Largazole Inhibits Ocular Angiogenesis by Modulating the Expression of VEGFR2 and p21
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Largazole Inhibits the Activation of Human Retinal Endothelial Cells (HRECs) in a Dose-Dependent Manner
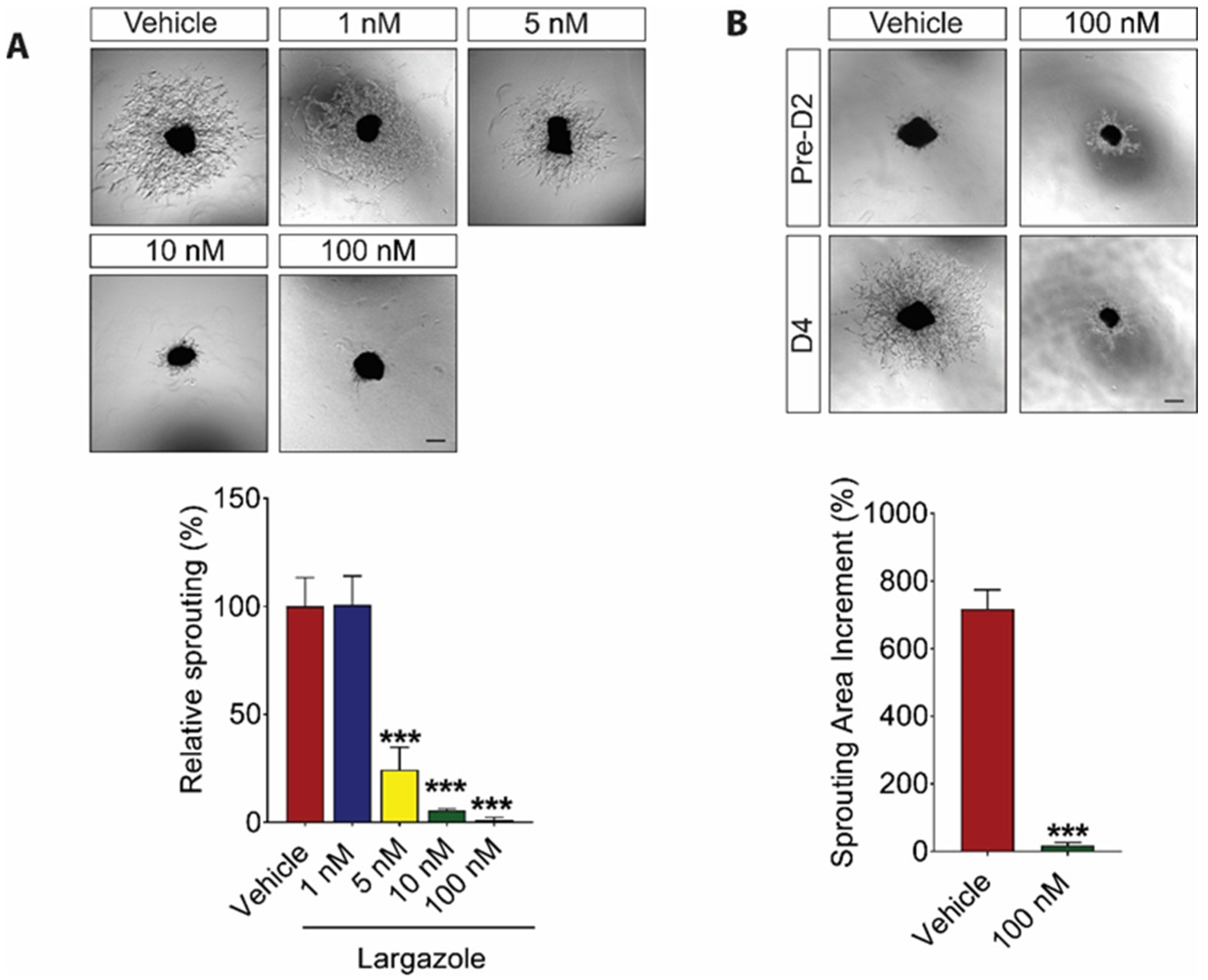
2.2. Largazole Inhibits Angiogenesis in Ex Vivo Models
2.3. Largazole Showed Cooperative Effect to Aflibercept in Choroidal Angiogenesis Assays
2.4. Largazole Exerts Its Anti-Angiogenic Effects through Controlling VEGF Signaling and the Expression of Cell Cycle Inhibitor, p21
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Materials, Cells, and Cell Culture
4.3. AlamarBlue Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Ki67 Proliferation Assay
4.5. Matrigel Assay
4.6. Choroid Sprouting Assay
4.7. Metatarsal Assay
4.8. Western Blotting
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dreyfuss, J.L.; Giordano, R.J.; Regatieri, C.V. Ocular Angiogenesis. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 2015, 892043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, H.R.; Ferris, F.L.; Chan, C.-C.; Chew, E.Y. Age-related macular degeneration. Lancet 2008, 372, 1835–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressler, N.M. Age-Related Macular Degeneration Is the Leading Cause of Blindness. JAMA 2004, 291, 1900–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, W.L.; Su, X.; Li, X.; Cheung, C.M.G.; Klein, R.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Wong, T.Y. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2014, 2, e106–e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jampol, L.M.; Glassman, A.R.; Sun, J. Evaluation and Care of Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.Y.; Tan, B.; Chua, J.; Lin, E. Diabetic retinopathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 16012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, D.S.; Aiello, L.; Gardner, T.W.; King, G.L.; Blankenship, G.; Cavallerano, J.D.; Ferris, F.; Klein, R. Retinopathy in Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003, 27, S84–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.-M.; Li, X.-R. Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy, proliferative diabetic retinopathy and non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy in Asian T2DM patients: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 12, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeben, A.; Landuyt, B.; Highley, M.S.; Wildiers, H.; Van Oosterom, A.T.; De Bruijn, E.A. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Angiogenesis. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 549–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Writing Committee for the Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research. Panretinal Photocoagulation vs Intravitreous Ranibizumab for Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2015, 314, 2137–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ip, M.S.; Domalpally, A.; Hopkins, J.J.; Wong, P.; Ehrlich, J.S. Long-term Effects of Ranibizumab on Diabetic Retinopathy Severity and Progression. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2012, 130, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, P.; Liew, G.; Gopinath, B.; Wong, T.Y. Age-related macular degeneration. Lancet 2018, 392, 1147–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lo, A.C.Y. Diabetic Retinopathy: Pathophysiology and Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurihara, T.; Westenskow, P.; Bravo, S.; Aguilar, E.; Friedlander, M. Targeted deletion of Vegfa in adult mice induces vision loss. