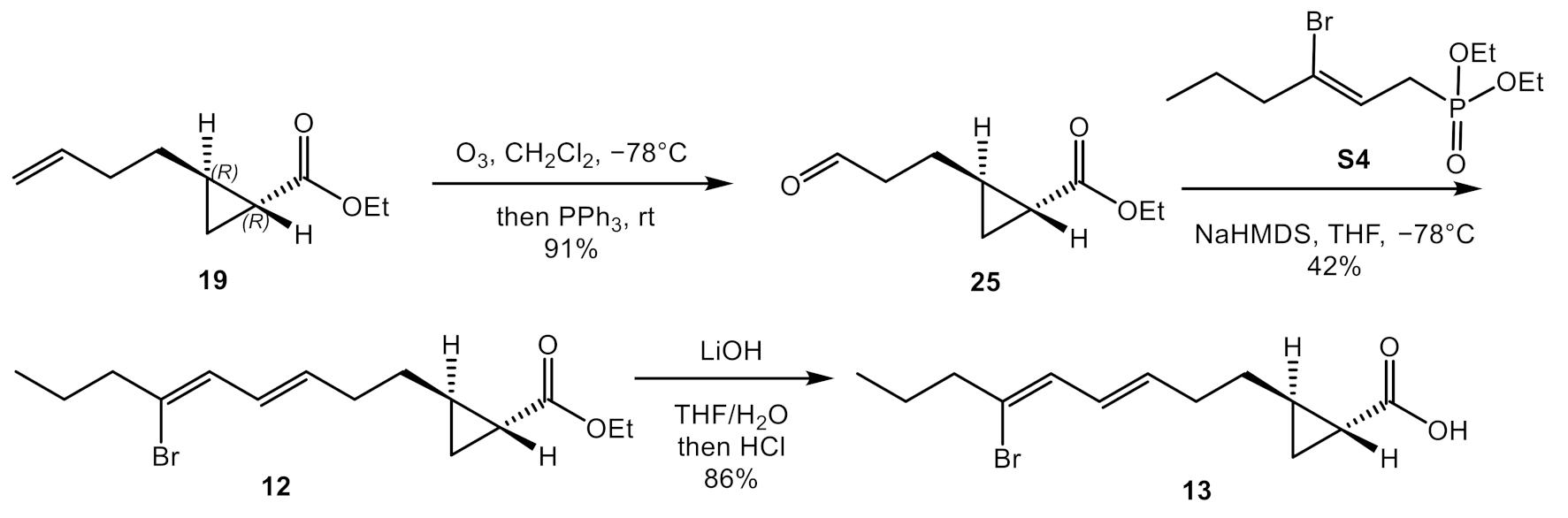
2.2. Total Synthesis of Majusculoic Acid Derivatives
2.3. Synthesis of Horner Reagent
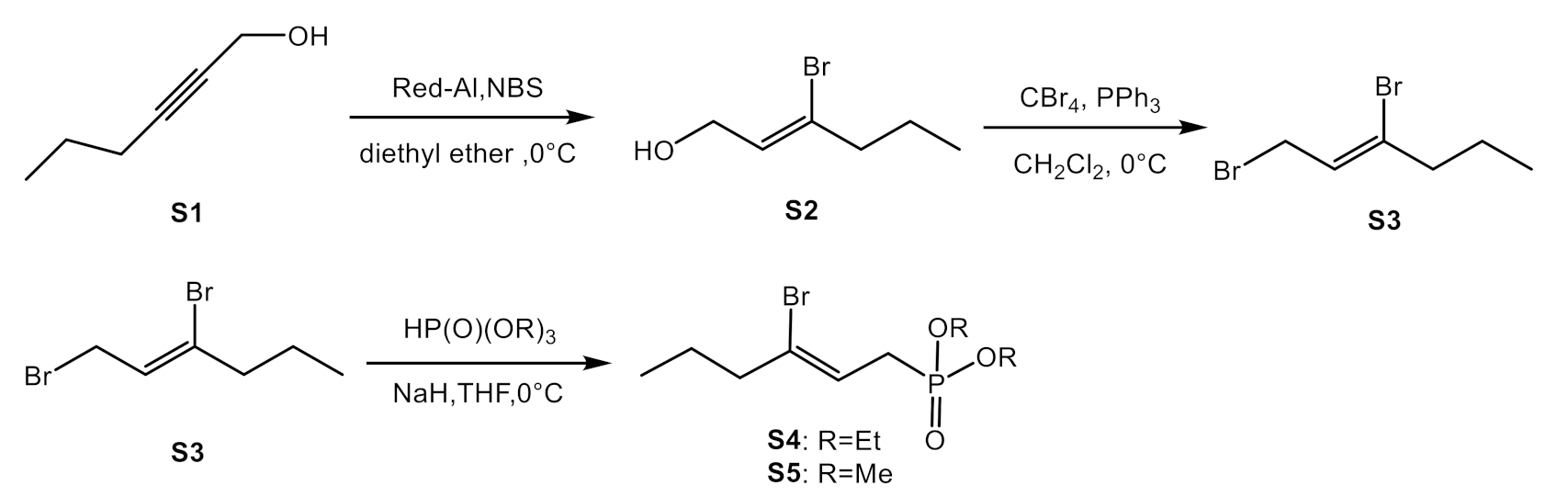
2.3.1. Synthesis of Horner Reagent for Bromo-Olefination (S4 and S5)
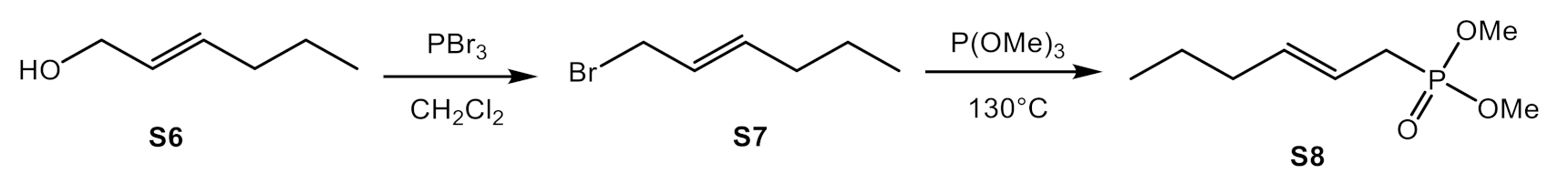
2.3.2. Synthesis of Horner Reagent (S8)
2.4. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Majusculoic Acie and Its Analogs
2.5. Cytotoxicity of Majusculoic Acid and Its Analogs
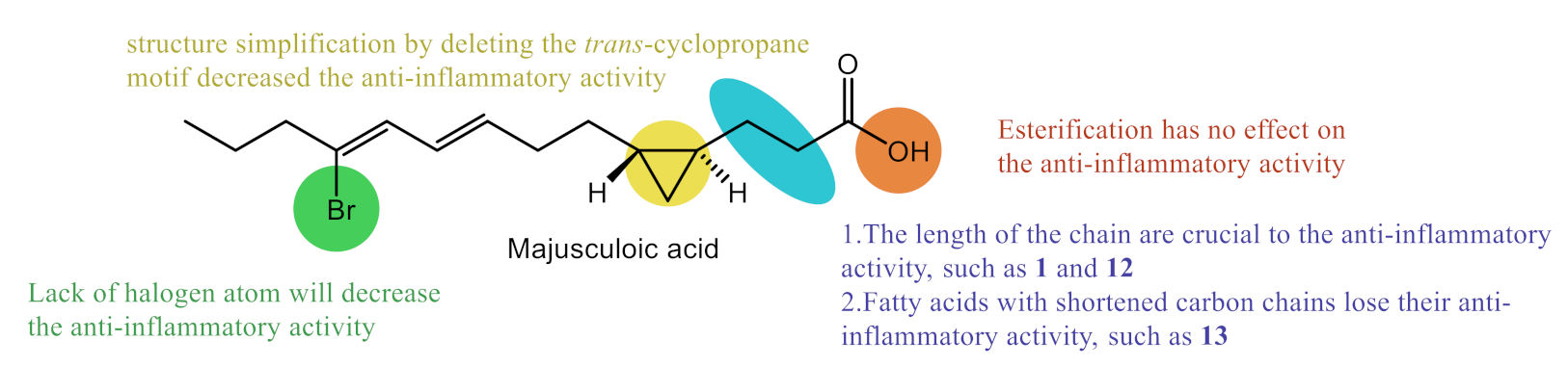
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Materials
4.2. Total Synthesis of Majusculoic Acid and Its Derivates
4.2.1. Synthesis of (S)-2-(but-3-en-1-yl)oxirane (18)
4.2.2. Synthesis of Ethyl (1R,2R)-2-(but-3-en-1-yl) cyclopropane-1-carboxylate (19)
4.2.3. Synthesis of (1R,2R)-2-(but-3-en-1-yl)-N-methoxy-N-methylcyclopropane-1-carboxamide (20)
4.2.4. Synthesis of (1R,2R)-2-(but-3-en-1-yl) cyclopropane-1-carbaldehyde (21)
4.2.5. Synthesis of Methyl (E)-3-((1R,2R)-2-(but-3-en-1-yl) cyclopropyl) Acrylate (22)
4.2.6. Synthesis of Methyl 3-((1R,2R)-2-(but-3-en-1-yl) cyclopropyl) Propanoate (23)
4.2.7. Synthesis of Methyl 3-((1R,2R)-2-(3-oxopropyl) cyclopropyl) Propanoate (24)
4.2.8. Synthesis of Methyl Majusculoate (9)
4.2.9. Synthesis of Majusculoic Acid (1)
4.3. General Method for the Synthesis of Majusculoic Acid Analogs
4.3.1. Synthesis of Methyl 3-((1R,2R)-2-((3E,5E)-nona-3,5-dien-1-yl) cyclopropyl) Propanoate (10)
4.3.2. Synthesis of Methyl 3-((1R,2R)-2-((3E,5E)-nona-3,5-dien-1-yl) cyclopropyl) Propanoic Acid (11)
4.3.3. Synthesis of Ethyl (1R,2R)-2-(3-oxopropyl) cyclopropane-1-carboxylate (25)
4.3.4. Synthesis of Ethyl (1R,2R)-2-((3E,5Z)-6-bromonona-3,5-dien-1-yl) cyclopropane-1-carboxylate (12)
4.3.5. Synthesis of (1R,2R)-2-((3E,5Z)-6-bromonona-3,5-dien-1-yl) cyclopropane-1-carboxylic Acid (13)
4.3.6. Synthesis of Methyl 9-oxononanoate (27)
4.3.7. Synthesis of Methyl (9E,11Z)-12-bromopentadeca-9,11-dienoate (14)
4.3.8. Synthesis of (9E,11Z)-12-bromopentadeca-9,11-dienoic Acid (15)
4.4. General Method for the Synthesis of Horner Reagent
4.4.1. Synthesis of Horner Reagent for Bromo-Olefination
4.4.2. Synthesis of Horner Reagent for Olefination
4.5. Spectroscopic Data of Majusculoic Acid and Its Analogs
4.6. Anti-Inflammatory Activity Testing
4.7. Cytotoxicity Determination
