First Insights into the Repertoire of Secretory Lectins in Rotifers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
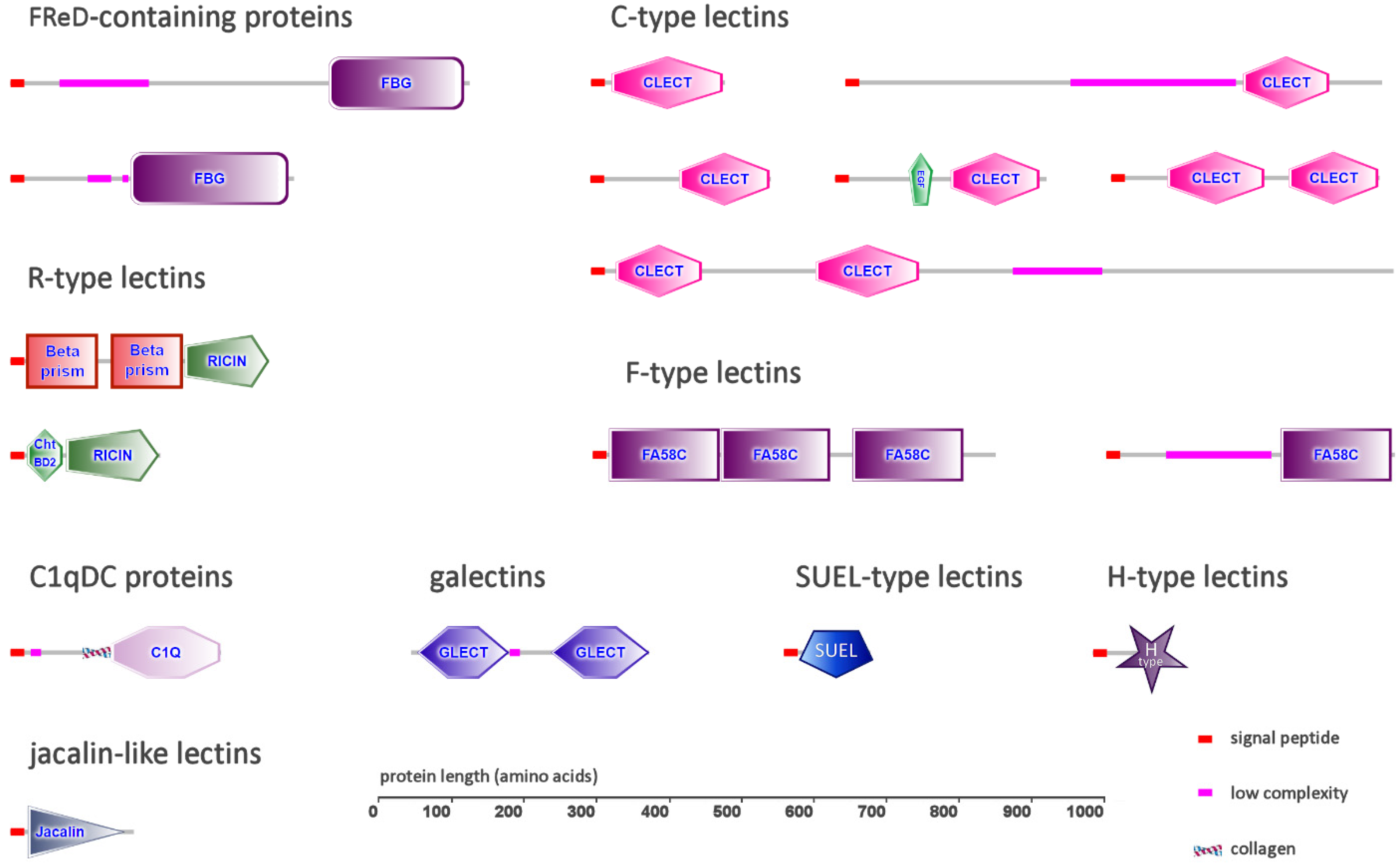
2.1. FReD-Containing Proteins
2.2. C-Type Lectins
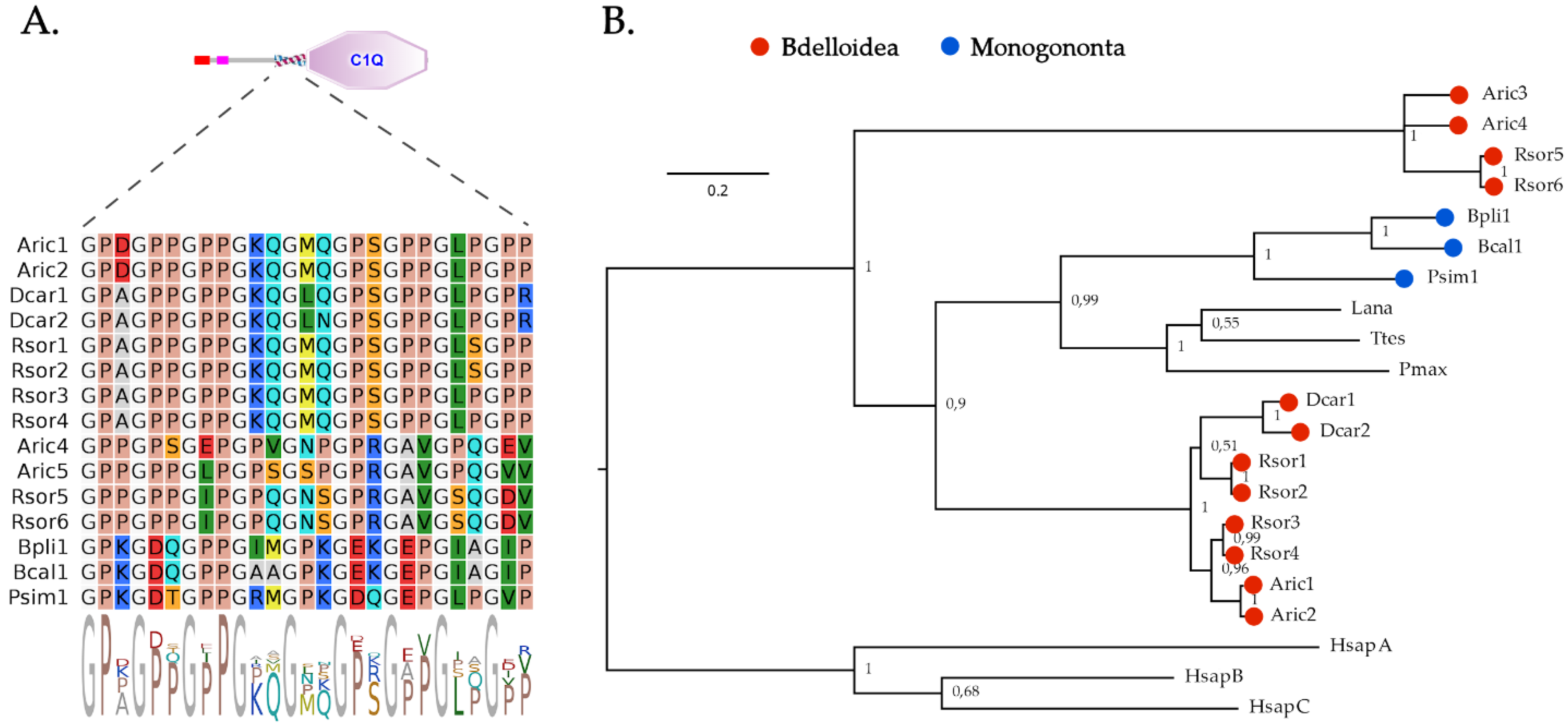
2.3. C1q Domain-Containing Proteins
2.4. Galectins
2.5. Ricin β-Trefoil Lectins
2.6. F-Type Lectins
2.7. Other Types of Lectins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of Lectin-Like Molecules
4.2. Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stuart, L.M.; Paquette, N.; Boyer, L. Effector-Triggered versus Pattern-Triggered Immunity: How Animals Sense Pathogens. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.-L.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.-S.; Wang, Y.-F. Involvement of a Pattern Recognition Receptor C-Type Lectin 7 in Enhancing Cellular Encapsulation and Melanization Due to Its Carboxyl-Terminal CRD Domain in the Cotton Bollworm, Helicoverpa Armigera. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 44, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-W.; Xu, J.-D.; Zhao, X.-F.; Vasta, G.R.; Wang, J.-X. A Shrimp C-Type Lectin Inhibits Proliferation of the Hemolymph Microbiota by Maintaining the Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 11779–11790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brouwer, N.; Dolman, K.M.; van Zwieten, R.; Nieuwenhuys, E.; Hart, M.; Aarden, L.A.; Roos, D.; Kuijpers, T.W. Mannan-Binding Lectin (MBL)–Mediated Opsonization Is Enhanced by the Alternative Pathway Amplification Loop. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 2051–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerrigan, A.M.; Brown, G.D. C-Type Lectins and Phagocytosis. Immunobiology 2009, 214, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pales Espinosa, E.; Allam, B. Reverse Genetics Demonstrate the Role of Mucosal C-Type Lectins in Food Particle Selection in the Oyster Crassostrea Virginica. J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221, jeb174094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyholm, S.V.; Graf, J. Knowing Your Friends: Invertebrate Innate Immunity Fosters Beneficial Bacterial Symbioses. Nature Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grossart, H.-P.; Riemann, L.; Tang, K. Molecular and Functional Ecology of Aquatic Microbial Symbionts. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.-H.; Cai, Y.; Li, J.-C.; Su, M.P.; Liu, W.-L.; Cheng, L.; Chou, S.-J.; Yu, G.-Y.; Wang, H.-D.; Chen, C.-H. C-Type Lectins Link Immunological and Reproductive Processes in Aedes Aegypti. iScience 2020, 23, 101486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, S.A.; Moy, G.W.; Friend, D.S.; Swanson, W.J.; Vacquier, V.D. Oyster Sperm Bindin Is a Combinatorial Fucose Lectin with Remarkable Intra-Species Diversity. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2008, 52, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauta, A.J.; Castellano, G.; Xu, W.; Woltman, A.M.; Borrias, M.C.; Daha, M.R.; van Kooten, C.; Roos, A. Opsonization with C1q and Mannose-Binding Lectin Targets Apoptotic Cells to Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 3044–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maki, J.S.; Mitchell, R. Involvement of Lectins in the Settlement and Metamorphosis of Marine Invertebrate Larvae. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1985, 37, 675–683. [Google Scholar]
- Emmanuelle, P.E.; Mickael, P.; Evan, W.; Shumway, S.E.; Bassem, A. Lectins Associated with the Feeding Organs of the Oyster Crassostrea Virginica Can Mediate Particle Selection. Biol. Bull. 2009, 217, 130–141. [Google Scholar]
- Kvennefors, E.C.E.; Leggat, W.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Degnan, B.M.; Barnes, A.C. An Ancient and Variable Mannose-Binding Lectin from the Coral Acropora Millepora Binds Both Pathogens and Symbionts. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giga, Y.; Ikai, A.; Takahashi, K. The Complete Amino Acid Sequence of Echinoidin, a Lectin from the Coelomic Fluid of the Sea Urchin Anthocidaris Crassispina. Homologies with Mammalian and Insect Lectins. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 6197–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaura, K.; Takahashi, K.G.; Suzuki, T. Identification and Tissue Expression Analysis of C-Type Lectin and Galectin in the Pacific Oyster, Crassostrea Gigas. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 149, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdol, M.; Gomez-Chiarri, M.; Castillo, M.G.; Figueras, A.; Fiorito, G.; Moreira, R.; Novoa, B.; Pallavicini, A.; Ponte, G.; Roumbedakis, K.; et al. Immunity in Molluscs: Recognition and Effector Mechanisms, with a Focus on Bivalvia. In Advances in Comparative Immunology; Cooper, E.L., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 225–234. ISBN 978-3-319-76768-0. [Google Scholar]
