Structure of the Lipooligosaccharide from the Deep-Sea Marine Bacterium Idiomarina zobellii KMM 231T, Isolated at a Depth of 4000 Meters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. LOS Extraction, Purification, and Chemical Analysis
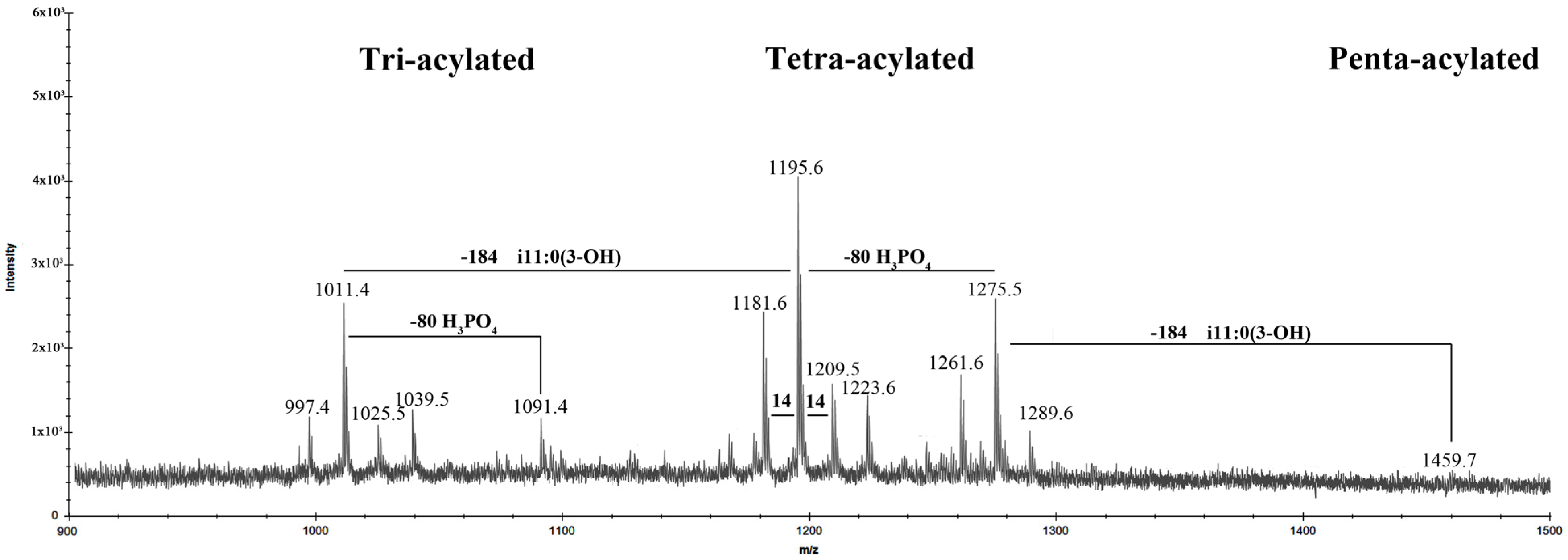
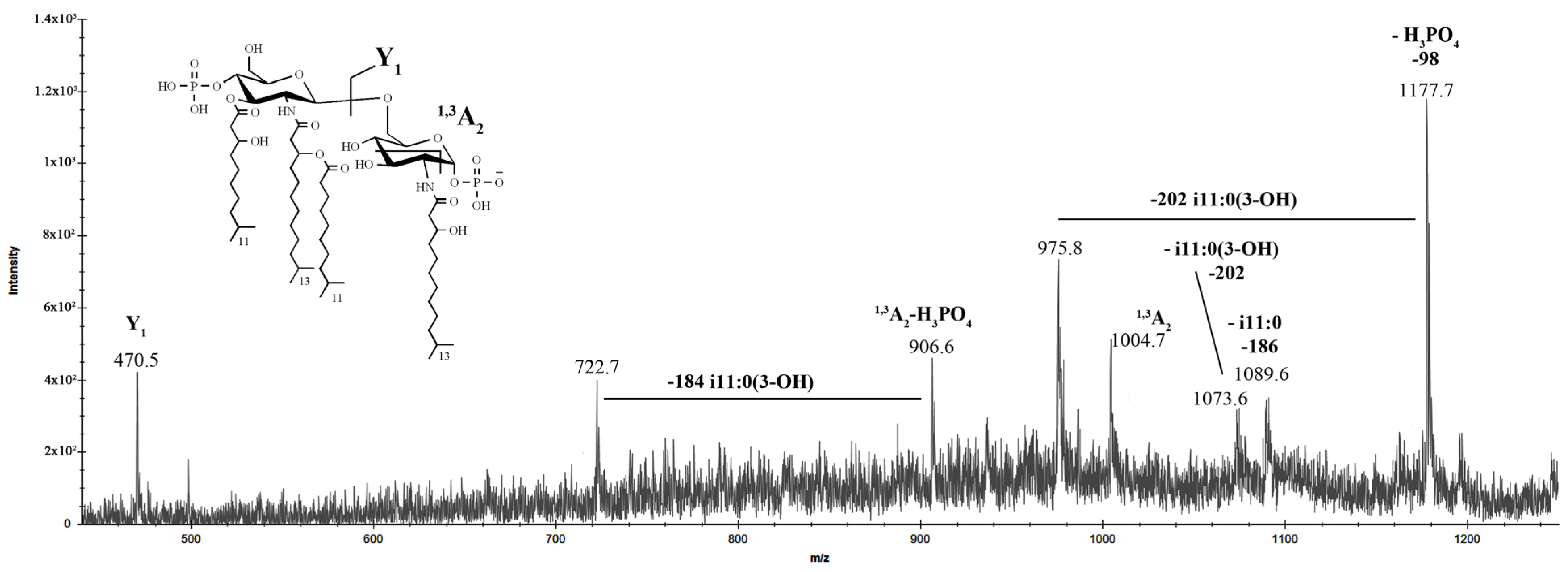
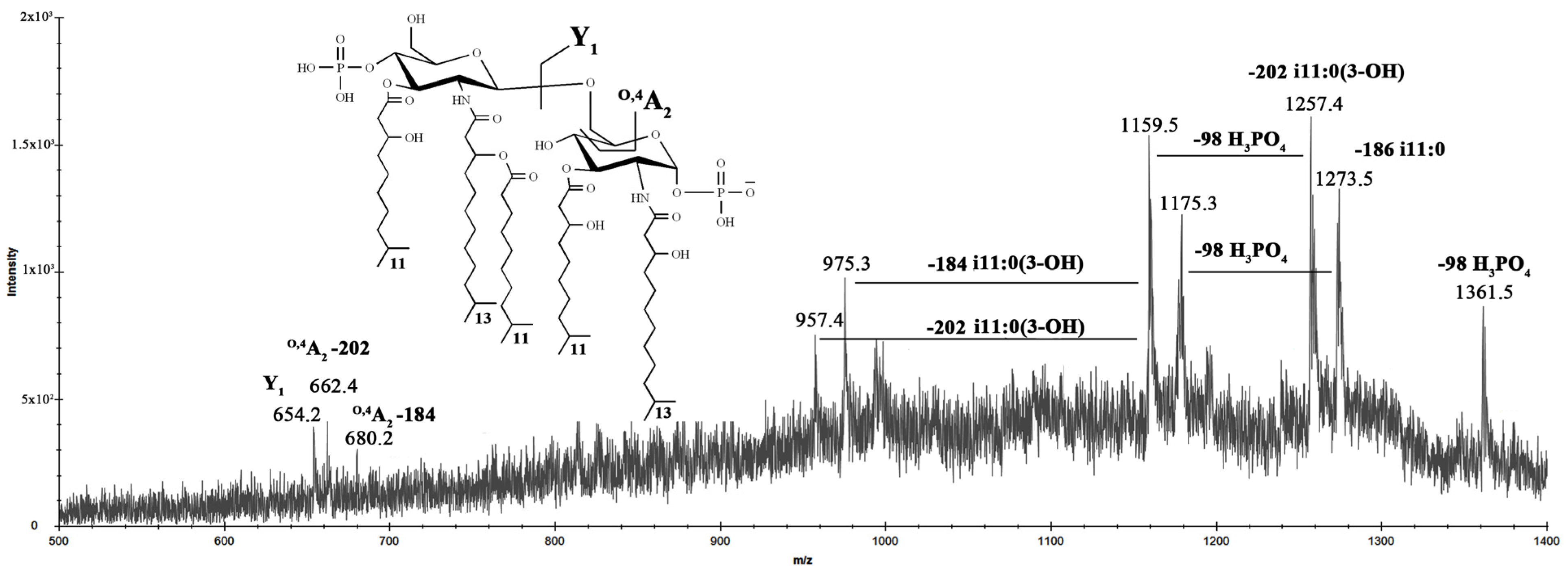
2.2. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) Analysis of LOS
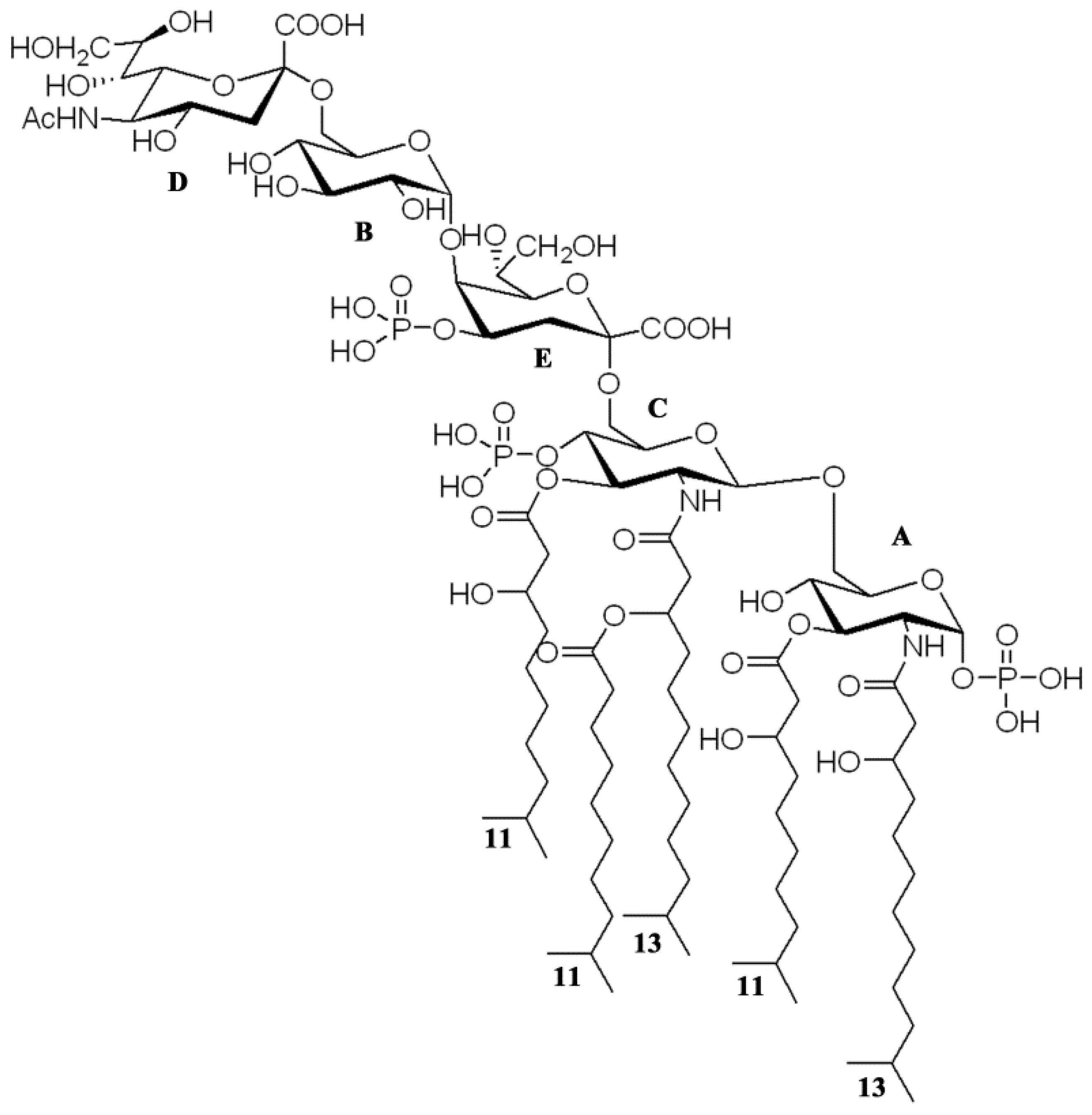
2.3. NMR Spectroscopy Structural Elucidation of the R-LPS Core Oligosaccharide
D B E C A
2.4. MALDI-TOF MS Analysis of Lipid A
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation and Purification of the LOS
4.2. SDS-PAGE Analysis of the LOS
4.3. Chemical Analysis of the LOS
4.4. Deacylation of the LOS
4.5. Isolation of the Lipid A
4.6. NMR Spectroscopy and MALDI-TOF MS Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jannasch, H.W.; Taylor, C.D. Deep-sea microbiology. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1984, 38, 487–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, B.B.; Boetius, A. Feast and famine—Microbial life in the deep-sea bed. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallmeyer, J.; Pockalny, R.; Adhikari, R.R.; Smith, D.C.; D’Hondt, S. Global distribution of microbial abundance and biomass in subseafloor