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, B.; Rietschel, E.T. Innate immune sensing and its roots: The story of endotoxin. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, M.M.; Hutchinson, M.; Watkins, L.R.; Yin, H. Toll-like receptor 4 in CNS pathologies. J. Neurochem. 2010, 114, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Huri, D.; Snyder, S. Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Binds, S-Nitrosylates, and Activates Cyclooxygenase-2. Science 2006, 310, 1966–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tungen, J.E.; Aursnes, M.; Vik, A.; Ramon, S.; Colas, R.A.; Dalli, J.; Serhan, C.N.; Hansen, T.V. Synthesis and Anti-inflammatory and Pro-resolving Activities of 22-OH-PD1, a Monohydroxylated Metabolite of Protectin D1. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2241–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aursnes, M.; Tungen, J.E.; Vik, A.; Colas, R.; Cheng, C.-Y.C.; Dalli, J.; Serhan, C.N.; Hansen, T.V. Total Synthesis of the Lipid Mediator PD1n-3 DPA: Configurational Assignments and Anti-inflammatory and Pro-resolving Actions. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.T.; Lee, H.J.; Yoo, E.S.; Shinde, P.B.; Lee, Y.M.; Hong, J.; Kim, D.K.; Jung, J.H. Anti-inflammatory Constituents of the Red Alga Gracilaria verrucosa and Their Synthetic Analogues. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tungen, J.E.; Primdahl, K.G.; Hansen, T.V. The First Total Synthesis of the Lipid Mediator PD2n-3 DPA. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2255–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessjohann, L.; Brandt, W.; Thiemann, T. Biosynthesis and Metabolism of Cyclopropane Rings in Natural Compounds. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 1625–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carballeira, N.; Montano, N.; Jan, V.; Rodriguez, D.A. Novel Cyclopropane Fatty Acids from the Phospholipids of the Caribbean Sponge Pseudospongosorites suberitoides. Lipids 2007, 42, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macmillan, J.; Molinski, T. Majusculoic Acid, a Brominated Cyclopropyl Fatty Acid from a Marine Cyanobacterial Mat Assemblage. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 604–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri Moghaddam, J.; Dávila-Céspedes, A.; Kehraus, S.; Crüsemann, M.; Köse, M.; Müller, C.E.; König, G.M. Cyclopropane-Containing Fatty Acids from the Marine Bacterium Labrenzia sp. 011 with Antimicrobial and GPR84 Activity. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sitachitta, N.; Gerwick, W. Grenadadiene and Grenadamide, Cyclopropyl-Containing Fatty Acid Metabolites from the Marine Cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, H.; Iwasaki, A.; Sumimoto, S.; Iwatsuki, M.; Ishiyama, A.; Hokari, R.; Otoguro, K.; Omura, S.; Suenaga, K. Isolation and Total Synthesis of Hoshinolactam, an Antitrypanosomal Lactam from a Marine Cyanobacterium. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 890–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemoto, T.; Yoshino, G.; Ojika, M.; Sakagami, Y. Amphimic Acids and Related Long-chain Fatty Acids as DNA Topoisomerase I Inhibitors from an Australian Sponge, Amphimedon sp.: Isolation, Structure, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation. Tetrahedron 1997, 53, 16699–16710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Li, L.; Lin, N.; Zhou, R.; Yuhui, H.; Deng, H.; Zhang, Y. Asymmetric Total Synthesis of (+)-Majusculoic Acid via a Dimerization–Dedimerization Strategy and Absolute Configuration Assignment. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 1477–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Line, N.; Witherspoon, B.; Hancock, E.; Brown, M. Synthesis of ent-[3]-Ladderanol: Development and Application of Intramolecular Chirality Transfer [2+2] Cycloadditions of Allenic Ketones and Alkenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 14392–14395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, M.H.; Croft, R.A.; Whittingham, W.G.; Bower, J.F. Modular Access to Substituted Azocanes via a Rhodium-Catalyzed Cycloaddition–Fragmentation Strategy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 8054–8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manzi, S.; Wasko, M.C. Inflammation-mediated rheumatic diseases and atherosclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2000, 59, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murdoch, J.; Lloyd, C. Chronic inflammation and asthma. Mutat. Res. 2009, 690, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, N.; Wang, T.; Buess, C. Potential inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis phosphonates derived from geraniol and congeners. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2002, 15, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Compound | Concentration (µM) | NO Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 10 | 35.75 ± 4.4 12.95 ± 4.4 |