- Shain, D.H.; Halldórsdóttir, K.; Pálsson, F.; Aðalgeirsdóttir, G.; Gunnarsson, A.; Jónsson, Þ.; Lang, S.A.; Pálsson, H.S.; Steinþórssson, S.; Arnason, E. Colonization of Maritime Glacier Ice by Bdelloid Rotifera. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 98, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hespeels, B.; Knapen, M.; Hanot-Mambres, D.; Heuskin, A.-C.; Pineux, F.; Lucas, S.; Koszul, R.; van Doninck, K. Gateway to Genetic Exchange? DNA Double-Strand Breaks in the Bdelloid Rotifer Adineta Vaga Submitted to Desiccation. J. Evol. Biol. 2014, 27, 1334–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, J.L.M.; Welch, D.B.M.; Meselson, M. Cytogenetic Evidence for Asexual Evolution of Bdelloid Rotifers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1618–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nowell, R.W.; Wilson, C.G.; Almeida, P.; Schiffer, P.H.; Fontaneto, D.; Becks, L.; Rodriguez, F.; Arkhipova, I.R.; Barraclough, T.G. Evolutionary Dynamics of Transposable Elements in Bdelloid Rotifers. eLife 2021, 10, e63194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyres, I.; Boschetti, C.; Crisp, A.; Smith, T.P.; Fontaneto, D.; Tunnacliffe, A.; Barraclough, T.G. Horizontal Gene Transfer in Bdelloid Rotifers Is Ancient, Ongoing and More Frequent in Species from Desiccating Habitats. BMC Biol. 2015, 13, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gladyshev, E.A.; Arkhipova, I.R. Genome Structure of Bdelloid Rotifers: Shaped by Asexuality or Desiccation? J. Hered. 2010, 101 (Suppl. S1), S85–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gabaldón, C.; Fontaneto, D.; Carmona, M.J.; Montero-Pau, J.; Serra, M. Ecological Differentiation in Cryptic Rotifer Species: What We Can Learn from the Brachionus Plicatilis Complex. Hydrobiologia 2017, 796, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekzadeh-Viayeh, R.; Pak-Tarmani, R.; Rostamkhani, N.; Fontaneto, D. Diversity of the Rotifer Brachionus Plicatilis Species Complex (Rotifera: Monogononta) in Iran through Integrative Taxonomy. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2014, 170, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam-Höai, T.; Rougier, C.; Lasserre, G. Tintinnids and Rotifers in a Northern Mediterranean Coastal Lagoon. Structural Diversity and Function through Biomass Estimations. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 152, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assefa, E.; Mengidtou, S. Seasonal Variation of Biomass and Secondary Production of Thermocyclops (Cyclopoida) and Brachionus (Rotifera) Spp. in a Shallow Tropical Lake Kuriftu, Ethiopia. SINET Ethiop. J. Sci. 2011, 34, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.D.; Geiling, W. Elevated Planktonic Rotifer Biomass in Acidified Metal-Contaminated Lakes near Sudbury, Ontario. Hydrobiologia 1985, 120, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubzens, E.; Tandler, A.; Minkoff, G. Rotifers as Food in Aquaculture. Hydrobiologia 1989, 186, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhont, J.; Dierckens, K.; Støttrup, J.; Van Stappen, G.; Wille, M.; Sorgeloos, P. 5–Rotifers, Artemia and Copepods as Live Feeds for Fish Larvae in Aquaculture. In Advances in Aquaculture Hatchery Technology; Allan, G., Burnell, G., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 157–202. ISBN 978-0-85709-119-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara, A.; Marcial, H.S. The Use of Non-Brachionus Plicatilis Species Complex Rotifer in Larviculture. Hydrobiologia 2019, 844, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hagiwara, A.; Kim, H.-J.; Marcial, H. Mass Culture and Preservation of Brachionus Plicatilis Sp. Complex. In Rotifers: Aquaculture, Ecology, Gerontology, and Ecotoxicology; Hagiwara, A., Yoshinaga, T., Eds.; Fisheries Science Series; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 35–45. ISBN 978-981-10-5635-2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Guo, X.; Litman, G.W.; Dishaw, L.J.; Zhang, G. Massive Expansion and Functional Divergence of Innate Immune Genes in a Protostome. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerdol, M.; Venier, P.; Pallavicini, A. The Genome of the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea Gigas Brings New Insights on the Massive Expansion of the C1q Gene Family in Bivalvia. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 49, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdol, M.; Greco, S.; Pallavicini, A. Extensive Tandem Duplication Events Drive the Expansion of the C1q-Domain-Containing Gene Family in Bivalves. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsushita, M. Ficolins: Complement-Activating Lectins Involved in Innate Immunity. J. Innate Immun. 