sediment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16213–16216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohamed, J.; Bruno, F.; Eric, G.; Philippe, O. Microbial diversity and adaptation to high hydrostatic pressure in deep-sea hydrothermal vents prokaryotes. Extremophiles 2015, 19, 721–740. [Google Scholar]
- Casillo, A.; Parrilli, E.; Tutino, M.L.; Corsaro, M.M. The outer membrane glycolipids of bacteria from cold environments: Isolation, characterization, and biological activity. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikoshi, K. Barophiles deep-sea microorganisms adapted to an extreme environment. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 1998, 1, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, Y.; Nakayama, A.; Ishihara, K.; Saito, H. Adaptive changes in membrane lipids of barophilic bacteria in response to changes in growth pressure. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poli, A.; Anzelmo, G.; Nicolaus, B. Bacterial exopolysaccharides from extreme marine habitats: Production, characterization and biological activities. Mar. Drugs. 2010, 8, 1779–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casillo, A.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Corsaro, M.M. Exopolysaccharides from marine and marine extremophilic bacteria: Structures, properties, ecological roles and applications. Mar. Drugs. 2018, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Lorenzo, F.; Duda, K.A.; Lanzetta, R.; Silipo, A.; De Castro, C.; Molinaro, A. A journey from structure to function of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 15767–15821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lorenzo, F.; De Castro, C.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Silipo, A.; Molinaro, A. Lipopolysaccharides as microbe-associated molecular patterns: A structural perspective. In Carbohydrates in Drug Design and Discovery; Jimenez-Barbero, J., Javier Canada, F., Martıín-Santamaría, S., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC): London, UK, 2015; pp. 38–63. [Google Scholar]
- Molinaro, A.; Holst, O.; Di Lorenzo, F.; Callaghan, M.; Nurisso, A.; D’Errico, G.; Zamyatina, A.; Peri, F.; Berisio, R.; Jerala, R.; et al. Chemistry of lipid A: At the heart of innate immunity. Chemistry 2015, 21, 500–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, K. Innate recognition of lipopolysaccharide by Toll-like receptor 4–MD-2. Trends Microbiol. 2004, 12, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lorenzo, F.; Billod, J.-M.; Martín-Santamaría, S.; Silipo, A.; Molinaro, A. Gram-negative extremophile lipopolysaccharides: Promising source of inspiration for a new generation of endotoxin antagonists. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 2017, 4055–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, F.; Palmigiano, A.; Paciello, I.; Pallach, M.; Garozzo, D.; Bernardini, M.L.; La Cono, V.; Yakimov, M.M.; Molinaro, A.; Silipo, A. The deep-sea polyextremophile Halobacteroides lacunaris TB21 rough-type LPS: Structure and inhibitory activity towards toxic LPS. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Vello, P.; Di Lorenzo, F.; Zucchetta, D.; Zamyatina, A.; De Castro, C.; Molinaro, A. Lipopolysaccharide lipid A: A promising molecule for new immunity-based therapies and antibiotics. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 230, 107970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parte, A.C.; Sarda Carbasse, J.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Reimer, L.C.; Göker, M. List of prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) moves to the DSMZ. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 5607–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilcoyne, M.; Perepelov, A.V.; Tomshich, S.V.; Komandrova, N.A.; Shashkov, A.S.; Romanenko, L.A.; Knirel, Y.A.; Savage, A.V. Structure of the O-polysaccharide of Idiomarina zobellii KMM 231T containing two unusual amino sugars with the free amino group, 4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-D-glucose and 2-amino-2-deoxy-L-guluronic acid. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokoulin, M.S.; Komandrova, N.A.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Tomshich, S.V.; Romanenko, L.A.; Vaskovsky, V.E. Structure of the O-specific polysaccharide from the deep-sea marine bacterium Idiomarina abyssalis KMM 227T containing a 2-O-sulfate-3-N-(4-hydroxybutanoyl)-3,6-dideoxy-D-glucose. Carbohydr. Res. 2015, 413, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasikova, I.N.; Kapustina, N.V.; Svetashev, V.I.; Gorshkova, R.P.; Tomshich, S.V.; Nazarenko, E.L.; Komandrova, N.A.; Ivanova, E.P.; Gorshkova, N.M.; Romanenko, L.A.; et al. Chemical characterization of lipid A from some marine Proteobacteria. Biochemistry 2001, 66, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Galanos, C.; Lüderitz, O.; Westphal, O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur. J. Biochem. 1969, 9, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenter, M.; Jann, B.; Jann, K. Structure of the K16 antigen from Escherichia coli O7:K16:H−: A Kdo-containing capsular polysaccharide. Carbohydr. Res. 1990, 197, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knirel, Y.A.; Shashkov, A.S.; Tsvetkov, Y.E.; Jansson, P.-E.; Zahringer, U. 5,7-Diamino-3,5,7,9-tetradeoxynon-2-ulosonic acids in bacterial glycopolymers: Chemistry and biochemistry. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 2003, 58, 371–417. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Costello, C.E.; Vath, J.E. Tandem mass spectrometry of glycolipids. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 193, 738–768. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barrau, C.; Di Lorenzo, F.; Menes, R.J.; Lanzetta, R.; Molinaro, A.; Silipo, A. The Structure of the Lipid A from the Halophilic Bacterium Spiribacter salinus M19-40T. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pither, M.D.; Sun, M.L.; Speciale, I.; Silipo, A.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Molinaro, A.; Di Lorenzo, F. Structural determination of the lipid A from the deep-sea bacterium Zunongwangia profunda SM-A87: A small-scale approach. Glycoconj J. 2022, 39, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, O. Chemical structure of the core region of lipopolysaccharides. An update. Trends Glycosci. Glycotechnol. 2002, 14, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ieranò, T.; Silipo, A.; Nazarenko, E.L.; Gorshkova, R.P.; Ivanova, E.P.; Garozzo, D.; Sturiale, L.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Molinaro, A. Against the rules: A marine bacterium, Loktanella rosea, possesses a unique lipopolysaccharide. Glycobiology 2010, 20, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.M.; Frasch, C.E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 119, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leontein, K.; Lindberg, B.; Lönngren, J. Assignment of absolute configuration of sugars by g.l.c. of their acetylated glycosides formed from chiral alcohols. Carb. Res. 1978, 62, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silipo, A.; Lanzetta, R.; Amoresano, A.; Parrilli, M.; Molinaro, A. Ammonium hydroxide hydrolysis: A valuable support in the MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry analysis of Lipid A fatty acid distribution. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 2188–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Speciale, I.; Notaro, A.; Garcia-Vello, P.; Di Lorenzo, F.; Armiento, S.; Molinaro, A.; Marchetti, R.; Silipo, A.; De Castro, C. Liquid-state NMR spectroscopy for complex carbohydrate structural analysis: A hitchhiker’s guide. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toukach, P.V. Bacterial Carbohydrate Structure Database 3: Principles and realization. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


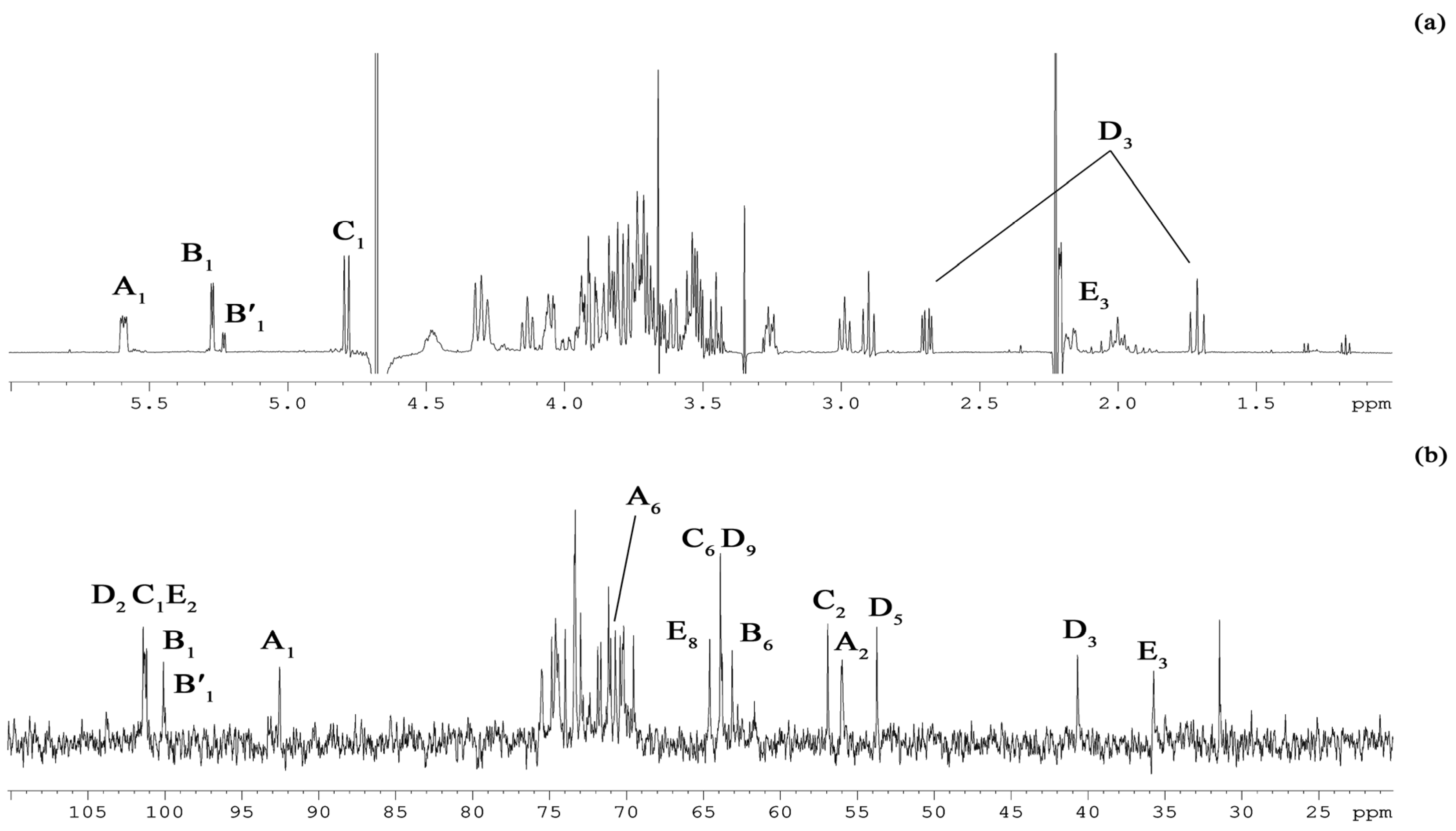


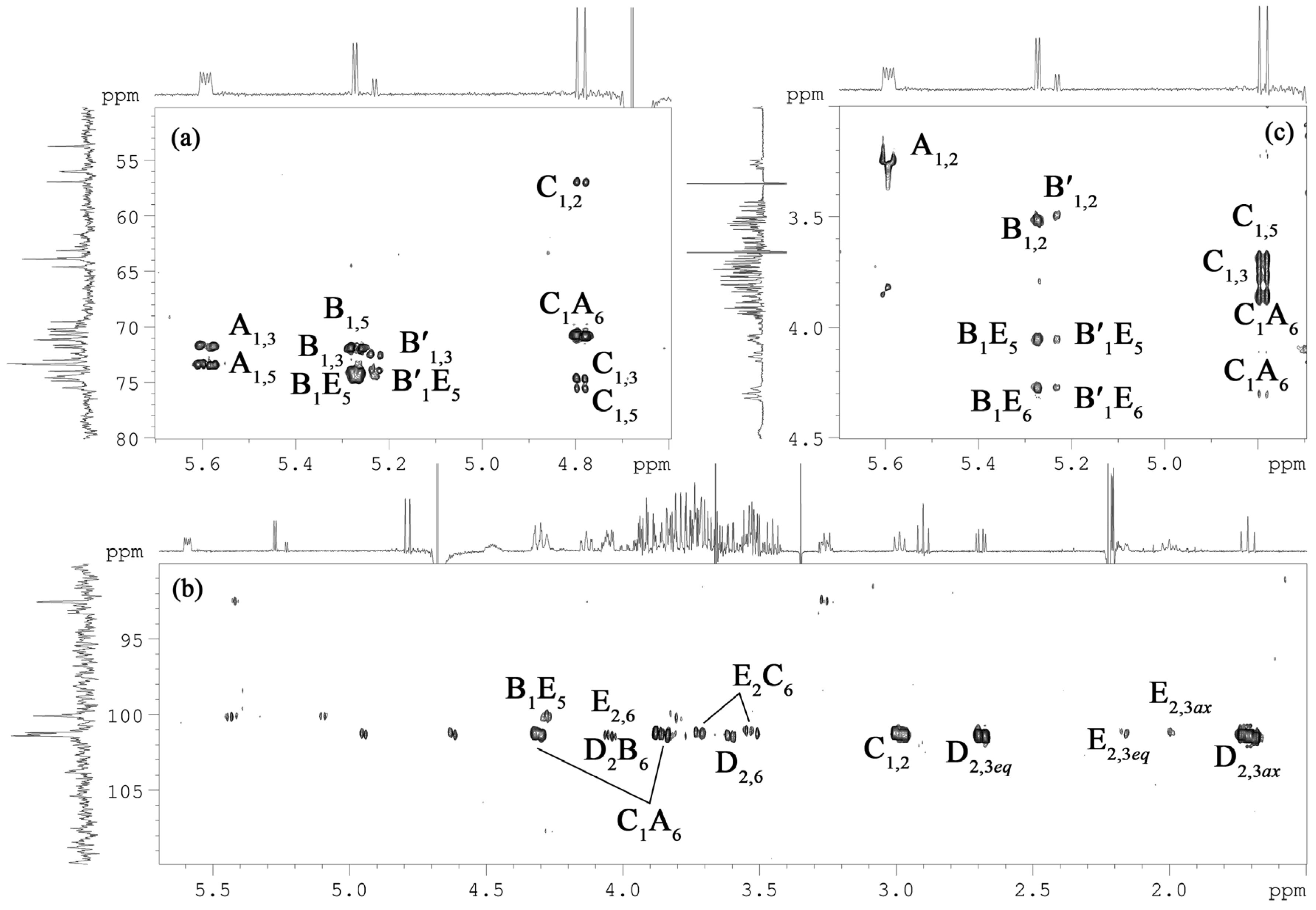

| Sugar Residue |
H-1 C-1 |
H-2 C-2 |
H-3eq,ax C-3 |
H-4 C-4 |
H-5 C-5 |
H-6a,b C-6 |
H-7 C-7 |
H-8 C-8 |
H-9 C-9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-D-GlcpN1P A | 5.59 92.5 | 3.26 56.0 | 3.84 71.7 | 3.45 71.2 | 4.13 73.3 | 4.31, 3.86 70.7 | |||
| →6)-α-D-Glcp-(1→ B | 5.27 100.1 | 3.51 73.4 | 3.81 74.0 | 3.54 70.4 | 4.31 71.9 | 4.05, 3.73 63.1 | |||
| →6)- α-D-Glcp-(1→ B′ | 5.23 100.0 | 3.49 73.4 | 3.82 74.0 | 3.26 72.4 | 4.31 71.9 | 3.99, 3.58 62.8 | |||
| →6)-α-D-GlcpN4P-(1→ C | 4.79 101.3 | 2.99 56.9 | 3.79 74.6 | 3.73 74.4 | 3.69 75.5 | 3.71, 3.53 63.9 | |||
| α-Neup-(1→ D | 175.3 | 101.4 | 2.69, 1.71 40.7 | 3.54 71.0 | 2.90 53.7 | 3.61 74.9 | 3.76 69.5 | 3.94 73.0 | 3.90, 3.68 63.8 |