| 9 | 30 10 | 33.68 ± 7.33 9.84 ± 2.93 |
| 10 | 30 10 | 11.92 ± 8.79 8.81 ± 7.33 |
| 11 | 30 10 | 18.13 ± 8.79 6.74 ± 7.33 |
| 12 | 30 10 | 43.01 ± 2.93 7.77 ± 5.86 |
| 13 | 30 10 | 26.42 ± 14.66 28.5 ± 2.93 |
| 14 | 30 10 | 15.03 ± 7.33 9.84 ± 5.86 |
| 15 | 30 10 | 19.17 ± 7.33 9.84 ± 8.79 |
| Compound | Concentration (µM) | Inhibition Rate of Cell Proliferation (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 10 | −24.38 ± 3.15 −16.02 ± 5.37 |
| 9 | 30 10 | −21.59 ± 0.07 −15.32 ± 10.95 |
| 10 | 30 10 | −22.05 ± 6.3 −10.66 ± 6.52 |
| 11 | 30 10 | −16.88 ± 1.15 −0.13 ± 19.26 |
| 12 | 30 10 | −6.25 ± 9.59 1.54 ± 0.57 |
| 13 | 30 10 | 11.01 ± 1.22 7.16 ± 0.07 |
| 14 | 30 10 | −25.74 ± 11.53 −8.33 ± 3.51 |
| 15 | 30 10 | −15.16 ± 17.04 −14.15 ± 5.87 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, H.-X.; Yan, Q.-X.; He, Z.-H.; Zou, Z.-B.; Le, Q.-Q.; Chen, T.-T.; Cai, B.; Yang, X.-W.; Luo, S.-L. Total Synthesis and Anti-Inflammatory Bioactivity of (−)-Majusculoic Acid and Its Derivatives. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060288
Xiao H-X, Yan Q-X, He Z-H, Zou Z-B, Le Q-Q, Chen T-T, Cai B, Yang X-W, Luo S-L. Total Synthesis and Anti-Inflammatory Bioactivity of (−)-Majusculoic Acid and Its Derivatives. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(6):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060288
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Hong-Xiu, Qing-Xiang Yan, Zhi-Hui He, Zheng-Biao Zou, Qing-Qing Le, Ting-Ting Chen, Bing Cai, Xian-Wen Yang, and Su-Lan Luo. 2021. "Total Synthesis and Anti-Inflammatory Bioactivity of (−)-Majusculoic Acid and Its Derivatives" Marine Drugs 19, no. 6: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060288
APA StyleXiao, H.-X., Yan, Q.-X., He, Z.-H., Zou, Z.-B., Le, Q.-Q., Chen, T.-T., Cai, B., Yang, X.-W., & Luo, S.-L. (2021). Total Synthesis and Anti-Inflammatory Bioactivity of (−)-Majusculoic Acid and Its Derivatives. Marine Drugs, 19(6), 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060288