2010, 2, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, M.; Fujita, T. The Role of Ficolins in Innate Immunity. Immunobiology 2002, 205, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamichi, Y.; Yokoyama, Y. Purification, Characterization and CDNA Cloning of a Novel Lectin from the Jellyfish Nemopilema Nomurai. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 156, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokudan, S.; Muta, T.; Tsuda, R.; Koori, K.; Kawahara, T.; Seki, N.; Mizunoe, Y.; Wai, S.N.; Iwanaga, S.; Kawabata, S. Horseshoe Crab Acetyl Group-Recognizing Lectins Involved in Innate Immunity Are Structurally Related to Fibrinogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 10086–10091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gout, E.; Garlatti, V.; Smith, D.F.; Lacroix, M.; Dumestre-Pérard, C.; Lunardi, T.; Martin, L.; Cesbron, J.-Y.; Arlaud, G.J.; Gaboriaud, C.; et al. Carbohydrate Recognition Properties of Human Ficolins: Glycan Array Screening Reveals the Sialic Acid Binding Specificity of M-Ficolin. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 6612–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adema, C.M. Fibrinogen-Related Proteins (FREPs) in Mollusks. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 2015, 57, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordy, M.A.; Pila, E.A.; Hanington, P.C. The Role of Fibrinogen-Related Proteins in the Gastropod Immune Response. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 46, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbushin, A.M.; Panchin, Y.V.; Iakovleva, N.V. In Search of the Origin of FREPs: Characterization of Aplysia Californica Fibrinogen-Related Proteins. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheilly, N.M.; Duval, D.; Mouahid, G.; Emans, R.; Allienne, J.-F.; Galinier, R.; Genthon, C.; Dubois, E.; Du Pasquier, L.; Adema, C.M.; et al. A Family of Variable Immunoglobulin and Lectin Domain Containing Molecules in the Snail Biomphalaria Glabrata. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 48, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skazina, M.A.; Gorbushin, A.M. Characterization of the Gene Encoding a Fibrinogen-Related Protein Expressed in Crassostrea Gigas Hemocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 54, 586–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurachi, S.; Song, Z.; Takagaki, M.; Yang, Q.; Winter, H.C.; Kurachi, K.; Goldstein, I.J. Sialic-Acid-Binding Lectin from the Slug Limax Flavus–Cloning, Expression of the Polypeptide, and Tissue Localization. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 254, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, B.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Tang, X.; Zhang, G. Highly Diverse Fibrinogen-Related Proteins in the Pacific Oyster Crassostrea Gigas. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 43, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Qu, F.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z. Characteristic and Functional Analysis of a Ficolin-like Protein from the Oyster Crassostrea Hongkongensis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 40, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Huang, M.; Sun, Z.; Sun, Y.; Song, L. A New Fibrinogen-Related Protein from Argopecten Irradians (AiFREP-2) with Broad Recognition Spectrum and Bacteria Agglutination Activity. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 38, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdol, M.; Luo, Y.-J.; Satoh, N.; Pallavicini, A. Genetic and Molecular Basis of the Immune System in the Brachiopod Lingula Anatina. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 82, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L. First Characterization of Two C-Type Lectins of the Tubeworm Alaysia Sp. from a Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vent. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 86, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, L.; Wang, H.; Song, L. C-Type Lectin in Chlamys Farreri (CfLec-1) Mediating Immune Recognition and Opsonization. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.; Song, X.; Zhao, J.; Mu, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, X.; Song, L. A C-Type Lectin (AiCTL-3) from Bay Scallop Argopecten Irradians with Mannose/Galactose Binding Ability to Bind Various Bacteria. Gene 2013, 531, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelensky, A.N.; Gready, J.E. The C-Type Lectin-like Domain Superfamily. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 6179–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pees, B.; Yang, W.; Zárate-Potes, A.; Schulenburg, H.; Dierking, K. High Innate Immune Specificity through Diversified C-Type Lectin-Like Domain Proteins in Invertebrates. J. Innate Immun. 2016, 8, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drickamer, K. Evolution of Ca2+-Dependent Animal Lectins11Abbreviations: CRD, Carbohydrate-Recognition Domain; EGF, Epidermal Growth Factor. In Progress in Nucleic Acid Research and Molecular Biology; Cohn, W.E., Moldave, K., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1993; Volume 45, pp. 207–232. [Google Scholar]