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 4213–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research. Aflibercept, bevacizumab, or ranibizumab for diabetic macular edema. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ciulla, T.; Hussain, R.M.; Ciulla, L.M.; Sink, B.; Harris, A. Ranibizumab for diabetic macular edema refractory to multiple prior treatments. Retinoids 2016, 36, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lordan, S.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Marine Bioactives as Functional Food Ingredients: Potential to Reduce the Incidence of Chronic Diseases. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1056–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munroa, M.H.; Prinsepd, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 382–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, B.; Tan, A.; Veluchamy, A.B.; Li, Y.; Murray, H.; Cheng, W.; Liu, C.; Busoy, J.M.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Sistla, S.; et al. Apratoxin S4 Inspired by a Marine Natural Product, a New Treatment Option for Ocular Angiogenic Diseases. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 3254–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taori, K.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Structure and activity of largazole, a potent antiproliferative agent from the Floridian marine cyanobacterium Symploca sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 1806–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Y.; Taori, K.; Kim, H.; Hong, J.; Luesch, H. Total Synthesis and Molecular Target of Largazole, a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8455–8459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Luesch, H. Largazole: From discovery to broad-spectrum therapy. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Awadhi, F.H.; Lilibeth, A.; Salvador-Reyes, A.; Lobna, A.E.; Ranjala, R.; Chen, Q.-C.; Luesch, H. Largazole is a Brain-Penetrant Class I HDAC Inhibitor with Extended Applicability to Glioblastoma and CNS Diseases. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 1937–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Salvador, L.A.; Byeon, S.; Ying, Y.; Kwan, J.C.; Law, B.K.; Hong, J.; Luesch, H. Anticolon Cancer Activity of Largazole, a Marine-Derived Tunable Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 335, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ucuzian, A.A.; Gassman, A.A.; East, A.T.; Greisler, H.P. Molecular Mediators of Angiogenesis. J. Burn. Care Res. 2010, 31, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Jiang, S.; Chen, J.; Ren, X.; Jin, J.; Su, S.B. Largazole, an inhibitor of class I histone deacetylases, attenuates inflammatory corneal neovascularization. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, M.S.; Ma, J.J.; Ratnayake, R.; Havre, P.A.; Yao, J.; Dang, N.H.; Paul, V.J.; Carney, T.J.; Dang, L.H.; Luesch, H. Multidimensional Screening Platform for Simultaneously Targeting Oncogenic KRAS and Hypoxia-Inducible Factors Pathways in Colorectal Cancer. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Potente, M.; Gerhardt, H.; Carmeliet, P. Basic and Therapeutic Aspects of Angiogenesis. Cell 2011, 146, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donovan, D.; Brown, N.; Bishop, E.; Lewis, C. Comparison of three in vitro human angiogenesis assays with capillaries formed in vivo. Angiogenesis 2001, 4, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemp, B.; Schmetterer, L. Ocular blood flow in diabetes and age-related macular degeneration. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 43, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, A.A.; Fine, B.S. Diabetic choroidopathy. Light and electron microscopic observations of seven cases. Ophthalmology 1985, 92. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.; Friedlander, M.; Hurst, C.G.; Cui, Z.; Pei, D.T.; Evans, L.P.; Juan, A.M.; Tahir, H.; Duhamel, F.; Chen, J.; et al. Choroid sprouting assay: An ex vivo model of microvascular angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Fhu, C.W.; Ang, K.H.; Liu, C.H.; Johari, N.A.B.; Lio, D.; Abraham, S.; Hong, W.; Moss, S.E.; Greenwood, J.; et al. The fetal mouse metatarsal bone explant as a model of angiogenesis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 1459–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, T.; Mello, L.G.M.; Lima, L.H.; Polido, J.; Regatieri, C.V.; Mahajan, V.B. Retinal and choroidal angiogenesis: A review of new targets. Int. J. Retin. Vitr. 2017, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, X.; Yin, B.; Hu, Z.; Liao, C.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Li, Z.; Nicklaus, M.C.; Zhou, G.; Jiang, S. Total Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Largazole and Derivatives with Promising Selectivity for Cancers Cells. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 1368–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M.E.; Corsino, P.E.; Jahn, S.C.; Davis, B.J.; Chen, S.; Patel, B.; Pham, K.; Lu, J.; Sheppard, B.; Nørgaard, P.; et al. Glucocorticoids and histone deacetylase inhibitors cooperate to block the invasiveness of basal-like breast cancer cells through novel mechanisms. Oncogene 2012, 32, 1316–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Whang, Z.; Lam, W.; Kwong, S.; Li, F.; Friedman, S.L.; Zhou, S.; Ren, Q.; Xu, Z.; et al. A histone deacetylase inhibitor, largazole, decreases liver fibrosis and angiogenesis by inhibiting transforming growth factor-beta and vascular endothelial growth factor signalling. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-Q.; Miao, Z.-H. Marine-Derived Angiogenesis Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 903–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shoda, C.; Miwa, Y.; Nimura, K.; Okamoto, K.; Yamagami, S.; Tsubota, K.; Kurihara, T. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Inhibitors Derived from Marine Products Suppress a Murine Model of Neovascular Retinopathy. Nutrition 2020, 12, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvador-Reyes, L.A.; Engene, N.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Targeted Natural Products Discovery from Marine Cyanobacteria Using Combined Phylogenetic and Mass Spectrometric Evaluation. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engene, N.; Tronholm, A.; Salvator-Ryese, L.A.; Luesch, H.; Paul, V.J. Caldora penicillata gen. nov., comb. nov. (cyanobacteria), a pantropical marine species with biomedical relevance. J. Phycol. 2015, 51, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wojnarowicz, P.M.; E Silva, R.L.; Ohnaka, M.; Lee, S.B.; Chin, Y.; Kulukian, A.; Chang, S.