Marine Transcriptomics Analysis for the Identification of New Antimicrobial Peptides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
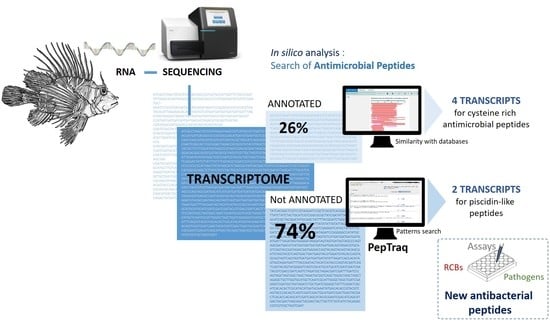
2.1. In Silico Analysis of the Transcriptome
2.2. Study of Peptides Derived from Pteroicidin B and C
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Animal Collection
3.2. Ethical Statement
3.3. Illumina Sequencing
3.4. Bioinformatic Analysis
3.5. Peptidomic Analysis
3.6. Selection and Synthesis of Peptides from Pteroicidins B and C
3.7. Antimicrobial Assay
3.8. Hemolytic Assay
3.9. Structural Circular Dichroism Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


| Sequence Name | Origin | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|
| Ch-piscidin | Chionodraco hamatus (Lönberg, 1905) (crocodile icefish) | CBX55949.1 |
| Dl-dicentracin | Dicentrarchus labrax (Linnaeus, 1758) (sea bass) | P59906.1 |
| Ec-piscidin-2 | Epinephelus coioides (Hamilton, 1822) (orange-spotted grouper) | ADY86111.1 |
| Ec-piscidin-1 | ACE78291.1 | |
| Ec-piscidin-4 | AKA60777.2 | |
| Gm-gaduscidin-1 | Gadus morhua 1758 (Atlantic cod) | ACS91329.1 |
| Gm-piscidin-2-ß | ADU34223.1 | |
| Gm-gaduscidin-2 | ADK63424.1 | |
| Gc-pleurocidin-3.8 | Glyptocephalus cynoglossus (Linnaeus, 1758) (witch flounder) | AAP55799.1 |
| Gc-pleurocidin-3.2 | AAP55800.1 | |
| Gc-pleurocidin-Sc4B7 | AAP55798.1 | |
| Hp-pleurocidin-AP3 | Hippoglossoides platessoides (Fabrissius, 1780) (american plaice) | ABB70232.1 |
| Hp-pleurocidin-AP2 | AAP55794.1 | |
| Hp-pleurocidin-AP1 | AAP55793.1 | |
| Lc-piscidin-1 | Larimichthys crocea (Richardson, 1846) (large yellowcroaker) | ACE78289.1 |
| Lc-piscidin-2 | AGN52988.1 | |
| Lc-piscidin-3-T5.2 | AIL82389.1 | |
| Lc-piscidin-3-T5 | AIL82388.1 | |
| Lc-piscidin-3-T5.3 | AQS27931.1 | |
| Mc-piscidin-6 | Morone chrysops (Rafinesque, 1820) (white bass) | APQ32044.1 |
| Mc-piscidin-5 | ADP37960.1 | |
| Mc-piscidin-3 | APQ32046.1 | |
| Mc-piscidin-4 | APQ32050.1 | |
| Mc-moronecidin | Q8UUG2.1 | |
| Ms-moronecidin | Morone saxatilis (Walbaun, 1792) (striped bass) | Q8UUG0.1 |
| Ms-piscidin-4 | ADP37959.1 | |
| Ms-piscidin-6 | APQ32043.1 | |
| Ms-piscidin-7 | APQ32054.1 | |
| Of-piscidin-1 | Oplegnathus fasciatus (Temminck & Schlegel, 1844) (barred knifejaw) | BAM99884.1 |
| Of-moronecidin | KT354978 | |
| On-piscidin-4 | Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) (Nile tilapia) | AGA16547.1 |
| On-piscidin-3 | AGA16546.1 | |
| On-piscidin-5 | AGA16548.1 | |
| On-piscidin-2 | AGA16545.1 | |
| On-piscidin-1 | AGA16544.1 | |
| Pc-moronecidin | Parachaenichthys charcoti (Vaillant, 1906) (Antartic dragon fish) | AOW44479.1 |
| Pa-pleurocidin | Pseudopleuronectes americanus (Walbaun, 1792) (winter flounder) | P81941.2 |
| Pa-pleurocidin-2 | Q90ZY0.1 | |
| Pa-pleurocidin-4 | Q90ZX8.1 | |
| Pa-pleurocidin-3 | Q90VW7.1 | |
| Pa-pleurocidin-6 | AAQ16623.1 | |
| Sl-piscidin | Seriola lalandi (Valenciennes, 183)3 (yellowtail amberjack) | ARK85994.1 |
| Sc-moronecidin | Siniperca chuatsi (Basilewsky, 1855) (mandarin fish) | AAV65044.1 |
| Pv-Pteroicidin-A | Pterois volitans (Linnaeus, 1758) (red lion-fish) | This study |
| Pv-Pteroicidin-B | This study | |
| Pv-Pteroicidin-C | This study | |
| Nc-moronecidin | Notothenia coriiceps (Richardson, 1844) (black rockcod) | XP_010768425.1. |
| HKPLP | Hippocampus kuda (Bleeker, 1852) (spotted seahorse) | AAX58115.1 |
References
- Ganz, T.; Lehrer, R.I. Antimicrobial peptides of vertebrates. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1998, 10, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.A.; Kafatos, F.C.; Janeway, C.; Ezekowitz, R. Phylogenetic perspectives in innate immunity. Science 1999, 284, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrer, R.I.; Ganz, T. Antimicrobial peptides in mammalian and insect host defence. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1999, 11, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zasloff, M. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 2002, 415, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masso-Silva, J.; Diamond, G. Antimicrobial peptides from fish. Pharmaceuticals 2014, 7, 265–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shike, H.; Lauth, X.; Westerman, M.E.; Ostland, V.E.; Carlberg, J.M.; Van Olst, J.C.; Shimizu, C.; Bulet, P.; Burns, J.C. Bass hepcidin is a novel antimicrobial peptide induced by bacterial challenge. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 2232–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, S.E.; Gallant, J.W.; Liebscher, R.S.; Dacanay, A.; Tsoi, S.C. Identification and expression analysis of hepcidin-like antimicrobial peptides in bony fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2003, 27, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chen, B.; Cai, J.-J.; Peng, H.; Cai, L.; Yuan, J.-J.; Wang, K.-J. Molecular characterization of hepcidin AS-hepc2 and AS-hepc6 in black porgy (Acanthopagrus schlegelii): Expression pattern responded to bacterial challenge and in vitro antimicrobial activity. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 158, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauth, X.; Babon, J.J.; Stannard, J.A.; Singh, S.; Nizet, V.; Carlberg, J.M.; Ostland, V.E.; Pennington, M.W.; Norton, R.S.; Westerman, M.E. Bass hepcidin synthesis, solution structure, antimicrobial activities and synergism, and in vivo hepatic response to bacterial infections. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9272–9282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, P.N.S.; Vázquez-Dorado, S.; Neves, J.V.; Wilson, J.M. Dual function of fish hepcidin: Response to experimental iron overload and bacterial infection in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-A.; Zou, J.; Chang, C.-I.; Secombes, C.J. Discovery and characterization of two types of liver-expressed antimicrobial peptide 2 (LEAP-2) genes in rainbow trout. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2004, 101, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Guo, H.; Li, H.; Shan, S.; Zhang, X.; Rombout, J.H.W.M.; An, L. Molecular characterization of LEAP-2 cDNA in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) and the differential expression upon a Vibrio anguillarum stimulus; indications for a significant immune role in skin. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 37, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Gao, Y.; Wang, R.; Xu, T. Characterization, evolution and functional analysis of the liver-expressed antimicrobial peptide 2 (LEAP-2) gene in miiuy croaker. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkar, S.; Nandanwar, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, H. Characterization of Four Liver-Expressed Antimicrobial Peptides from Antarctic Fish and Their Antibacterial Activity. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafee, T.M.A.; Lay, F.T.; Phan, T.K.; Anderson, M.A.; Hulett, M.D. Convergent evolution of defensin sequence, structure and function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, T. Defensins: Antimicrobial peptides of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, A.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.Á. Molecular and functional characterization of the gilthead seabream β-defensin demonstrate its chemotactic and antimicrobial activity. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Mercier, C.; Koussounadis, A.; Secombes, C. Discovery of multiple beta-defensin like homologues in teleost fish. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadei, E.; Wang, T.; Zou, J.; González Vecino, J.L.; Wadsworth, S.; Secombes, C.J. Characterization of three novel β-defensin antimicrobial peptides in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 3358–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.G.; Zhou, L.; Jin, J.Y.; Zhao, Z.; Lan, J.; Zhang, Y.B.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Gui, J.F. Antimicrobial activity-specific to Gram-negative bacteria and immune modulation-mediated NF-κB and Sp1 of a medaka β-defensin. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 624–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, J.-G.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Gui, J.-F. Antibacterial and antiviral roles of a fish β-defensin expressed both in pituitary and testis. PLoS One 2010, 5, e12883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirono, I.; Kondo, H.; Koyama, T.; Arma, N.R.; Hwang, J.Y.; Nozaki, R.; Midorikawa, N.; Aoki, T. Characterization of Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) NK-lysin, an antimicrobial peptide. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 22, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.