- Drickamer, K.; Fadden, A.J. Genomic Analysis of C-Type Lectins. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 2002, 69, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmskov, U.L. Collectins and Collectin Receptors in Innate Immunity. APMIS Suppl. 2000, 100, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-J.; Lan, J.-F.; Zhao, X.-F.; Vasta, G.R.; Wang, J.-X. Binding of a C-Type Lectin’s Coiled-Coil Domain to the Domeless Receptor Directly Activates the JAK/STAT Pathway in the Shrimp Immune Response to Bacterial Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vasta, G.R.; Ahmed, H.; Tasumi, S.; Odom, E.W.; Saito, K. Biological Roles of Lectins in Innate Immunity: Molecular and Structural Basis for Diversity in Self/Non-Self Recognition. In Current Topics in Innate Immunity; Lambris, J.D., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 389–406. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, S.; Wang, W.; Xin, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Song, L. A Single-CRD C-Type Lectin from Oyster Crassostrea Gigas Mediates Immune Recognition and Pathogen Elimination with a Potential Role in the Activation of Complement System. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 44, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdol, M.; Venier, P. An Updated Molecular Basis for Mussel Immunity. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 46, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.-Q.; Gan, H.; Kanost, R.M. Immulectin, an Inducible C-Type Lectin from an Insect, Manduca Sexta, Stimulates Activation of Plasma Prophenol Oxidase. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 29, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couser, L.M. A Mannose Receptor-like Molecule Likely Serves as the Mate Recognition Pheromone Receptor in the Male Rotifer Brachionus Manjavacas. Bachelor’s Thesis, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kishore, U.; Gaboriaud, C.; Waters, P.; Shrive, A.K.; Greenhough, T.J.; Reid, K.B.M.; Sim, R.B.; Arlaud, G.J. C1q and Tumor Necrosis Factor Superfamily: Modularity and Versatility. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carland, T.M.; Gerwick, L. The C1q Domain Containing Proteins: Where Do They Come from and What Do They Do? Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghai, R.; Waters, P.; Roumenina, L.T.; Gadjeva, M.; Kojouharova, M.S.; Reid, K.B.M.; Sim, R.B.; Kishore, U. C1q and Its Growing Family. Immunobiology 2007, 212, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, I.; Gerdol, M.; Fujii, Y.; Ozeki, Y. Functional Characterization of OXYL, A SghC1qDC LacNAc-Specific Lectin from The Crinoid Feather Star Anneissia Japonica. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerlach, D.; Schlott, B.; Schmidt, K.-H. Cloning and Expression of a Sialic Acid-Binding Lectin from the Snail Cepaea Hortensis. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 40, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, X.; Li, C.; Zheng, Z.; Du, X. Novel Globular C1q Domain-Containing Protein (PmC1qDC-1) Participates in Shell Formation and Responses to Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns Stimulation in Pinctada Fucata Martensii. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, L.; Jin, M.; Hui, K.; Ren, Q. A C1qDC Protein (HcC1qDC6) with Three Tandem C1q Domains Is Involved in Immune Response of Triangle-Shell Pearl Mussel (Hyriopsis Cumingii). Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, K.; Wang, Y.; Lian, S.; Hu, N.; Chen, X.; Dai, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Hu, J.; Hu, X.; et al. Expansion of C1Q Genes in Zhikong Scallop and Their Expression Profiling After Exposure to the Toxic Dinoflagellates. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbushin, A.M. Derivatives of the Lectin Complement Pathway in Lophotrochozoa. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 94, 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasta, G.R.; Ahmed, H.; Nita-Lazar, M.; Banerjee, A.; Pasek, M.; Shridhar, S.; Guha, P.; Fernández-Robledo, J.A. Galectins as Self/Non-Self Recognition Receptors in Innate and Adaptive Immunity: An Unresolved Paradox. Front. Immun. 2012, 3, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Mu, C.; Song, L.; Qiu, L.; Liu, X. A Galectin with Quadruple-Domain from Bay Scallop Argopecten Irradians Is Involved in Innate Immune Response. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jiang, S.; Hu, Y.; Cui, S.; Guo, H.; Wu, K.; Li, Y.; Su, T. A Multidomain Galectin Involved in Innate Immune Response of Pearl Oyster Pinctada Fucata. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbushin, A.M.; Borisova, E.A. Lectin-like Molecules in Transcriptome of Littorina Littorea Hemocytes. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 48, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, L.; Xu, H.; Lin, W.; Shi, H.; Cui, Z.; Xu, X. A Novel Beta-Galactose-Specific Lectin of the Tubeworm, Ridgeia Piscesae, from the Hydrothermal Vent. Acta Oceanologica Sinica 2017, 36, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasta, G.R.; Feng, C.; Bianchet, M.A.; Bachvaroff, T.R.; Tasumi, S. Structural, Functional, and Evolutionary Aspects of Galectins in Aquatic Mollusks: From a Sweet Tooth to the Trojan Horse. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 46, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Popa, S.J.; Stewart, S.E.; Moreau, K. Unconventional Secretion of Annexins and Galectins. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 83, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, R.D.; Schnaar, R. R-Type Lectins. In Essentials of Glycobiology, 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Chapter 31. [Google Scholar]
- Kawsar, S.M.A.; Takeuchi, T.; Kasai, K.; Fujii, Y.; Matsumoto, R.; Yasumitsu, H.; Ozeki, Y. Glycan-Binding Profile of a D-Galactose Binding Lectin Purified from the Annelid, Perinereis Nuntia Ver. Vallata. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 152, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, J.; Dutta, S.K.; Kasai, K. Novel Galactose-Binding Proteins in Annelida. Characterization of 29-KDa Tandem Repeat-Type Lectins from the Earthworm Lumbricus Terrestris. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 14450–14460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawsar, S.M.A.; Hasan, I.; Rajia, S.; Koide, Y.; Fujii, Y.; Hayashi, R.; Yamada, M.; Ozeki, Y. Diverse Localization Patterns of an R-Type Lectin in Marine Annelids. Molecules 2021, 26, 4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Gerdol, M.; Kawsar, S.M.A.; Hasan, I.; Spazzali, F.; Yoshida, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Rajia, S.; Kamata, K.; Koide, Y.; et al. A GM1b/Asialo-GM1 Oligosaccharide-Binding R-Type Lectin from Purplish Bifurcate Mussels Mytilisepta Virgata and Its Effect on MAP Kinases. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 2612–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasan, I.; Sugawara, S.; Fujii, Y.; Koide, Y.; Terada, D.; Iimura, N.; Fujiwara, T.; Takahashi, K.G.; Kojima, N.; Rajia, S.; et al. MytiLec, a Mussel R-Type Lectin, Interacts with Surface Glycan Gb3 on Burkitt’s Lymphoma Cells to Trigger Apoptosis through Multiple Pathways. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 7377–7389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujii, Y.; Dohmae, N.; Takio, K.; Kawsar, S.M.A.; Matsumoto, R.; Hasan, I.; Koide, Y.; Kanaly, R.A.; Yasumitsu, H.; Ogawa, Y.; et al. A Lectin from the Mussel Mytilus Galloprovincialis Has a Highly Novel Primary Structure and Induces Glycan-Mediated Cytotoxicity of Globotriaosylceramide-Expressing Lymphoma Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 44772–44783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, T.; Vassylyev, D.; Kido, S.; Doi, Y.; Morikawa, K. Crystal Structure of Vitelline Membrane Outer Layer Protein I (VMO-I): A Folding Motif with Homologous Greek Key Structures Related by an Internal Three-Fold Symmetry. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankaranarayanan, R.; Sekar, K.; Banerjee, R.; Sharma, V.; Surolia, A.; Vijayan, M. A Novel Mode of Carbohydrate Recognition in Jacalin, a Moraceae Plant Lectin with a Beta-Prism Fold. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1996, 3, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, X.; Thompson, A.; Zhang, Z.; Ton-that, H.; Biesterfeldt, J.; Ogata, C.; Xu, L.; Johnston, R.A.Z.; Young, N.M. Structure of the Complex of Maclura PomiferaAgglutinin and the T-Antigen Disaccharide, Galβ1,3GalNAc*. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 6312–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosa, J.C.; De Oliveira, P.S.; Garratt, R.; Beltramini, L.; Resing, K.; Roque-Barreira, M.C.; Greene, L.J. KM+, a Mannose-Binding Lectin from Artocarpus Integrifolia: Amino Acid Sequence, Predicted Tertiary Structure, Carbohydrate Recognition, and Analysis of the Beta-Prism Fold. Protein Sci. 1999, 8, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, K.N.; Suresh, C.G.; Katre, U.V.; Gaikwad, S.M.; Khan, M.I. Two Orthorhombic Crystal Structures of a Galactose-Specific Lectin from Artocarpus Hirsuta in Complex with Methyl-Alpha-D-Galactose. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suetake, T.; Tsuda, S.; Kawabata, S.; Miura, K.; Iwanaga, S.; Hikichi, K.; Nitta, K.; Kawano, K. Chitin-Binding Proteins in Invertebrates and Plants Comprise a Common Chitin-Binding Structural Motif. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 17929–17932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawabata, S.; Nagayama, R.; Hirata, M.; Shigenaga, T.; Agarwala, K.L.; Saito, T.; Cho, J.; Nakajima, H.; Takagi, T.; Iwanaga, S. Tachycitin, a Small Granular Component in Horseshoe Crab Hemocytes, Is an Antimicrobial Protein with Chitin-Binding Activity. J. Biochem. 1996, 120, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.-M.; Dai, H.-X.; Gao, X.-F.; Zhao, J.-F.; Guo, Y.-J.; Ling, X.; Dong, B.; Zhang, Z.-Q.; Fan, Z.-C. Expression, Purification and Initial Characterization of a Novel Recombinant Antimicrobial Peptide Mytichitin-A in Pichia Pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 2016, 127, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauters, L.; Naalden, D.; Gheysen, G. The Distribution of Lectins across the Phylum Nematoda: A Genome-Wide Search. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odom, E.W.; Vasta, G.R. Characterization of a Binary Tandem Domain F-Type Lectin from Striped Bass (Morone Saxatilis). J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 1698–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianchet, M.A.; Odom, E.W.; Vasta, G.R.; Amzel, L.M. A Novel Fucose Recognition Fold Involved in Innate Immunity. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2002, 9, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arivalagan, J.; Marie, B.; Sleight, V.A.; Clark, M.S.; Berland, S.; Marie, A. Shell Matrix Proteins of the Clam, Mya Truncata: Roles beyond Shell Formation through Proteomic Study. Mar. Genom. 2016, 27, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moy, G.W.; Springer, S.A.; Adams, S.L.; Swanson, W.J.; Vacquier, V.D. Extraordinary Intraspecific Diversity in Oyster Sperm Bindin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1993–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruben, E.A.; Rau, M.J.; Fitzpatrick, J.A.J.; Di Cera, E. Cryo-EM Structures of Human Coagulation Factors V and Va. Blood 2021, 137, 3137–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, S.V.; Aragão, K.S.; Imberty, A.; Varrot, A. Discoidin I from Dictyostelium Discoideum and Interactions with Oligosaccharides: Specificity, Affinity, Crystal Structures, and Comparison with Discoidin II. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 400, 540–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tateno, H. SUEL-Related Lectins, a Lectin Family Widely Distributed throughout Organisms. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 1141–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozeki, Y.; Matsui, T.; Suzuki, M.; Titani, K. Amino Acid Sequence and Molecular Characterization of a D-Galactoside-Specific Lectin Purified from Sea Urchin (Anthocidaris Crassispina) Eggs. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 2391–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, R.F.; Teixeira, C.S.; de Melo, A.A.; de Almeida, A.S.; Cavada, B.S.; de Sousa, O.V.; da Rocha, B.A.M.; Nagano, C.S.; Sampaio, A.H. L-Rhamnose-Binding Lectin from Eggs of the Echinometra Lucunter: Amino Acid Sequence and Molecular Modeling. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 78, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gasparini, F.; Franchi, N.; Spolaore, B.; Ballarin, L. Novel Rhamnose-Binding Lectins from the Colonial Ascidian Botryllus Schlosseri. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, N.; Schiavon, F.; Carletto, M.; Gasparini, F.; Bertoloni, G.; Tosatto, S.C.E.; Ballarin, L. Immune Roles of a Rhamnose-Binding Lectin in the Colonial Ascidian Botryllus Schlosseri. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganuma, T.; Ogawa, T.; Hirabayashi, J.; Kasai, K.; Kamiya, H.; Muramoto, K. Isolation, Characterization and Molecular Evolution of a Novel Pearl Shell Lectin from a Marine Bivalve, Pteria Penguin. Mol. Divers. 2006, 10, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlenbruck, G.; Prokop, O. An Agglutinin from Helix Pomatia, Which Reacts with Terminal N-Acetyl-D-Galactosamine. Vox Sang. 1966, 11, 519–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, J.-F.; Lescar, J.; Chazalet, V.; Audfray, A.; Gagnon, J.; Alvarez, R.; Breton, C.; Imberty, A.; Mitchell, E.P. Biochemical and Structural Analysis of Helix Pomatia Agglutinin: A hexameric lectin with a novel fold. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 20171–20180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerdol, M. Immune-Related Genes in Gastropods and Bivalves: A Comparative Overview. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2017, 14, 95–111. [Google Scholar]