| →5)-α-Kdop4P-(1→ E | 176.1 | 101.2 | 2.17, 2.00 35.7 | 4.48 70.3 | 4.28 74.5 | 4.05 70.2 | 3.82 73.3 | 3.93, 3.72 64.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kokoulin, M.S.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Romanenko, L.A. Structure of the Lipooligosaccharide from the Deep-Sea Marine Bacterium Idiomarina zobellii KMM 231T, Isolated at a Depth of 4000 Meters. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110700
Kokoulin MS, Dmitrenok PS, Romanenko LA. Structure of the Lipooligosaccharide from the Deep-Sea Marine Bacterium Idiomarina zobellii KMM 231T, Isolated at a Depth of 4000 Meters. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(11):700. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110700
Chicago/Turabian StyleKokoulin, Maxim S., Pavel S. Dmitrenok, and Lyudmila A. Romanenko. 2022. "Structure of the Lipooligosaccharide from the Deep-Sea Marine Bacterium Idiomarina zobellii KMM 231T, Isolated at a Depth of 4000 Meters" Marine Drugs 20, no. 11: 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110700
APA StyleKokoulin, M. S., Dmitrenok, P. S., & Romanenko, L. A. (2022). Structure of the Lipooligosaccharide from the Deep-Sea Marine Bacterium Idiomarina zobellii KMM 231T, Isolated at a Depth of 4000 Meters. Marine Drugs, 20(11), 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110700