-J.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Qiao, Y.; Hong, W.-S.; Su, Y.-Q.; Han, K.-H.; Ke, Q.-Z.; Zheng, W.-Q. Identification, expression and antibacterial activities of an antimicrobial peptide NK-lysin from a marine fish Larimichthys crocea. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 55, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Gunne, H.; Agerberth, B.; Boman, A.; Bergman, T.; Sillard, R.; Jörnvall, H.; Mutt, V.; Olsson, B.; Wigzell, H. NK-lysin, a novel effector peptide of cytotoxic T and NK cells. Structure and cDNA cloning of the porcine form, induction by interleukin 2, antibacterial and antitumour activity. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Chen, D.; Dong, X.; Liu, T.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, D. Expression, Purification and Antibacterial Activity of NK-Lysin Mature Peptides from the Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scocchi, M.; Pallavicini, A.; Salgaro, R.; Bociek, K.; Gennaro, R. The salmonid cathelicidins: A gene family with highly varied C-terminal antimicrobial domains. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 152, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, V.H.; Dorn, K.V.; Gudmundsdottir, B.K.; Gudmundsson, G.H. Characterisation of cathelicidin gene family members in divergent fish species. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 3723–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scocchi, M.; Furlan, M.; Venier, P.; Pallavicini, A. Cathelicidins. In Lessons in Immunity; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 225–237. [Google Scholar]
- Uzzell, T.; Stolzenberg, E.D.; Shinnar, A.E.; Zasloff, M. Hagfish intestinal antimicrobial peptides are ancient cathelicidins. Peptides 2003, 24, 1655–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-I.; Pleguezuelos, O.; Zhang, Y.-A.; Zou, J.; Secombes, C.J. Identification of a novel cathelicidin gene in the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 5053–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broekman, D.C.; Frei, D.M.; Gylfason, G.; Steinarsson, A.; Jörnvall, H.; Agerberth, B.; Gudmundsson, G.H.; Maier, V.H. Cod cathelicidin: Isolation of the mature peptide, cleavage site characterisation and developmental expression. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, J.; Nie, P.; Secombes, C.J. Two Cathelicidin Genes Are Present in both Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar). Society 2006, 50, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Z.A.; Shi, Y.H.; Lυ¨, J.N. Identification and characterization of a novel cathelicidin from ayu, Plecoglossus altivelis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salger, S.A.; Cassady, K.R.; Reading, B.J.; Noga, E.J. A Diverse Family of Host-Defense Peptides (Piscidins) Exhibit Specialized Anti-Bacterial and Anti-Protozoal Activities in Fishes. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0159423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salger, S.A.; Reading, B.J.; Baltzegar, D.A.; Sullivan, C.V.; Noga, E.J. Molecular characterization of two isoforms of piscidin 4 from the hybrid striped bass (Morone chrysops ?? Morone saxatilis). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noga, E.J.; Silphaduang, U.; Park, N.G.; Seo, J.K.; Stephenson, J.; Kozlowicz, S. Piscidin 4, a novel member of the piscidin family of antimicrobial peptides. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. - B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 152, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, A.M. Isolation and Characterization of Pleurocidin, an Antimicrobial Peptide in the Skin Secretions of Winter Flounder. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 12008–12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silphaduang, U.; Colorni, A.; Noga, E.J. Evidence for widespread distribution of piscidin antimicrobial peptides in teleost fish. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2006, 72, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauth, X.; Shike, H.; Burns, J.C.; Westerman, M.E.; Ostland, V.E.; Carlberg, J.M.; Van Olst, J.C.; Nizet, V.; Taylor, S.W.; Shimizu, C.; et al. Discovery and characterization of two isoforms of moronecidin, a novel antimicrobial peptide from hybrid striped bass. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 5030–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houyvet, B.; Bouchon-Navaro, Y.; Bouchon, C.; Goux, D.; Bernay, B.; Corre, E.; Zatylny-Gaudin, C. Identification of a moronecidin-like antimicrobial peptide in the venomous fish Pterois volitans: Functional and structural study of pteroicidin-α. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 72, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schofield, P.J. Geographic extent and chronology of the invasion of non-native lionfish (Pterois volitans [Linnaeus 1758] and P. miles [Bennett 1828]) in the Western North Atlantic and Caribbean Sea. Aquat. Invasions 2009, 4, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.J.; Akins, J.L.; Maljković, A.; Côté, I.M. Invasive Lionfish Drive Atlantic Coral Reef Fish Declines. PLoS One 2012, 7, e32596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-González, J.E.; González-Gándara, C.; Luis Cabrera, J.; Christensen, V. Predicted impact of the invasive lionfish Pterois volitans on the food web of a Caribbean coral reef. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullard, S.A.; Barse, A.M.; Curran, S.S.; Morris, J.A. First Record of a Digenean from Invasive Lionfish, Pterois cf. volitans, (Scorpaeniformes: Scorpaenidae) in the Northwestern Atlantic Ocean. J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, D.; Ellis, M.E.F. Native grouper indirectly ameliorates the negative effects of invasive lionfish. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 558, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maljković, A.; Van Leeuwen, T.E.; Cove, S.N. Predation on the invasive red lionfish, Pterois volitans (Pisces: Scorpaenidae), by native groupers in the Bahamas. Coral Reefs 2008, 27, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumby, P.J.; Harborne, A.R.; Brumbaugh, D.R. Grouper as a Natural Biocontrol of Invasive Lionfish. PLoS One 2011, 6, e21510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikkel, P.C.; Tuttle, L.J.; Cure, K.; Coile, A.M.; Hixon, M.A. Low Susceptibility of Invasive Red Lionfish (Pterois volitans) to a Generalist Ectoparasite in Both Its Introduced and Native Ranges. PLoS One 2014, 9, e95854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sellers, A.J.; Ruiz, G.M.; Leung, B.; Torchin, M.E. Regional Variation in Parasite Species Richness and Abundance in the Introduced Range of the Invasive Lionfish, Pterois volitans. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0131075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Ascherl, Z.; Williams, E.H.; Bunkley-Williams, L.; Tuttle, L.J.; Sikkel, P.C.; Hixon, M.A. Parasitism in Pterois volitans (Scorpaenidae) from Coastal Waters of Puerto Rico, the Cayman Islands, and the Bahamas. J. Parasitol. 2015, 101, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, H.E.; Fogg, A.Q.; Allen, M.S.; Ahrens, R.N.M.; Patterson, W.F. Precipitous Declines in Northern Gulf of Mexico Invasive Lionfish Populations Following the Emergence of an Ulcerative Skin Disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkwitt, C.E.; Albins, M.A.; Buch, K.L.; Ingeman, K.E.; Kindinger, T.L.; Pusack, T.J.; Stallings, C.D.; Hixon, M.A. Is the lionfish invasion waning? Evidence from The Bahamas. Coral Reefs 2017, 36, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiriake, A.; Shiomi, K. Some properties and cDNA cloning of proteinaceous toxins from two species of lionfish (Pterois antennata and Pterois volitans). Toxicon 2011, 58, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiriake, A.; Madokoro, M.; Shiomi, K. Enzymatic properties and primary structures of hyaluronidases from two species of lionfish (Pterois antennata and Pterois volitans). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosaka, M.; Nagahama, M.; Kim, W.S.; Watanabe, T.; Hatsuzawa, K.; Ikemizu, J.; Murakami, K.; Nakayama, K. Arg-X-Lys/Arg-Arg motif as a signal for precursor cleavage catalyzed by furin within the constitutive secretory pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 12127–12130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Liu, S.; Hu, L.; Zhang, S. Characterization and bioactivity of hepcidin-2 in zebrafish: Dependence of antibacterial activity upon disulfide bridges. Peptides 2014, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, E.; Preza, G.C.; Jung, C.