- Gerdol, M.; Fujii, Y.; Hasan, I.; Koike, T.; Shimojo, S.; Spazzali, F.; Yamamoto, K.; Ozeki, Y.; Pallavicini, A.; Fujita, H. The Purplish Bifurcate Mussel Mytilisepta Virgata Gene Expression Atlas Reveals a Remarkable Tissue Functional Specialization. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogawa, T.; Sato, R.; Naganuma, T.; Liu, K.; Lakudzala, A.E.; Muramoto, K.; Osada, M.; Yoshimi, K.; Hiemori, K.; Hirabayashi, J.; et al. Glycan Binding Profiling of Jacalin-Related Lectins from the Pteria Penguin Pearl Shell. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanagawa, M.; Satoh, T.; Ikeda, A.; Nakano, Y.; Yagi, H.; Kato, K.; Kojima-Aikawa, K.; Yamaguchi, Y. Crystal Structures of Human Secretory Proteins ZG16p and ZG16b Reveal a Jacalin-Related β-Prism Fold. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 404, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garénaux, E.; Kanagawa, M.; Tsuchiyama, T.; Hori, K.; Kanazawa, T.; Goshima, A.; Chiba, M.; Yasue, H.; Ikeda, A.; Yamaguchi, Y.; et al. Discovery, Primary, and Crystal Structures and Capacitation-Related Properties of a Prostate-Derived Heparin-Binding Protein WGA16 from Boar Sperm. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 5484–5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, N.; Liu, N.; Cheng, W.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, H.; Chen, L.; Peng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Structural Basis for Receptor Recognition and Pore Formation of a Zebrafish Aerolysin-like Protein. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carneiro, R.F.; Torres, R.C.F.; Chaves, R.P.; de Vasconcelos, M.A.; de Sousa, B.L.; Goveia, A.C.R.; Arruda, F.V.; Matos, M.N.C.; Matthews-Cascon, H.; Freire, V.N.; et al. Purification, Biochemical Characterization, and Amino Acid Sequence of a Novel Type of Lectin from Aplysia Dactylomela Eggs with Antibacterial/Antibiofilm Potential. Mar. Biotechnol. 2017, 19, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Huang, S.; Yan, X.; Yang, P.; Li, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R.; Yu, Y.; Yuan, S.; et al. Two Apextrin-like Proteins Mediate Extracellular and Intracellular Bacterial Recognition in Amphioxus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13469–13474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Gong, C.; Han, Z.; Lv, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Song, L. The Lectin Domain Containing Proteins with Mucosal Immunity and Digestive Functions in Oyster Crassostrea Gigas. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 89, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, L.; Van Damme, E.J.M. Genome-Wide Identification and Domain Organization of Lectin Domains in Cucumber. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 108, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubyaga, Y.A.; Dolgikh, A.V.; Drozdova, P.B.; Nazarova, A.A.; Timofeyev, M.A. Transcriptome-Based Analysis of the Diversity of Membrane-Bound Lectins in Baikal Amphipods Eulimnogammarus Sp. and the Holarctic Amphipod Gammarus Lacustris. Limnol. Freshw. Biol. 2020, 797–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zárate-Potes, A.; Ocampo, I.D.; Cadavid, L.F. The Putative Immune Recognition Repertoire of the Model Cnidarian Hydractinia Symbiolongicarpus Is Large and Diverse. Gene 2019, 684, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simão, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing Genome Assembly and Annotation Completeness with Single-Copy Orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angata, T.; Brinkman-Van der Linden, E. I-Type Lectins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1572, 294–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jiang, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Xu, J.; Lv, Z.; Song, L. A Novel Siglec (CgSiglec-1) from the Pacific Oyster (Crassostrea Gigas) with Broad Recognition Spectrum and Inhibitory Activity to Apoptosis, Phagocytosis and Cytokine Release. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 61, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzenbacher, G.; Roig-Zamboni, V.; Peumans, W.J.; Henrissat, B.; van Damme, E.J.M.; Bourne, Y. Structural Basis for Carbohydrate Binding Properties of a Plant Chitinase-like Agglutinin with Conserved Catalytic Machinery. J. Struct. Biol. 2015, 190, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, I.; Gerdol, M.; Fujii, Y.; Rajia, S.; Koide, Y.; Yamamoto, D.; Kawsar, S.M.A.; Ozeki, Y. CDNA and Gene Structure of MytiLec-1, A Bacteriostatic R-Type Lectin from the Mediterranean Mussel (Mytilus Galloprovincialis). Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, J.; Park, J.C.; Choi, B.-S.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, H.-S.; Hagiwara, A.; Park, H.G.; Lee, B.-Y.; Lee, J.-S. The Genome of the Marine Monogonont Rotifer Brachionus Plicatilis: Genome-Wide Expression Profiles of 28 Cytochrome P450 Genes in Response to Chlorpyrifos and 2-Ethyl-Phenanthrene. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 214, 105230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-S.; Lee, B.-Y.; Han, J.; Jeong, C.-B.; Hwang, D.-S.; Lee, M.