-H.; Desai, B.; Escolano, M.G.; Shah, R.; et al. A Small-Molecule Pan-Id Antagonist Inhibits Pathologic Ocular Neovascularization. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sulaiman, R.S.; Merrigan, S.; Quigley, J.; Qi, X.; Lee, B.; Boulton, M.E.; Kennedy, B.; Seo, S.-Y.; Corson, T.W. A novel small molecule ameliorates ocular neovascularisation and synergises with anti-VEGF therapy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ying, Y.; Liu, Y.; Byeon, S.R.; Kim, H.; Luesch, H.; Hong, J. Synthesis and Activity of Largazole Analogues with Linker and Macrocycle Modification. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 4021–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMay, J.; Bernard, C.; Reinhardt, A.; Marie, B. Natural Products from Cyanobacteria: Focus on Beneficial Activities. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenfeld, P.J.; Brown, D.M.; Heier, J.S.; Boyer, D.S.; Kaiser, P.; Chung, C.Y.; Kim, R.Y. Ranibizumab for Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, D.M.; Kaiser, P.; Michels, M.; Soubrane, G.; Heier, J.S.; Kim, R.Y.; Sy, J.P.; Schneider, S. Ranibizumab versus Verteporfin for Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1432–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, M.; Nagai, N.; Izumi-Nagai, K.; Shinoda, H.; Koto, T.; Uchida, A.; Mochimaru, H.; Yuki, K.; Sasaki, M.; Tsubota, K.; et al. Predictive factors for non-response to intravitreal ranibizumab treatment in age-related macular degeneration. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 98, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lux, A.; Llacer, H.; Heussen, F.M.A.; Joussen, A.M. Non-responders to bevacizumab (Avastin) therapy of choroidal neovascular lesions. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 91, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falavarjani, K.G.; Nguyen, Q.D. Adverse events and complications associated with intravitreal injection of anti-VEGF agents: A review of literature. Eye 2013, 27, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.-Y.; Chaturvedi, P.R.; Luesch, H. Process Development and Scale-up Total Synthesis of Largazole, a Potent Class I Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2018, 22, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, B.; Tan, A.; Tan, Y.Z.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Luesch, H.; Wang, X. Largazole Inhibits Ocular Angiogenesis by Modulating the Expression of VEGFR2 and p21. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19080471
Qiu B, Tan A, Tan YZ, Chen Q-Y, Luesch H, Wang X. Largazole Inhibits Ocular Angiogenesis by Modulating the Expression of VEGFR2 and p21. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(8):471. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19080471
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Beiying, Alison Tan, Yu Zhi Tan, Qi-Yin Chen, Hendrik Luesch, and Xiaomeng Wang. 2021. "Largazole Inhibits Ocular Angiogenesis by Modulating the Expression of VEGFR2 and p21" Marine Drugs 19, no. 8: 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19080471
APA StyleQiu, B., Tan, A., Tan, Y. Z., Chen, Q. -Y., Luesch, H., & Wang, X. (2021). Largazole Inhibits Ocular Angiogenesis by Modulating the Expression of VEGFR2 and p21. Marine Drugs, 19(8), 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19080471