-L.; Kaplan, J.; Waring, A.J.; Ganz, T. The N-terminus of hepcidin is essential for its interaction with ferroportin: Structure-function study. Blood 2006, 107, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.S.; Iwanowicz, L.R.; Marranca, J.M. Identification of centrarchid hepcidins and evidence that 17??-estradiol disrupts constitutive expression of hepcidin-1 and inducible expression of hepcidin-2 in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2009, 26, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shike, H.; Shimizu, C.; Lauth, X.; Burns, J.C. Organization and expression analysis of the zebrafish hepcidin gene, an antimicrobial peptide gene conserved among vertebrates. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2004, 28, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirono, I.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Ono, Y.; Kurobe, T.; Ohira, T.; Nozaki, R.; Aoki, T. Two different types of hepcidins from the Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 5257–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocquellet, A.; Odaert, B.; Cabanne, C.; Noubhani, A.; Dieryck, W.; Joucla, G.; Le Senechal, C.; Milenkov, M.; Chaignepain, S.; Schmitter, J.-M.; et al. Structure–activity relationship of human liver-expressed antimicrobial peptide 2. Peptides 2010, 31, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.; Curstedt, T.; Jörnvall, H.; Johansson, J. An amphipathic helical motif common to tumourolytic polypeptide NK-lysin and pulmonary surfactant polypeptide SP-B. FEBS Lett. 1995, 362, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.H.; Sawaya, M.R.; Cascio, D.; Ernst, W.; Modlin, R.; Krensky, A.; Eisenberg, D. Granulysin crystal structure and a structure-derived lytic mechanism. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 325, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liepinsh, E.; Andersson, M.; Ruysschaert, J.M.; Otting, G. Saposin fold revealed by the NMR structure of NK-lysin. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1997, 4, 793–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatylny-Gaudin, C.; Cornet, V.; Leduc, A.; Zanuttini, B.; Corre, E.; Le Corguillé, G.; Bernay, B.; Garderes, J.; Kraut, A.; Couté, Y.; et al. Neuropeptidome of the Cephalopod Sepia officinalis: Identification, Tissue Mapping, and Expression Pattern of Neuropeptides and Neurohormones during Egg Laying. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 48–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Gong, Q.; Song, M.; Lai, J.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y. Identification and characterization of three novel antimicrobial peptides from Acipenser dabryanus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 88, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietschel, B.; Baeumlisberger, D.; Arrey, T.N.; Bornemann, S.; Rohmer, M.; Schuerken, M.; Karas, M.; Meyer, B. The Benefit of Combining nLC-MALDI-Orbitrap MS Data with nLC-MALDI-TOF/TOF Data for Proteomic Analyses Employing Elastase. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 5317–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar, A.; Ren, D. Antimicrobial Peptides. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 1543–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; Kumar, G.; Saleh, M.; El-Matbouli, M. Aeromonas salmonicida: Updates on an old acquaintance. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2016, 120, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, W.L.; Jenkins, C.; Seymour, J.R.; Labbate, M. Oyster disease in a changing environment: Decrypting the link between pathogen, microbiome and environment. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 143, 124–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.M.; Edwards, M.A.; Li, J.; Yip, C.M.; Deber, C.M. Roles of Hydrophobicity and Charge Distribution of Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides in Peptide-Membrane Interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 7738–7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dathe, M.; Wieprecht, T.; Nikolenko, H.; Handel, L.; Maloy, W.L.; MacDonald, D.L.; Beyermann, M.; Bienert, M. Hydrophobicity, hydrophobic moment and angle subtended by charged residues modulate antibacterial and haemolytic activity of amphipathic helical peptides. FEBS Lett. 1997, 403, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.K.; Nick Pace, C.; Martin Scholtz, J. Trifluoroethanol effects on helix propensity and electrostatic interactions in the helical peptide from ribonuclease T 1. Protein Sci. 1998, 7, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roccatano, D.; Colombo, G.; Fioroni, M.; Mark, A.E. Mechanism by which 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol/water mixtures stabilize secondary-structure formation in peptides: A molecular dynamics study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2002, 99, 12179–12184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.-F.; Jin, Y.; Xu, X.; Qiao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Mao, Y.; Su, Y.-Q.; Wang, J. Characterization of a novel piscidin-like antimicrobial peptide from Pseudosciaena crocea and its immune response to Cryptocaryon irritans. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, K.-C.; Lee, S.-H.; Hour, A.-L.; Pan, C.-Y.; Lee, L.-H.; Chen, J.-Y. Five Different Piscidins from Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus: Analysis of Their Expressions and Biological Functions. PLoS One 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruangsri, J.; Salger, S.A.; Caipang, C.M.A.; Kiron, V.; Fernandes, J.M.O. Differential expression and biological activity of two piscidin paralogues and a novel splice variant in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, J.G. BACTERICIDAL ACTION OF HISTONE. J. Exp. Med. 1958, 108, 925–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, A.B.; Allen, M.S.; Frazer, T.K.; Sherman, K.D. Evaluating the Potential Efficacy of Invasive Lionfish (Pterois volitans) Removals. PLoS One 2011, 6, e19666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornet, V.; Henry, J.; Corre, E.; Le Corguille, G.; Zanuttini, B.; Zatylny-Gaudin, C. Dual role of the cuttlefish salivary proteome in defense and predation. J. Proteomics 2014, 108, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, T.N.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 4.0: Discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden markov model: Application to complete genomes-Edited by F. Cohen. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.D.; Bateman, A.; Clements, J.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Heger, A.; Hetherington, K.; Holm, L.; Mistry, J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houyvet, B.; Zanuttini, B.; Corre, E.; Le Corguillé, G.; Henry, J.; Zatylny-Gaudin, C. Design of antimicrobial peptides from a cuttlefish database. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoist, L.; Houyvet, B.; Henry, J.; Corre, E.; Zanuttini, B.; Zatylny-Gaudin, C. In-Depth In Silico Search for Cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) Antimicrobial Peptides Following Bacterial Challenge of Haemocytes. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syvitski, R.T.; Burton, I.; Mattatall, N.R.; Douglas, S.E.; Jakeman, D.L. Structural Characterization of the Antimicrobial Peptide Pleurocidin from Winter Flounder. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 7282–7293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lu, X.-J.; Chai, F.-C.; Chen, J. Molecular characterization and functional analysis of a piscidin gene in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Sci. Press Zool. Res. 2016, 37, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. APD3: The antimicrobial peptide database as a tool for research and education. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautier, R.; Douguet, D.; Antonny, B.; Drin, G. HELIQUEST: A web server to screen sequences with specific -helical properties. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2101–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetru, C.; Bulet, P. Strategies for the isolation and characterization of antimicrobial peptides of invertebrates. Methods Mol. Biol. 1997, 78, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duval, E.; Zatylny, C.; Laurencin, M.; Baudy-Floc’h, M.; Henry, J. KKKKPLFGLFFGLF: A cationic peptide designed to exert antibacterial activity. Peptides 2009, 30, 1608–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micsonai, A.; Wien, F.; Kernya, L.; Lee, Y.-H.; Goto, Y.; Réfrégiers, M.; Kardos, J. Accurate secondary structure prediction and fold recognition for circular dichroism spectroscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3095–E3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Peptide | Amino Acid Sequence | Number of AA | MW (Da) | Net Charge | Hydrophobicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-Pte20 | FFKRLKNAFKSARQAWRDYK | 20 | 2561 | 6 | 40% |