-C.; Kang, H.-M.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; Papakostas, S.; et al. The Genome of the Freshwater Monogonont Rotifer Brachionus Calyciflorus. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2018, 18, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.-H.; Kim, M.-S.; Hagiwara, A.; Lee, J.-S. The Genome of the Minute Marine Rotifer Proales Similis: Genome-Wide Identification of 401 G Protein-Coupled Receptor (GPCR) Genes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 39, 100861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, T.N.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 4.0: Discriminating Signal Peptides from Transmembrane Regions. Nat. Meth. 2011, 8, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendtsen, J.D.; Jensen, L.J.; Blom, N.; Von Heijne, G.; Brunak, S. Feature-Based Prediction of Non-Classical and Leaderless Protein Secretion. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2004, 17, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting Transmembrane Protein Topology with a Hidden Markov Model: Application to Complete Genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Käll, L.; Krogh, A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L. A Combined Transmembrane Topology and Signal Peptide Prediction Method. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 338, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Clements, J.; Eddy, S.R. HMMER Web Server: Interactive Sequence Similarity Searching. Nucl. Acids Res. 2011, 39, W29–W37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.-Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-Scale Protein Function Classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Söding, J.; Biegert, A.; Lupas, A.N. The HHpred Interactive Server for Protein Homology Detection and Structure Prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W244–W248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple Sequence Alignment with High Accuracy and High Throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Talavera, G.; Castresana, J. Improvement of Phylogenies after Removing Divergent and Ambiguously Aligned Blocks from Protein Sequence Alignments. Syst. Biol. 2007, 56, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian Inference of Phylogenetic Trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darriba, D.; Posada, D.; Kozlov, A.M.; Stamatakis, A.; Morel, B.; Flouri, T. ModelTest-NG: A New and Scalable Tool for the Selection of DNA and Protein Evolutionary Models. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior Summarization in Bayesian Phylogenetics Using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Bdelloidea | Monogononta | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adineta ricciae | Rotaria sordida | Didymodactylos carnosus | Proales similis | Brachionus calyciflorus | Brachionus plicatilis | |
| FReDs | 6 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| C-type lectins | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 25 | 17 |
| C1qDC proteins | 4 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Galectins | 4 | 8 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| R-type lectins | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 a |
| F-type lectins | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 b |
| SUEL-type lectins | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 0 c |
| H-type lectins | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Jacalin-like lectins | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Apextrins | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| DUF3011 lectins | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Species Name | Class | Genome Size (Mb) | Protein-Coding Genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adineta ricciae | Bdelloidea | 173 | 49,015 |
| Rotaria sordida | Bdelloidea | 361 | 61,901 |
| Didymodactylos carnosus | Bdelloidea | 356 | 46,863 |
| Proales similis | Monogononta | 33 | 10,785 |
| Brachionus calyciflorus | Monogononta | 30 | 24,328 |
| Brachionus plicatilis | Monogononta | 107 | 52,502 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gerdol, M. First Insights into the Repertoire of Secretory Lectins in Rotifers. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020130
Gerdol M. First Insights into the Repertoire of Secretory Lectins in Rotifers. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(2):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020130
Chicago/Turabian StyleGerdol, Marco. 2022. "First Insights into the Repertoire of Secretory Lectins in Rotifers" Marine Drugs 20, no. 2: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020130
APA StyleGerdol, M. (2022). First Insights into the Repertoire of Secretory Lectins in Rotifers. Marine Drugs, 20(2), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20020130