| β-Pte17 | FFKRLKNAFKSARQAWR | 17 | 2155 | 6 | 47% |
| β-Pte13 | FFKRLKNAFKSAR | 13 | 1613 | 5 | 46% |
| β-Pte10 | FFKRLKNAFK | 10 | 1299 | 4 | 50% |
| γ-Pte20 | FFRHLKSLWKGAKAAFRGAR | 20 | 2348 | 6 | 50% |
| γ-Pte17 | FFRHLKSLWKGAKAAFR | 17 | 2063 | 5 | 52% |
| γ-Pte13 | FFRHLKSLWKGAK | 13 | 1618 | 4 | 46% |
| γ-Pte10 | FFRHLKSLWK | 10 | 1362 | 3 | 50% |
| Bacteria | Peptides from Pteroicidin B | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-Pte20 | β-Pte17 | β-Pte13 | β-Pte10 | ||||||
| MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | ||
| Gram-positive | Listeria monocytogenes | 1–5 | 5–10 | 5–10 | 25–50 | NA | ND | NA | ND |
| Enterococcus faecalis | NA | ND | NA | NA | NA | ND | NA | ND | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 1–5 | 10–25 | 10–25 | 25–50 | NA | ND | NA | ND | |
| Gram-negative | Escherichia coli | 1–5 | 5–10 | 1–5 | 1–5 | 1–5 | 10–25 | 25–50 | ND |
| Salmonella typhimurium | 10–25 | 10–25 | 10–25 | 10–25 | NA | ND | NA | ND | |
| Aeromonas salmonicida | 1–5 | 1–5 | 5–10 | 5–10 | NA | ND | NA | ND | |
| Vibrio aesturianus | 1–5 | 5–10 | 10–25 | 10–25 | NA | ND | NA | ND | |
| Vibrio splendidus | 1–5 | 5–10 | 10–25 | 10–25 | NA | ND | NA | ND | |
| Vibrio vulnificus | 5–10 | 5–10 | 10–25 | 10–25 | NA | ND | NA | ND | |
| Bacteria | Peptides from Pteroicidin C | ||||||||
| γ-Pte20 | γ-Pte17 | γ-Pte13 | γ-Pte10 | ||||||
| MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | ||
| Gram-positive | Listeria monocytogenes | 1–5 | 5–10 | 1–5 | 5–10 | NA | ND | NA | ND |
| Enterococcus faecalis | 1–5 | NA | 1–5 | NA | NA | ND | NA | ND | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 1–5 | 1–5 | 1–5 | 1–5 | NA | ND | NA | ND | |
| Gram-negative | Escherichia coli | 1–5 | 1–5 | 1–5 | 10–25 | 10–25 | 10–25 | 25–50 | 25–50 |
| Salmonella typhimurium | 5–10 | 5-10 | 5–10 | 5–10 | NA | ND | NA | ND | |
| Aeromonas salmonicida | 1–5 | 1–5 | 1–5 | 1–5 | 25–50 | NA | 25–50 | NA | |
| Vibrio aestuarianus | 5–10 | 10–25 | 5–10 | 5–10 | NA | ND | NA | ND | |
| Vibrio splendidus | 5–10 | 5–10 | 10–25 | 10–25 | NA | ND | NA | ND | |
| Vibrio vulnificus | 10–25 | 10–25 | 10–25 | 10–25 | NA | ND | NA | ND | |
| Bacterial Strain | Reference Number | Culture Medium | Temperature | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-positive | Listeria monocytogenes | CIP 110871 | BHI | 37 |
| Enterococcus faecalis | CIP 76.117 | LB | 37 | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | CIP 53.1 56 | CL | 37 | |
| Gram-negative | Escherichia coli | CIP 54.8T | LB | 37 |
| Salmonella typhimurium | CIP 103446 | TSB | 37 | |
| Aeromonas salmonicida | CIP 103209T | CL | 30 | |
| Vibrio aestuarianus | CIP 109791T | MB | 25 | |
| Vibrio splendidus LGP32 | CIP 107715 | MB | 25 | |
| Vibrio vulnificus | CIP 109783 | MB | 30 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Houyvet, B.; Bouchon-Navaro, Y.; Bouchon, C.; Corre, E.; Zatylny-Gaudin, C. Marine Transcriptomics Analysis for the Identification of New Antimicrobial Peptides. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19090490
Houyvet B, Bouchon-Navaro Y, Bouchon C, Corre E, Zatylny-Gaudin C. Marine Transcriptomics Analysis for the Identification of New Antimicrobial Peptides. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(9):490. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19090490
Chicago/Turabian StyleHouyvet, Baptiste, Yolande Bouchon-Navaro, Claude Bouchon, Erwan Corre, and Céline Zatylny-Gaudin. 2021. "Marine Transcriptomics Analysis for the Identification of New Antimicrobial Peptides" Marine Drugs 19, no. 9: 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19090490
APA StyleHouyvet, B., Bouchon-Navaro, Y., Bouchon, C., Corre, E., & Zatylny-Gaudin, C. (2021). Marine Transcriptomics Analysis for the Identification of New Antimicrobial Peptides. Marine Drugs, 19(9), 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19090490